Micromachining Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: micromachining
Micromachining Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an extensive analysis of the Micromachining market, encompassing insights into market size, trends, regional analysis, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It aims to assist stakeholders in making informed business decisions based on comprehensive data and projections.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
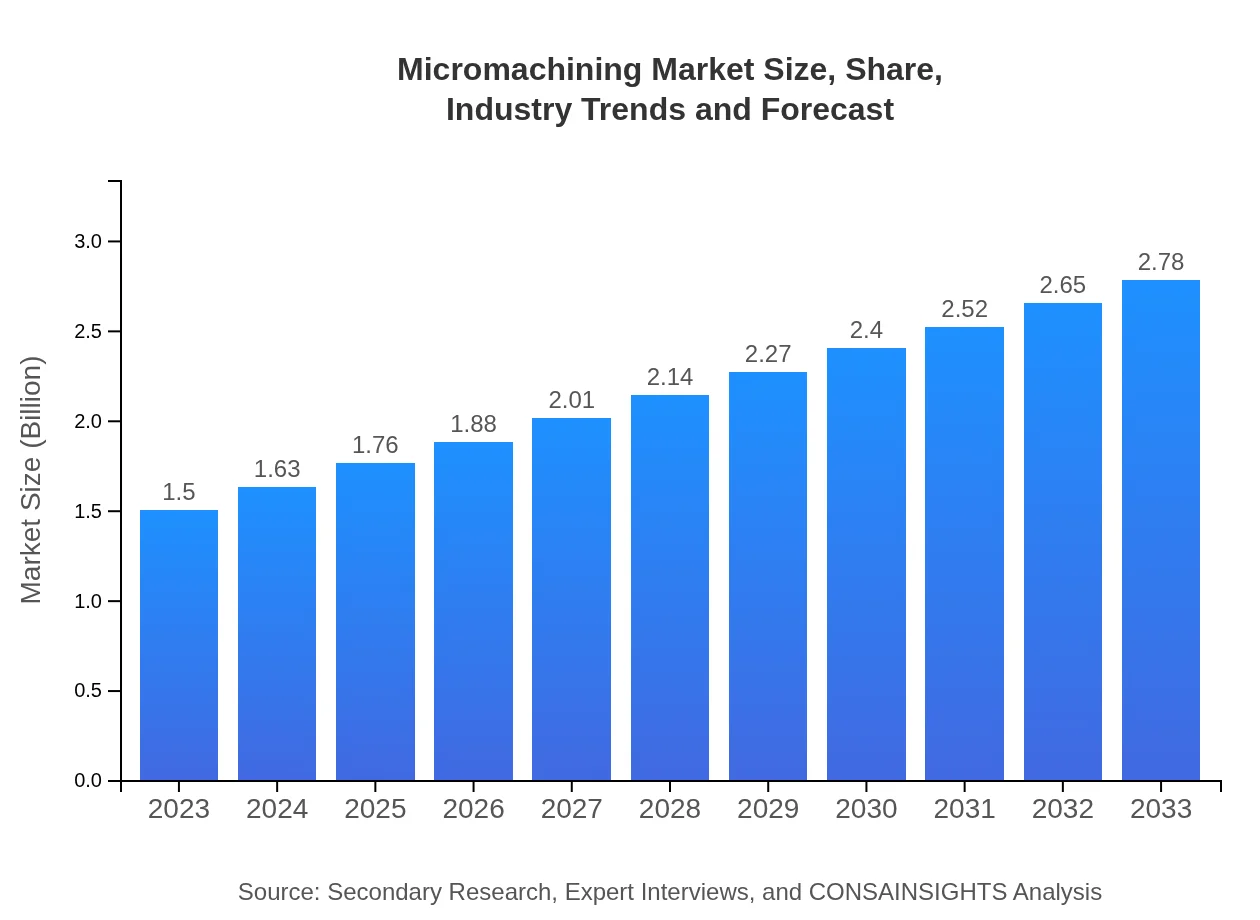
| 2023 Market Size | $1.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $2.78 Billion |
| Top Companies | MEC (Micro-Electronic Component AG), Boeing , Mitsubishi Electric, Sandei Industry Co. |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Micromachining Market Overview
Customize Micromachining Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Micromachining market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Micromachining's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Micromachining
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Micromachining market in 2023 and 2033?
Micromachining Industry Analysis
Micromachining Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Micromachining Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Micromachining Market Report:
The European micromachining market is expected to rise from $0.51 billion in 2023 to $0.95 billion by 2033, driven by technological innovations and an increase in the automotive sector's demand for lightweight, precision-engineered components.Asia Pacific Micromachining Market Report:
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to dominate the Micromachining market, projected to increase from $0.28 billion in 2023 to $0.53 billion by 2033. The region's growth is driven by high manufacturing activities, particularly in China and Japan, which are ramping up their investments in automation and precision technologies.North America Micromachining Market Report:
North America is projected to experience growth from $0.52 billion in 2023 to $0.97 billion by 2033. The U.S. leads the region in adopting technological innovations and is anticipated to remain a key market due to robust aerospace and medical device manufacturing sectors pushing for micromachining technologies.South America Micromachining Market Report:
In South America, the Micromachining market is estimated to grow from $0.14 billion in 2023 to $0.25 billion by 2033. Growth in this region is supported by the rising automotive and electronics industries, along with increasing adherence to advanced manufacturing technologies.Middle East & Africa Micromachining Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market, though smaller, is projected to grow from $0.04 billion in 2023 to $0.08 billion by 2033, fueled by increasing industrialization and a rising focus on adopting advanced manufacturing processes.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
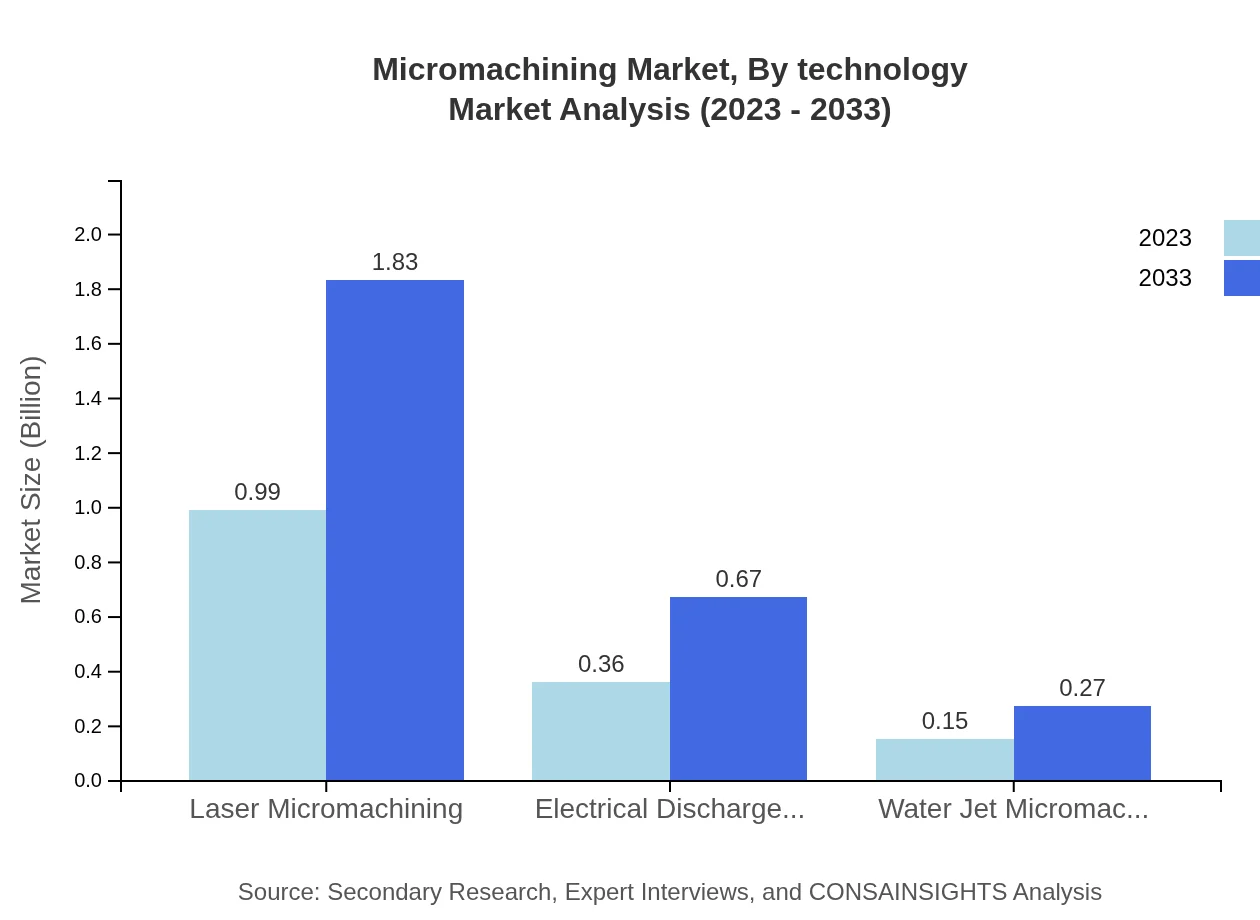
Micromachining Market Analysis By Technology
The Micromachining market by technology is dominated by Laser Micromachining, which boasts a market size of $0.99 billion in 2023, expected to increase to $1.83 billion by 2033. Technologies like Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) and Water Jet Micromachining also hold significant shares, emphasizing precise and efficient machining methods.
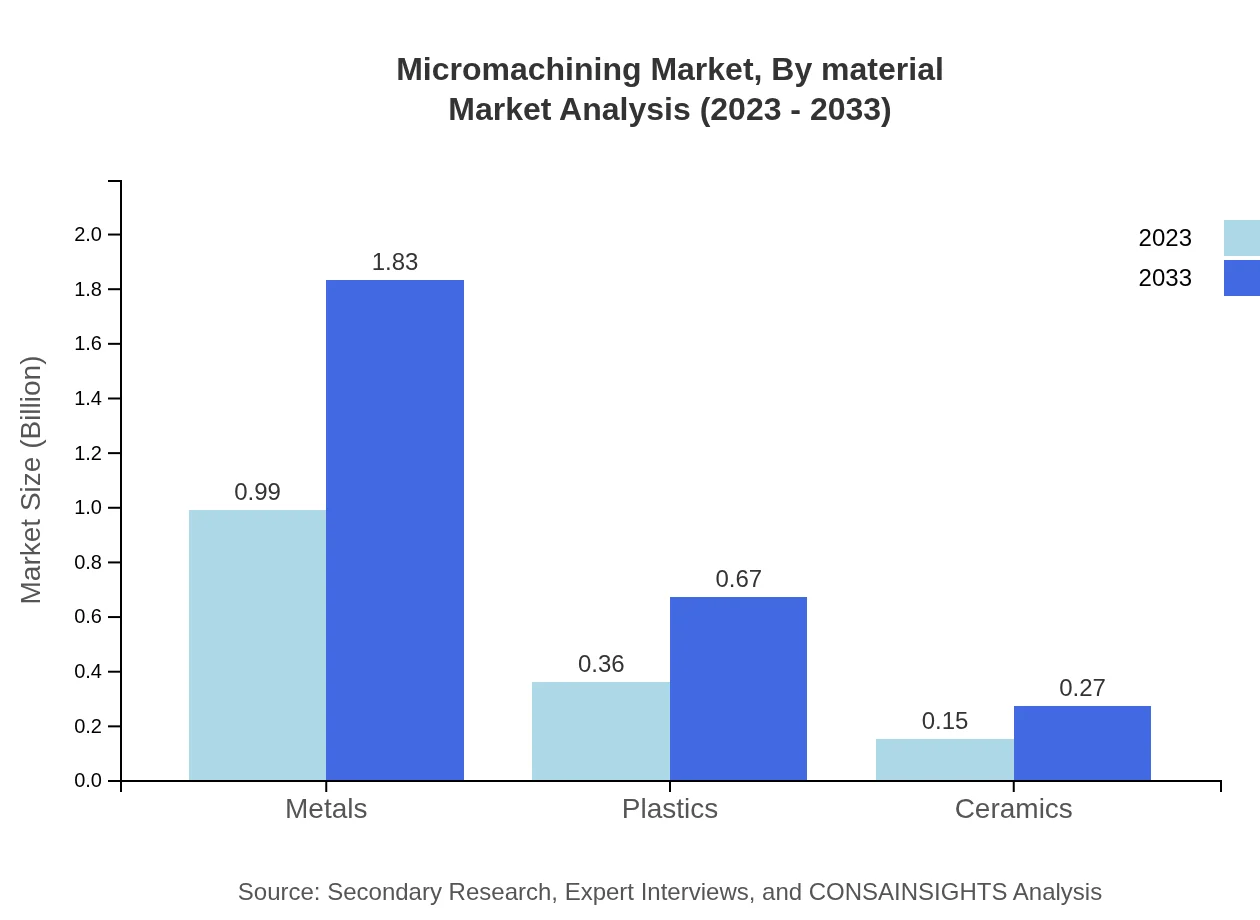
Micromachining Market Analysis By Material
In terms of materials, metals lead the market with a notable size of $0.99 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $1.83 billion by 2033. Plastics and ceramics are also important segments, reflecting the material diversity utilized in micromachining applications.
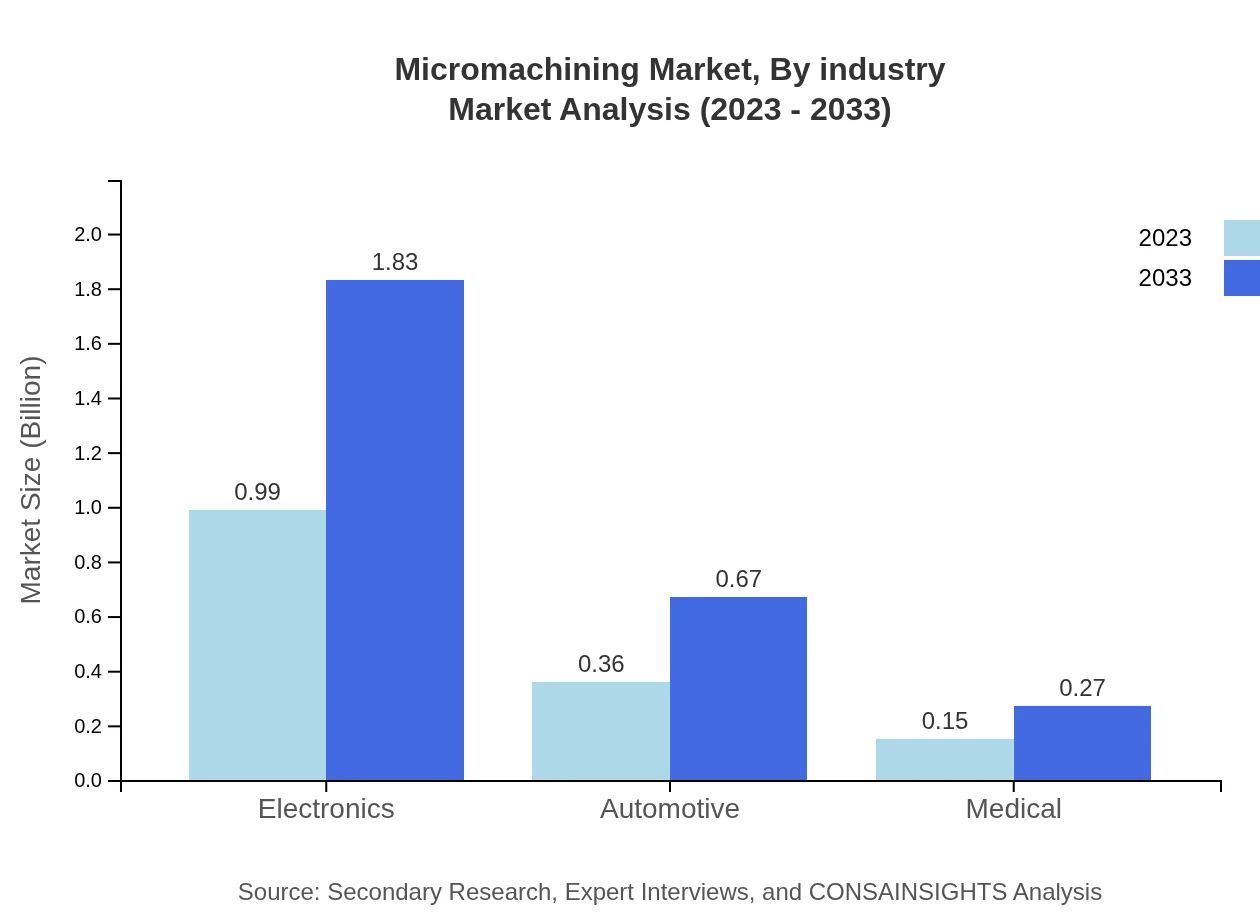
Micromachining Market Analysis By Industry
The Micromachining market by industry highlights the electronics sector with a market size of $0.99 billion in 2023, expected to reach $1.83 billion by 2033. The automotive industry also shows significant potential, with growing demands for high-precision components.
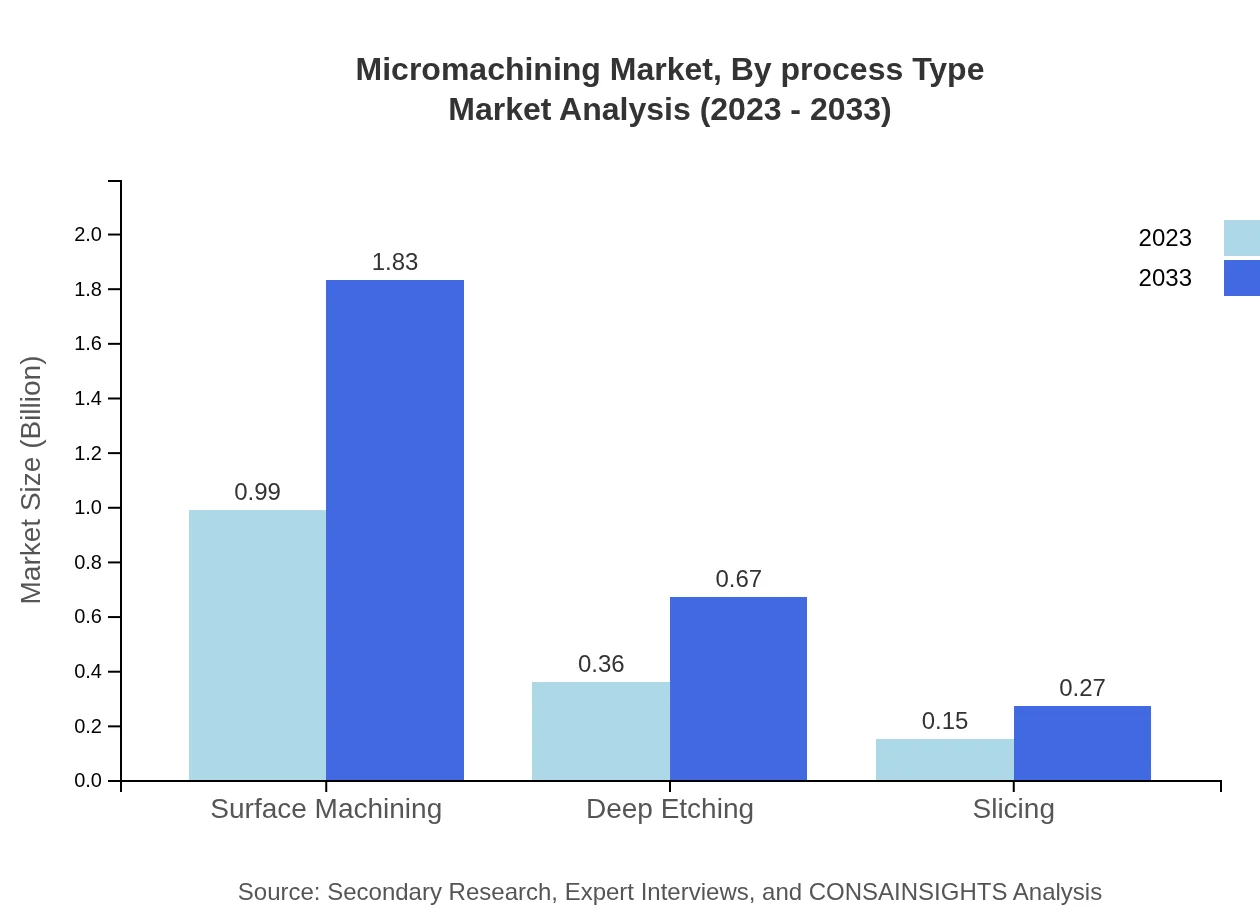
Micromachining Market Analysis By Process Type
Different process types contribute uniquely to the Micromachining market. Surface machining dominates with a $0.99 billion market size in 2023, reflecting its widespread application in component manufacturing. This is closely followed by deep etching and slicing processes, illustrating a diverse operational landscape.
Micromachining Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Micromachining Industry
MEC (Micro-Electronic Component AG):
A leading provider of precision micromachining technology solutions, specializing in advanced laser and EDM technologies.Boeing :
An aerospace giant utilizing micromachining for manufacturing lightweight components essential for aircraft performance and efficiency.Mitsubishi Electric:
Known for innovation in micromachining and automation, Mitsubishi Electric provides solutions across various industrial sectors.Sandei Industry Co.:
Focused on semiconductor designs and manufacturing, which heavily relies on advanced micromachining techniques.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Micromachining?
The global micromachining market is currently valued at approximately $1.5 billion, with an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% through 2033. This indicates robust growth driven by various applications across different industries.
What are the key market players or companies in the Micromachining industry?
Key players in the micromachining industry include major companies like 3M, Piller Group, and ASML. These companies leverage advanced technologies to provide innovative solutions in micromachining applications across sectors.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Micromachining industry?
The growth in the micromachining industry is driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing, advancements in technology, and the rising applications of micromachining in sectors such as electronics and automotive.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Micromachining market?
The fastest-growing region for micromachining is Europe, expecting a market expansion from $0.51 billion in 2023 to $0.95 billion by 2033, showcasing significant growth opportunities in this region.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Micromachining industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific client needs. This service includes detailed insights and data relevant to the micromachining industry to better inform strategic decisions.
What deliverables can I expect from this Micromachining market research project?
From this micromachining market research project, clients can expect comprehensive market analysis, insights into trends and forecasts, regional data, segment analysis, and strategic recommendations.
What are the market trends of Micromachining?
Current micromachining market trends include increased automation in manufacturing processes, a focus on sustainable production techniques, and innovations in materials used, particularly in electronics and medical applications.