Mobility As A Service Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: mobility-as-a-service
Mobility As A Service Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Mobility as a Service (MaaS) market from 2023 to 2033, highlighting market dynamics, size, segments, regional insights, and future trends to guide stakeholders in strategic decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
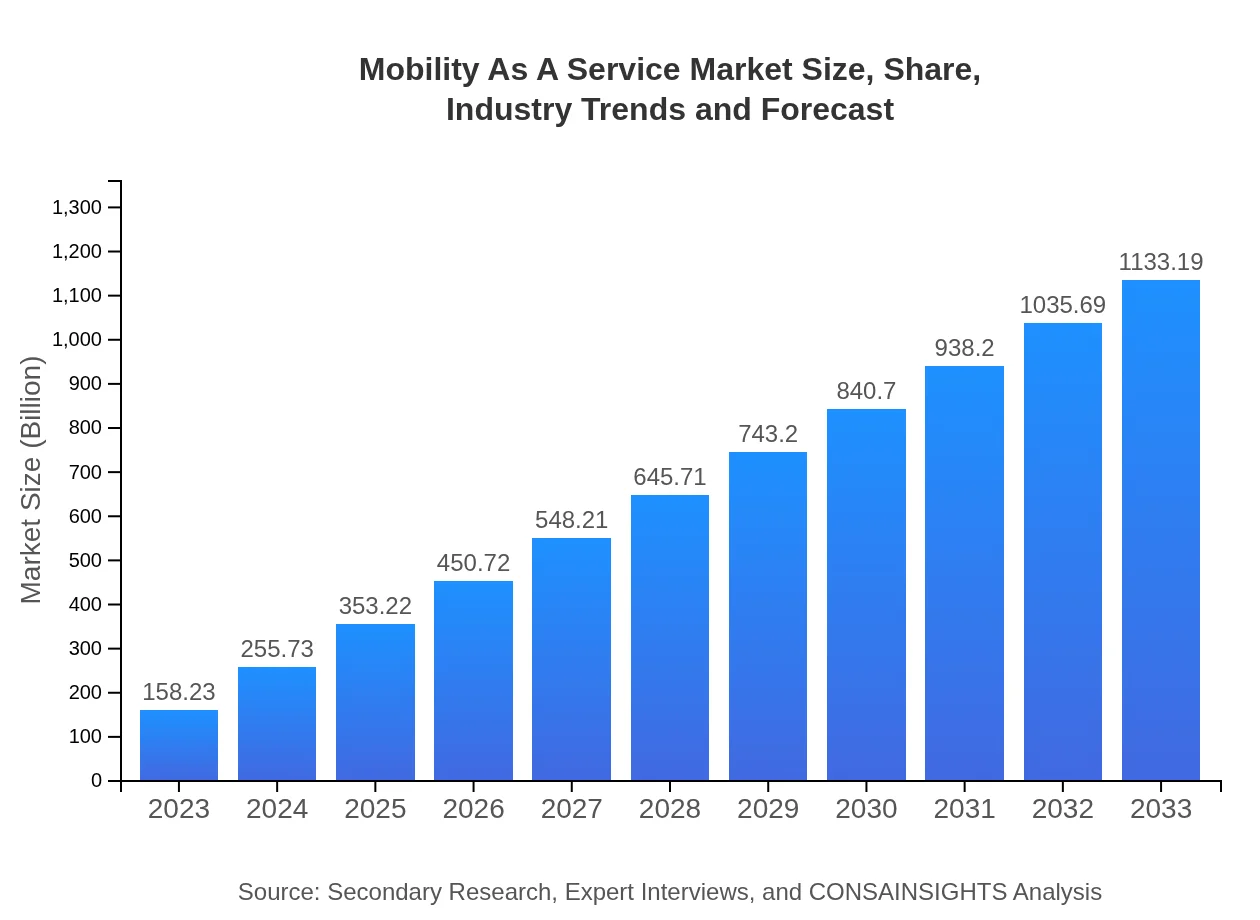
| 2023 Market Size | $158.23 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 20.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $1133.19 Billion |
| Top Companies | Uber Technologies, Inc., Lyft, Inc., Moovit, Via Transportation, Inc., Grab Holdings Limited |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Mobility As A Service Market Overview
Customize Mobility As A Service Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Mobility As A Service market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Mobility As A Service's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Mobility As A Service
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Mobility As A Service market in 2023?
Mobility As A Service Industry Analysis
Mobility As A Service Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Mobility As A Service Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Mobility As A Service Market Report:
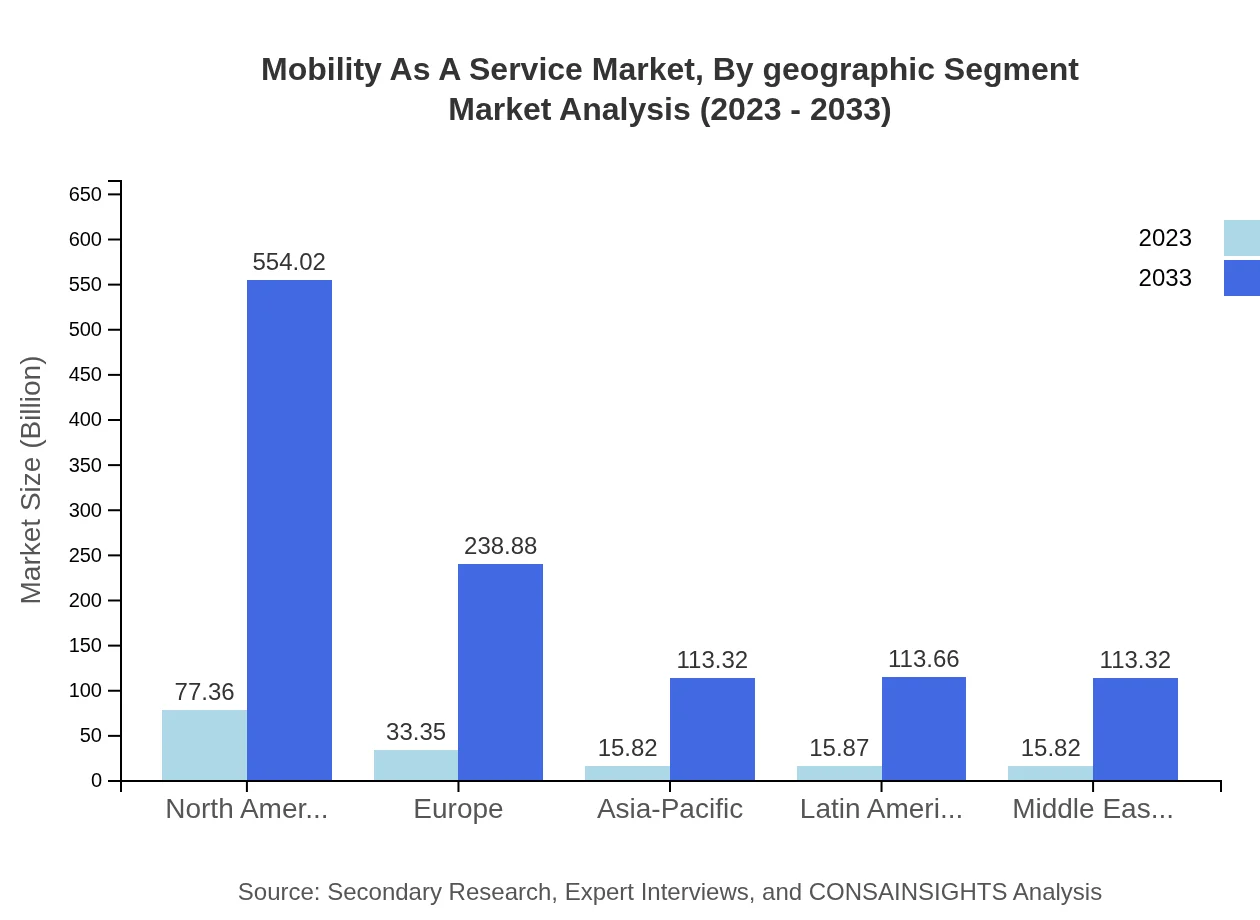
Europe's MaaS market is forecasted to escalate from 51.95 billion USD in 2023 to 372.03 billion USD by 2033. Strong regulatory support and a focus on green initiatives are critical drivers in this region.Asia Pacific Mobility As A Service Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the MaaS market is projected to grow from 29.79 billion USD in 2023 to 213.38 billion USD by 2033. Rapid urbanization and increasing smartphone penetration are driving this growth, alongside governments' push for sustainable transport alternatives.North America Mobility As A Service Market Report:
North America, valued at 52.75 billion USD in 2023, is anticipated to reach 377.80 billion USD by 2033, spurred by substantial tech investment and an increasing shift towards shared mobility solutions.South America Mobility As A Service Market Report:
The South American market is expected to increase from 13.77 billion USD in 2023 to 98.59 billion USD by 2033. Urban mobility challenges and the integration of public transport solutions are key factors supporting this growth.Middle East & Africa Mobility As A Service Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are projected to grow from 9.97 billion USD in 2023 to 71.39 billion USD by 2033, with investments in smart city projects and transport infrastructure fueling market expansion.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Mobility As A Service Market Analysis By User Type
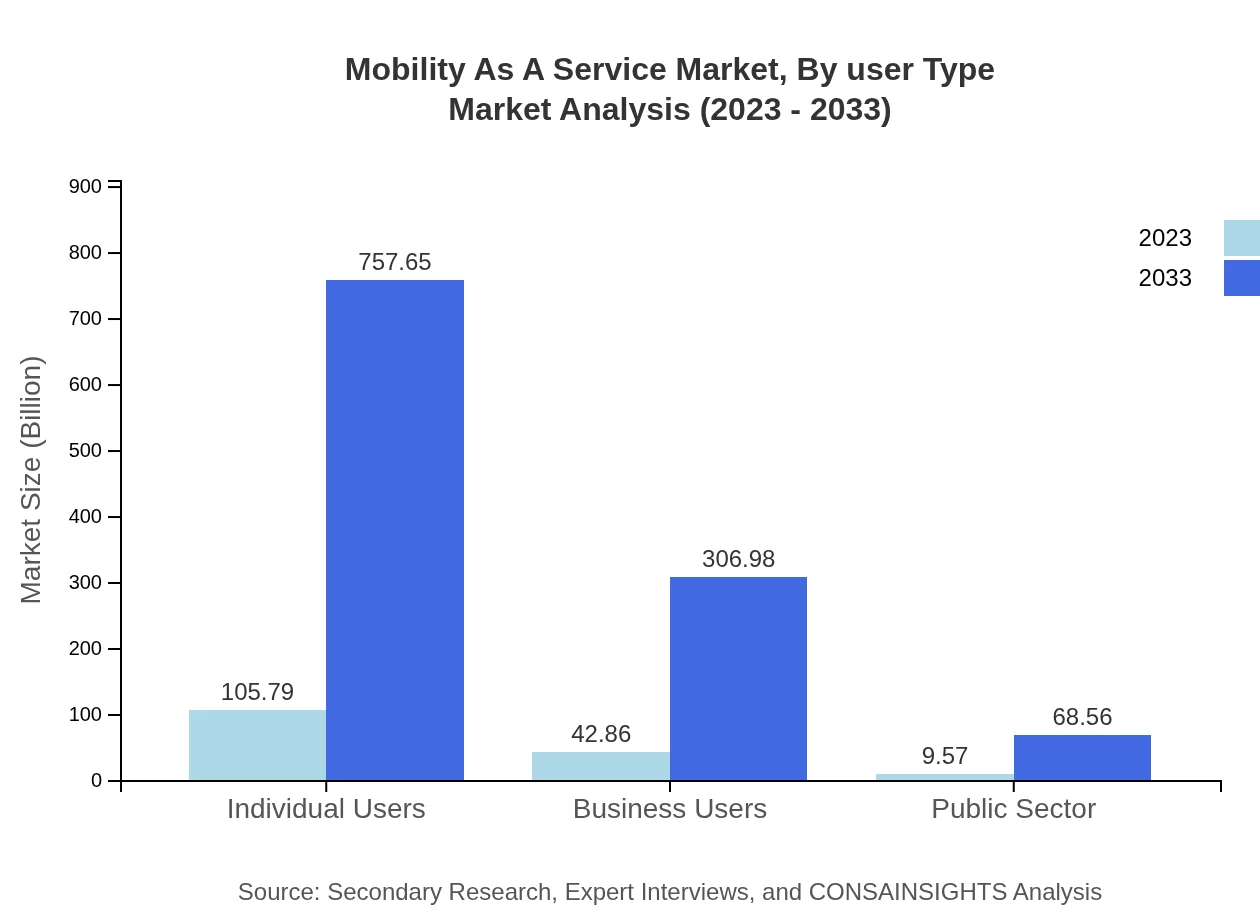
The Mobility-as-a-Service market by user type is divided into individual users, business users, and the public sector. Individual users dominate the market, representing a significant size increase from 105.79 billion USD in 2023 to 757.65 billion USD by 2033. Business users are gaining traction due to the convenience and operational efficiency of shared mobility solutions, expected to grow from 42.86 billion USD to 306.98 billion USD in the same period. The public sector, though smaller, reveals growth potential, reaching 68.56 billion USD, driven by government partnerships aimed at enhancing urban mobility.
Mobility As A Service Market Analysis By Service Type
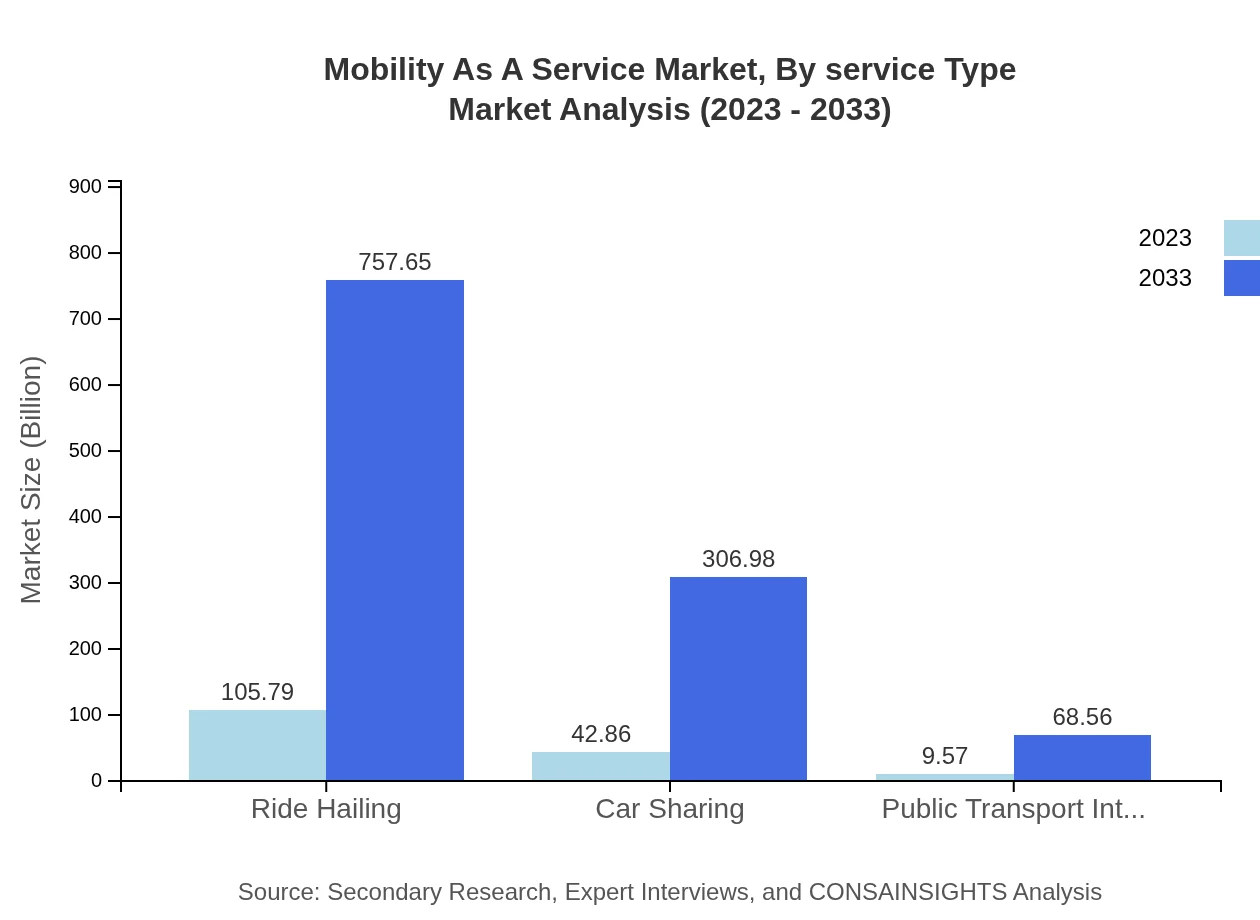
In this sector, ride-hailing services lead, expected to grow from 105.79 billion USD to 757.65 billion USD by 2033. Car sharing also shows promise, expanding from 42.86 billion USD to 306.98 billion USD, while public transport integration will increase to 68.56 billion USD, driven by the need to streamline urban transportation.
Mobility As A Service Market Analysis By Pricing Model
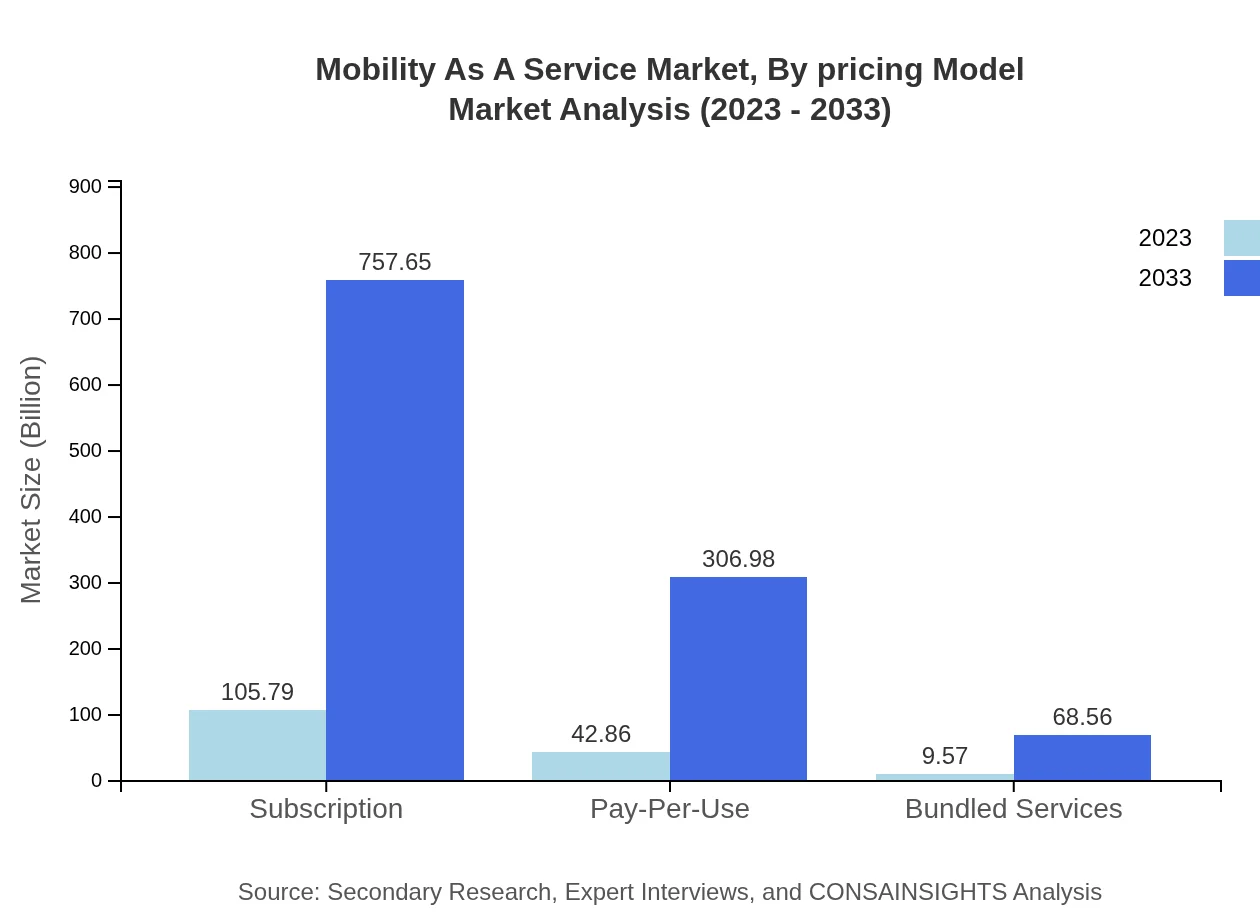
The pricing models include subscription, pay-per-use, and bundled services. The subscription model is rapidly growing, increasing from 105.79 billion USD to 757.65 billion USD by 2033. The pay-per-use model currently stands at 42.86 billion USD and is expected to reach 306.98 billion USD. Bundled services are gaining traction, valued at 68.56 billion by 2033, as users seek cost-effective transportation solutions.
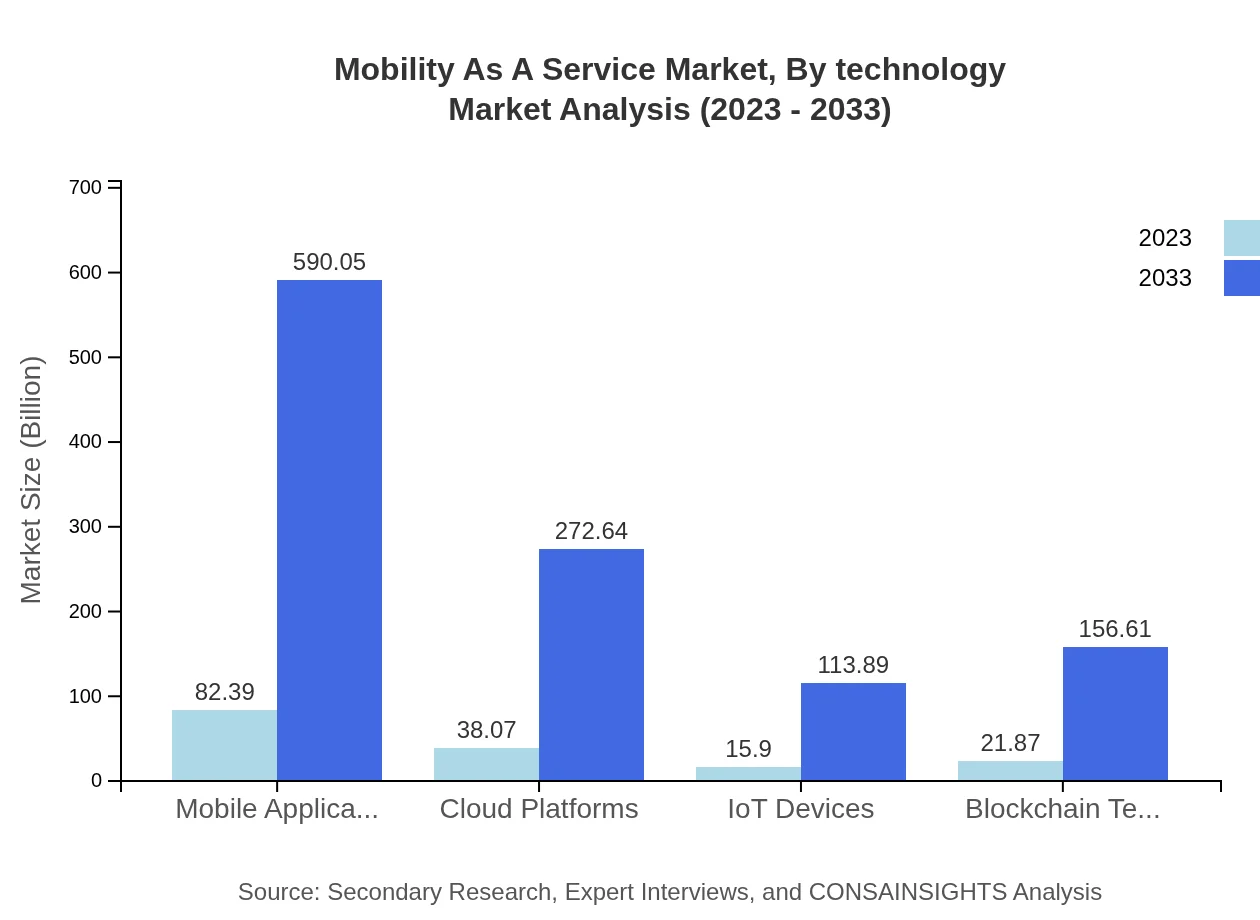
Mobility As A Service Market Analysis By Technology
The technology-driven segment includes cloud platforms, mobile applications, IoT devices, and blockchain technology. Mobile applications lead the sector, expanding from 82.39 billion USD in 2023 to 590.05 billion USD by 2033. Cloud platforms and IoT devices are also expected to grow significantly, demonstrating the critical role of technology in enhancing service delivery in the MaaS ecosystem.
Mobility As A Service Market Analysis By Geographic Segment
Geographically, North America commands a leading share, with the highest growth rate expected in Europe, where the move towards sustainable transport solutions is more pronounced. The Asia Pacific market also demonstrates robust growth potential due to rapid urbanization and technological adoption.
Mobility As A Service Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Mobility As A Service Industry
Uber Technologies, Inc.:
A pioneer in ride-hailing services, Uber is continuously expanding its offerings to include bike-sharing, public transport options, and delivery services.Lyft, Inc.:
Lyft is known for its ride-sharing platform and is enhancing services to include integrated transport solutions across urban landscapes.Moovit:
Moovit provides urban mobility solutions and public transport data, empowering users to plan their journeys effectively.Via Transportation, Inc.:
Via is focused on optimizing public transport using technology to provide smarter urban mobility solutions, emphasizing vehicle pooling.Grab Holdings Limited:
Grab operates in Southeast Asia, offering a diversified platform that includes ride-hailing, delivery, and payment services.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Mobility As A-Service?
The Mobility-as-a-Service market is projected to reach approximately $158.23 billion by 2033, expanding at a CAGR of 20.5%. This growth reflects increasing demand for integrated transport solutions globally.
What are the key market players or companies in the Mobility As A-Service industry?
Key players in the Mobility-as-a-Service market include firms like Uber, Lyft, Gett, and various regional public transport operators that provide ride-hailing, car-sharing, and integrated transport solutions.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Mobility As A-Service industry?
Factors driving growth include rising urban populations, increased focus on sustainability, technological advancements in mobile applications, and a shift toward shared mobility over personal vehicle use.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Mobility As A-Service market?
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to be the fastest-growing market, projected to grow from $29.79 billion in 2023 to $213.38 billion by 2033, driven by urbanization and increasing transport needs.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Mobility As A-Service industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the Mobility-as-a-Service industry, providing insights that suit unique business contexts.
What deliverables can I expect from this Mobility As A-Service market research project?
Deliverables typically include comprehensive market analysis, regional insights, competitive landscape evaluations, and detailed forecasts by segments and demographics to guide strategic decisions.
What are the market trends of Mobility As A-Service?
Current trends in Mobility-as-a-Service include increasing investment in smart transportation technologies, the rise of autonomous vehicles, and growing collaboration between public and private transport sectors.