Molecular Breeding Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: molecular-breeding
Molecular Breeding Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides comprehensive insights into the Molecular Breeding market, covering key trends, forecasts, and segmentation from 2023 to 2033. It includes data on market size, technology advancements, regional insights, and leading companies to offer stakeholders valuable information for strategic decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
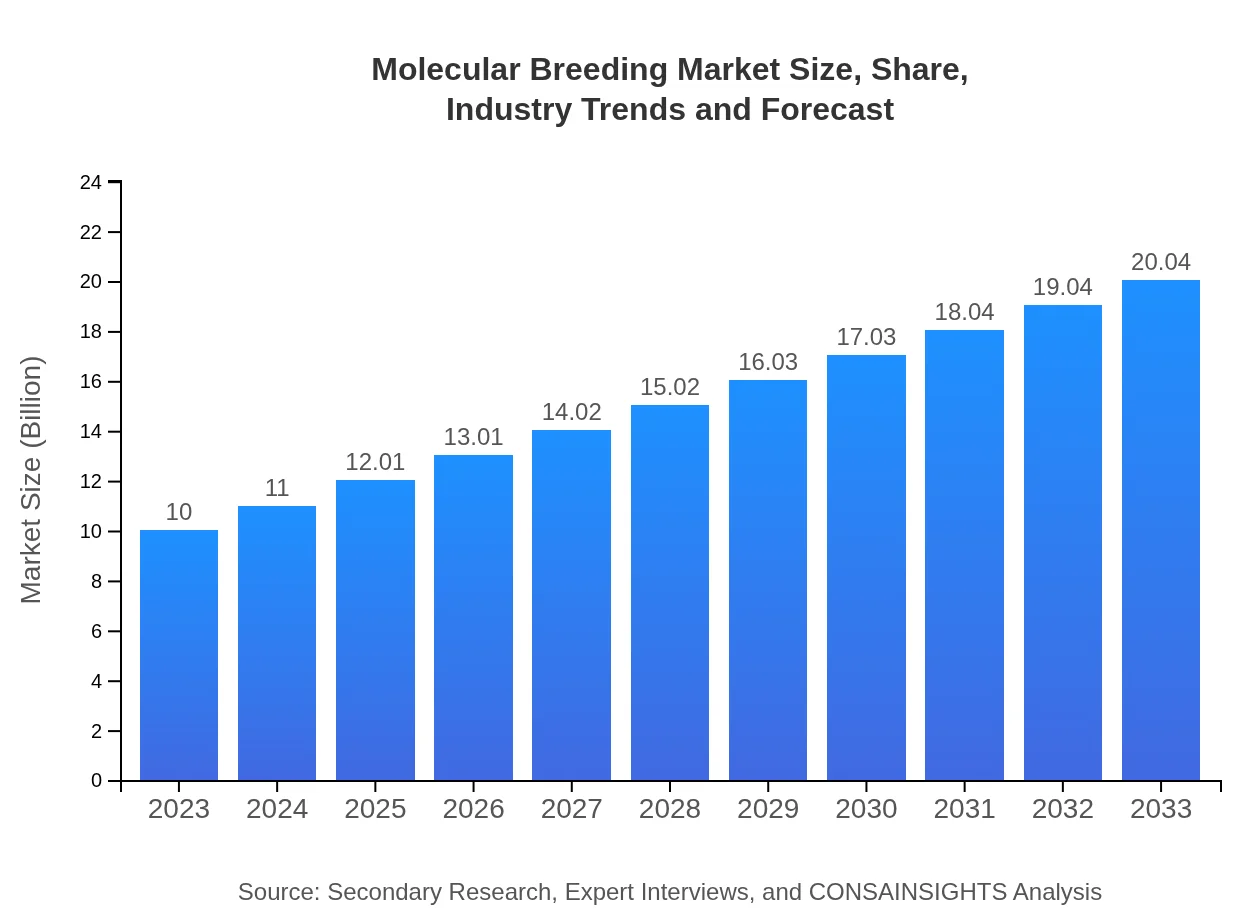
| 2023 Market Size | $10.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $20.04 Billion |
| Top Companies | BASF SE, Syngenta AG, Monsanto Company (now part of Bayer), DuPont de Nemours, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Molecular Breeding Market Overview
Customize Molecular Breeding Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Molecular Breeding market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Molecular Breeding's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Molecular Breeding
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Molecular Breeding market in 2023?
Molecular Breeding Industry Analysis
Molecular Breeding Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Molecular Breeding Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Molecular Breeding Market Report:
Europe's market size is estimated to be $3.09 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand to $6.19 billion by 2033, driven by consumer demand for sustainable agricultural practices and advancements in biotechnology. Strict regulations for genetically modified organisms and an increasing emphasis on organic farming create an intricate landscape for molecular breeding trends.Asia Pacific Molecular Breeding Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is witnessing significant advancement in Molecular Breeding, with a market size of $1.77 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $3.55 billion by 2033. The growth is fueled by a strong focus on food security, government initiatives to promote biotechnology in agriculture, and collaboration between local farmers and research institutions. Countries like India and China are leading the adoption of molecular techniques to enhance crop productivity.North America Molecular Breeding Market Report:
North America represents a robust market for Molecular Breeding, with a valuation of $3.72 billion in 2023 anticipated to rise to $7.45 billion by 2033. The U.S. is a key player, emphasizing the use of advanced breeding technologies in various crops, driven by strong funding for agricultural research and a favorable regulatory environment for biotechnology.South America Molecular Breeding Market Report:
In South America, the market is valued at $0.91 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $1.83 billion by 2033. Brazil and Argentina are at the forefront, leveraging molecular breeding to develop crops resistant to pests and diseases while meeting the demand for biofuels. The region's favorable climate for agriculture bodes well for the technology's growth.Middle East & Africa Molecular Breeding Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region, with a market size of $0.51 billion in 2023 projected to grow to $1.03 billion by 2033, is experiencing a gradual acceptance of molecular breeding technologies. With arid climates affecting ~60% of the land, innovations in drought-resistant crops are being prioritized, aided by increased investment from agricultural startups and multinational collaborations.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Molecular Breeding Market Analysis By Technology
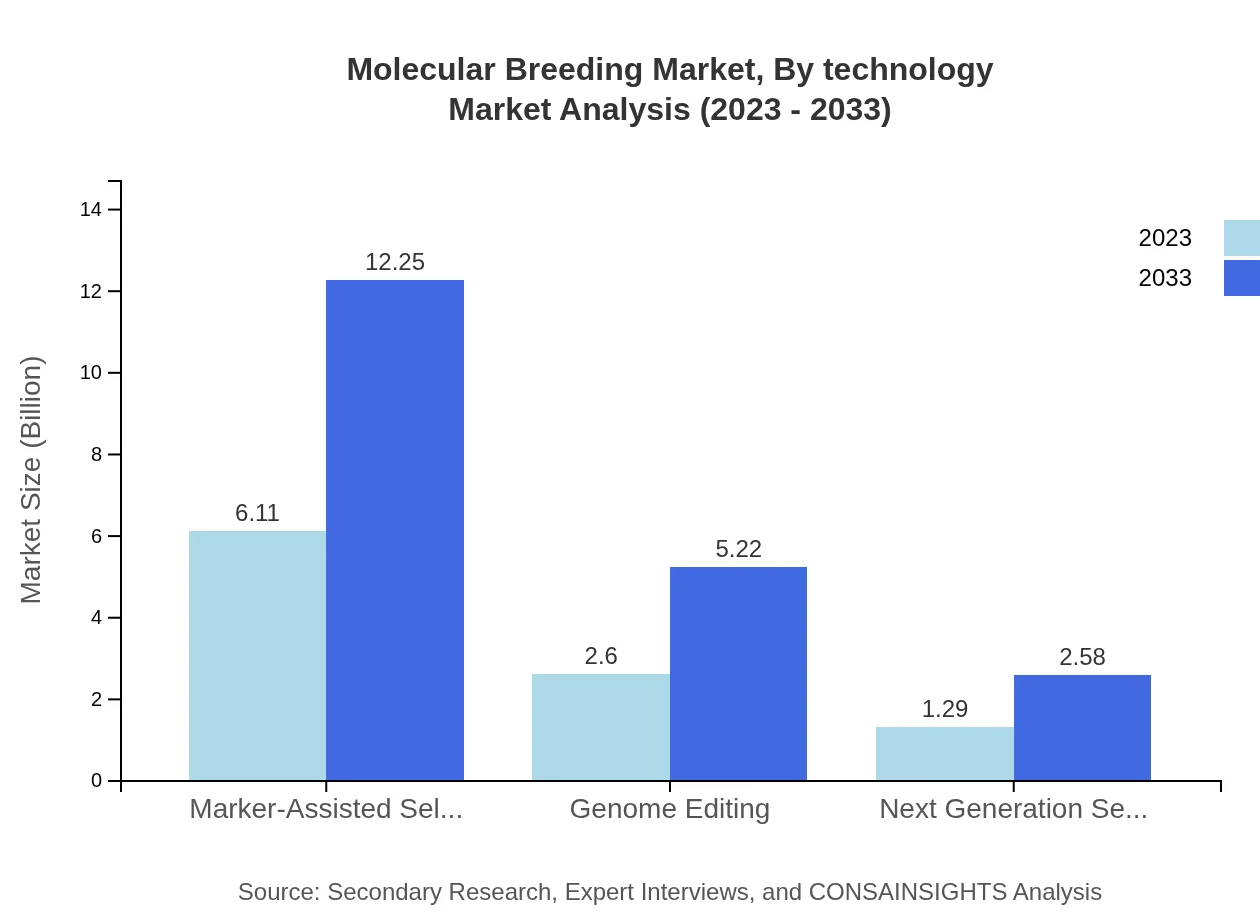
In the Molecular Breeding market segmented by technology, Marker-Assisted Selection leads with a market size of $6.11 billion in 2023 and is projected to double by 2033. Genome Editing follows closely with a size of $2.60 billion, indicating a growing trend towards precision breeding techniques. Next Generation Sequencing is also gaining traction, albeit at a slightly lower market size of $1.29 billion in 2023.
Molecular Breeding Market Analysis By Crop Type
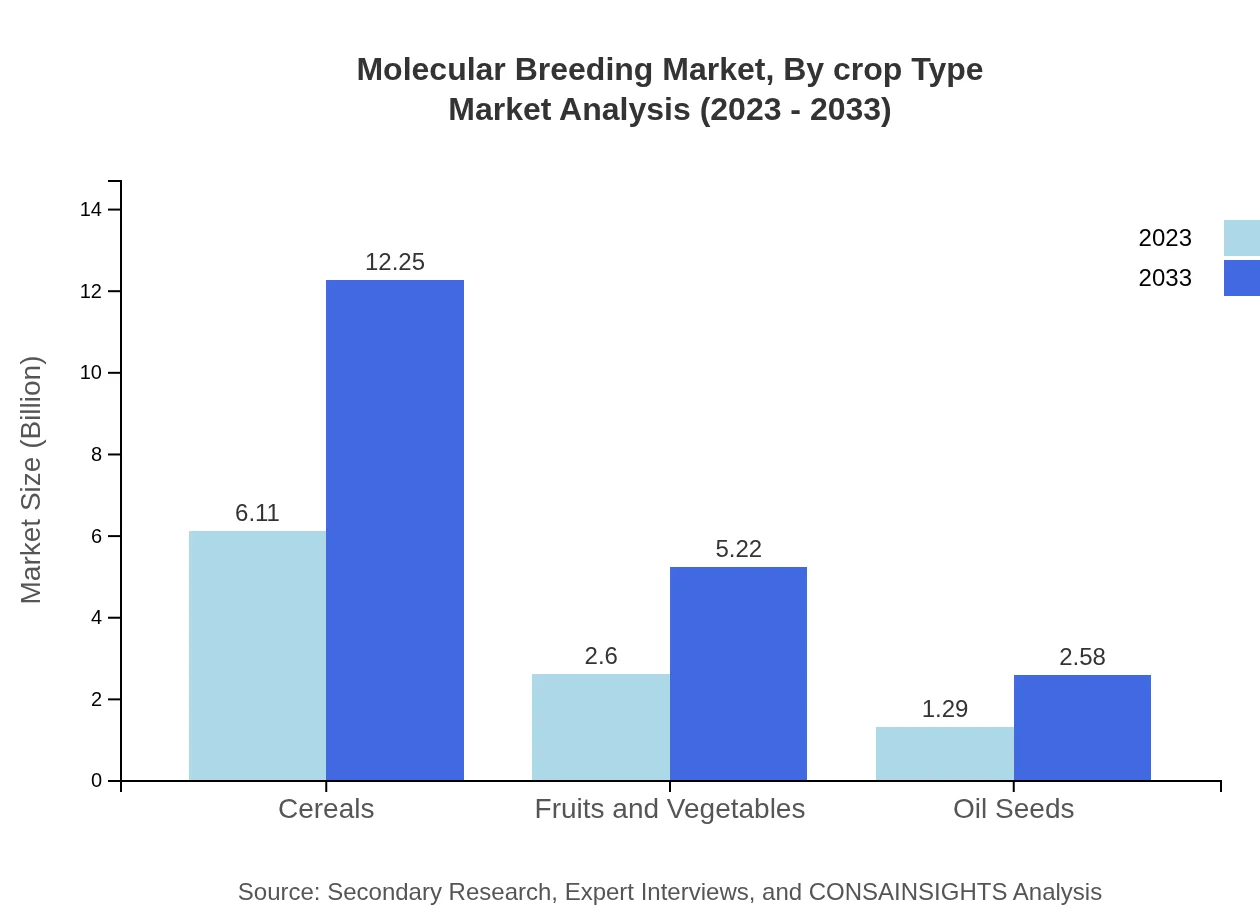
By crop type, cereals dominate the Molecular Breeding market with a size of $6.11 billion in 2023, enhanced by substantial investment in breeding technologies that increase yield and resistance. Fruits and Vegetables follow with a notable size of $2.60 billion, reflecting the sector's focus on quality and health benefits. Oil seeds represent a smaller segment but show potential growth as demand for non-gmo products rises.
Molecular Breeding Market Analysis By End User
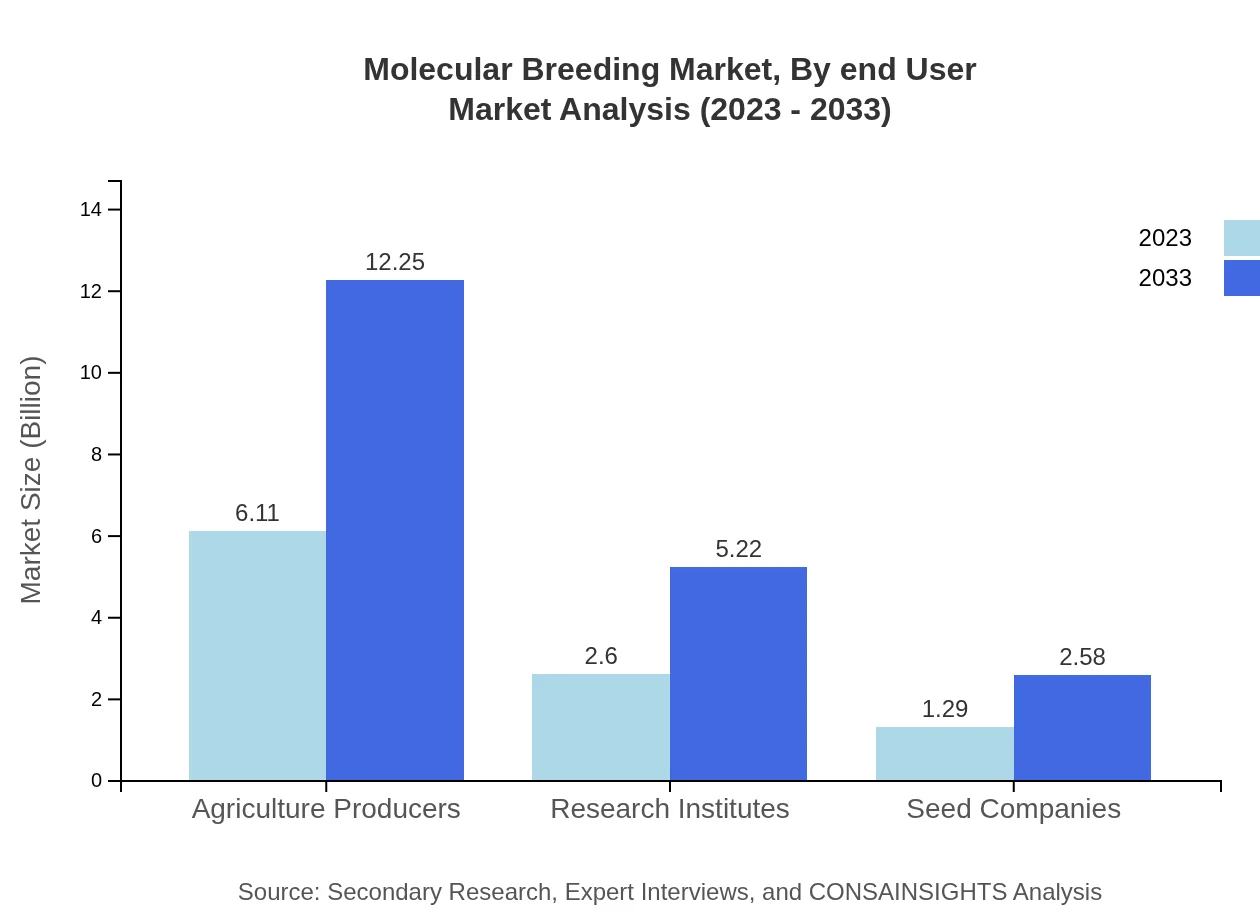
Agricultural producers are the primary end-users in the Molecular Breeding market, holding a significant market share of 61.1% in 2023, which is expected to remain stable through 2033. Research institutes contribute significantly with a 26.02% market share, reflecting their role in technological advancements and partnerships with seed companies.
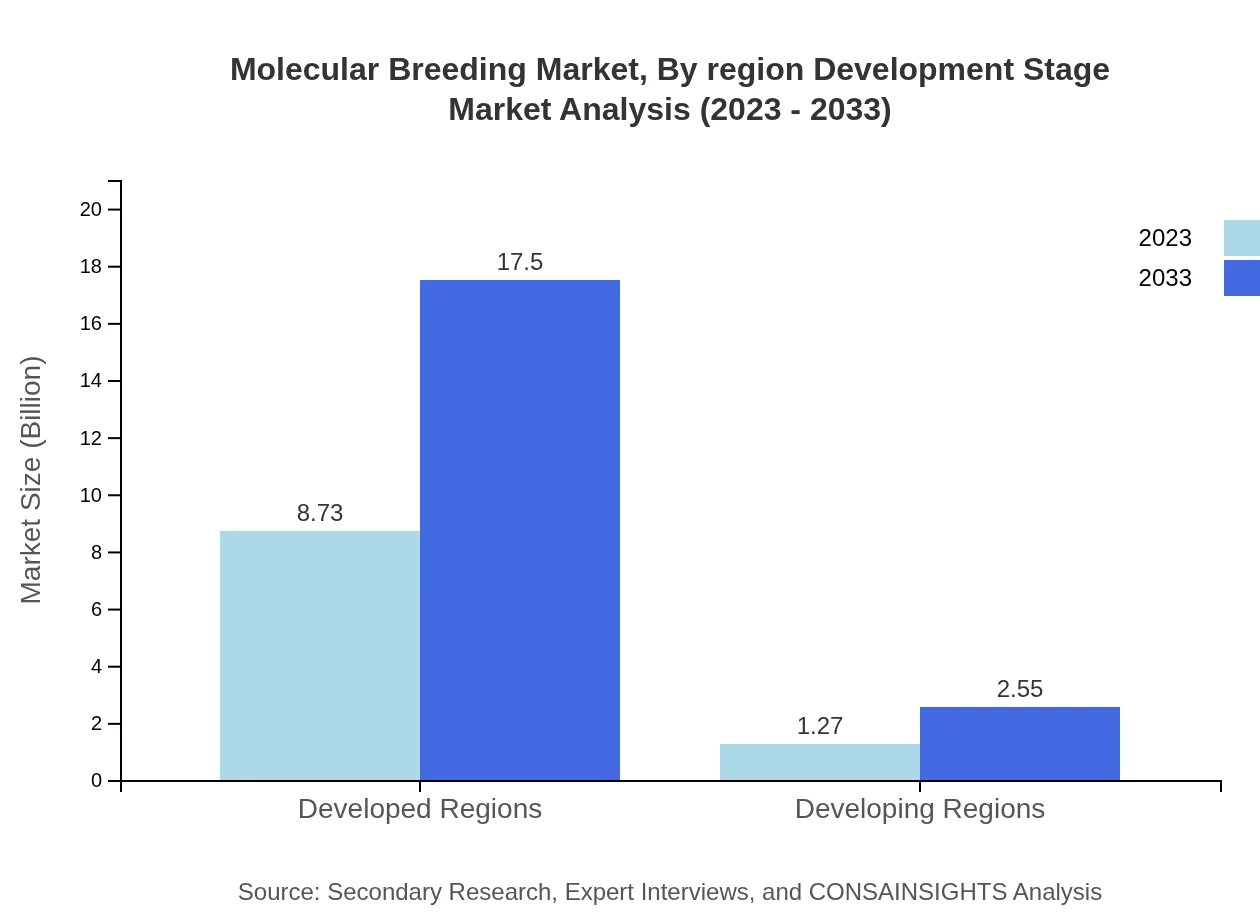
Molecular Breeding Market Analysis By Region Development Stage
The market is largely segmented into developed and developing regions, with developed regions accounted for 87.3% of the market share in 2023 due to established agricultural practices and advanced technology adoption. Developing regions hold a modest share of 12.7% but are projected to experience faster growth rates as biotechnology becomes more accessible.
Molecular Breeding Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Molecular Breeding Industry
BASF SE:
A global leader in agricultural solutions, BASF invests significantly in R&D and innovative breeding technologies to develop high-quality crops while supporting sustainable practices.Syngenta AG:
Syngenta is at the forefront of molecular breeding, focusing on enhancing crop yield and resilience through cutting-edge technology and genomic research.Monsanto Company (now part of Bayer):
Monsanto, now a part of Bayer, has a long history in developing GM crops and has made substantial contributions to advancing molecular breeding techniques.DuPont de Nemours, Inc.:
DuPont's Pioneer brand is recognized for its leadership in developing corn and soy breeding technologies, leveraging CRISPR and other genome editing techniques.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of molecular Breeding?
The molecular breeding market is currently valued at approximately $10 billion in 2023, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7%, suggesting significant growth potential through 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the molecular Breeding industry?
Key players are primarily found in agriculture and biotechnology sectors, including renowned firms focused on plant genetics, seed technology, and gene editing innovations. Specific names, however, depend on detailed market reports.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the molecular breeding industry?
Driving factors include increased demand for food security, advancements in biotechnology, regulatory support, and rising investments in agricultural research and development tailored to enhance crop yields and resilience.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the molecular breeding?
North America is currently the fastest-growing region in the molecular breeding market, expected to expand from $3.72 billion in 2023 to $7.45 billion by 2033, fueled by innovations and strong agricultural policies.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the molecular breeding industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers tailored market research services, providing customized data and insights suited to specific client requirements in the molecular breeding industry.
What deliverables can I expect from this molecular breeding market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables including market size assessments, growth forecasts, regional analyses, competitive landscape evaluations, and detailed segmentation insights reflecting key trends and drivers.
What are the market trends of molecular breeding?
Current trends include increasing adoption of genome editing technologies, rising investment in plant breeding research, collaboration among public and private sectors, and a growing emphasis on sustainability and climate-resilient crops.