Next Generation Network Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: next-generation-network
Next Generation Network Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report offers a comprehensive analysis of the Next Generation Network (NGN) market, highlighting key trends and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. Insights include market size, growth rates, technology advancements, and regional analyses, supporting decision-making and investment strategies.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
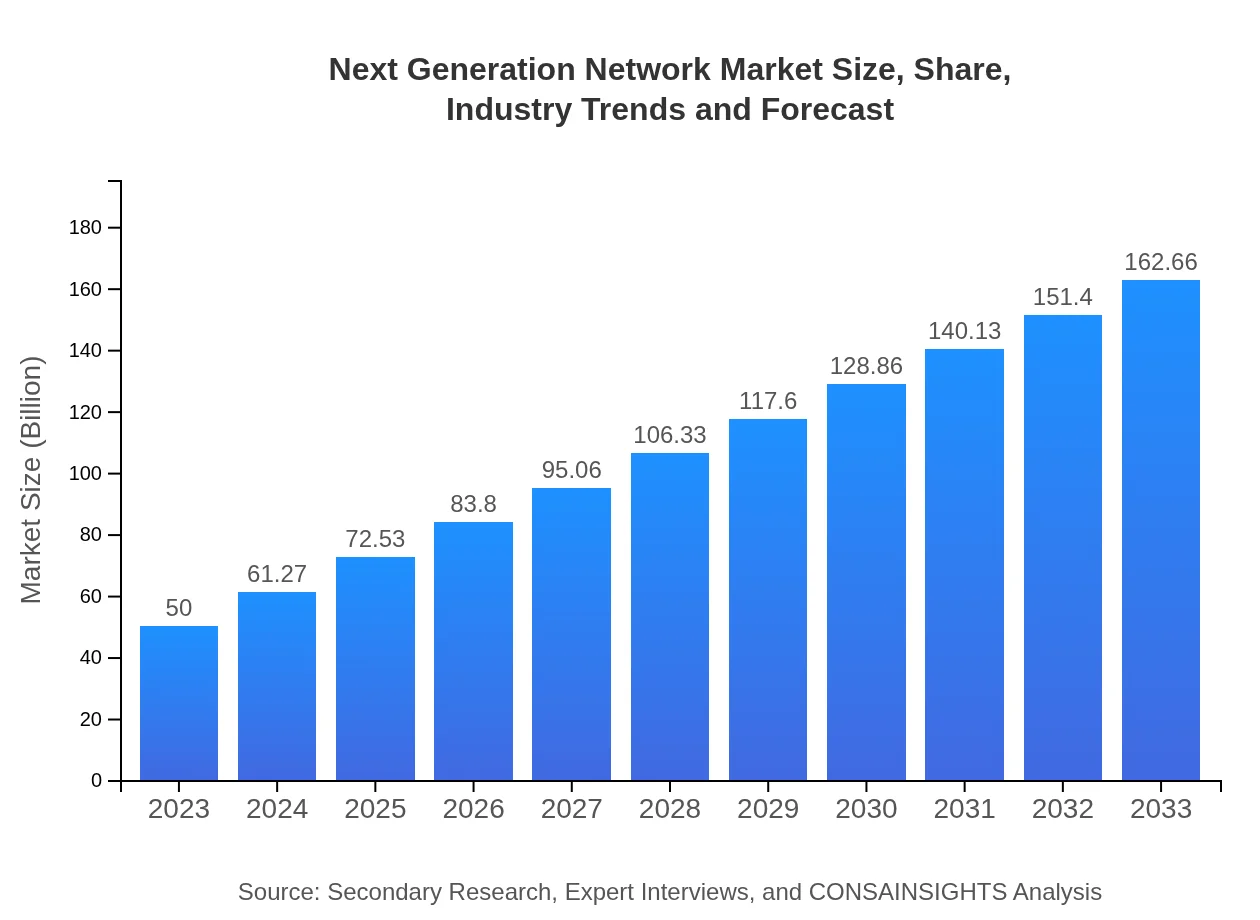
| 2023 Market Size | $50.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 12% |
| 2033 Market Size | $162.66 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cisco Systems, Inc., Nokia Corporation, Ericsson , Juniper Networks |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Next Generation Network Market Overview
Customize Next Generation Network Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Next Generation Network market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Next Generation Network's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Next Generation Network
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Next Generation Network market in 2023?
Next Generation Network Industry Analysis
Next Generation Network Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Next Generation Network Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Next Generation Network Market Report:
Europe showcases a significant market growth trajectory, increasing from USD 13.94 billion in 2023 to USD 45.35 billion by 2033. The European market leaders are focusing on sustainability and energy-efficient technologies, fostering advancements in NGN to meet rigorous regulatory standards.Asia Pacific Next Generation Network Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is anticipated to witness exponential growth in the NGN market, expanding from USD 9.24 billion in 2023 to USD 30.08 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by rapid urbanization, increased internet penetration, and significant investments in telecommunications infrastructure, particularly in countries like China and India.North America Next Generation Network Market Report:
North America dominates the NGN market, projected to rise from USD 19.32 billion in 2023 to USD 62.85 billion by 2033. The region is characterized by early technology adoption, vast investments in IT infrastructure, and extensive 5G deployment. The presence of leading technology firms drives innovation and competition in this sector.South America Next Generation Network Market Report:
In South America, the NGN market is expected to grow from USD 3.98 billion in 2023 to USD 12.95 billion by 2033. The rising demand for advanced communication services and increasing smartphone adoption are key factors enhancing market growth. Governments and enterprises are pushing for improved digital connectivity as part of their development agendas.Middle East & Africa Next Generation Network Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are expected to experience steady growth in the NGN market, rising from USD 3.52 billion in 2023 to USD 11.44 billion by 2033. The region's telecommunications sector is rapidly advancing, driven by government support and investments in smart city projects.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
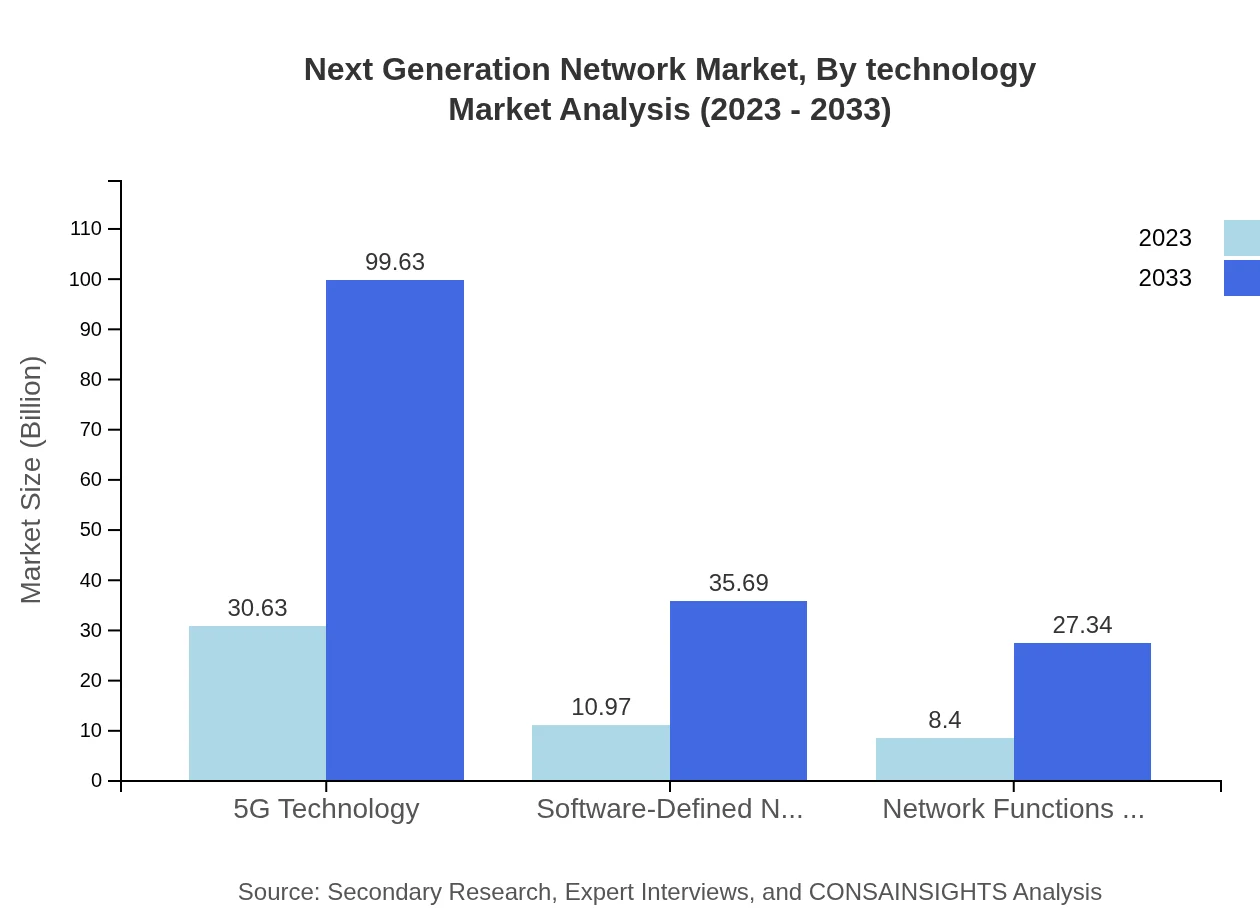
Next Generation Network Market Analysis By Technology
The technology segment includes key components such as 5G technology, SDN, and NFV. Each technology significantly influences the NGN landscape. For instance, 5G technology is expected to grow from USD 30.63 billion in 2023 to USD 99.63 billion by 2033, emphasizing its pivotal role in enabling high-speed, low-latency connections. SDN and NFV are also gaining traction, enhancing flexibility and improving operational efficiencies within networks.
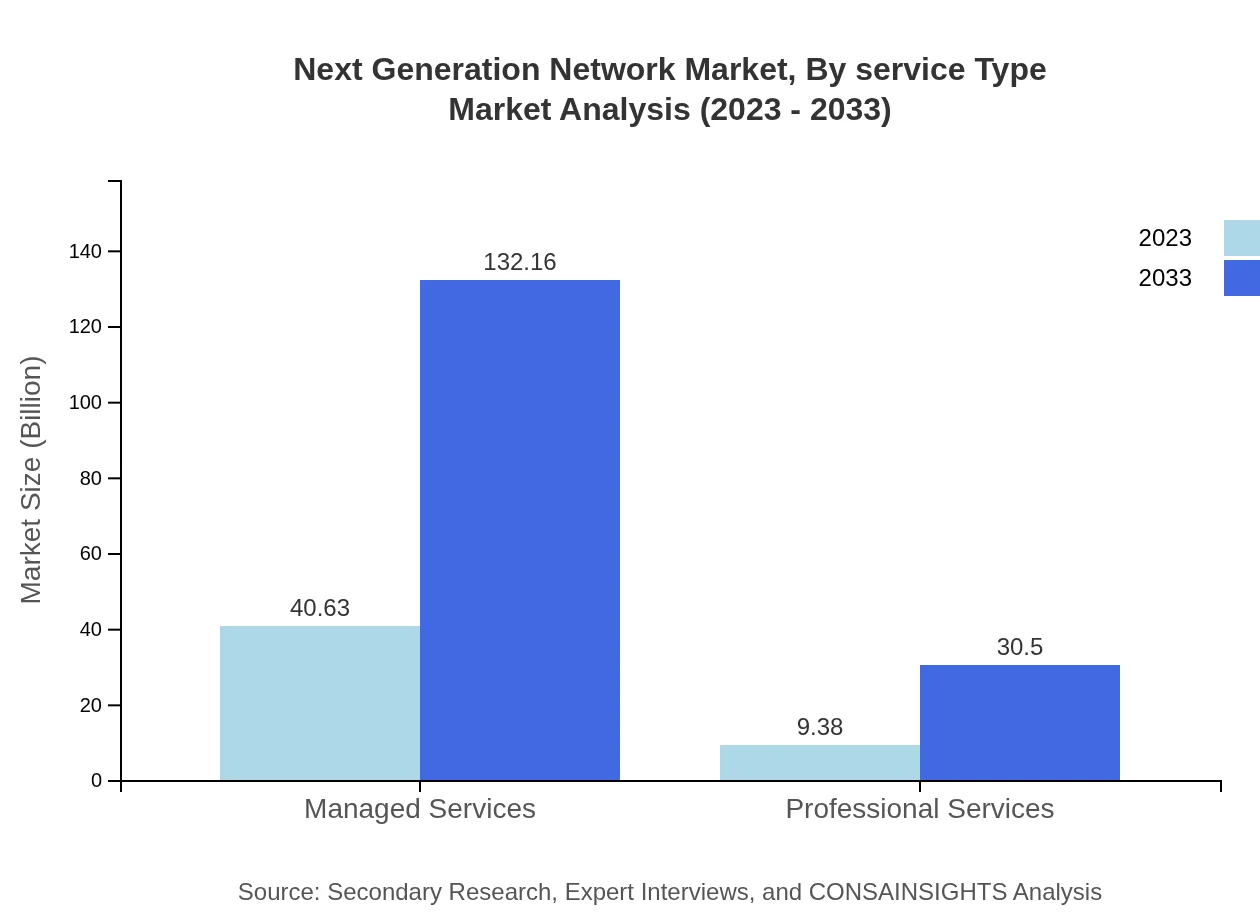
Next Generation Network Market Analysis By Service Type
Managed services dominate the NGN market, growing from USD 40.63 billion in 2023 to USD 132.16 billion by 2033, showing the escalating demand for outsourcing IT-related operations. Professional services also reflect substantial growth, indicating the increasing necessity of specialized providers to support NGN implementations and maintenance.
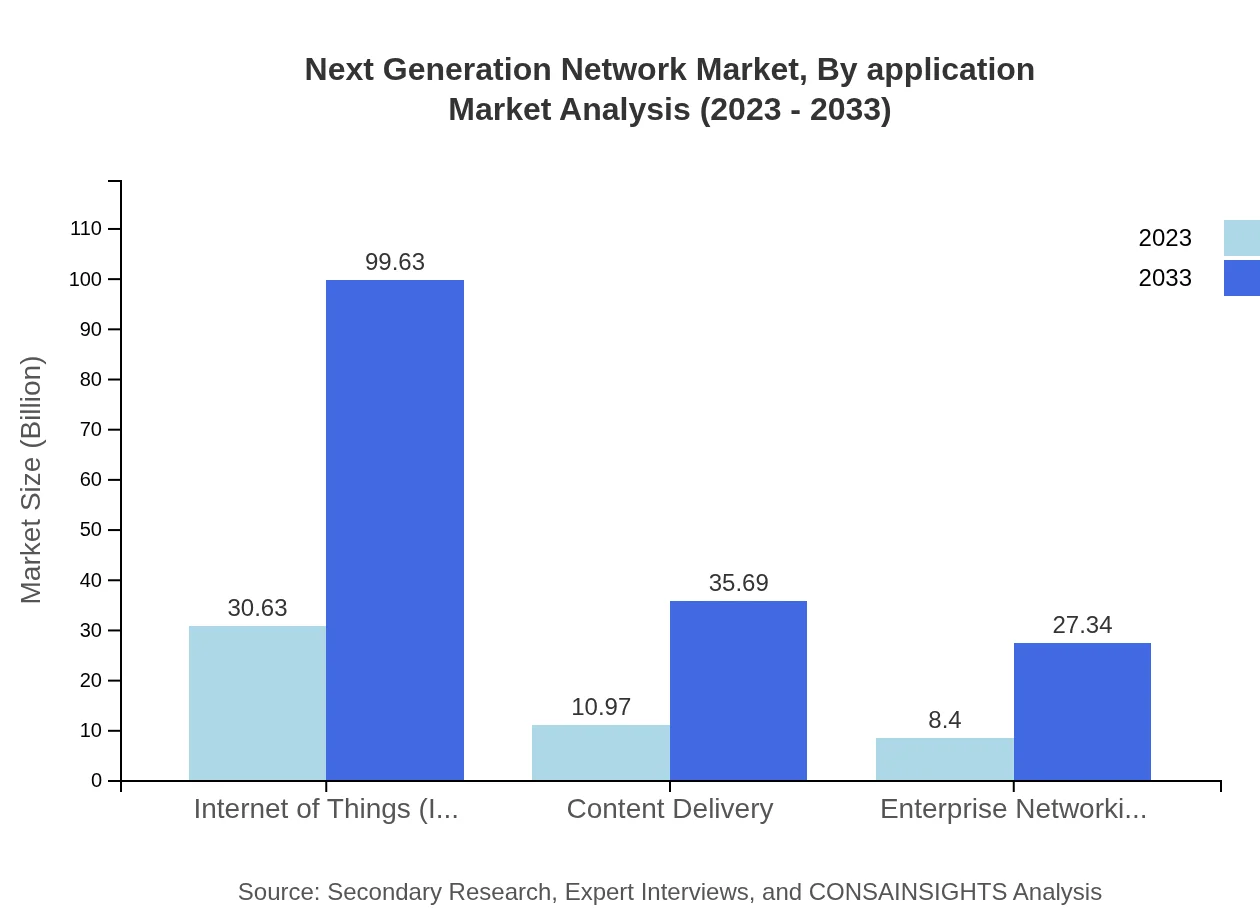
Next Generation Network Market Analysis By Application
The application segment covers various industries such as telecommunications, financial services, healthcare, manufacturing, and retail. Telecommunications leads with a market size projected to increase from USD 20.14 billion in 2023 to USD 65.50 billion by 2033, highlighting the critical importance of enhanced networking capabilities in facilitating communication.
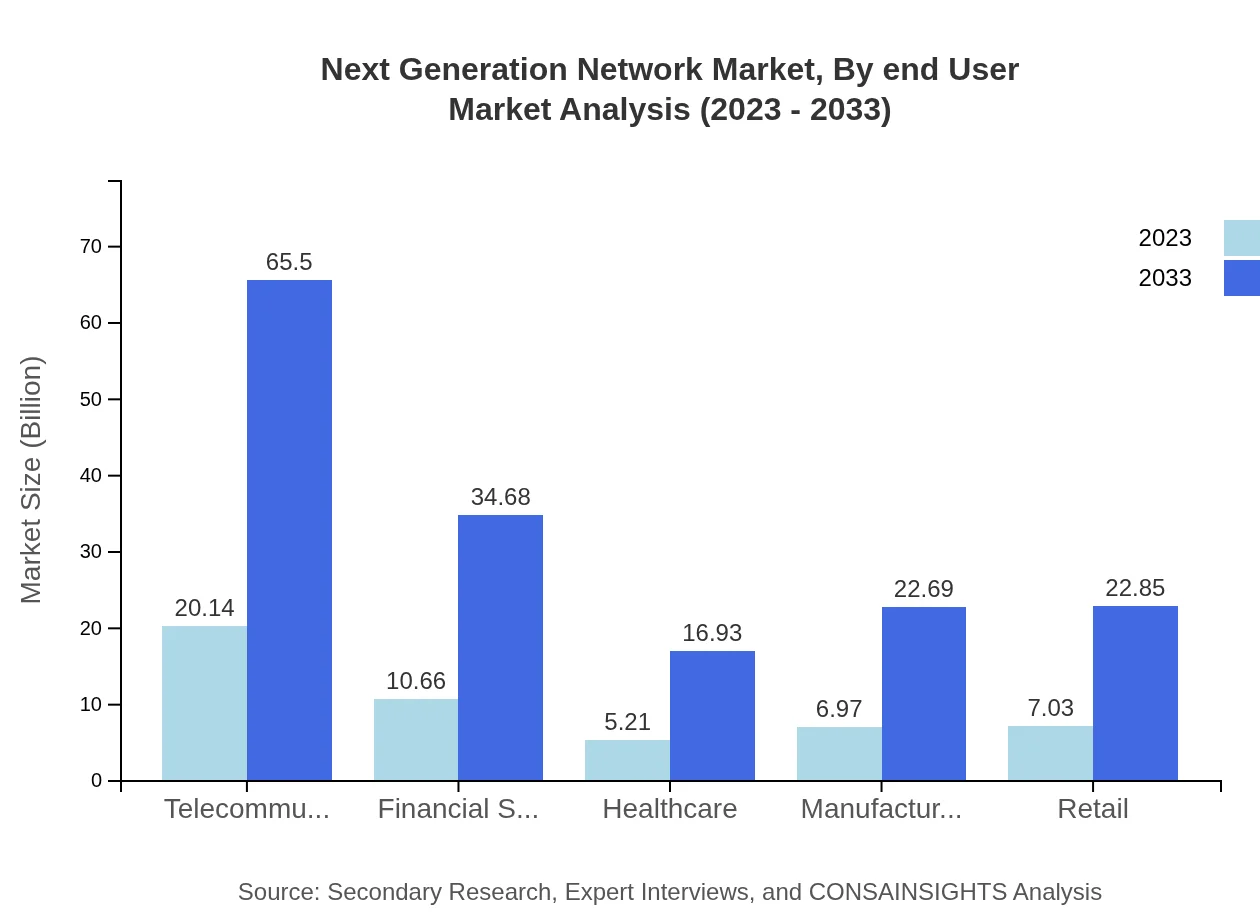
Next Generation Network Market Analysis By End User
The end-user segmentation illustrates diverse requirements across industries, with telecommunications and financial services making substantial contributions. The financial services sector anticipates growth from USD 10.66 billion in 2023 to USD 34.68 billion by 2033, reflecting the industry's transformation through digital financial solutions.
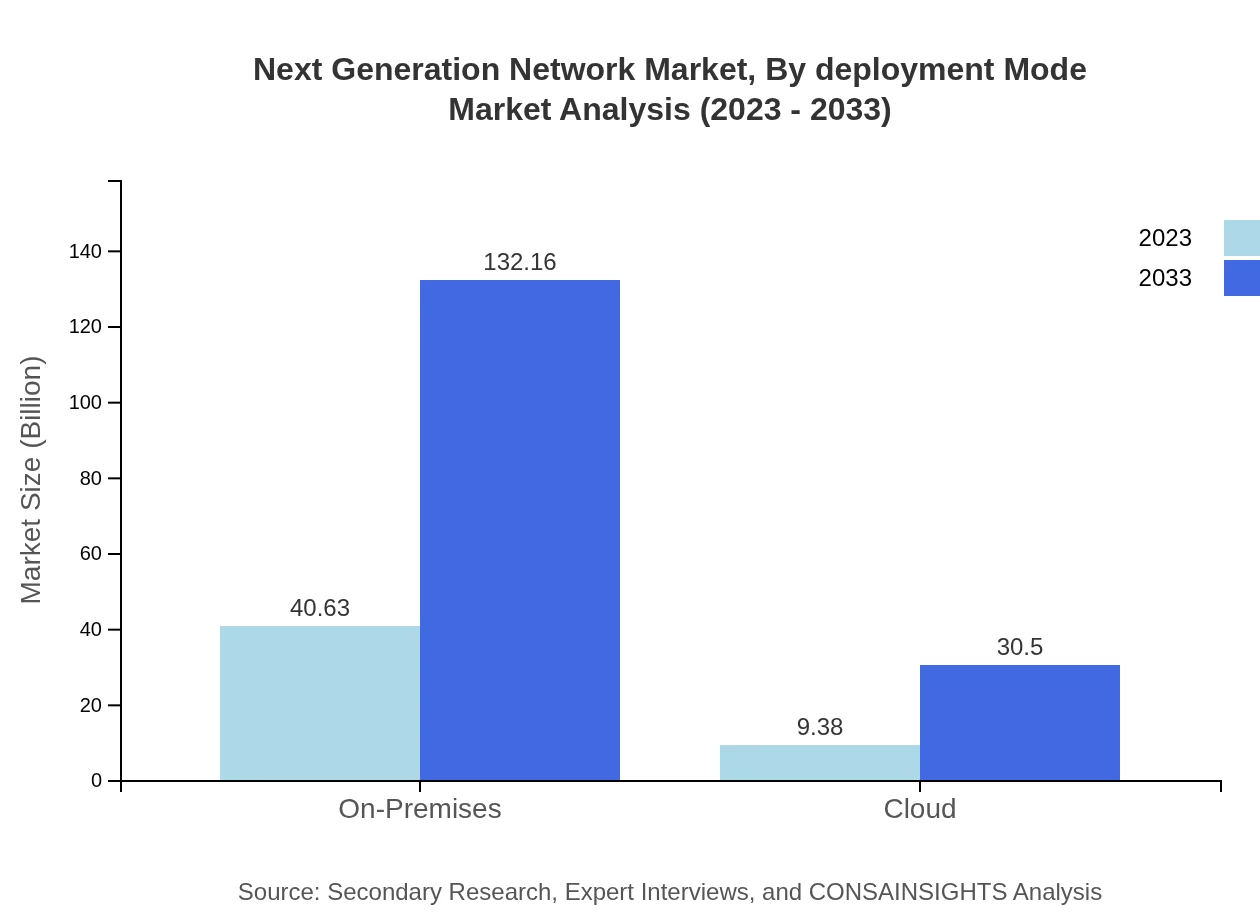
Next Generation Network Market Analysis By Deployment Mode
The deployment mode segment encompasses cloud-based and on-premises solutions. The on-premises model is set to increase from USD 40.63 billion in 2023 to USD 132.16 billion by 2033, driven by enterprises seeking to retain control over their network infrastructure, even as the cloud model experiences robust growth from USD 9.38 billion to USD 30.50 billion over the same period.
Next Generation Network Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Next Generation Network Industry
Cisco Systems, Inc.:
A leader in IT, networking, and cybersecurity solutions, Cisco provides innovative NGN technologies and services that enable businesses to securely connect, collaborate, and operate efficiently.Nokia Corporation:
Nokia is a global leader in telecommunications equipment and services, offering diverse NGN solutions designed to enhance connectivity, optimize network performance, and support digital transformation.Ericsson :
Ericsson specializes in telecommunications and reliable network solutions, focusing on advancing NGN through pioneering technologies such as 5G, SDN, and IoT solutions.Juniper Networks:
Juniper Networks is known for its high-performance networking technologies and robust security solutions, significantly contributing to the evolution of NGNs worldwide.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of next Generation Network?
The global market size of the Next Generation Network is projected to reach $50 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 12% from 2023 to 2033. In 2023, the market stands at $50 billion.
What are the key market players or companies in this next Generation Network industry?
Key players in the Next Generation Network industry include major telecommunications operators, software developers, and hardware manufacturers. Prominent companies focus on innovative solutions in cloud computing, SDN, NFV, and IoT to enhance network efficiency.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the next Generation Network industry?
Growth in the Next Generation Network industry is driven by increasing demand for advanced telecommunications infrastructure, the rise in IoT devices, and the shift towards 5G adoption, boosting service delivery and operational efficiency across sectors.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the next Generation Network?
The fastest-growing region in the Next Generation Network market is North America, expected to grow from $19.32 billion in 2023 to $62.85 billion by 2033. Europe and Asia Pacific also show significant growth potential during the forecast period.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the next Generation Network industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs. Clients can request detailed analysis, including forecasts by region, segment, and diverse market dynamics for the Next Generation Network industry.
What deliverables can I expect from this next Generation Network market research project?
Deliverables from the Next Generation Network market research project include comprehensive reports, data tables, trend analyses, visualizations, and actionable insights on market size, growth rates, and major segments across various regions.
What are the market trends of next Generation Network?
Current market trends in the Next Generation Network include the deployment of 5G technologies, increased cloud computing adoption, emphasis on network security, and a shift towards software-defined networking, enhancing connectivity, speed, and flexibility.