Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: nuclear-reactor-construction
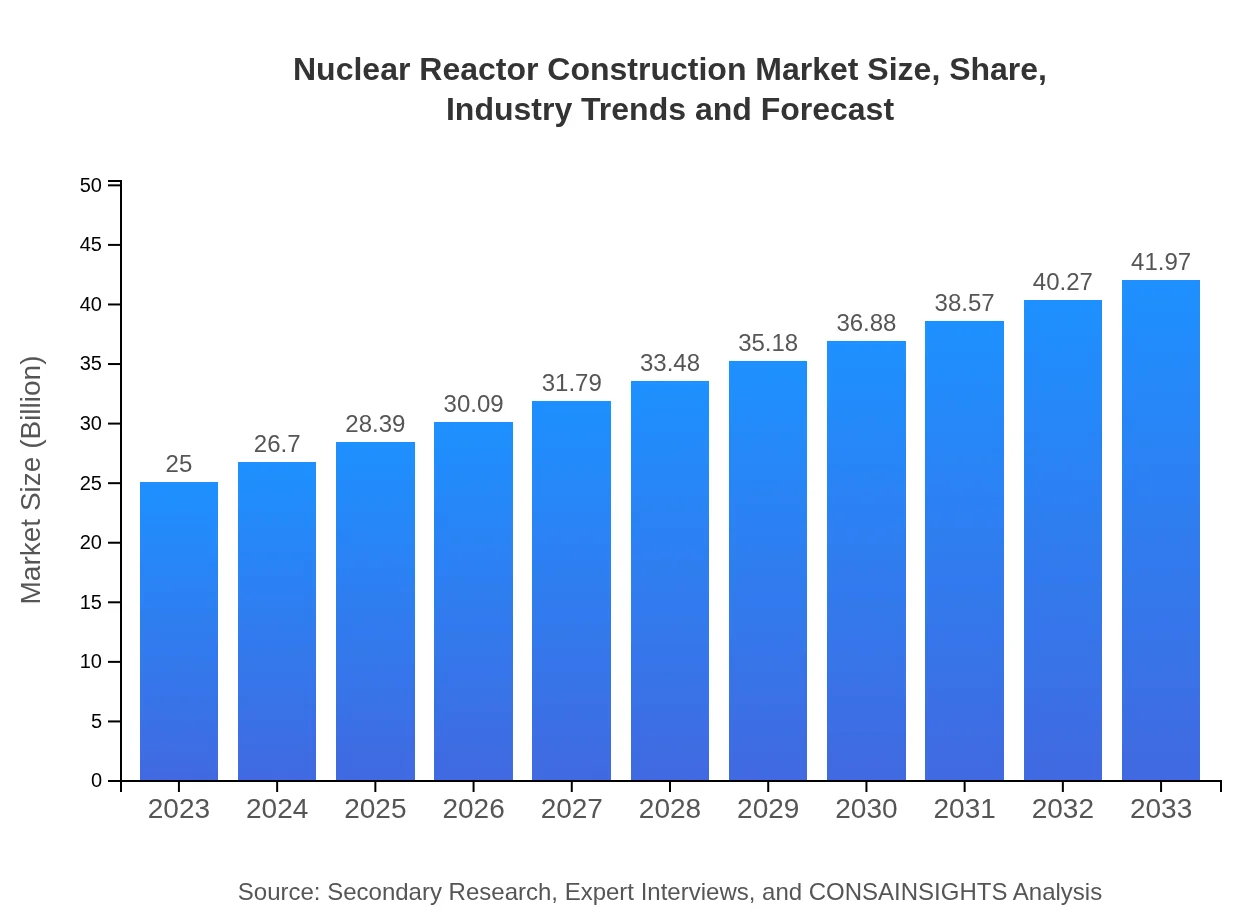
Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Nuclear Reactor Construction market, including insights on market size, segments, regional dynamics, and future forecasts from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $25.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $41.97 Billion |
| Top Companies | General Electric, Areva NP, Westinghouse Electric Company, Hitachi-GE Nuclear Energy, Rosatom |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Overview
Customize Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Nuclear Reactor Construction market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Nuclear Reactor Construction's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Nuclear Reactor Construction
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Nuclear Reactor Construction market in 2023?
Nuclear Reactor Construction Industry Analysis
Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Report:
In Europe, the Nuclear Reactor Construction market is projected to grow from $7.45 billion in 2023 to $12.51 billion by 2033. With countries like France prioritizing nuclear energy in their long-term sustainability plans and others revisiting nuclear options, investments in new plants are expected to increase.Asia Pacific Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Nuclear Reactor Construction market is set to grow from $4.72 billion in 2023 to approximately $7.92 billion by 2033. Countries like China and India are investing significantly in building nuclear facilities as part of their energy diversification strategies, promoting sustainable power generation.North America Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Report:
The North American Nuclear Reactor Construction market will see a rise from $9.23 billion in 2023 to $15.50 billion by 2033. The U.S. and Canada are expanding existing infrastructures while focusing on innovations such as small modular reactors (SMRs) to rejuvenate their aging facilities and ensure energy resilience.South America Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Report:
South America’s Nuclear Reactor Construction market is expected to increase from $1.50 billion in 2023 to $2.52 billion in 2033. Brazil and Argentina lead the efforts by pursuing nuclear energy alternatives to reduce reliance on hydroelectric sources, reflecting a growing commitment to nuclear investments.Middle East & Africa Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa’s Nuclear Reactor Construction market will expand from $2.10 billion in 2023 to $3.52 billion by 2033. Nations such as the UAE are pioneering nuclear projects to address energy demands while maintaining economic diversification strategies.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
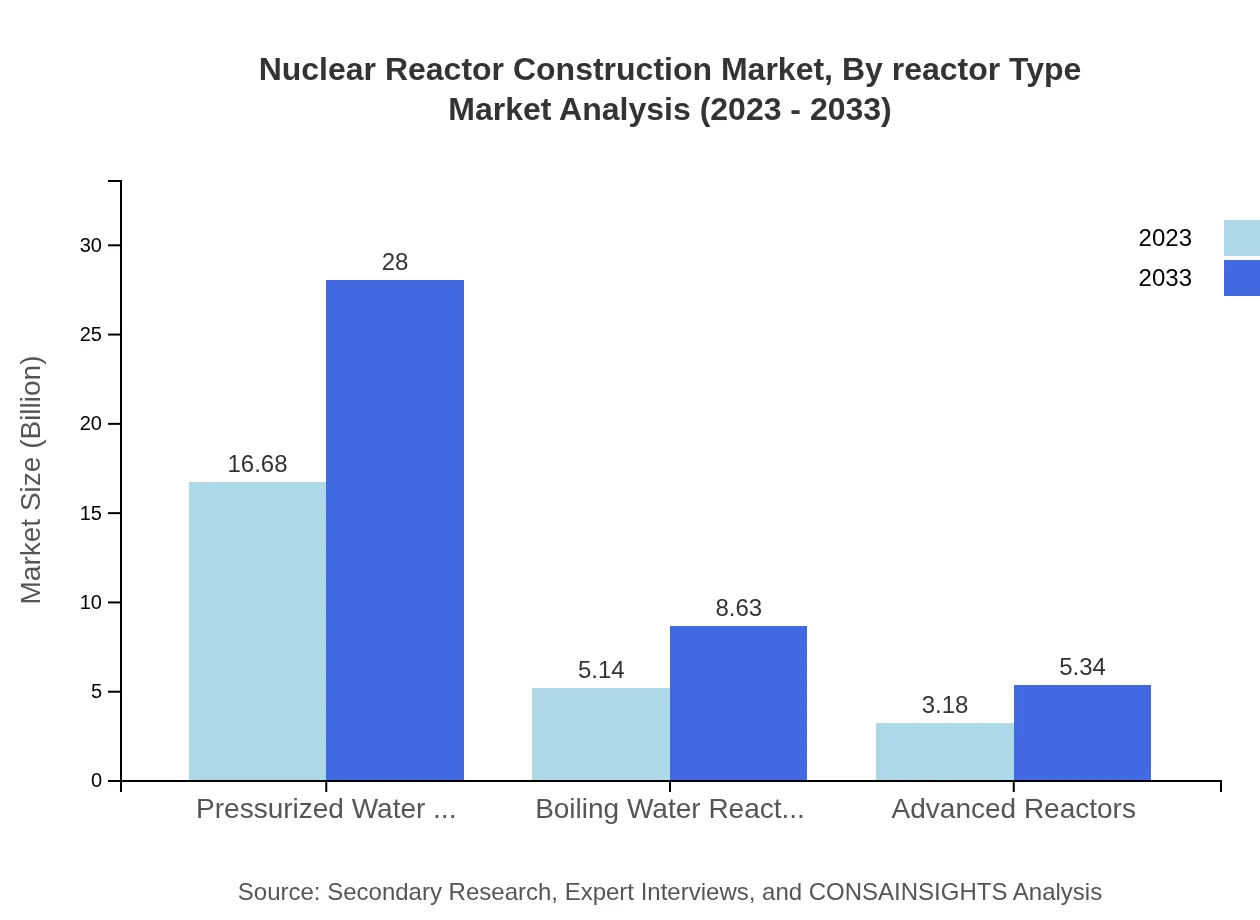
Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Analysis By Reactor Type
The Nuclear Reactor Construction market by reactor type is dominated by Pressurized Water Reactors (PWRs), which accounted for a market size of $16.68 billion in 2023, scaling to $28 billion by 2033. PWRs maintain a market share of approximately 66.71%, providing a reliable energy output. Boiling Water Reactors (BWRs) follow, with a size of $5.14 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $8.63 billion. Advanced Reactors contribute significantly with a size of $3.18 billion in 2023, projected to reach $5.34 billion by 2033, showing promise for future innovations.
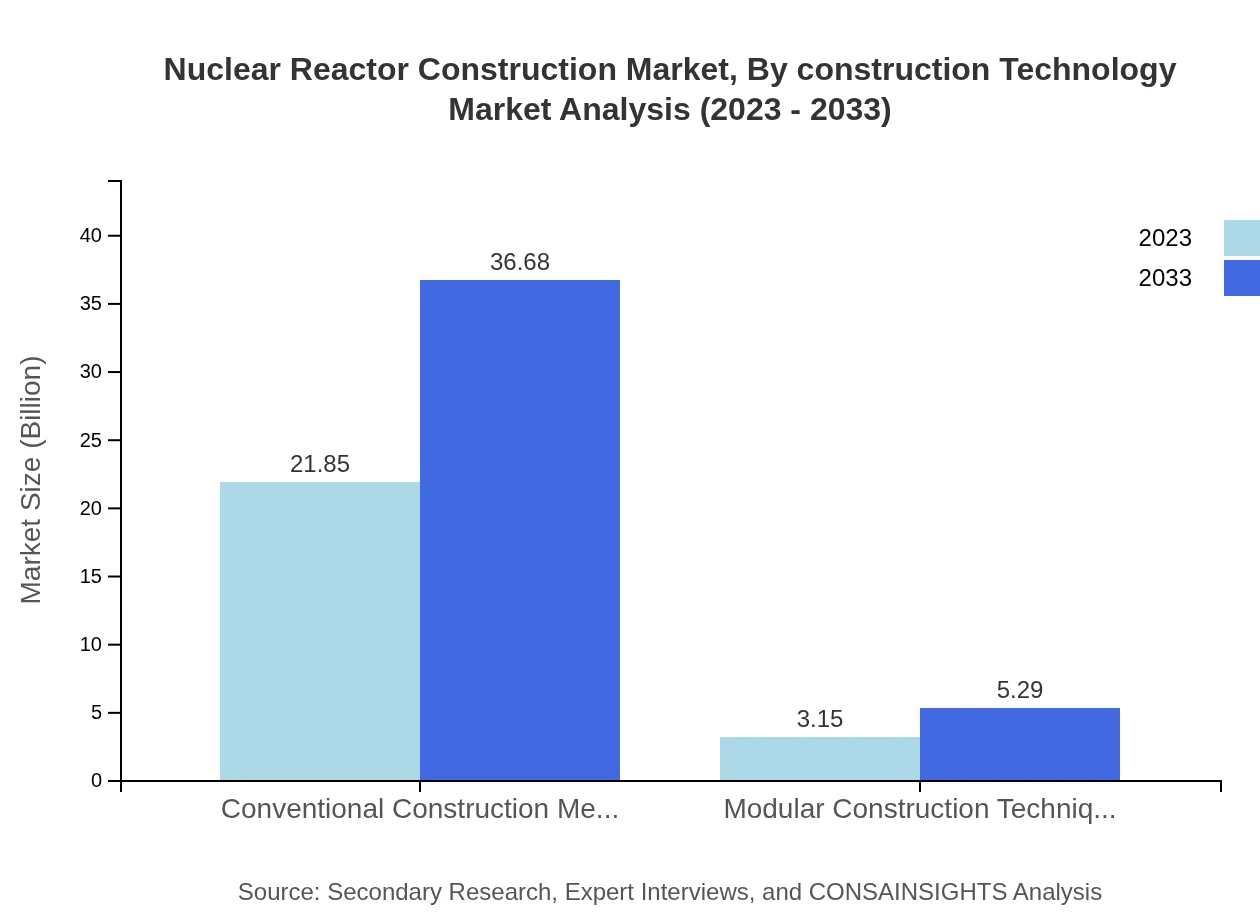
Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Analysis By Construction Technology
In the context of construction technology, Conventional Construction Methods dominate the Nuclear Reactor Construction market, holding a size of $21.85 billion in 2023 and expected to expand to $36.68 billion by 2033. Modular Construction Techniques, though smaller in market size at $3.15 billion in 2023, are predicted to rise to $5.29 billion, reflecting a shift towards more efficient building practices.
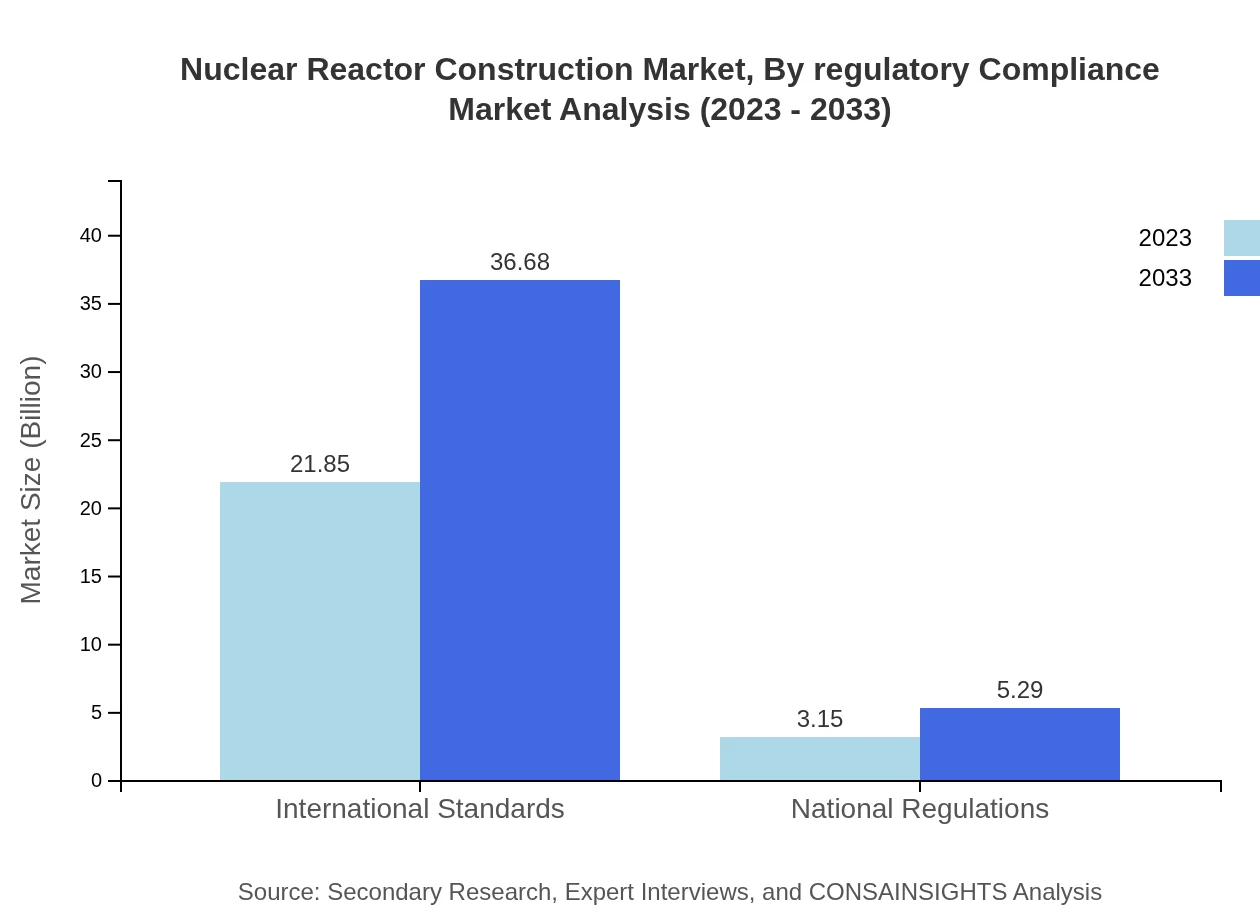
Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Analysis By Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance remains a critical aspect of the Nuclear Reactor Construction market. International Standards impact a market size of $21.85 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to $36.68 billion by 2033. National Regulations also hold significance, starting at $3.15 billion and expected to rise to $5.29 billion. These frameworks shape the construction processes and ensure safety across projects.
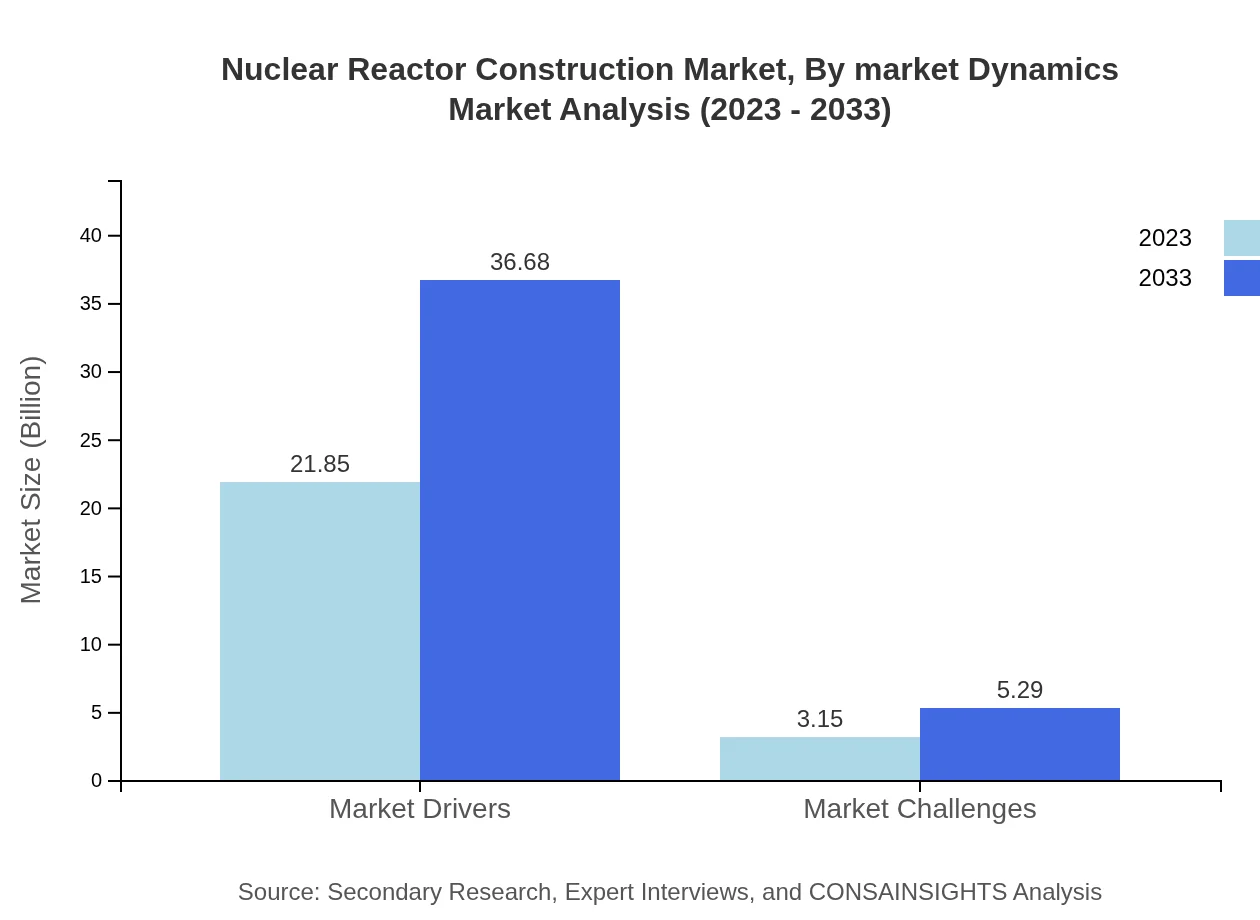
Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Analysis By Market Dynamics
Market Dynamics reveal a significant portion of the Nuclear Reactor Construction industry is driven by robust demand and regulatory frameworks. Market Drivers are at a size of $21.85 billion in 2023, likely increasing to $36.68 billion, while Market Challenges face lesser size comparisons, at $3.15 billion and growing to $5.29 billion by 2033, emphasizing the need for sustained adaptation to challenges and innovations.
Nuclear Reactor Construction Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Nuclear Reactor Construction Industry
General Electric:
A leader in energy technology, General Electric offers expertise in the design and construction of nuclear reactors, focusing on enhancing reactor efficiency and safety.Areva NP:
Areva NP specializes in nuclear reactor construction and maintenance, providing advanced technology and nuclear solutions worldwide.Westinghouse Electric Company:
Westinghouse is renowned for its PWR technology and plays a pivotal role in global nuclear reactor construction projects.Hitachi-GE Nuclear Energy:
A joint venture focusing on nuclear reactor engineering and construction, Hitachi-GE provides innovative solutions in reactor technology.Rosatom:
The Russian state atomic energy corporation is a major player in nuclear reactor construction, known for its robust project development in various countries.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of nuclear Reactor Construction?
The nuclear reactor construction market is valued at approximately $25 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2%, depicting a robust trajectory through 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the nuclear Reactor Construction industry?
Key players in the nuclear reactor construction industry include major firms like Areva, Westinghouse Electric Company, and General Electric. These companies lead in technology and project execution, shaping market developments and competition.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the nuclear reactor construction industry?
Driving factors in the nuclear reactor construction industry include increasing global energy demands, a shift towards low-carbon power sources, and major investments in nuclear technology for enhanced safety and efficiency.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the nuclear reactor construction?
The fastest-growing region in nuclear reactor construction is North America, expected to increase from $9.23 billion in 2023 to $15.50 billion by 2033, driven by infrastructure investments and government policies.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the nuclear Reactor Construction industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data catering to specific needs in the nuclear reactor construction industry, enabling tailored insights and analyses for optimal decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this nuclear reactor construction market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables including market analysis reports, trend forecasts, competitive landscapes, regional assessments, and insights into market dynamics and segment performances.
What are the market trends of nuclear reactor construction?
Current trends in nuclear reactor construction emphasize modular construction techniques, adherence to international standards, improved safety measures, and a growing shift towards advanced reactor technologies.