Oil And Gas Robotics Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: oil-and-gas-robotics
Oil And Gas Robotics Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Oil and Gas Robotics market, covering insights from 2023 to 2033. It delves into market size, growth forecasts, technology trends, regional insights, and key players in the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
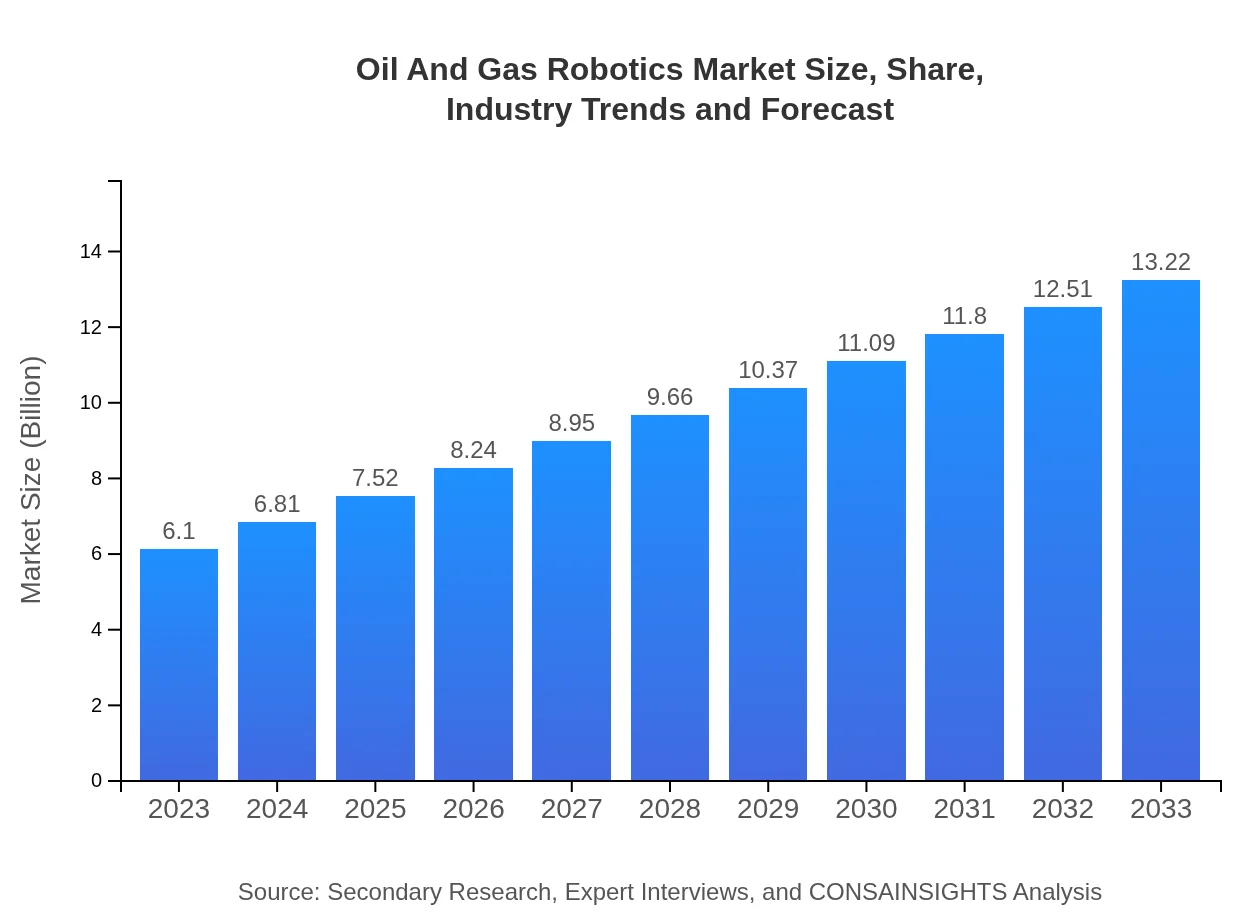
| 2023 Market Size | $6.10 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $13.22 Billion |
| Top Companies | Schlumberger, Halliburton, Fugro, Danfoss |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Oil And Gas Robotics Market Overview
Customize Oil And Gas Robotics Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Oil And Gas Robotics market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Oil And Gas Robotics's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Oil And Gas Robotics
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Oil And Gas Robotics market in 2023?
Oil And Gas Robotics Industry Analysis
Oil And Gas Robotics Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Oil And Gas Robotics Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Oil And Gas Robotics Market Report:
In Europe, the market is projected to grow from USD 2.09 billion in 2023 to USD 4.53 billion by 2033. Factors influencing growth include stringent safety regulations and the need for automation in traditional oil and gas operations.Asia Pacific Oil And Gas Robotics Market Report:
In the Asia-Pacific region, the Oil and Gas Robotics market is anticipated to grow from USD 1.01 billion in 2023 to USD 2.19 billion by 2033. The growth is driven by increasing investments in energy infrastructure and the adoption of advanced technology to enhance operational efficiency.North America Oil And Gas Robotics Market Report:
The North American market is expected to rise from USD 2.14 billion in 2023 to USD 4.64 billion by 2033. As a leader in adopting advanced robotics, the region benefits from a strong technology base and significant investment in exploration and production.South America Oil And Gas Robotics Market Report:
The South American market is projected to increase from USD 0.25 billion in 2023 to USD 0.55 billion by 2033. Growth factors include the region's rich natural resources and efforts to modernize traditional oil and gas operations through technology.Middle East & Africa Oil And Gas Robotics Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is forecasted to expand from USD 0.61 billion in 2023 to USD 1.31 billion by 2033. The region's focus on enhancing production efficiencies and reducing operational costs drives the adoption of robotics technology.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Oil And Gas Robotics Market Analysis By Robot Type
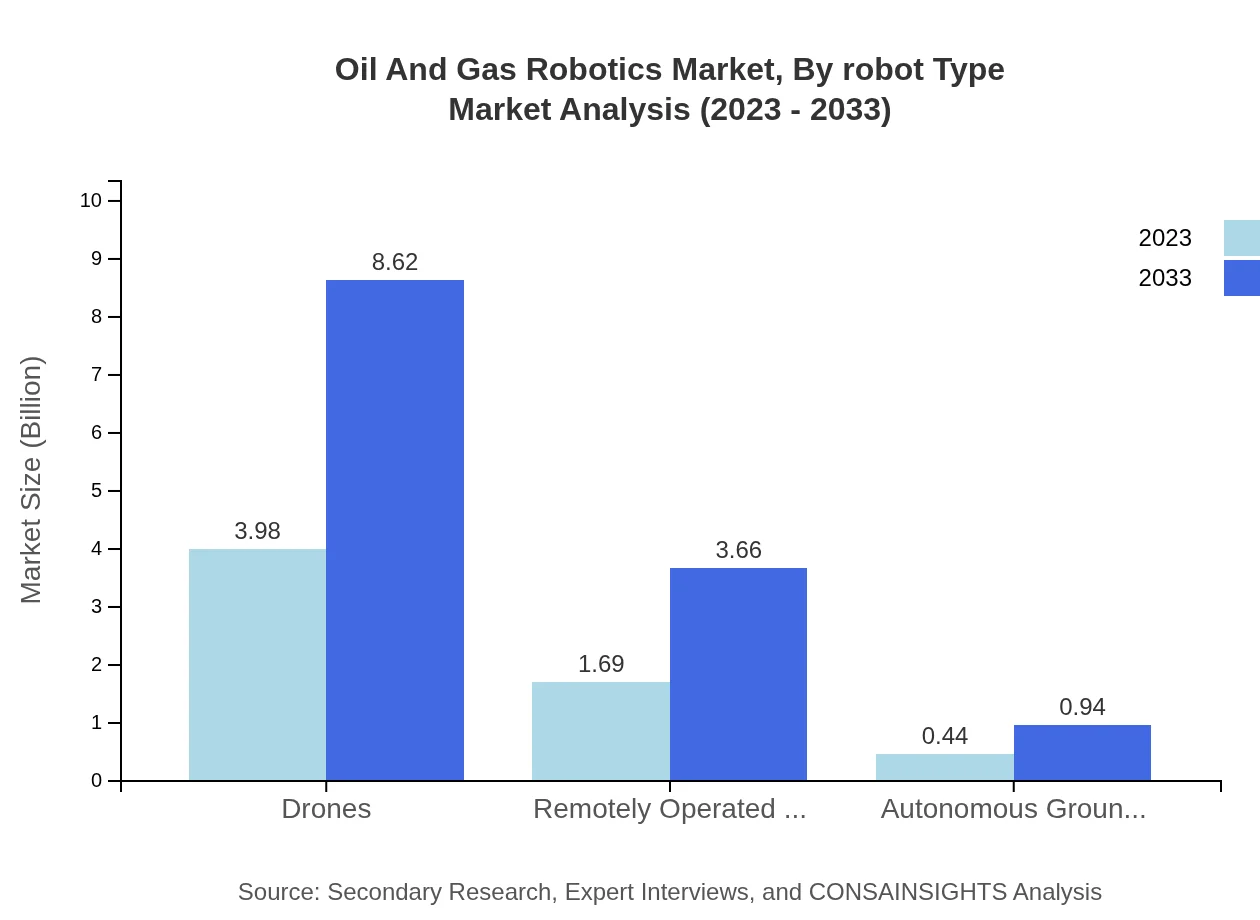
Drones dominate the market with a share of 65.17% in 2023 and projected to double by 2033, owing to their efficiency in aerial surveying and monitoring. ROVs are significant contributors, maintaining a 27.69% share, especially in underwater operations. Autonomous Ground Vehicles represent 7.14% in 2023, gradually increasing as their applications diversify.
Oil And Gas Robotics Market Analysis By Application
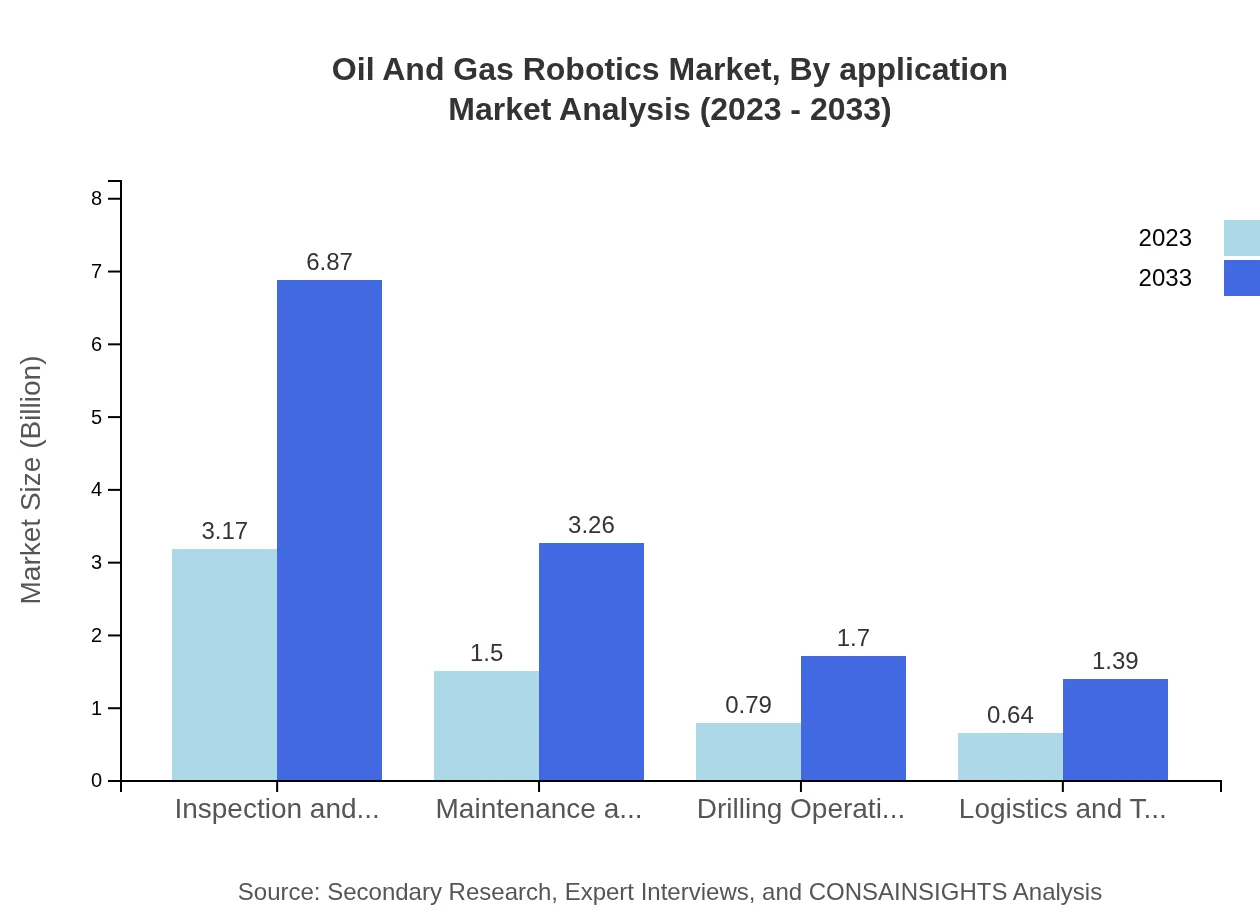
Inspection and Monitoring account for 51.98% of the market in 2023, crucial for safety and compliance. Drilling Operations follow closely with 12.89%, driven by advancements in precision drilling technology. Maintenance Operations represent 24.62%, reflecting the growing emphasis on reducing downtime and extending equipment lifespan.
Oil And Gas Robotics Market Analysis By Technology
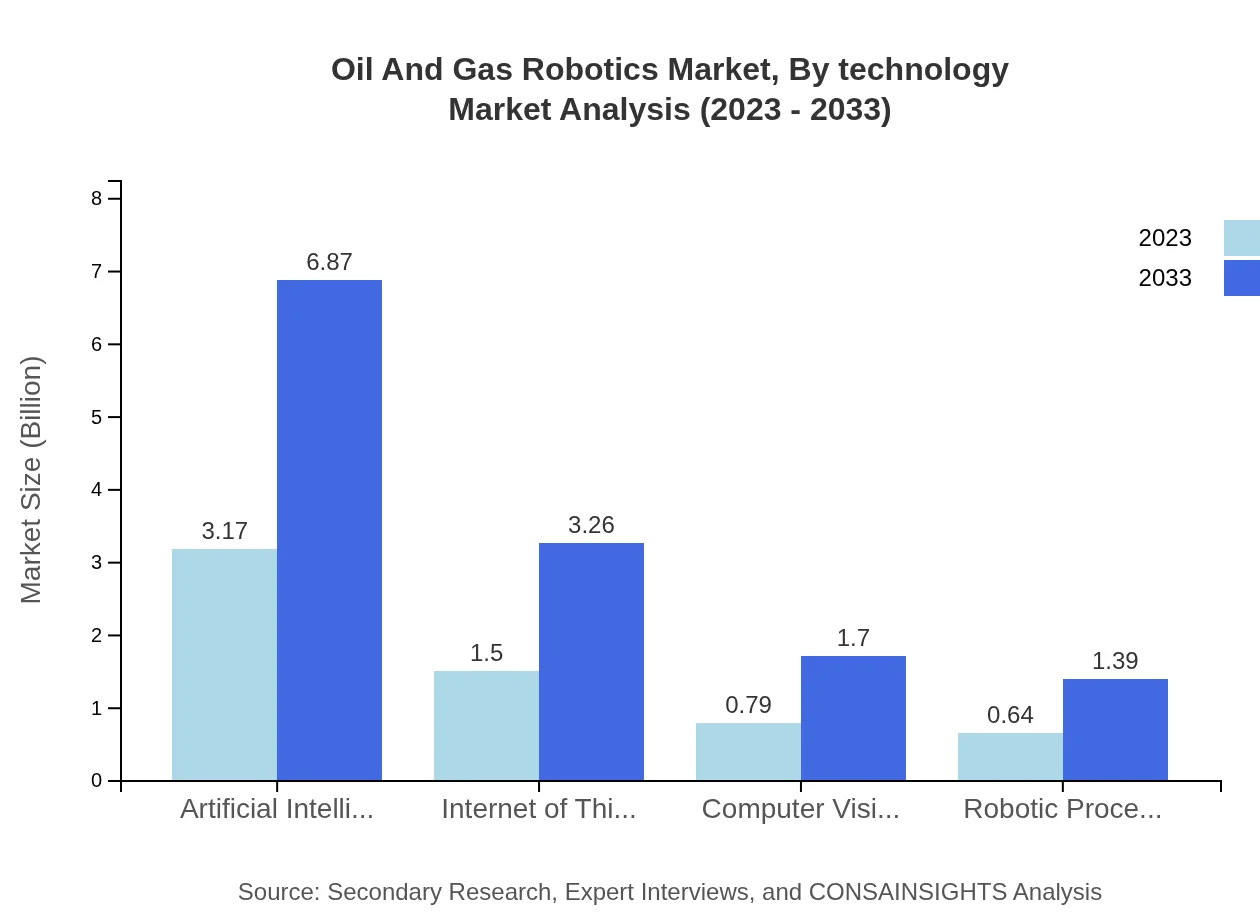
AI and Machine Learning hold a dominant 51.98% market share, facilitating predictive maintenance and autonomous operations. The IoT segment captures 24.62%, enhancing connectivity between devices. Other technologies, including Computer Vision and Robotic Process Automation, contribute to overall efficiency.
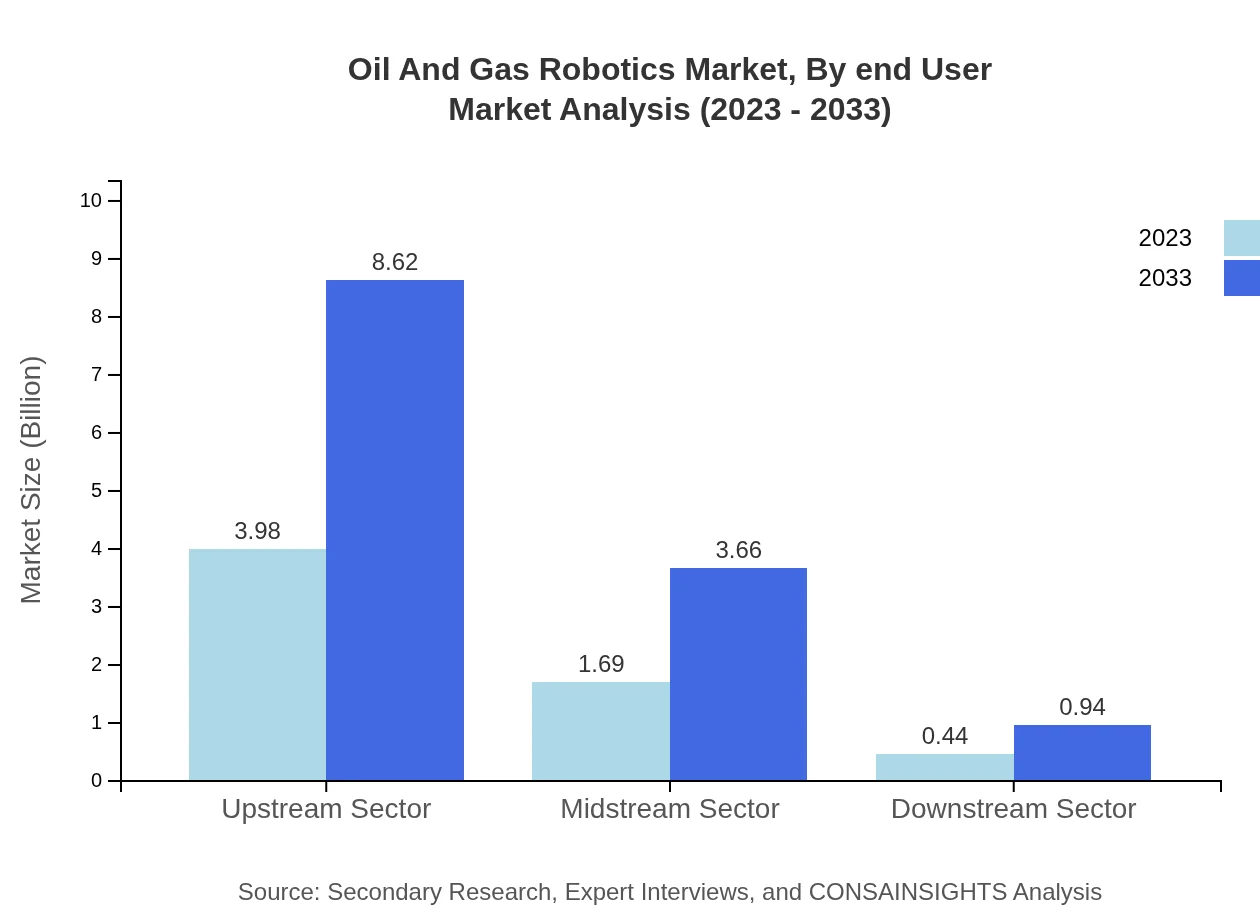
Oil And Gas Robotics Market Analysis By End User
Exploration companies make up 40% of the market share, emphasizing robotics for exploration and production efficiencies. Pipeline operators represent 35%, leveraging technology for monitoring and inspection tasks. Production facilities account for 25%, focusing on enhancing operational workflows.
Oil And Gas Robotics Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Oil And Gas Robotics Industry
Schlumberger:
A leading oilfield services company offering advanced robotic solutions for enhanced oil recovery and operational safety.Halliburton:
Provides advanced robotics and automation solutions, focusing on optimizing drilling and production operations.Fugro:
Specializes in geodata services, utilizing autonomous underwater vehicles for subsea inspection and mapping.Danfoss:
Offers innovative automation and control solutions, enhancing operational efficiency in the oil and gas sector.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of oil And Gas Robotics?
The global oil-and-gas-robotics market is currently valued at approximately $6.1 billion and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2023 to 2033, reflecting increasing adoption of advanced robotic technologies in the sector.
What are the key market players or companies in the oil And Gas Robotics industry?
Key players in the oil-and-gas-robotics market include major multinational corporations and specialized technology firms. These include Halliburton, Schlumberger, and Chevron, focusing on robotics for drilling, maintenance, and logistics within the industry.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the oil And Gas Robotics industry?
Growth drivers include the increasing demand for automation to enhance operational efficiency, safety concerns leading to reduced human exposure in hazardous environments, and advancements in robotic technologies, AI, and IoT applications in oil and gas operations.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the oil And Gas Robotics?
The fastest-growing region is Europe, projected to expand from $2.09 billion in 2023 to $4.53 billion in 2033. This growth is fueled by significant investments in automation and technology by key European oil and gas companies.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the oil And Gas Robotics industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the specific needs of clients in the oil-and-gas-robotics industry, ensuring relevant insights and analytics to facilitate informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this oil And Gas Robotics market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis reports, insights on trends, competitive landscape assessments, forecasts, segmentation data, and tailored recommendations based on the latest industry developments.
What are the market trends of oil And Gas Robotics?
Current trends in the oil-and-gas-robotics market include increased use of drones for inspection, integration of AI and machine learning for predictive maintenance, and expanding applications of IoT for real-time monitoring and analytics.