Organic Seed Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: organic-seed
Organic Seed Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This comprehensive report provides an in-depth analysis of the Organic Seed market from 2023 to 2033, exploring market size, growth trends, regional performance, and competitive landscape to offer valuable insights for stakeholders and decision-makers.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
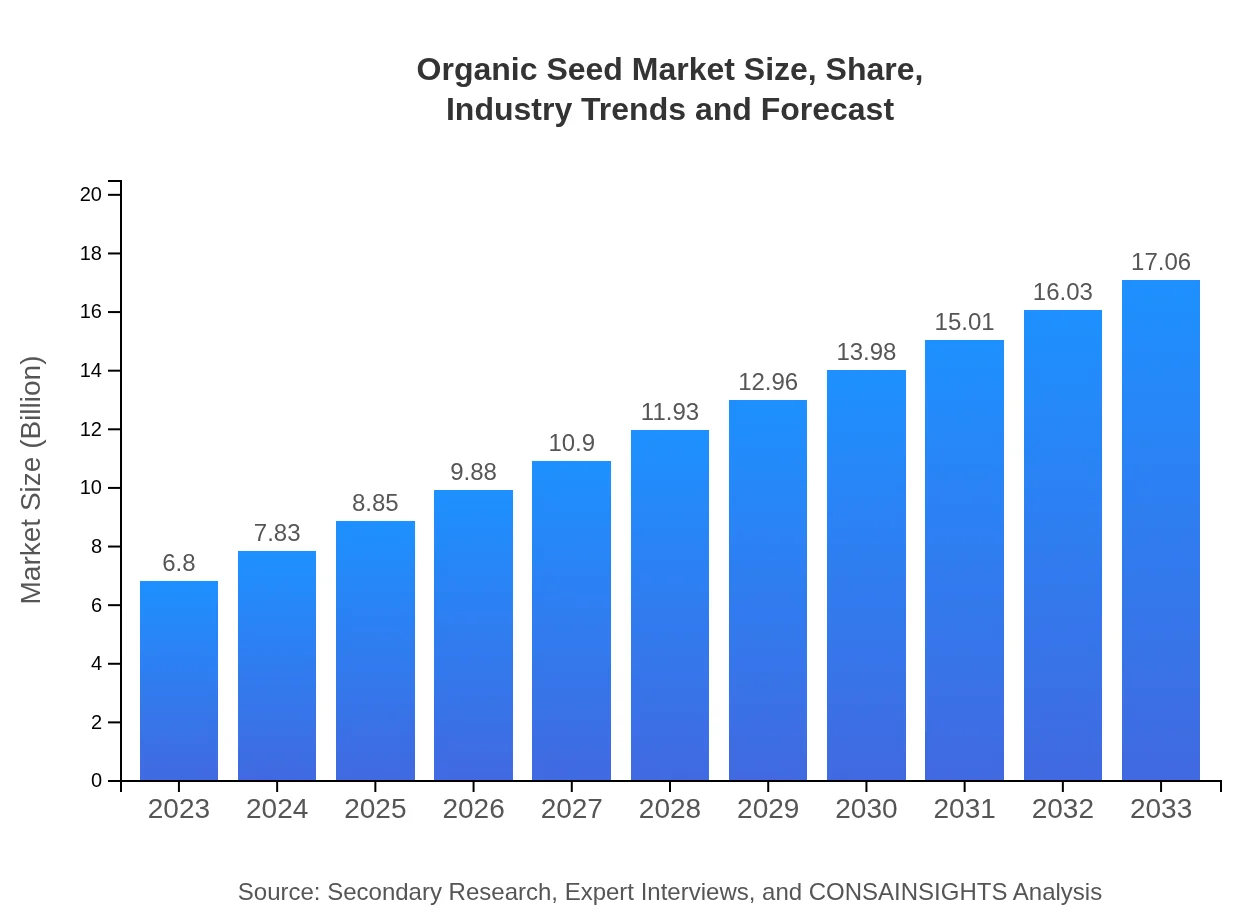
| 2023 Market Size | $6.80 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $17.06 Billion |
| Top Companies | BASF, Seed Savers Exchange, Seminis, Johnny's Selected Seeds, Renée's Garden Seeds |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Organic Seed Market Overview
Customize Organic Seed Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Organic Seed market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Organic Seed's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Organic Seed
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Organic Seed market in 2033?
Organic Seed Industry Analysis
Organic Seed Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Organic Seed Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Organic Seed Market Report:
The European Organic Seed market is set to increase from USD 1.84 billion in 2023 to USD 4.61 billion by 2033. The European Union's policies favoring organic agriculture and consumer trends towards sustainability are driving this significant growth.Asia Pacific Organic Seed Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Organic Seed market is forecasted to grow from USD 1.30 billion in 2023 to USD 3.26 billion by 2033, reflecting a strong CAGR of 9.5%. This growth is attributed to increasing health-conscious consumers, rising disposable incomes, and government initiatives encouraging organic farming practices.North America Organic Seed Market Report:
North America, a leading market for organic seeds, is projected to grow from USD 2.62 billion in 2023 to USD 6.58 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by a high consumer demand for organic food, supported by numerous local regulations and retailers advocating organic options.South America Organic Seed Market Report:
The South American Organic Seed market is expected to rise from USD 0.24 billion in 2023 to USD 0.59 billion by 2033. With significant agricultural land devoted to organic farming, this region shows potential for expansion, particularly in countries like Brazil and Argentina where organic farming practices are gaining traction.Middle East & Africa Organic Seed Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region's market size is expected to grow from USD 0.80 billion in 2023 to USD 2.01 billion by 2033, driven by growing interest in sustainable farming and increasing investments in agricultural technologies.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
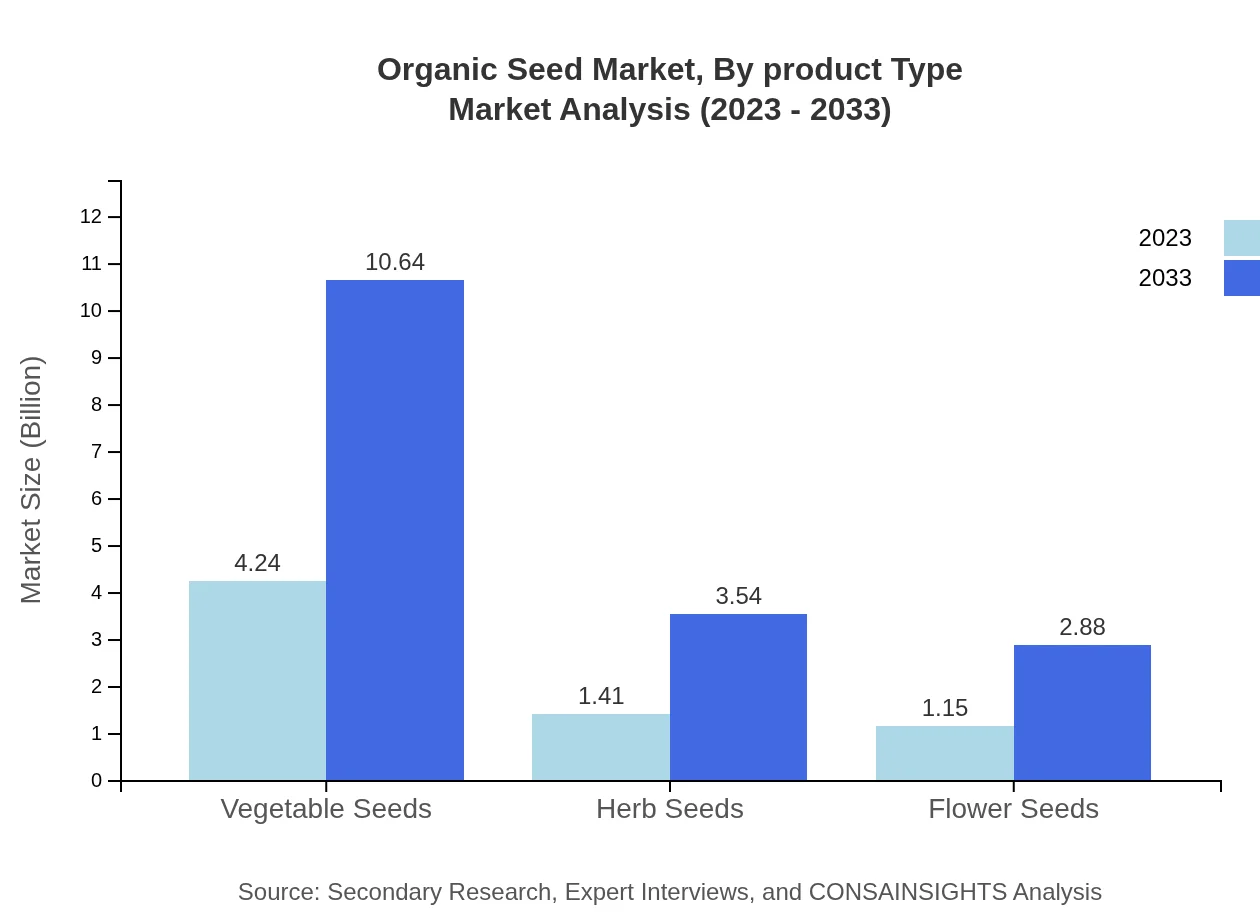
Organic Seed Market Analysis By Product Type
The Organic Seed market, segmented by product type, features grains leading with a market size of USD 4.24 billion in 2023 and projected to reach USD 10.64 billion by 2033. Fruits and legumes follow, reflecting preferences in health and nutrition, which is driving their respective sizes of USD 1.41 billion and USD 1.15 billion in the same year.
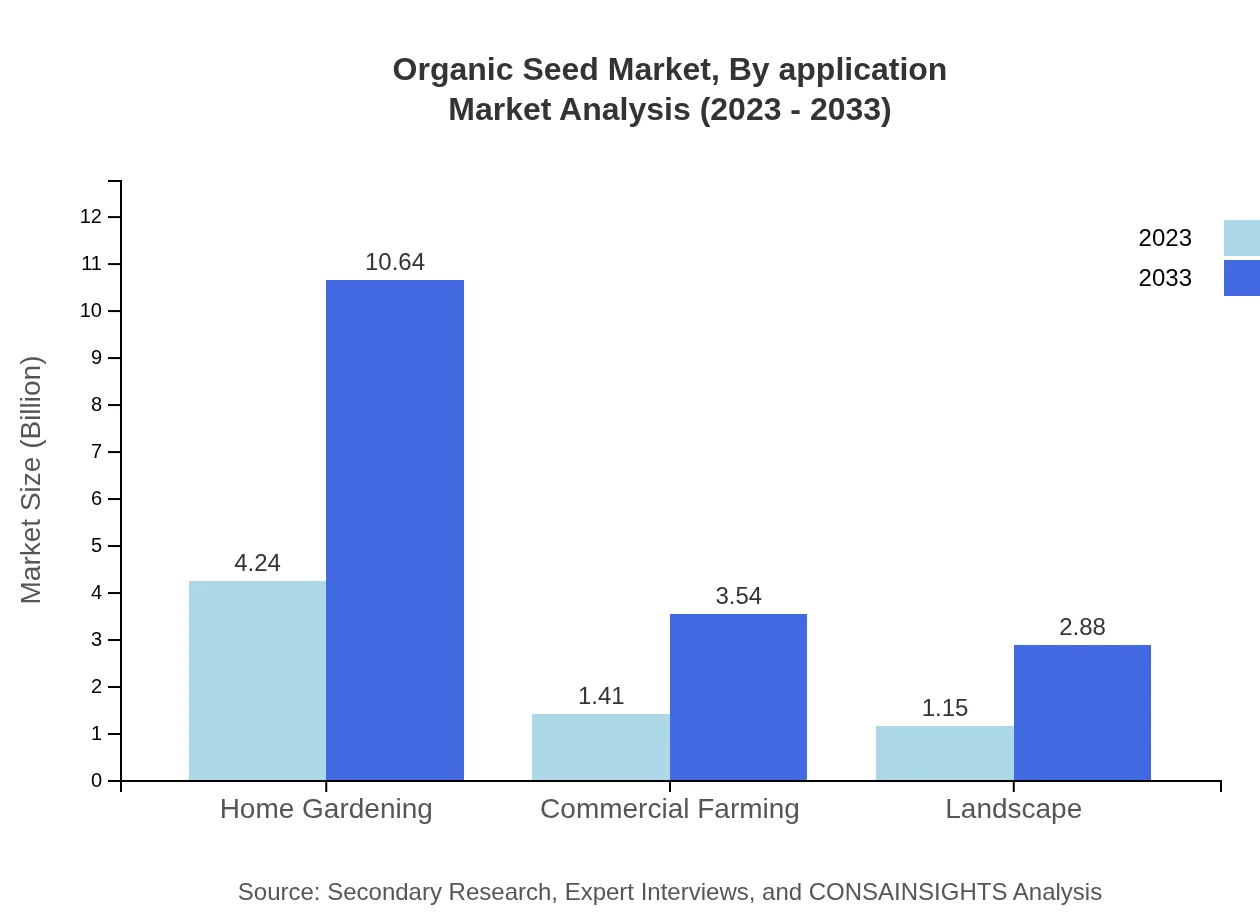
Organic Seed Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, the home gardening segment dominates, with a market size of USD 4.24 billion in 2023 set to rise to USD 10.64 billion by 2033. Commercial farming, which reached USD 1.41 billion in 2023, is also growing, fueled by demands for organic food production in various regions.
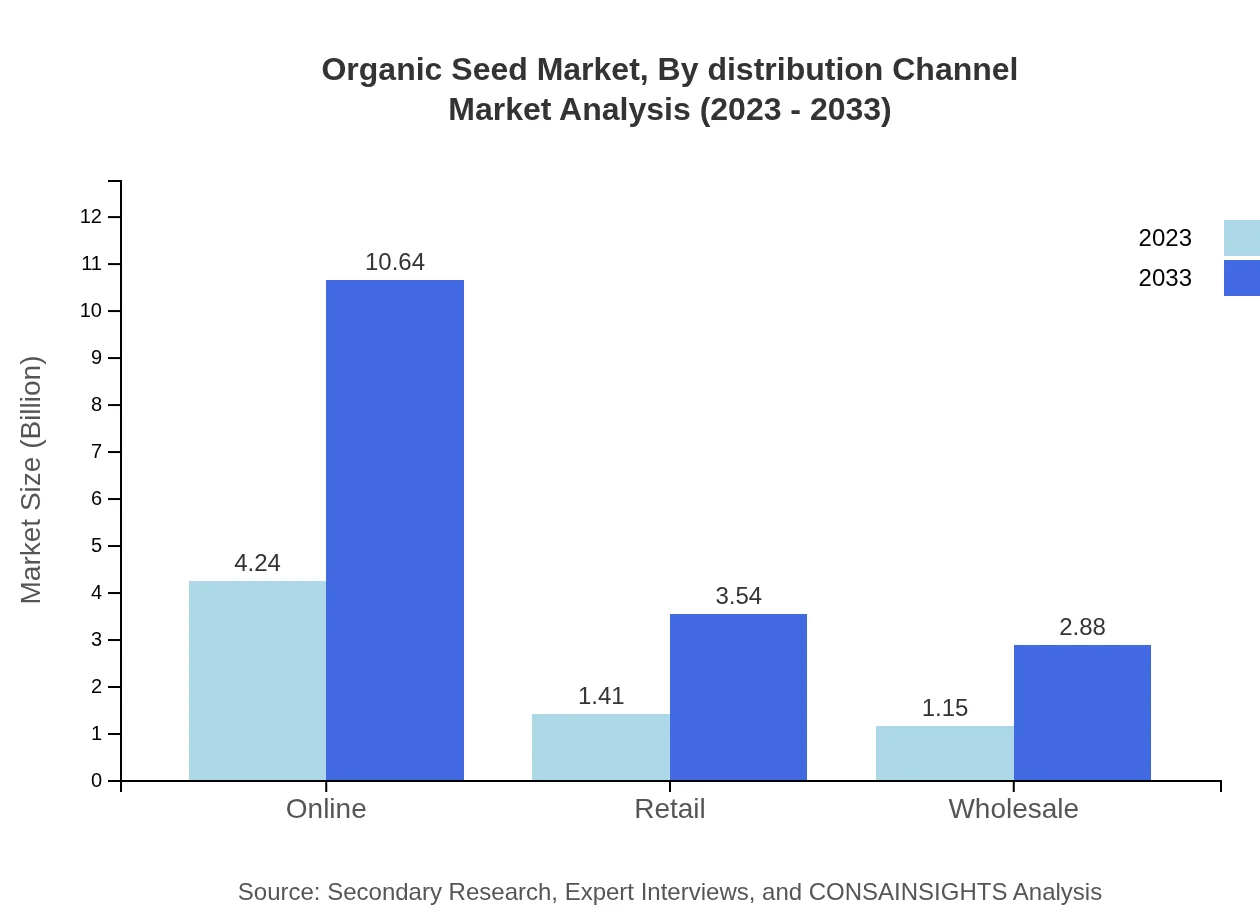
Organic Seed Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
By distribution, the online segment is growing rapidly, having a significant size of USD 4.24 billion in 2023, anticipating expanded growth to USD 10.64 billion by 2033. Retail and wholesale also play a crucial role in facilitating access to organic seeds for end-users.
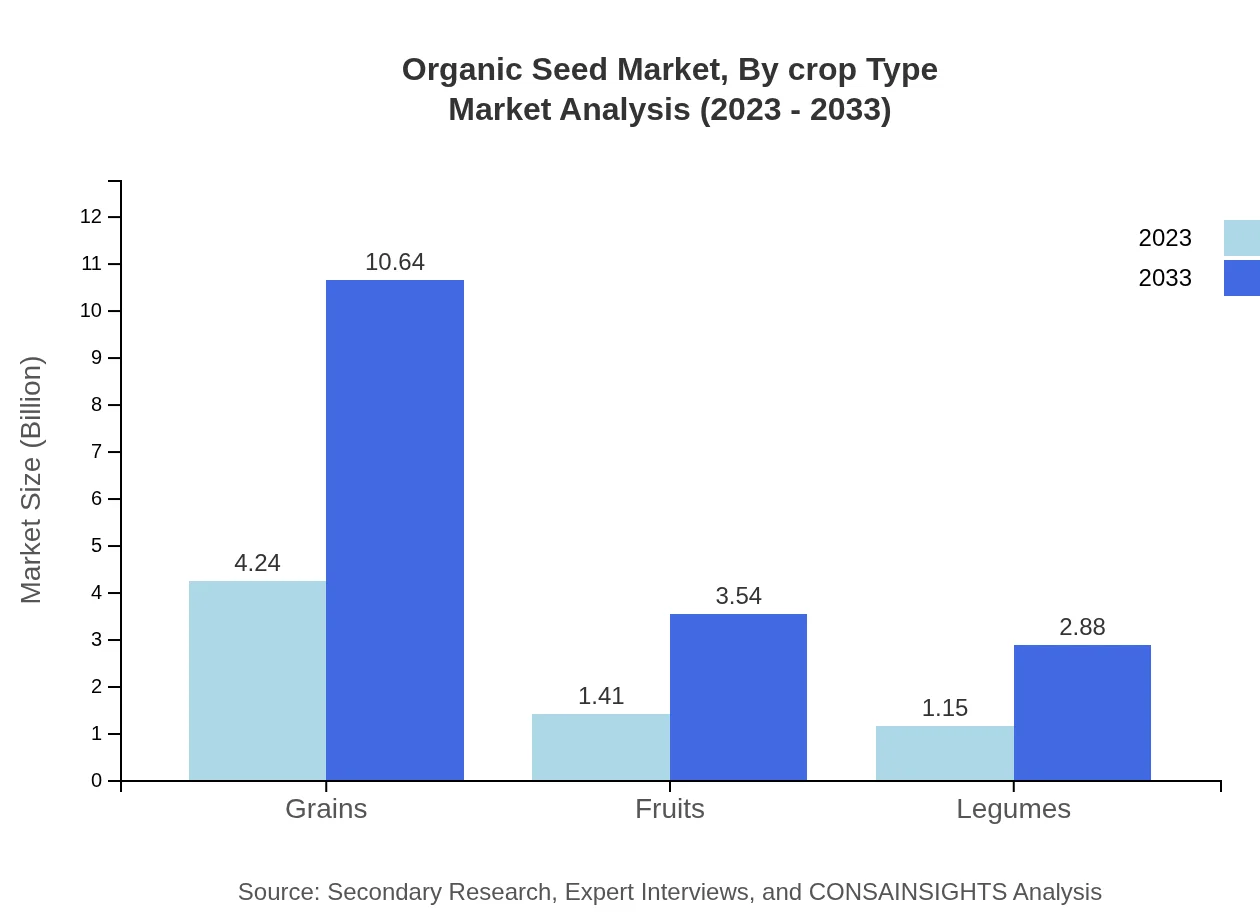
Organic Seed Market Analysis By Crop Type
Grains, fruits, and legumes comprise the majority of the Organic Seed market, where grains lead with a size of USD 4.24 billion and fruits at USD 1.41 billion in 2023. The diverse cropping types cater to a wide range of agricultural needs across various regions.
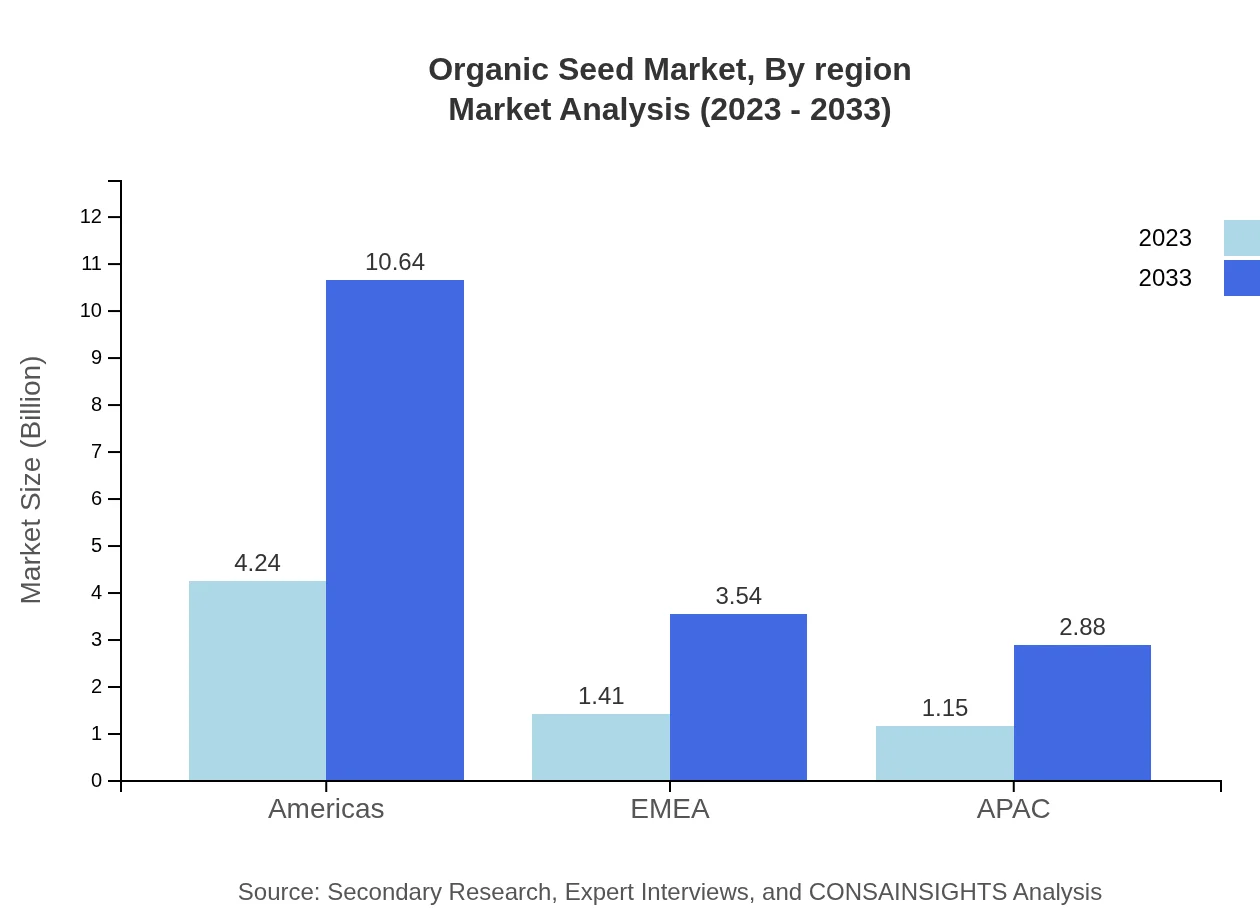
Organic Seed Market Analysis By Region
Regionally, the Americas dominated the market with a size of USD 4.24 billion in 2023, expected to grow significantly. EMEA (European, Middle Eastern, and African) holds around USD 1.41 billion, while APAC has a smaller yet notable contribution of USD 1.15 billion, slated for robust increases by 2033.
Organic Seed Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Organic Seed Industry
BASF:
BASF is a leading chemical company that has a significant presence in the organic seed segment, offering innovative seed solutions to enhance agricultural productivity.Seed Savers Exchange:
Seed Savers Exchange is a non-profit organization that preserves heirloom seeds, promoting biodiversity and sustainable agricultural practices among organic farmers.Seminis:
Part of Bayer Crop Science, Seminis specializes in vegetable seeds, focusing on sustainable practices and providing a wide array of organic seed products.Johnny's Selected Seeds:
A reputable supplier, Johnny's offers a broad selection of organic seeds, catering to home gardeners and commercial growers alike, with a strong emphasis on quality.Renée's Garden Seeds:
Renée's Garden is known for its premium organic seeds, providing unique varieties and dedicated to organic gardening and sustainable practices.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of organic Seed?
The organic seed market is estimated to reach $6.8 billion by 2033, growing at a robust CAGR of 9.3%. As consumers shift towards organic farming and sustainable practices, the market is expected to expand significantly in the upcoming decade.
What are the key market players or companies in the organic seed industry?
Key players in the organic seed market include prominent companies providing diverse seed types, such as Seminis Vegetable Seeds, Organic Seed Alliance, and Baker Creek Heirloom Seeds, contributing to various sectors including grains, fruits, and vegetables.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the organic seed industry?
The growth of the organic seed market is driven by increasing consumer awareness of health benefits, the rising popularity of organic farming, governmental support for organic agricultural practices, and heightened demand for organic products globally.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the organic seed market?
North America is the fastest-growing region, projecting an increase from $2.62 billion in 2023 to $6.58 billion by 2033, driven by strong consumer demand for organic products and investment in sustainable farming practices.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the organic seed industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the organic seed industry, focusing on key aspects such as market trends, competitive landscape, and geographic insights for informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this organic seed market research project?
Deliverables from the organic seed market research project include detailed market analysis, growth forecasts, segmentation insights, competitive landscape evaluations, and strategic recommendations, crafted to aid stakeholders in strategic planning.
What are the market trends of organic seed?
Current trends in the organic seed market include increasing consumer focus on sustainability, expansion of e-commerce platforms for seed distribution, a rise in home gardening activities, and a growing interest in heirloom and specialty seed varieties.