Organic Shrimp Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: organic-shrimp
Organic Shrimp Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report presents a comprehensive analysis of the Organic Shrimp market, examining key trends, market size, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It provides valuable insights into industry dynamics, segmentation, and regional performance, aiming to serve as a strategic guide for stakeholders.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
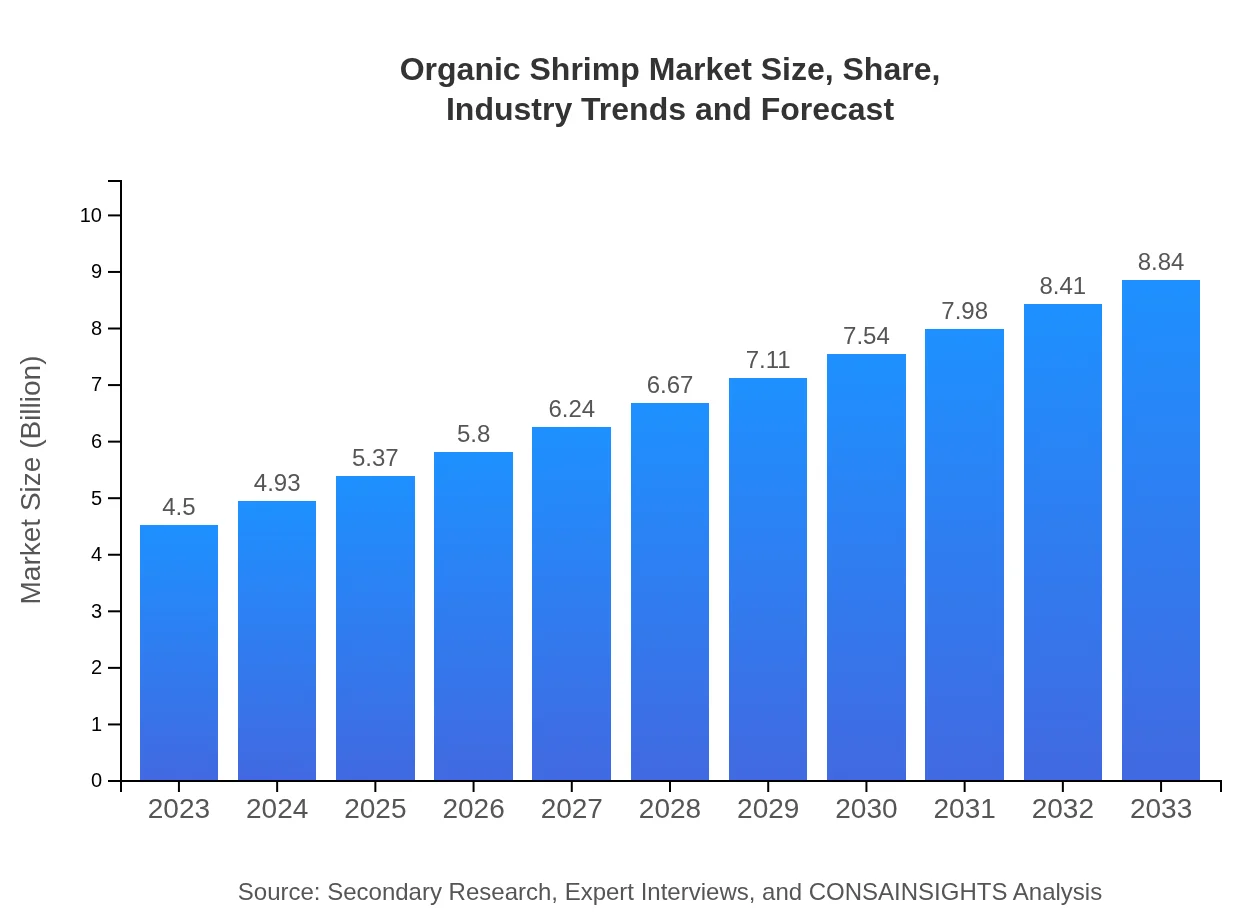
| 2023 Market Size | $4.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $8.84 Billion |
| Top Companies | Marine Harvest, Clearwater Seafoods, Thai Union Group |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Organic Shrimp Market Overview
Customize Organic Shrimp Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Organic Shrimp market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Organic Shrimp's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Organic Shrimp
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Organic Shrimp market in 2023 and 2033?
Organic Shrimp Industry Analysis
Organic Shrimp Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Organic Shrimp Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Organic Shrimp Market Report:
Europe's Organic Shrimp market is also significant, with sizes of $1.23 billion in 2023, growing to $2.41 billion by 2033. The region's awareness regarding food safety, quality, and environmental impact fuels demand, making it a vital market for new entrants and established players alike.Asia Pacific Organic Shrimp Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region dominates the Organic Shrimp market with an estimated size of $0.91 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $1.78 billion by 2033. This growth is attributed to high shrimp consumption rates in countries like India and Thailand, where organic farming practices are being increasingly adopted. The focus on sustainability and environmentally friendly practices is also influential in this market.North America Organic Shrimp Market Report:
North America shows a robust market for Organic Shrimp, starting at $1.63 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $3.21 billion by 2033. The U.S. leads the market due to high consumer awareness and demand for organic products, alongside stringent regulations that promote better farming practices.South America Organic Shrimp Market Report:
In South America, the Organic Shrimp market is valued at $0.11 billion in 2023, with projections to double to $0.22 billion by 2033. Brazil's expanding aquaculture sector and its emphasis on organic standards contribute to this gradual uptake, although challenges in infrastructure may hinder faster growth.Middle East & Africa Organic Shrimp Market Report:
The market in the Middle East and Africa is valued at $0.62 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $1.21 billion by 2033. Increased seafood consumption and the rising interest in organic products drive growth in this region, despite lagging infrastructure in aquaculture.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
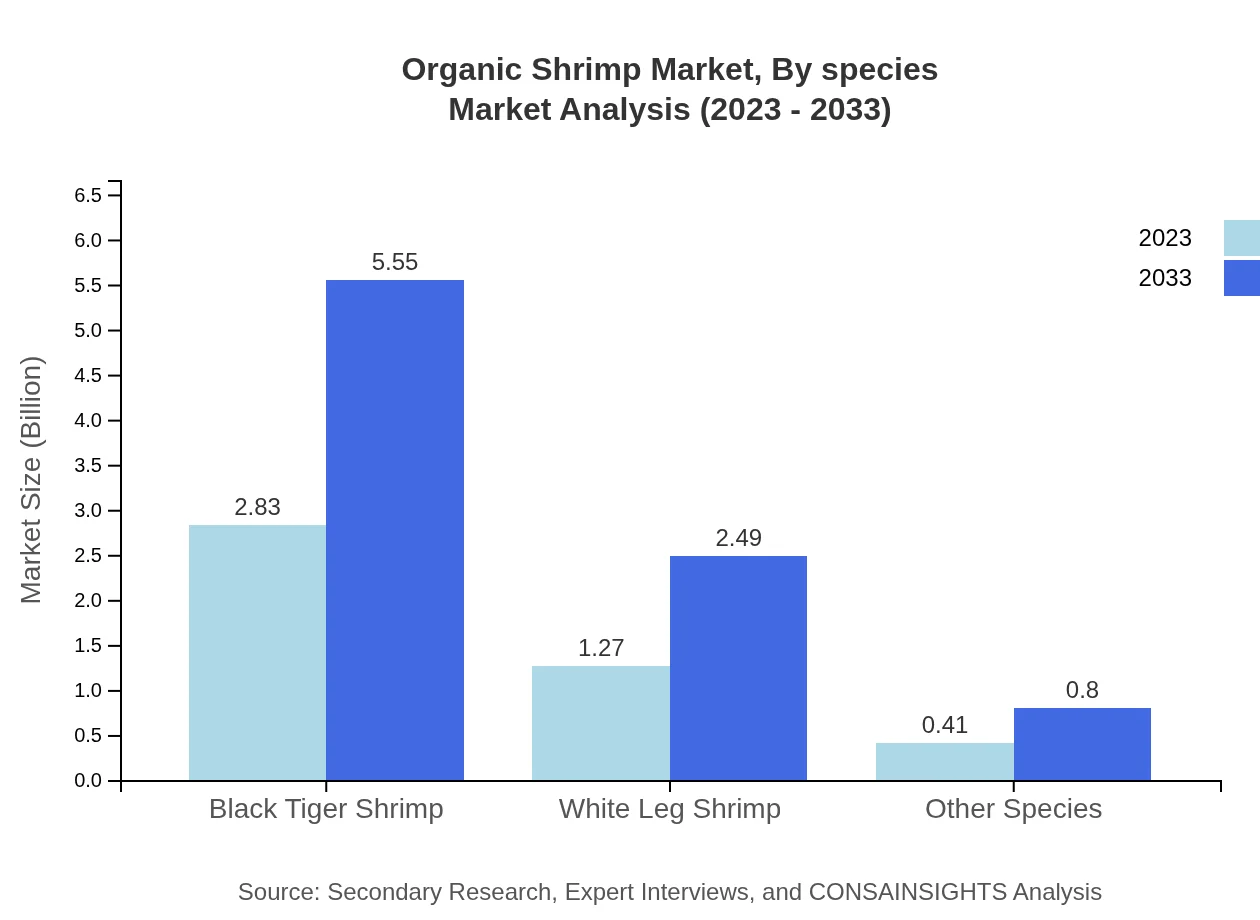
Organic Shrimp Market Analysis By Species
The major species in the Organic Shrimp market include Black Tiger Shrimp, which holds a substantial market size of $2.83 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $5.55 billion by 2033. White Leg Shrimp, representing $1.27 billion in 2023, is expected to reach $2.49 billion by 2033. Other species, while smaller, also show significant market growth potential.
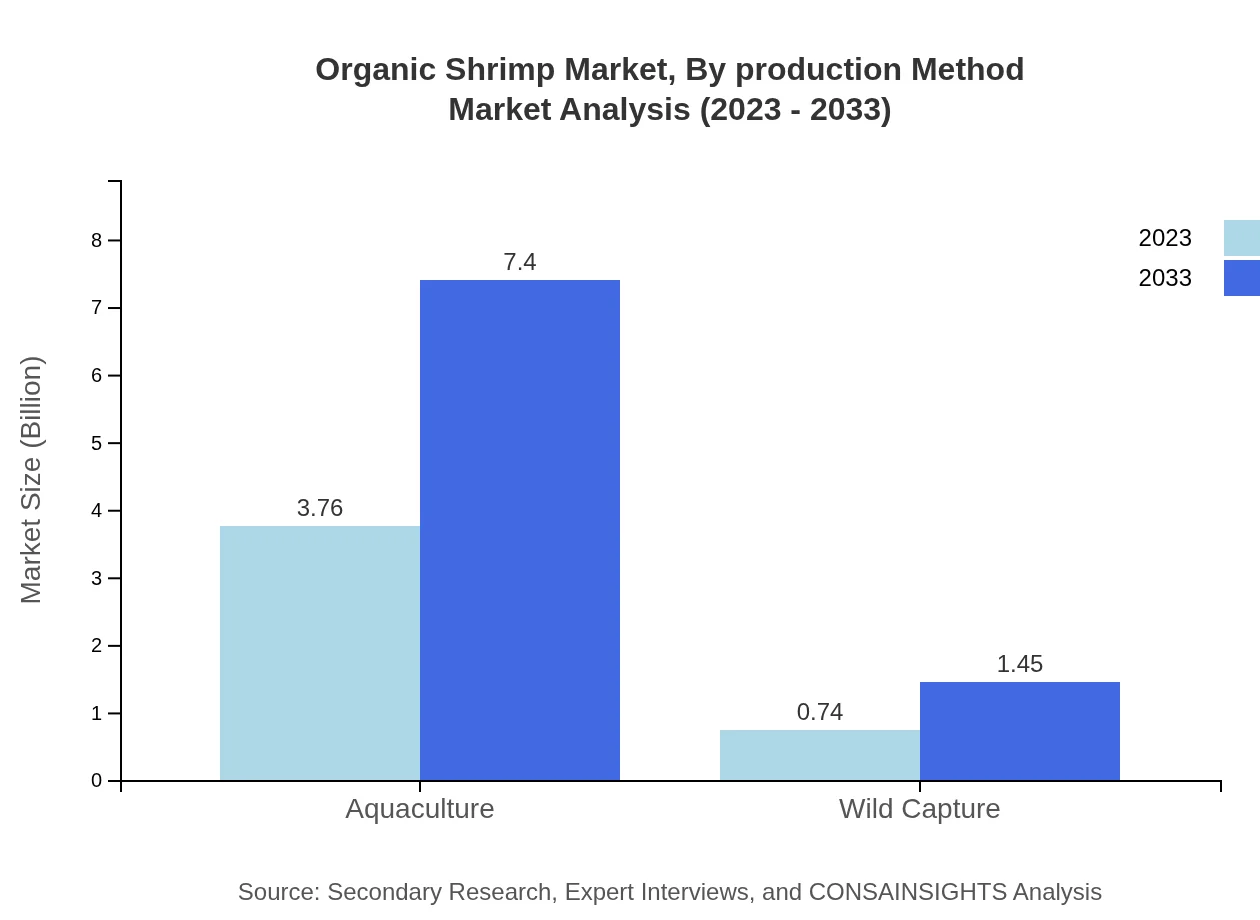
Organic Shrimp Market Analysis By Production Method
Aquaculture is the primary production method for Organic Shrimp, accounting for a substantial share of the market. The sector emphasizes sustainable farming techniques, and the organic certification process is crucial in establishing consumer trust and ensuring product quality.
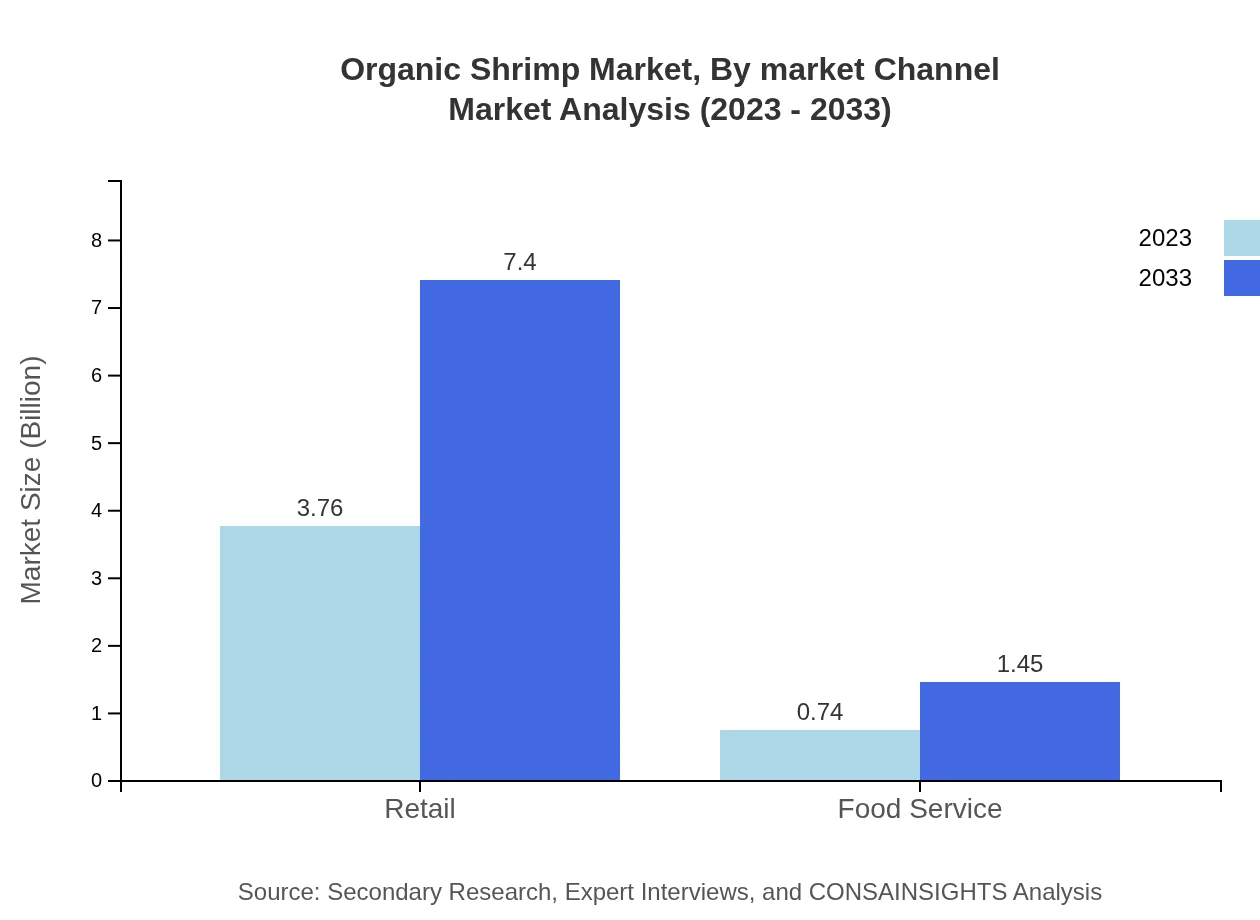
Organic Shrimp Market Analysis By Market Channel
The market is segmented into Retail and Food Service channels, with retail sales dominating the sector, representing $3.76 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $7.40 billion by 2033. The retail sector's growth is driven by an increase in consumer preference for organic products available in supermarkets and specialized organic stores.
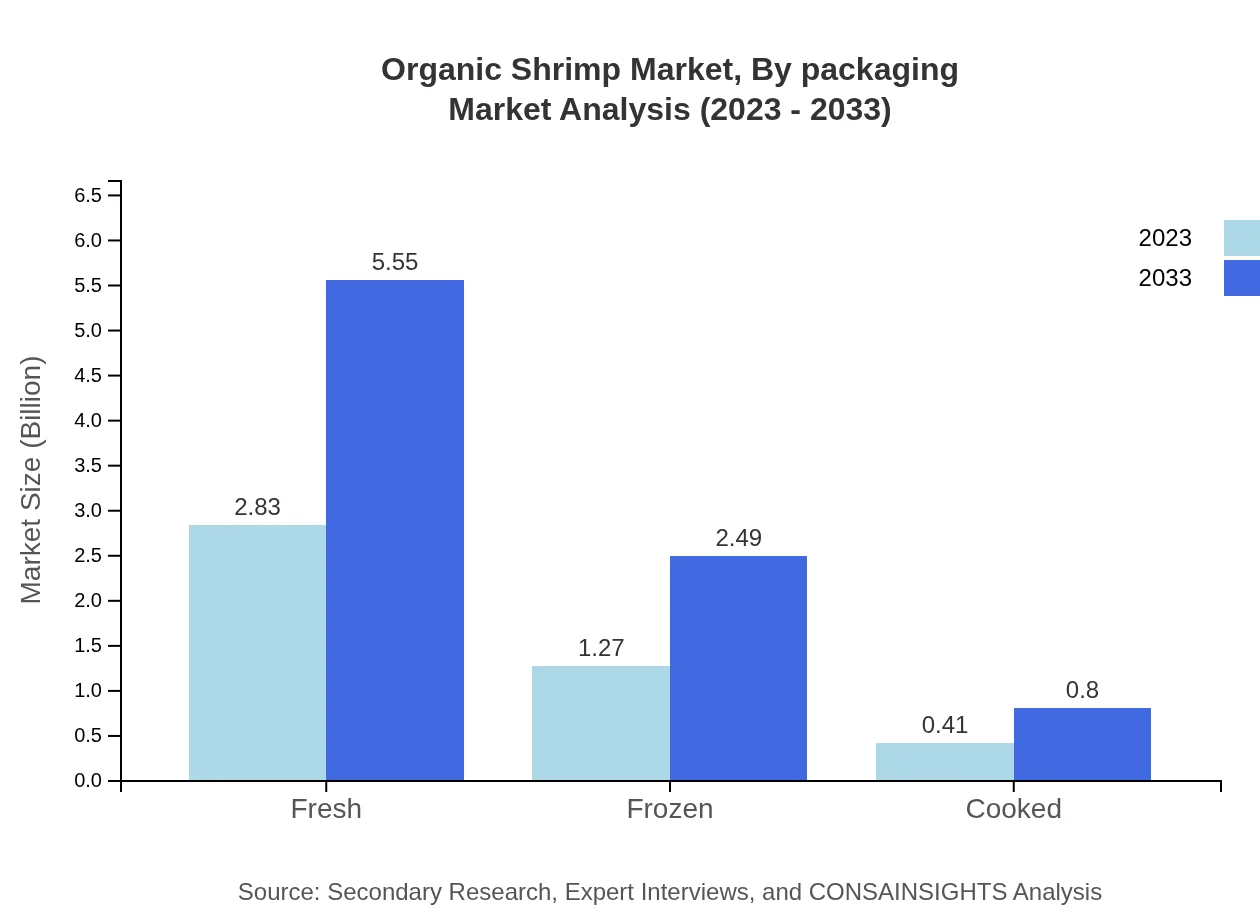
Organic Shrimp Market Analysis By Packaging
Packaging in the Organic Shrimp market emphasizes sustainability with a shift towards eco-friendly materials. Fresh packaging options are preferred to maintain quality and appeal, aligning with consumer expectations for freshness in organic products.
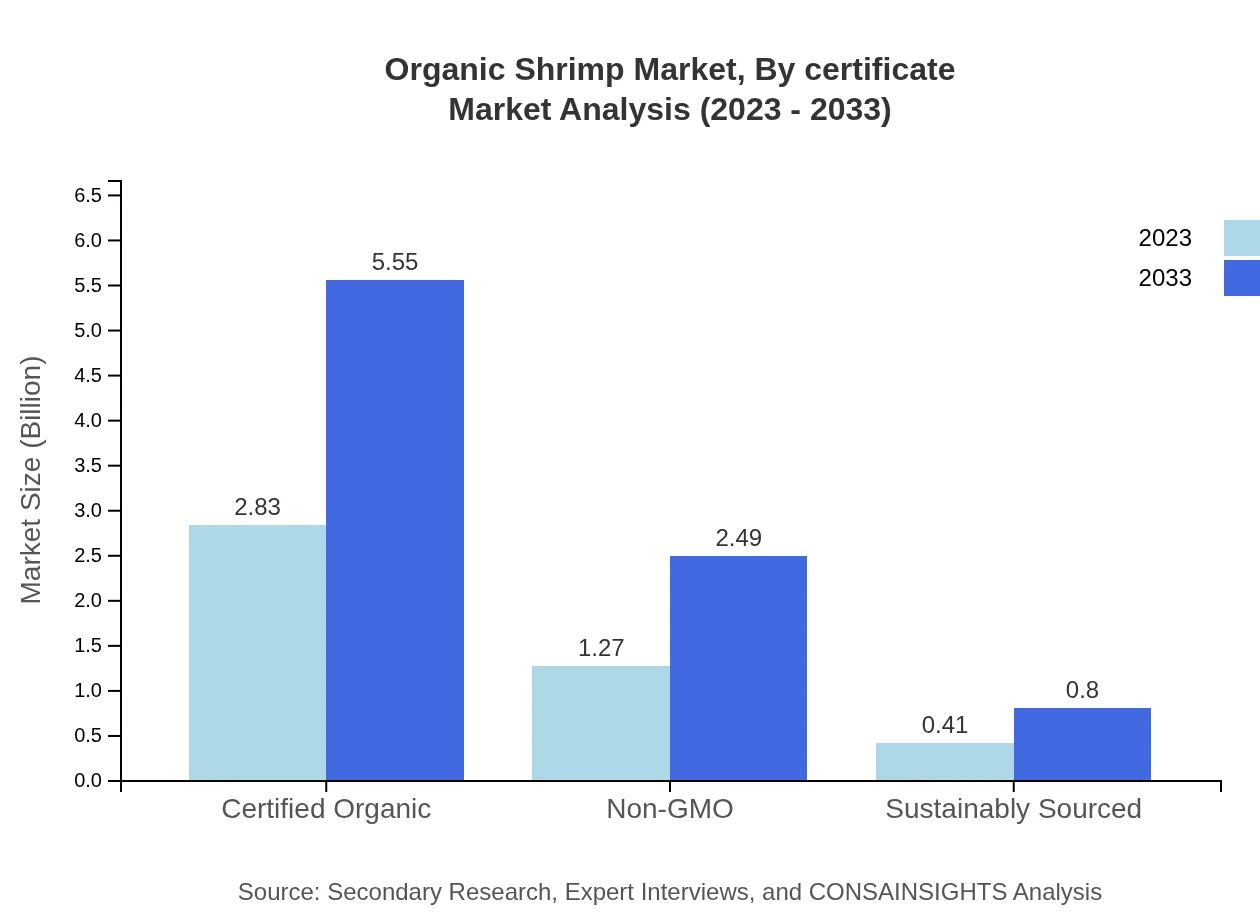
Organic Shrimp Market Analysis By Certificate
Certified Organic shrimp lead the market with stringent standards ensuring environmental sustainability and product quality. This segment represents $2.83 billion in 2023, expected to reach $5.55 billion by 2033, highlighting the importance of certifications in consumer purchasing decisions.
Organic Shrimp Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Organic Shrimp Industry
Marine Harvest:
Marine Harvest is a leader in the aquaculture industry and one of the largest producers of organic shrimp globally. Their commitment to sustainability and innovative farming methods has positioned them as a trusted brand in the market.Clearwater Seafoods:
Known for their quality seafood, Clearwater Seafoods focuses on organic and sustainably sourced products, establishing a strong presence in the North American market.Thai Union Group:
Thai Union Group is a significant player in the seafood market, offering a range of organic shrimp products and leading initiatives in sustainability across their operations.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of organic shrimp?
The global organic shrimp market is valued at approximately $4.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8%, indicating significant expansion over the next decade, driven by increasing demand for sustainable seafood alternatives.
What are the key market players or companies in the organic shrimp industry?
Key players in the organic shrimp market include major aquaculture firms and distributors specializing in organic seafood. Innovative startups focusing on sustainable practices also play a crucial role, enhancing product availability and market dynamics.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the organic shrimp industry?
Growth in the organic shrimp industry is driven by rising consumer awareness regarding health and environmental impact, increasing demand for sustainable aquaculture, and evolving dietary preferences favoring organic products.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the organic shrimp market?
North America emerges as the fastest-growing region in the organic shrimp market, expected to grow from $1.63 billion in 2023 to $3.21 billion by 2033, fueled by increasing consumer preference for high-quality and sustainably sourced seafood.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the organic shrimp industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific needs, including tailored insights, regional analyses, and specific segmentation data to aid strategic decision-making in the organic shrimp sector.
What deliverables can I expect from this organic shrimp market research project?
Deliverables from the organic shrimp market research project include comprehensive market analysis, detailed segmentation data, trend insights, competitive landscape assessment, and forecasts to support strategic operational planning.
What are the market trends of organic shrimp?
Current trends in the organic shrimp market include a shift towards certified organic products, increasing interest in various shrimp species, and a growing demand for retail and food service channels as consumers prioritize quality and sustainability.