Organic Wine Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: organic-wine
Organic Wine Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Organic Wine market, exploring trends, growth forecasts, and market conditions from 2023 to 2033. It includes data on market size, segmentation, regional insights, and key players shaping the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
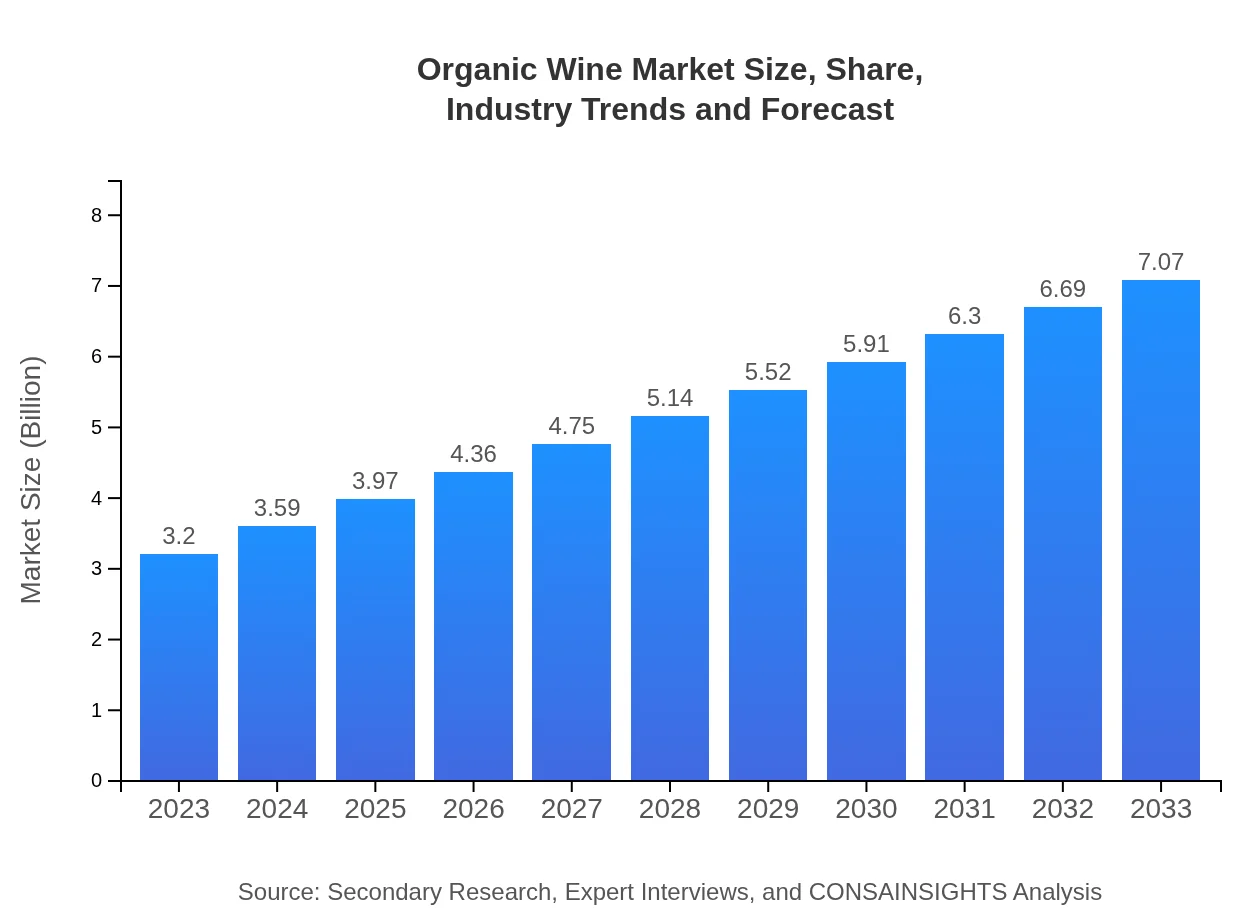
| 2023 Market Size | $3.20 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 8.0% |
| 2033 Market Size | $7.07 Billion |
| Top Companies | Chateau Margaux, Bodegas Torres, Montinore Estate, Organic Wine Company |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Organic Wine Market Overview
Customize Organic Wine Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Organic Wine market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Organic Wine's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Organic Wine
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Organic Wine market in 2023?
Organic Wine Industry Analysis
Organic Wine Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Organic Wine Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Organic Wine Market Report:
Europe, known for its established wine industry, is projected to experience growth from $0.99 billion in 2023 to $2.20 billion by 2033. The EU's stringent organic regulations and the rising popularity of organic wines among consumers drive this growth, particularly in countries like France and Germany, where wine culture is deeply rooted.Asia Pacific Organic Wine Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is becoming a major player in the Organic Wine market, projected to grow from $0.60 billion in 2023 to $1.32 billion by 2033. The shift towards organic consumption in countries like Japan and Australia enhances market growth. Consumer education on organic benefits and the rise in wine tourism also contribute to increased demand.North America Organic Wine Market Report:
North America remains the largest market for Organic Wine, estimated at $1.13 billion in 2023, with growth expected to $2.50 billion by 2033. The U.S. leads in organic wine consumption, supported by a robust health-oriented consumer base and strong e-commerce growth facilitating wider product accessibility.South America Organic Wine Market Report:
In South America, particularly in countries like Chile and Argentina, the Organic Wine market is anticipated to increase from $0.21 billion in 2023 to $0.46 billion by 2033. These nations are known for their wine production, and the increasing focus on organic farming is expected to boost market opportunities.Middle East & Africa Organic Wine Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market for Organic Wine is projected to rise from $0.27 billion in 2023 to $0.59 billion by 2033. The region's emerging wine market combined with increasing expatriate populations and tourism is likely to propel the growth of organic wine consumption.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
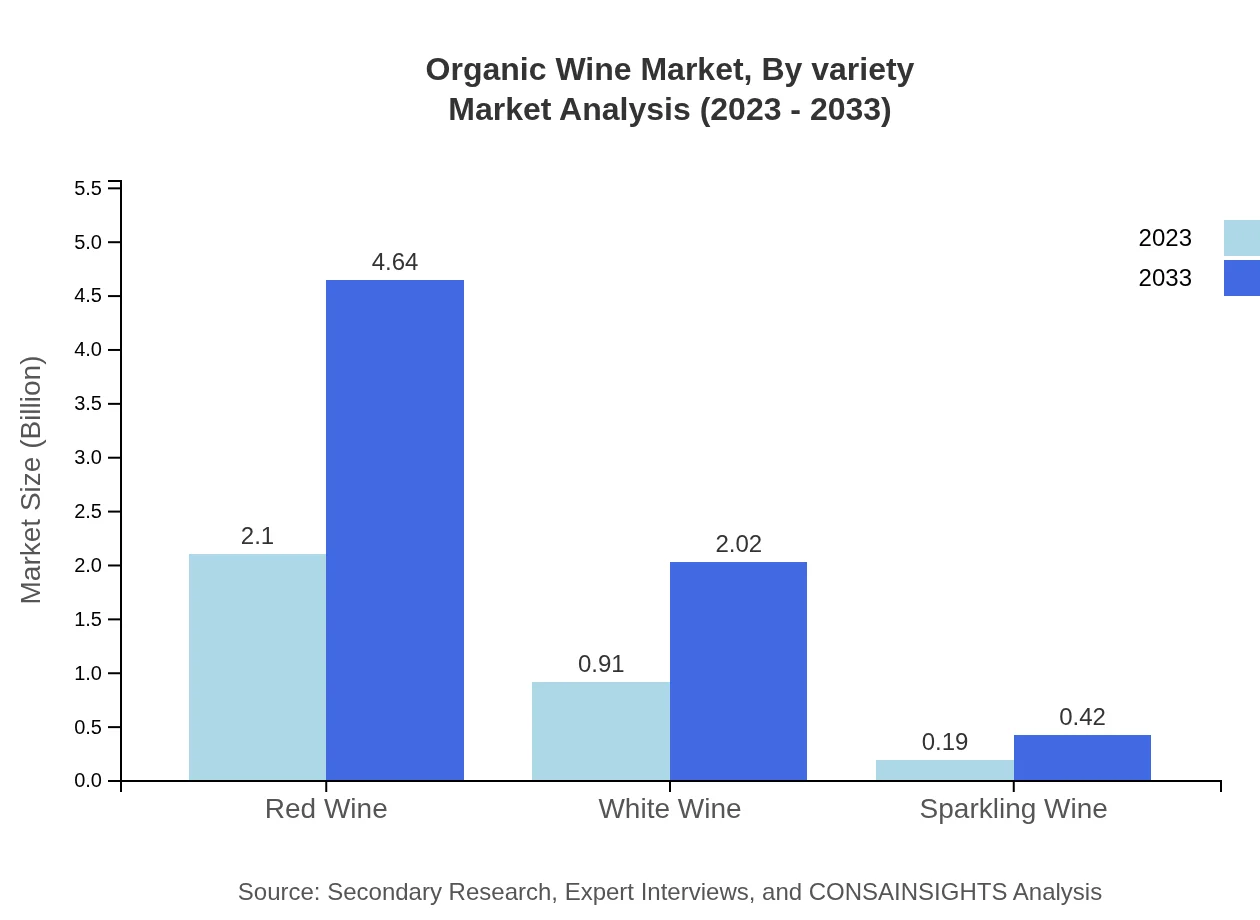
Organic Wine Market Analysis By Variety
In the Organic Wine segment by variety, Red Wine remains the leading category, expected to grow from $2.10 billion in 2023 to $4.64 billion in 2033, holding a significant market share of 65.55%. White Wine follows with a growth from $0.91 billion to $2.02 billion and a share of 28.53%. Sparkling Wine, while smaller, is also projected to increase in value, indicating diversification in consumer preferences.
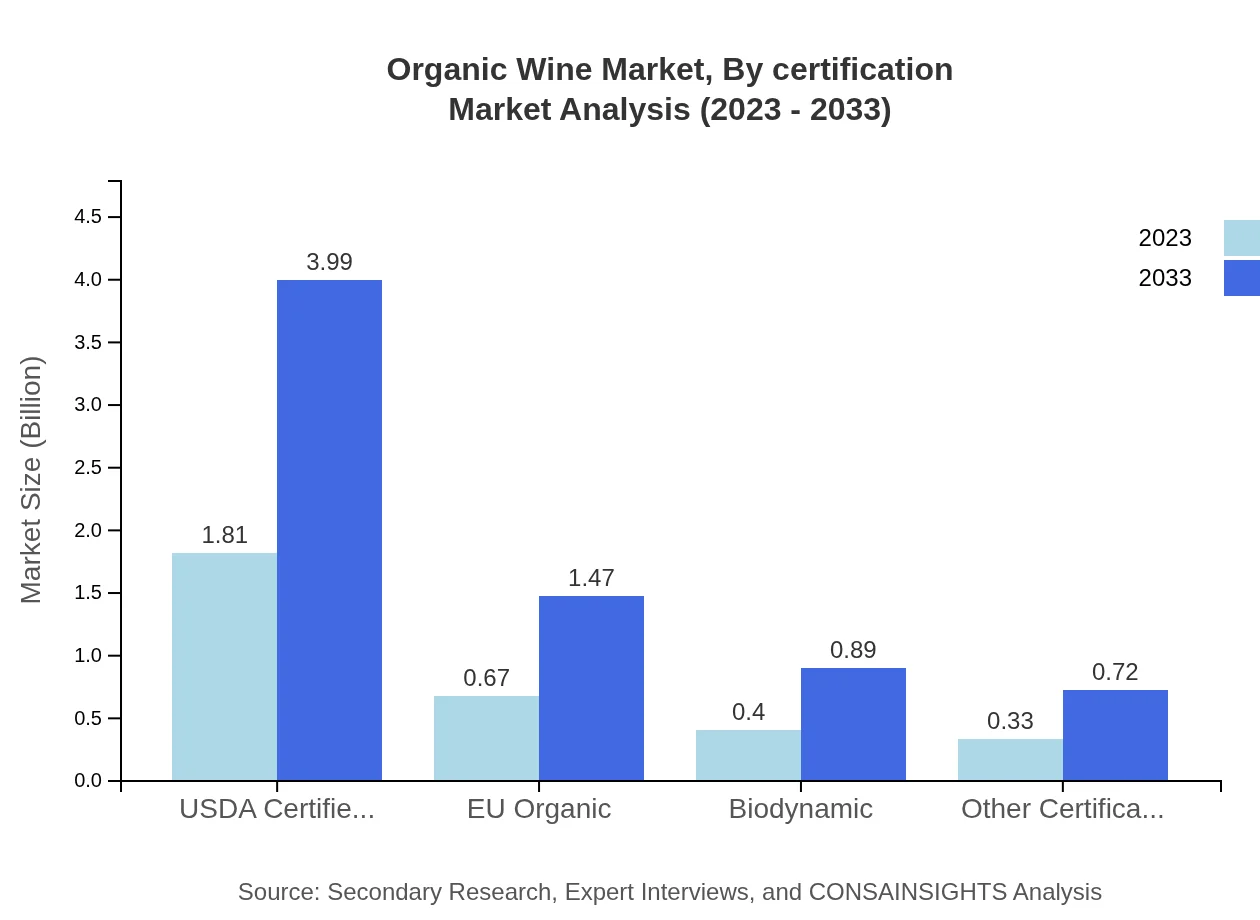
Organic Wine Market Analysis By Certification
By certification, USDA Certified Organic accounts for a substantial share at 56.46% in 2023, growing to 3.99 billion by 2033. EU Organic, while smaller at 20.79%, shows significant growth potential in Europe. Biodynamic and other certifications also represent niche segments, catering to increasingly diverse consumer preferences.
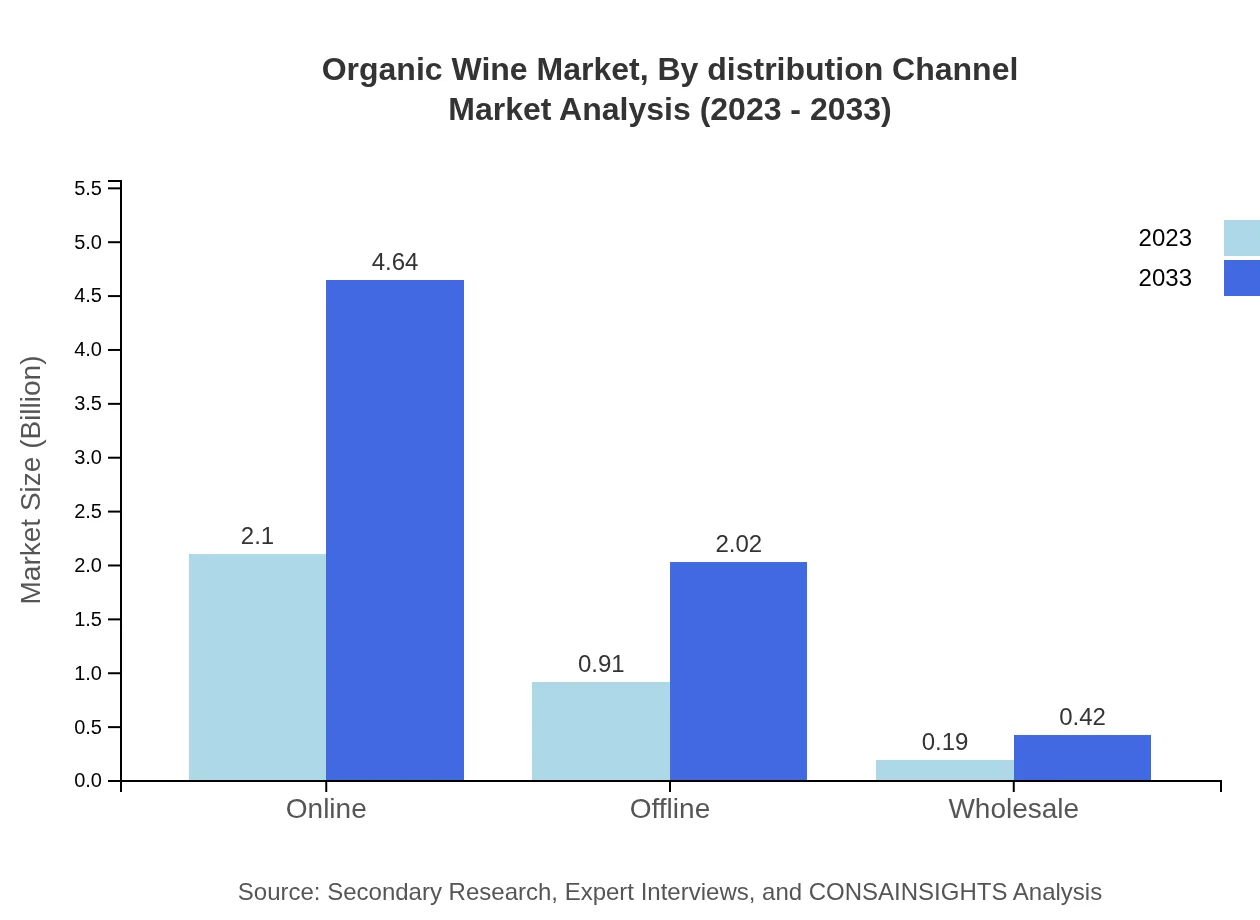
Organic Wine Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The Organic Wine market is heavily influenced by distribution channels, with a notable performance in online sales projected to experience growth from $2.10 billion to $4.64 billion, capturing 65.55% of the market share. Offline channels remain strong, particularly in traditional markets, while wholesale also sees a gradual increase, reflecting shifting consumer buying habits.
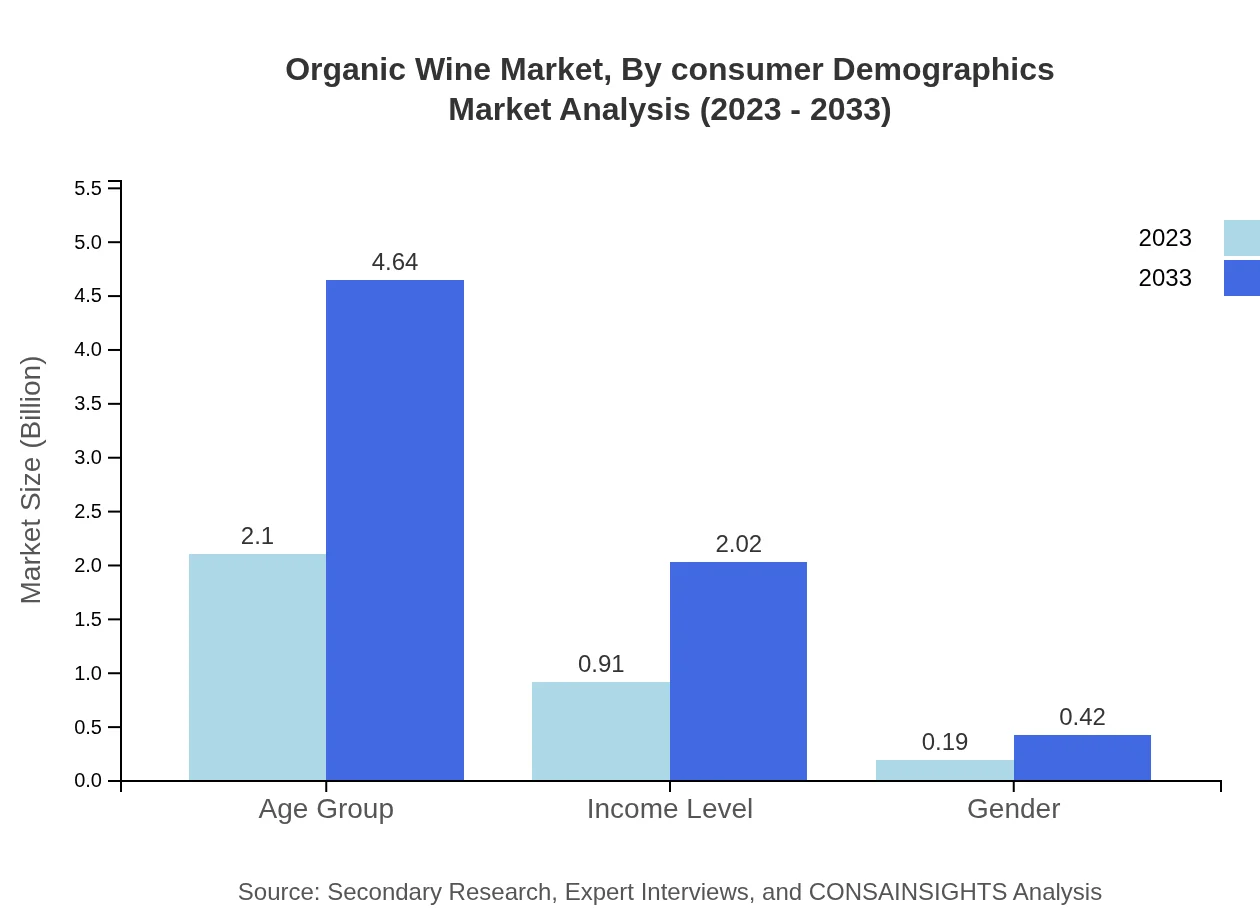
Organic Wine Market Analysis By Consumer Demographics
The Organic Wine consumption among various demographics indicates a strong preference among millennials, who are driving demand for sustainable products. The analysis shows a consumption share of 65.55% attributed to the age group, while income levels also play a significant role, reflecting a market size increase from $0.91 billion to $2.02 billion by 2033.
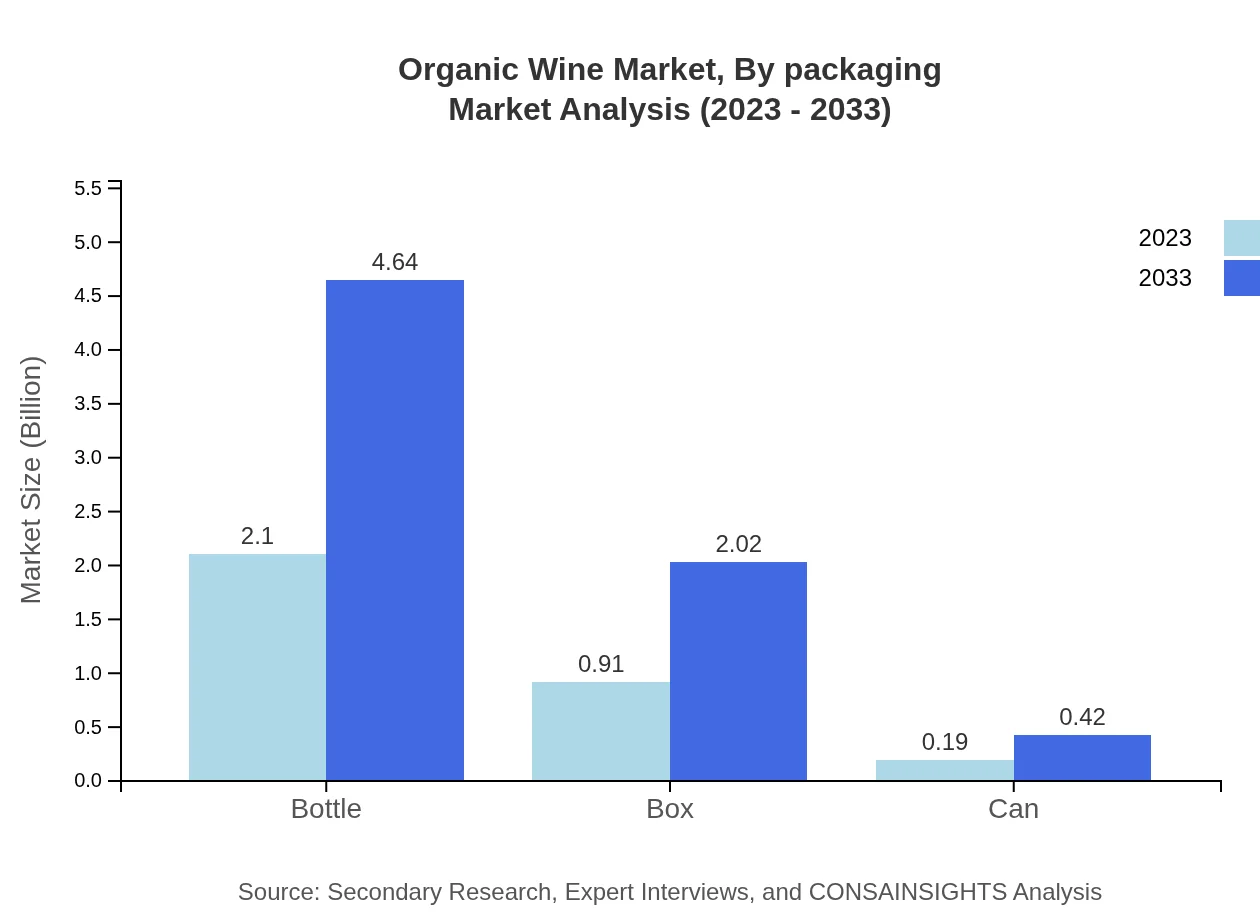
Organic Wine Market Analysis By Packaging
In the packaging segment, traditional bottles dominate with a market size of $2.10 billion in 2023. Box and can packaging are emerging trends, reflecting changing consumer lifestyles and preferences for convenience, indicating a significant growth trajectory and adaptation to market needs.
Organic Wine Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Organic Wine Industry
Chateau Margaux:
A prestigious French winery known for its biodynamic practices and premium organic wines, leading in high-quality offerings.Bodegas Torres:
A prominent Spanish vineyard focusing on sustainable and organic cultivation methods, expanding its global presence.Montinore Estate:
An influential player in the U.S. market, recognized for its organic vineyard in Oregon, producing a range of certified organic wines.Organic Wine Company:
Specializes in importing and distributing a variety of organic wines from around the world, promoting sustainable practices.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of organic Wine?
The organic wine market is valued at approximately $3.2 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 8.0% from 2023 to 2033, indicating significant growth potential in the coming decade.
What are the key market players or companies in this organic Wine industry?
Leading companies in the organic wine sector include well-established brands known for sustainable practices. Notable players focus on unique production techniques and cater to the growing consumer demand for organic options, boosting their market presence.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the organic Wine industry?
Growth in the organic wine market is driven by increasing health consciousness, demand for sustainable products, and a rising preference among consumers for organic alcoholic beverages. Marketing strategies focused on eco-friendliness also contribute.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the organic Wine market?
Europe is the fastest-growing region in the organic wine market, projected to reach $2.2 billion by 2033. Other regions, like North America and Asia-Pacific, also show promising growth, indicating a global trend toward organic wine.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the organic Wine industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to client needs in the organic wine industry. This includes specific insights, trends, and regional analyses to support informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this organic Wine market research project?
Clients can expect comprehensive reports detailing market size, growth projections, competitive analysis, regional performance, and segment breakdowns, providing valuable insights for strategic planning in the organic wine sector.
What are the market trends of organic Wine?
Key market trends in organic wine include a shift towards e-commerce sales, increased consumer awareness of organic certifications, and a growing preference for biodynamic wines as sustainability becomes central to purchasing decisions.