Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: overview-of-residential-real-estate
Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive overview of the residential real estate market, analyzing key trends and insights for the forecasting period from 2023 to 2033. Expect detailed market sizing, growth rates, regional insights, and an examination of industry segments.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
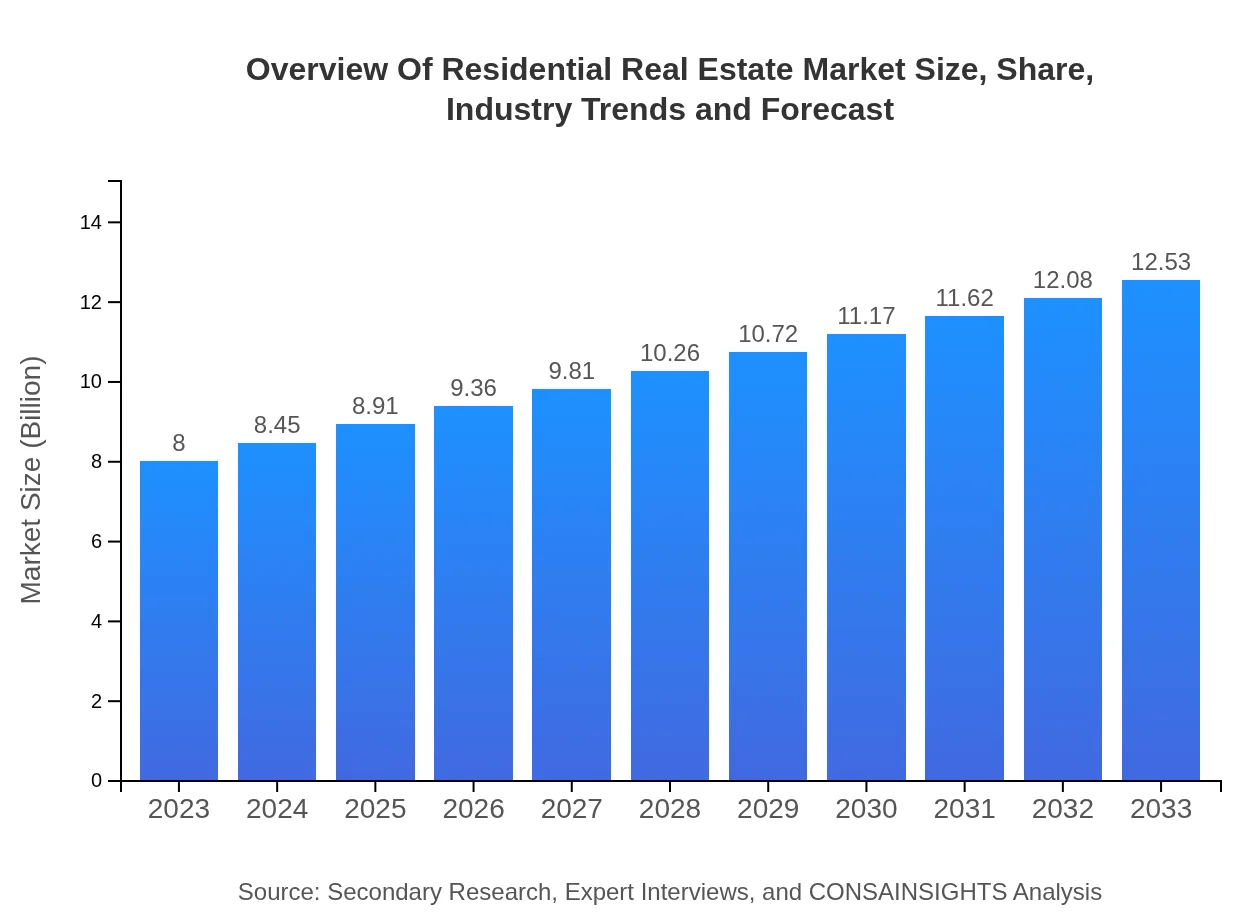
| 2023 Market Size | $8.00 Trillion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $12.53 Trillion |
| Top Companies | RE/MAX, Zillow Group, Keller Williams Realty |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Overview
Customize Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Overview Of Residential Real Estate market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Overview Of Residential Real Estate's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Overview Of Residential Real Estate
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Overview Of Residential Real Estate market in 2023?
Overview Of Residential Real Estate Industry Analysis
Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Report:
Europe's market is estimated at $2.94 trillion in 2023, expected to expand to $4.60 trillion by 2033. The demand for luxury real estate and green building initiatives is significant, particularly in cities like London and Berlin. Additionally, demographic shifts are influencing housing preferences across the continent.Asia Pacific Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Report:
In 2023, the residential real estate market in Asia Pacific is valued at $1.24 trillion and is expected to grow to $1.94 trillion by 2033. Factors such as rapid urbanization, growing middle-class income levels, and increasing foreign investment are driving this growth. Countries like India and China are leading the charge, with significant developments in urban infrastructure.North America Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Report:
North America's residential real estate market is valued at $2.66 trillion in 2023, projected to reach $4.17 trillion by 2033. The U.S. leads this growth with factors such as low unemployment rates, strong job growth, and attractive mortgage options driving demand. Urban centers continue to experience increased residential development.South America Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Report:
The South American market stands at $0.73 trillion in 2023 with an anticipated growth to $1.15 trillion by 2033. Economic recovery post-pandemic, along with government incentives for housing investments, is fostering growth. Emerging markets in Brazil and Colombia are particularly promising, attracting attention from domestic and international investors.Middle East & Africa Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Report:
The residential real estate market in the Middle East and Africa is valued at $0.43 trillion in 2023, anticipated to increase to $0.67 trillion by 2033. Urbanization and the growth of cities are creating demand, while investment in residential developments in countries like UAE and South Africa signals potential for further expansion.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
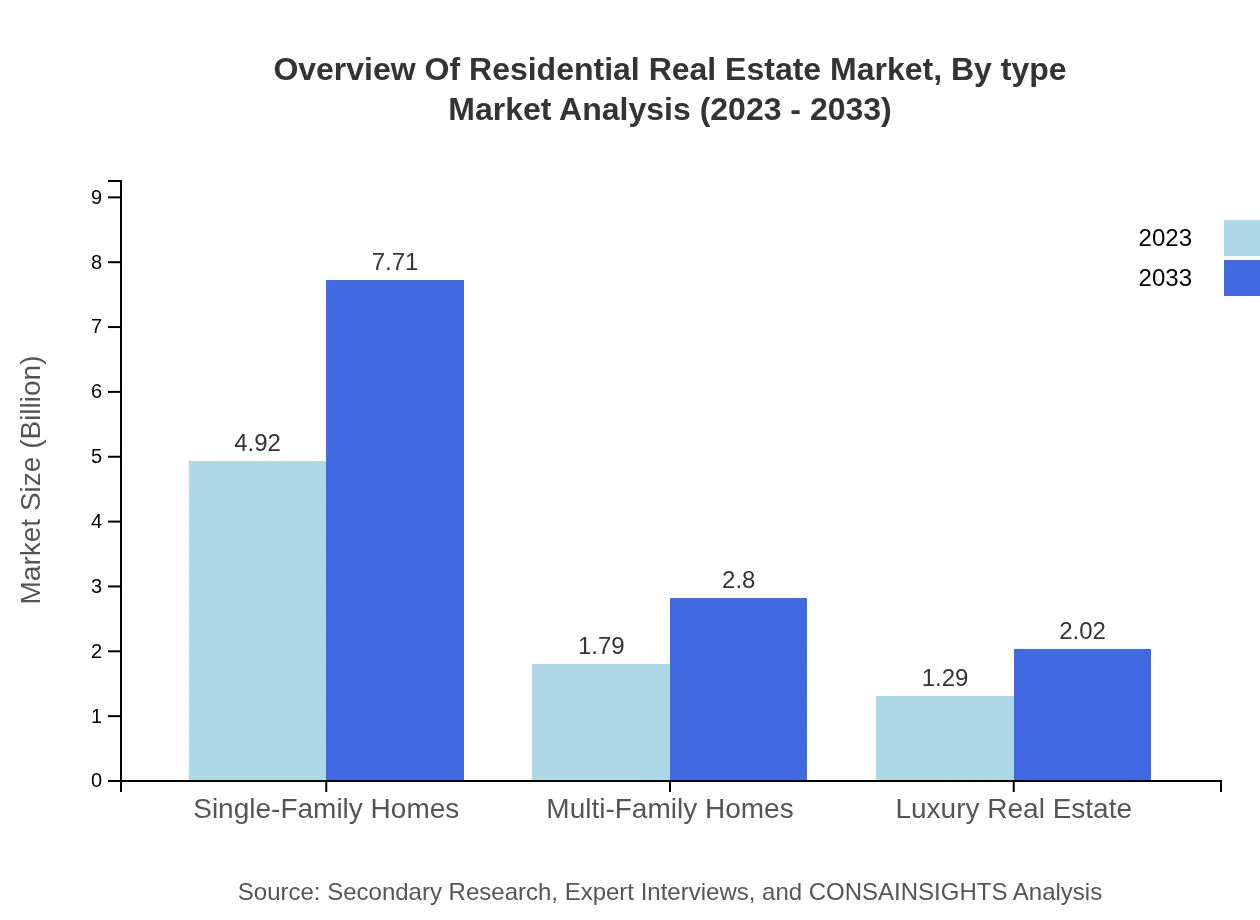
Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Analysis By Type
The market shows strong performance across various types of residential properties. Single-family homes dominate the market, valued at $4.92 trillion in 2023 and expected to reach $7.71 trillion by 2033, holding a significant share of 61.52%. Multi-family homes, valued at $1.79 trillion in 2023, will grow to $2.80 trillion, representing 22.32% of the market. Luxury real estate is also notable, expanding from $1.29 trillion to $2.02 trillion, affirming a 16.16% share.
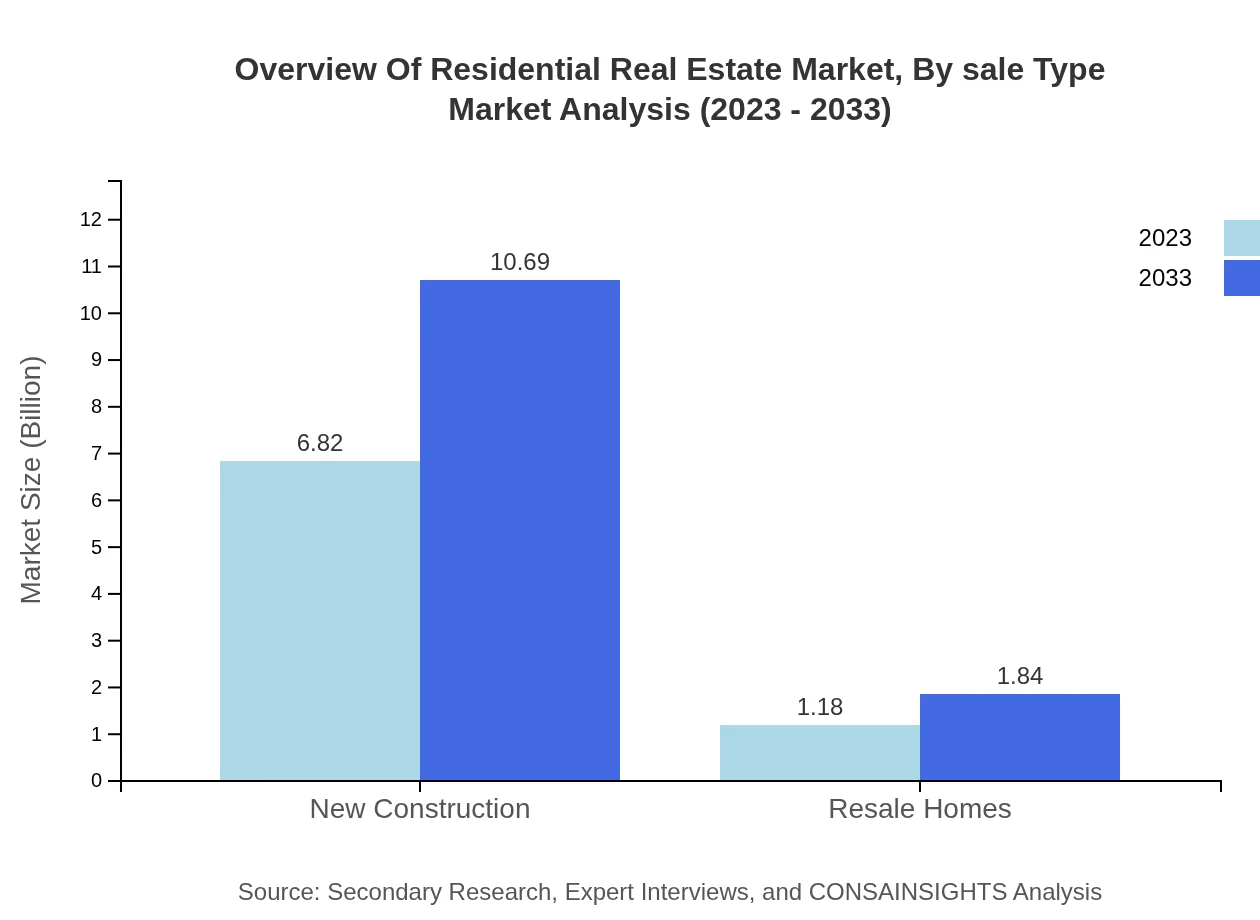
Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Analysis By Sale Type
New construction remains a significant segment at $6.82 trillion in 2023, expected to grow to $10.69 trillion, representing 85.29% of the market. Conversely, resale homes will increase from $1.18 trillion to $1.84 trillion, accounting for 14.71% of overall sales, highlighting the vital duality of new and existing home markets.
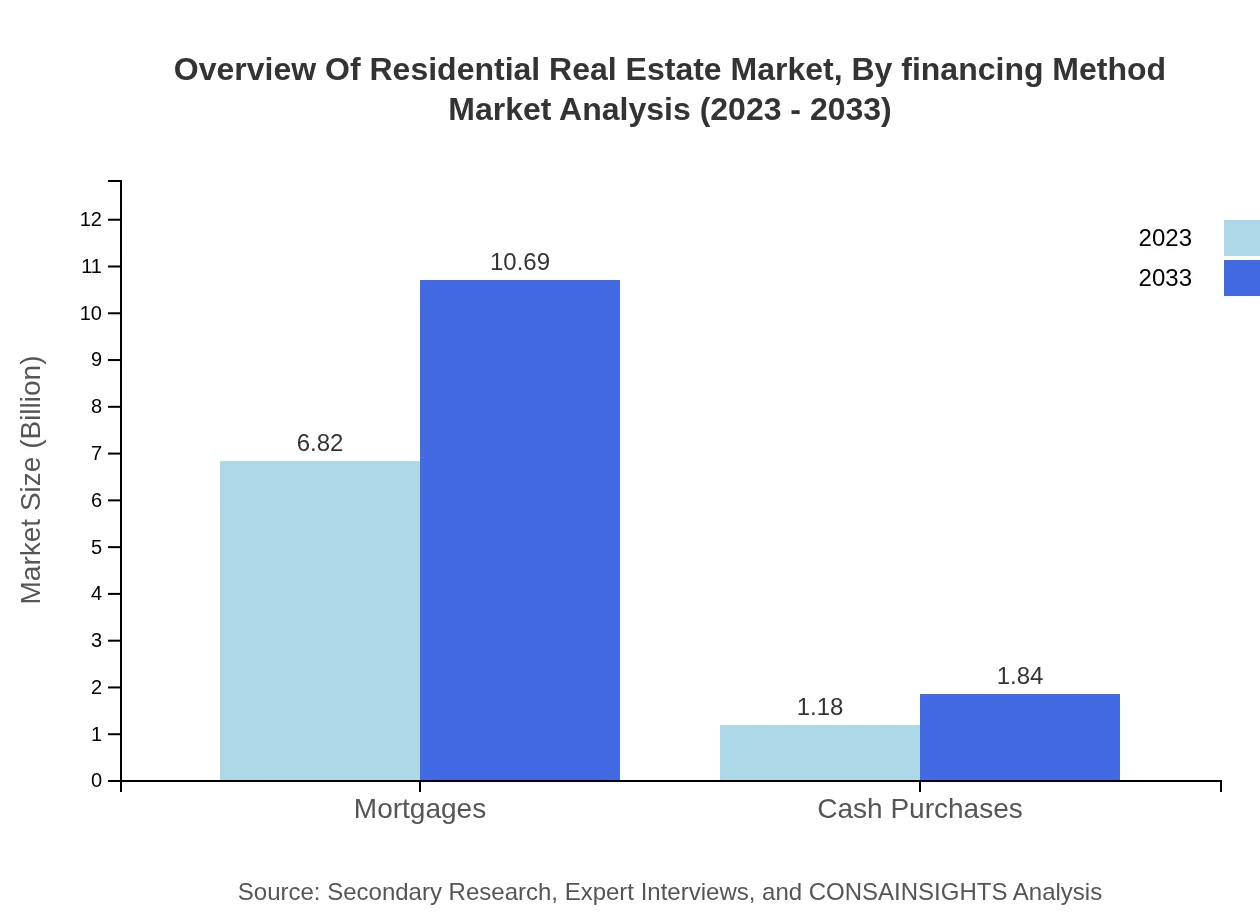
Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Analysis By Financing Method
Mortgages are critical in financing residential real estate, representing a market size of $6.82 trillion in 2023 and anticipated to climb to $10.69 trillion by 2033, comprising 85.29% of financing methods. Cash purchases are growing, moving from $1.18 trillion to $1.84 trillion, making up 14.71% of the total market, reflecting a steady trend among investors and affluent buyers.
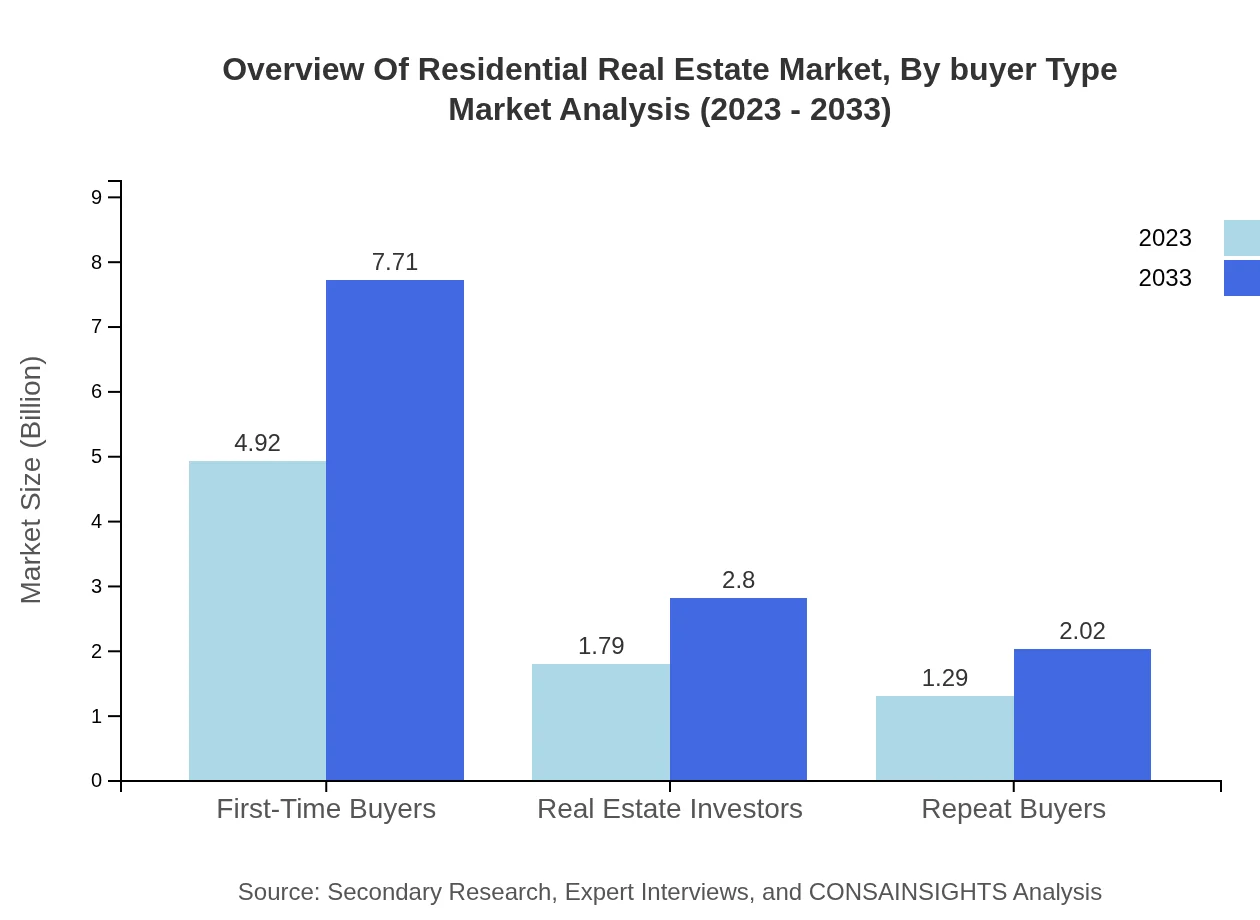
Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Analysis By Buyer Type
First-time buyers constitute a significant portion of the market, valued at $4.92 trillion in 2023 and projected to increase to $7.71 trillion with a market share of 61.52%. Real estate investors and repeat buyers also play crucial roles, with respective market activities growing from $1.79 trillion and $1.29 trillion to $2.80 trillion and $2.02 trillion by 2033.
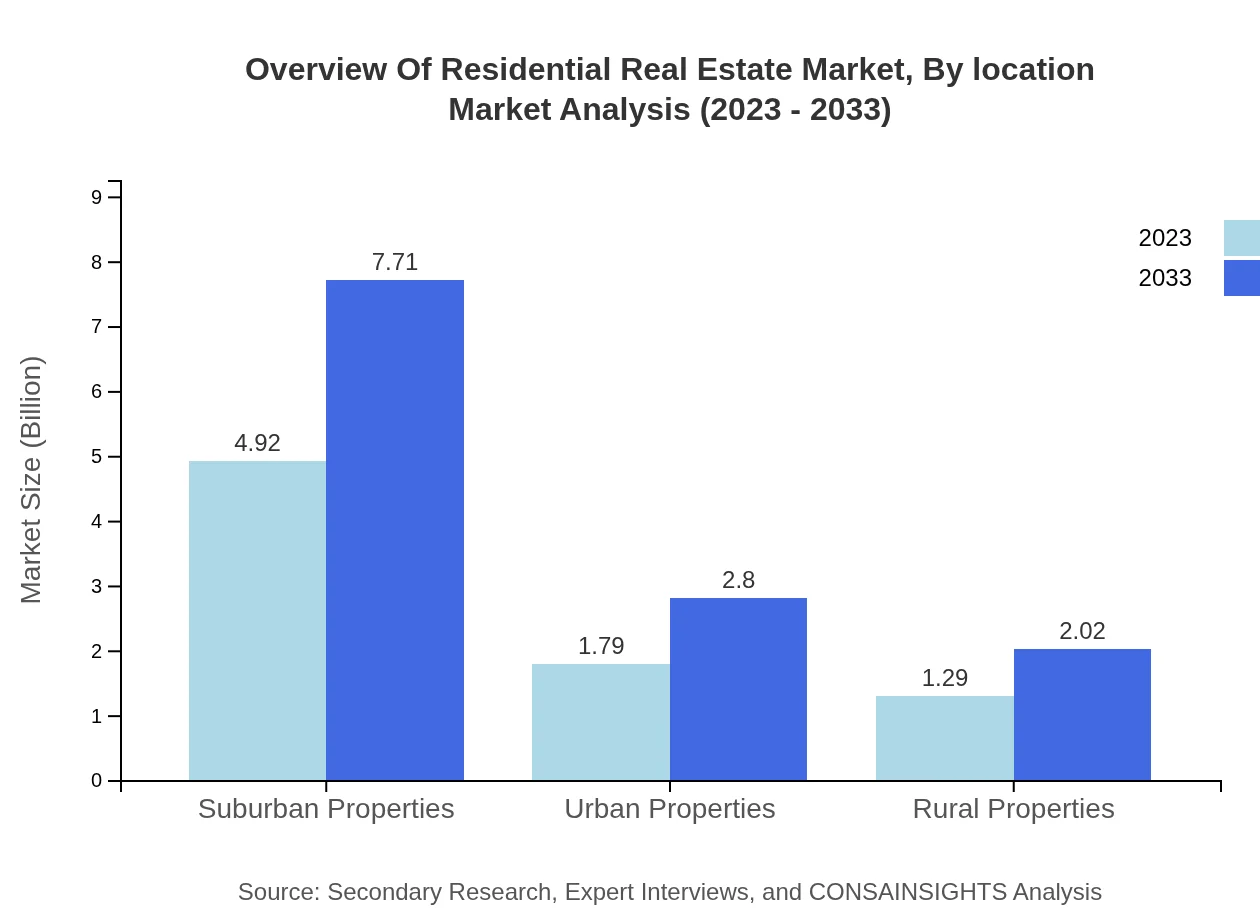
Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Analysis By Location
Location analysis reveals a steady interest in suburban properties, which account for $4.92 trillion in 2023 and are forecasted to grow alongside urban properties and rural estates. Urban properties hold a strong value of $1.79 trillion, while rural properties are also capturing attention as lifestyle choices evolve, expected to reach valuations of $2.02 trillion by 2033.
Overview Of Residential Real Estate Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Overview Of Residential Real Estate Industry
RE/MAX:
A leading global real estate franchisor based in the U.S., RE/MAX is known for its extensive network of agents and a strong presence in residential property transactions.Zillow Group:
An influential online real estate marketplace that provides digital housing information, Zillow Group is central to property searches, offers, and real estate analytics.Keller Williams Realty:
A prominent real estate franchise in North America, Keller Williams Realty emphasizes technology and agent-driven models for residential property sales.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of overview Of Residential Real Estate?
The global residential real estate market is currently valued at approximately $8 trillion, with a projected CAGR of 4.5% from 2023 to 2033. This growth indicates a consistent demand for housing, influenced by demographic changes worldwide.
What are the key market players or companies in this overview Of Residential Real Estate industry?
Key players in the residential real estate market include major real estate agencies, property management firms, and investment companies across various regions. Their influence shapes market trends by innovating offerings and improving customer engagement through technology.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the overview Of Residential Real Estate industry?
Growth in the residential real estate industry is driven by urbanization, rising disposable incomes, ongoing population growth, and the increased demand for housing. Additionally, favorable mortgage rates and governmental policies also contribute to market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the overview Of Residential Real Estate?
The North American region is the fastest-growing segment, projected to expand from $2.66 trillion in 2023 to $4.17 trillion by 2033. Europe follows closely, indicating the lucrative market dynamics established in these areas.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the overview Of Residential Real Estate industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific client needs within the residential real estate industry, helping stakeholders gain pertinent insights and strategies crucial for informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this overview Of Residential Real Estate market research project?
Deliverables from the residential real estate market research project typically include comprehensive reports, detailed forecasts, regional analysis, competitive landscape assessments, and tailored recommendations for businesses looking to succeed in this market.
What are the market trends of overview Of Residential Real Estate?
Current trends in the residential real estate market include a shift towards sustainable housing solutions, increased use of technology for property management, and growing demand for urban properties. As investors focus on diverse segments, new construction strategies are also evolving.