Pc Based Automation Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: pc-based-automation
Pc Based Automation Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report delves into the PC-Based Automation market, providing insights on market trends, size, segmentation, and forecasts for the period 2023-2033, aiming to equip stakeholders with critical data for informed decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
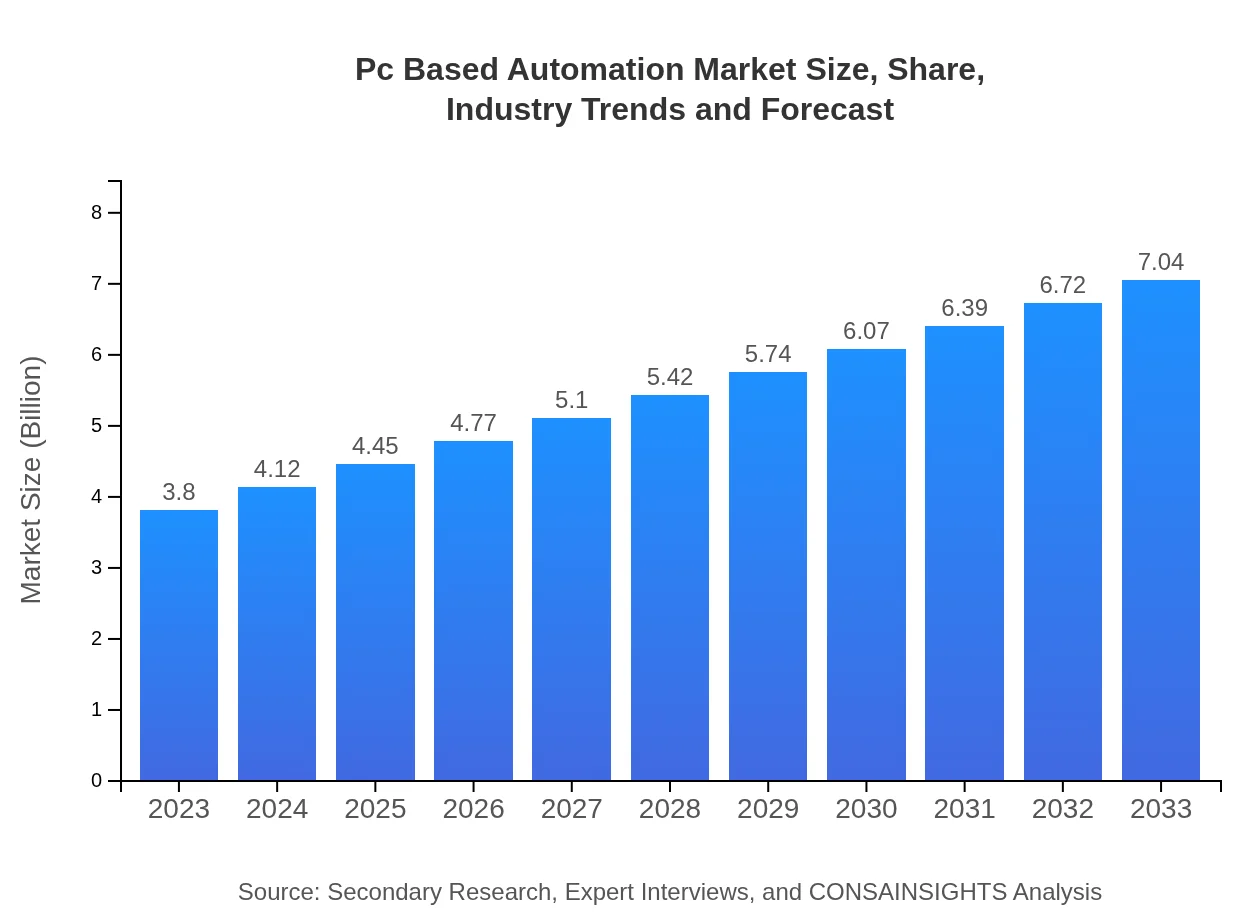
| 2023 Market Size | $3.80 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $7.04 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Rockwell Automation, Schneider Electric, ABB Ltd. |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
PC Based Automation Market Overview
Customize Pc Based Automation Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Pc Based Automation market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Pc Based Automation's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Pc Based Automation
What is the Market Size & CAGR of the PC Based Automation market in 2023?
PC Based Automation Industry Analysis
PC Based Automation Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
PC Based Automation Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Pc Based Automation Market Report:
In Europe, the PC-based automation market is estimated at $0.93 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $1.71 billion by 2033. Strong regulations promoting industry standards and energy efficiency, combined with a robust manufacturing backbone, result in significant market traction across Germany, France, and the UK.Asia Pacific Pc Based Automation Market Report:
In Asia Pacific, the market size in 2023 is approximately $0.79 billion and is projected to reach $1.47 billion by 2033. Rapid industrialization and adoption of smart manufacturing practices in countries like China and India significantly contribute to this growth. Government initiatives promoting automation to enhance productivity witness diverse cross-sector implementation.North America Pc Based Automation Market Report:
North America stands out with an initial market size of $1.31 billion in 2023, expected to expand to $2.42 billion by 2033. The region leads in implementing advanced automation solutions fueled by technological advancements and a focus on operational efficiency across major sectors, including manufacturing and automotive.South America Pc Based Automation Market Report:
South America shows a market size of $0.30 billion in 2023, forecasted to grow to $0.55 billion by 2033. The region anticipates increased investments in automation technologies with a keen interest in enhancing operational efficiency within major industries, such as mining and agriculture.Middle East & Africa Pc Based Automation Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region reflects a market size of $0.48 billion in 2023, likely reaching $0.89 billion by 2033. Growth is stimulated by increased strategic investments in infrastructure and industrial automation in Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries aimed at diversifying their economies.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
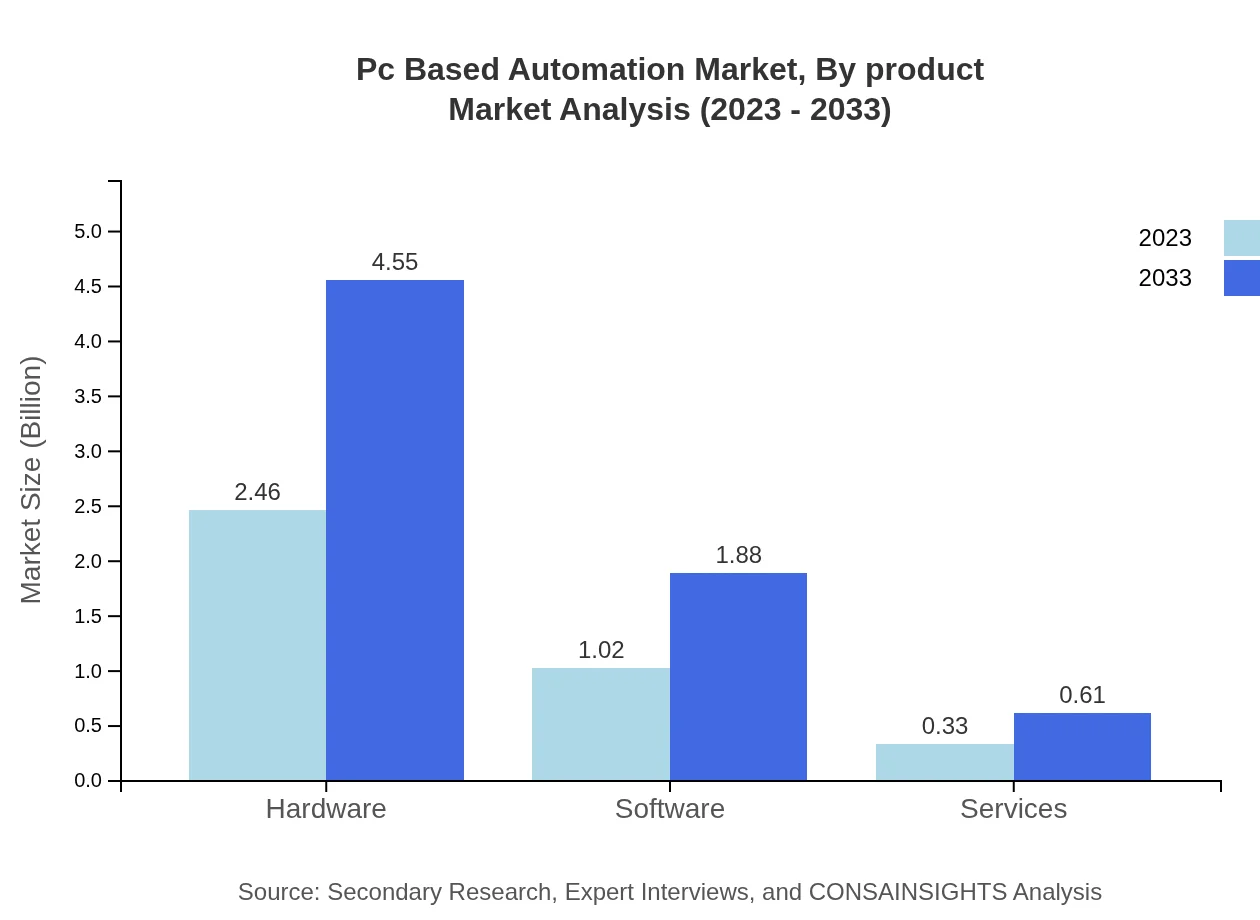
Pc Based Automation Market Analysis By Product
The PC-Based Automation market is majorly driven by hardware solutions, which dominated the market with a size of $2.46 billion in 2023 and is expected to rise to $4.55 billion by 2033, maintaining a market share of around 64.66%. Software solutions also play a significant role, contributing $1.02 billion in 2023 with projections rising to $1.88 billion by 2033. Services, despite being smaller at $0.33 billion in 2023, show promise with growth expectations to $0.61 billion.
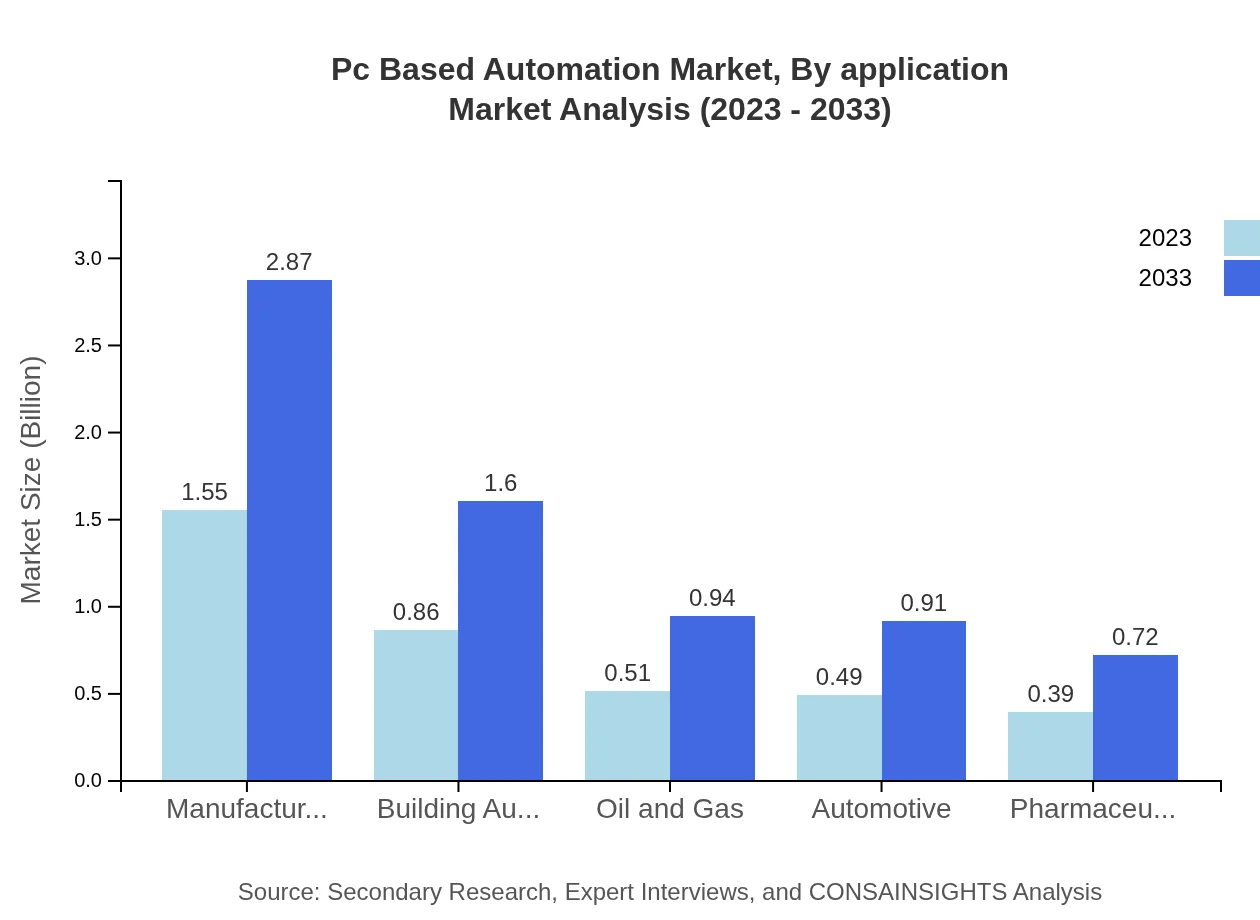
Pc Based Automation Market Analysis By Application
Applications in industries like food and beverage, logistics, chemical, and energy showcase robust growth. The food and beverage sector leads with sizes of $1.55 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $2.87 billion by 2033, holding a consistent market share of 40.74%. Logistics and transportation also exhibit strong demand, projected to increase from $0.86 billion in 2023 to $1.60 billion by 2033, indicating a growing emphasis on efficient supply chain management.
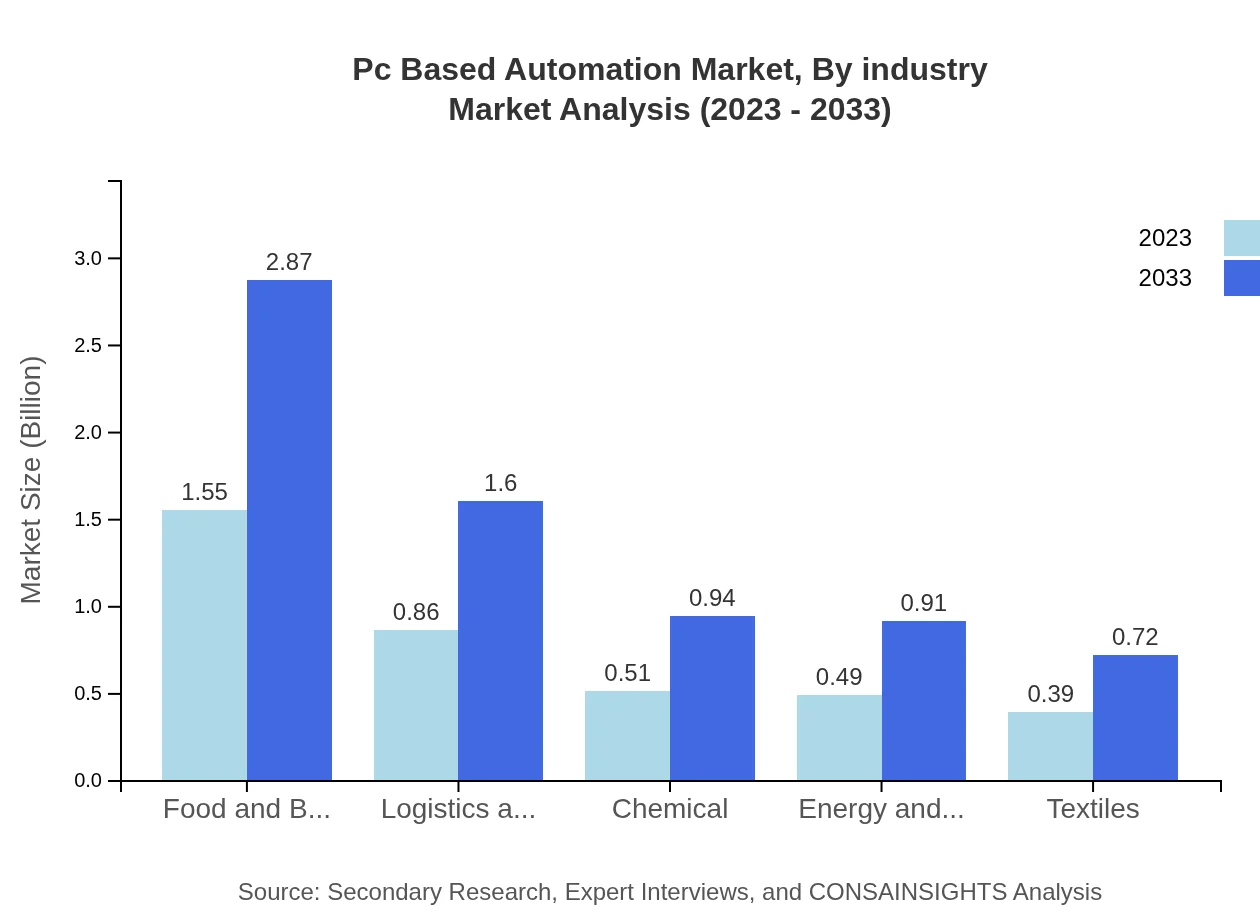
Pc Based Automation Market Analysis By Industry
The manufacturing sector represents a significant share within the PC-Based Automation market, estimated at $1.55 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $2.87 billion by 2033. Other industries such as automotive, pharmaceuticals, and energy also witness substantial growth, indicative of increasing process automation across various sectors. The chemical industry showcases a stable market performance with $0.51 billion projected to $0.94 billion growth in the same timeframe.
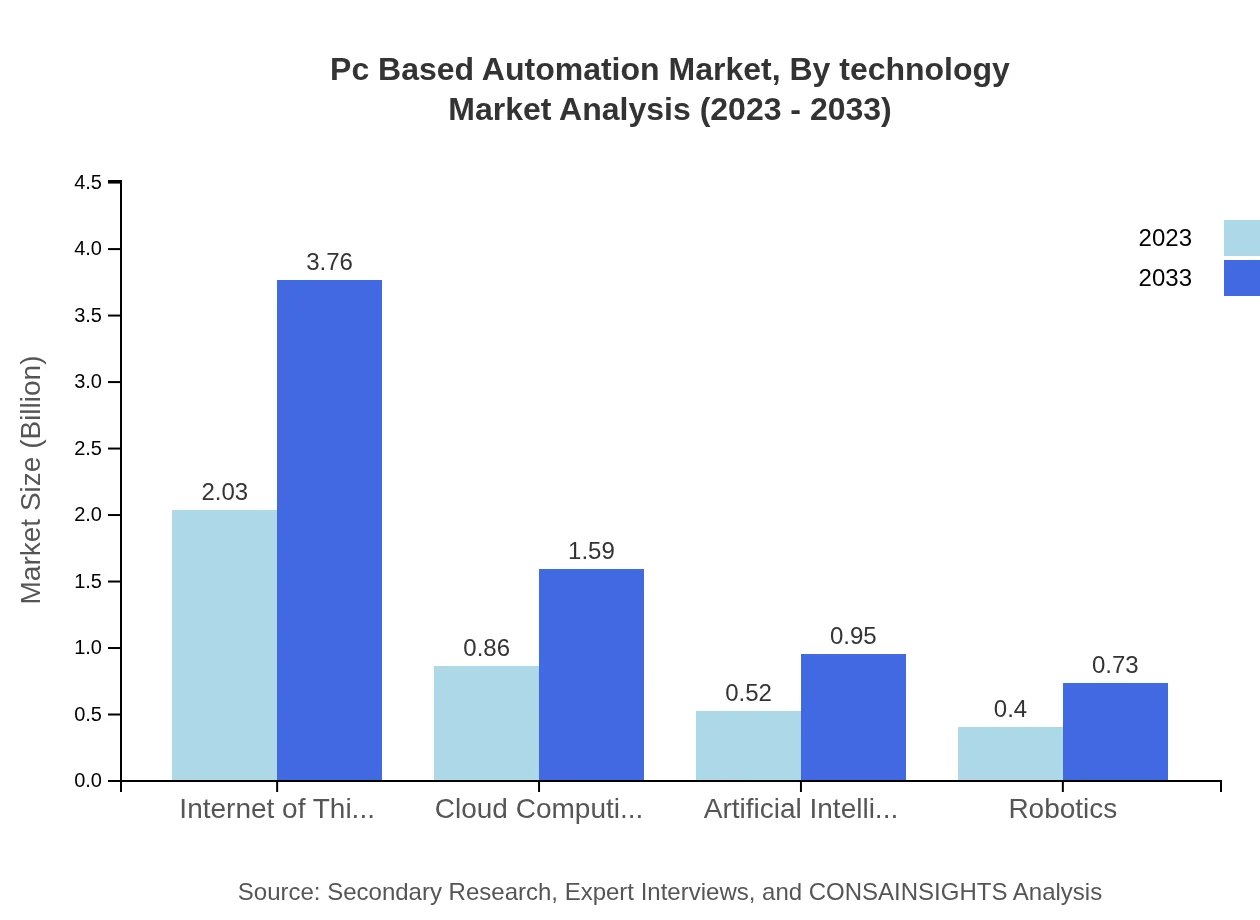
Pc Based Automation Market Analysis By Technology
Innovations in technology, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (AI), significantly influence the PC-Based Automation landscape. The market for IoT applications is expected to expand from $2.03 billion in 2023 to $3.76 billion in 2033. Cloud computing solutions are also essential in facilitating data management and automation operations, growing from $0.86 billion to $1.59 billion.
PC Based Automation Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in the PC Based Automation Industry
Siemens AG:
Siemens is a global leader in electrical engineering and automation technology, providing comprehensive automation solutions that improve efficiency and productivity across multiple sectors.Rockwell Automation:
Rockwell Automation specializes in industrial automation and information technology, optimizing manufacturing performance through cutting-edge technologies and innovations.Schneider Electric:
Schneider Electric is a pioneer in digital transformation, primarily providing energy management and automation solutions that boost sustainability and efficiency.ABB Ltd.:
ABB is a technology leader in power and automation, enhancing productivity and safety in industrial and utility sectors through innovative solutions.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of pc Based Automation?
The market size of the PC-Based Automation industry is estimated at $3.8 billion in 2023, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2%, projected to reach significant growth by 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in this pc Based Automation industry?
Key players in the PC-Based Automation industry include Siemens, Schneider Electric, and Rockwell Automation, known for their innovative solutions and strong market presence, which significantly influence industry dynamics.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the pc Based Automation industry?
The growth of the PC-Based Automation industry is driven by advancements in IoT technology, increasing demand for automation in manufacturing processes, and the need for improved operational efficiency, all contributing to higher adoption rates.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the pc Based Automation?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing for PC-Based Automation, with market sizes projected to grow from $0.79 billion in 2023 to $1.47 billion by 2033, showcasing robust expansion and increasing automation adoption.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the pc Based Automation industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the PC-Based Automation industry, tailored to meet specific client needs and addressing various aspects of market research for informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this pc Based Automation market research project?
Deliverables from the PC-Based Automation market research project include comprehensive reports, market analysis data, trends, and insights into key players, ensuring a well-rounded perspective for stakeholders.
What are the market trends of pc Based Automation?
Current trends in the PC-Based Automation industry include increasing integration of AI and IoT, rising demand for smart factories, and evolving cybersecurity measures, which shape the future landscape of automation technologies.