Pea Processed Ingredients Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: pea-processed-ingredients
Pea Processed Ingredients Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Pea Processed Ingredients market, covering key insights, industry trends, regional analysis, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
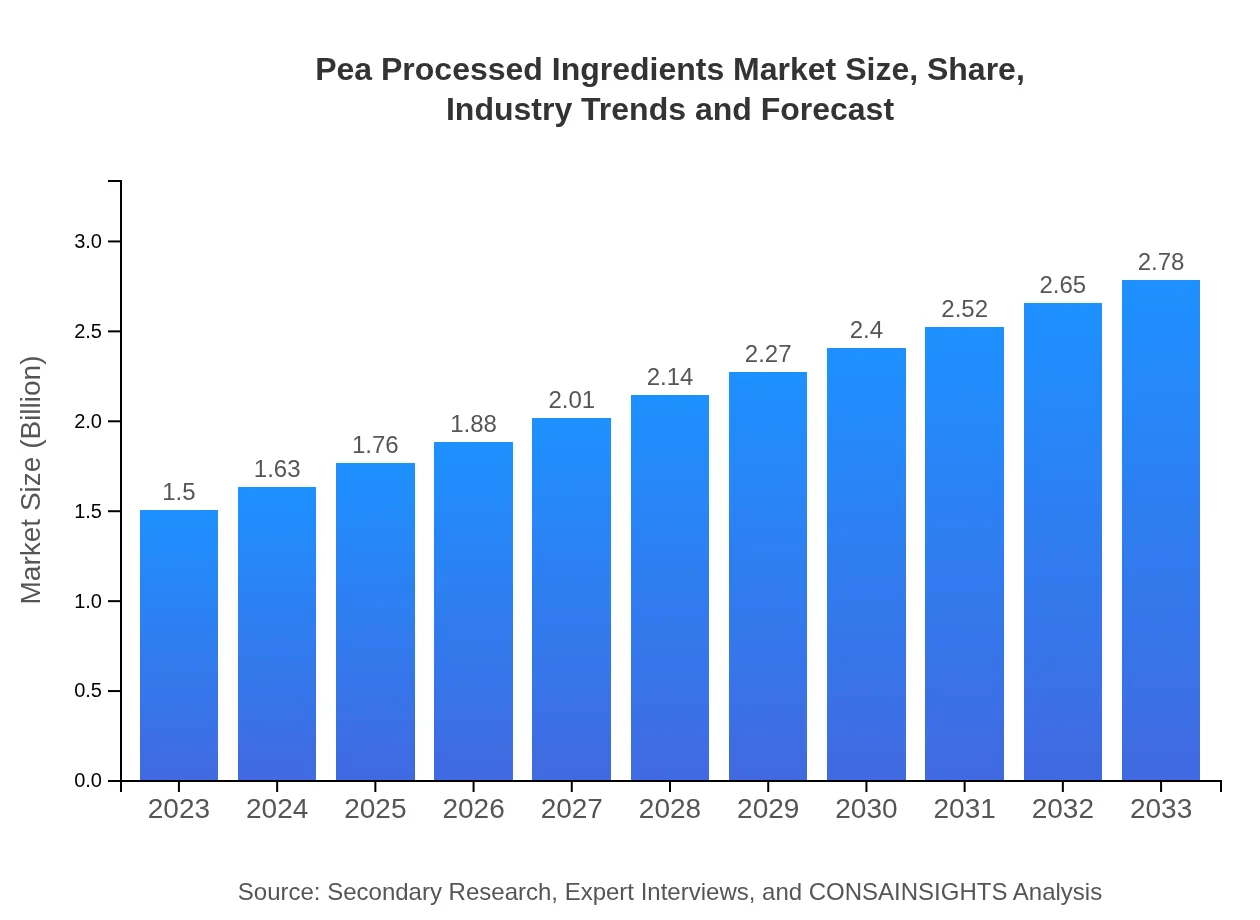
| 2023 Market Size | $1.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $2.78 Billion |
| Top Companies | Roquette Frères, Ingredion Incorporated, Pea Protein Co. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Pea Processed Ingredients Market Overview
Customize Pea Processed Ingredients Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Pea Processed Ingredients market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Pea Processed Ingredients's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Pea Processed Ingredients
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Pea Processed Ingredients market in 2023?
Pea Processed Ingredients Industry Analysis
Pea Processed Ingredients Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Pea Processed Ingredients Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Pea Processed Ingredients Market Report:
In Europe, the market for Pea Processed Ingredients is projected to grow from $0.38 billion in 2023 to $0.70 billion by 2033, primarily due to stringent regulations promoting plant-based diets and increasing demand for organic products.Asia Pacific Pea Processed Ingredients Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Pea Processed Ingredients market size was approximately $0.29 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $0.55 billion by 2033. The growth is driven by rising health awareness among consumers, growing vegetarianism, and increasing applications in baby food and plant-based innovations.North America Pea Processed Ingredients Market Report:
North America holds a significant share of the market with an estimated size of $0.58 billion in 2023, expected to reach $1.07 billion by 2033. This growth is supported by a robust consumer shift towards health and wellness products.South America Pea Processed Ingredients Market Report:
South America's Pea Processed Ingredients market is anticipated to grow from $0.11 billion in 2023 to approximately $0.21 billion by 2033, fueled by a trend towards plant-based diets and increased exports to global markets.Middle East & Africa Pea Processed Ingredients Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is expected to see growth from $0.13 billion in 2023 to $0.25 billion by 2033. The increasing awareness of nutrition's role in health is driving demand for plant-based ingredients in these regions.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
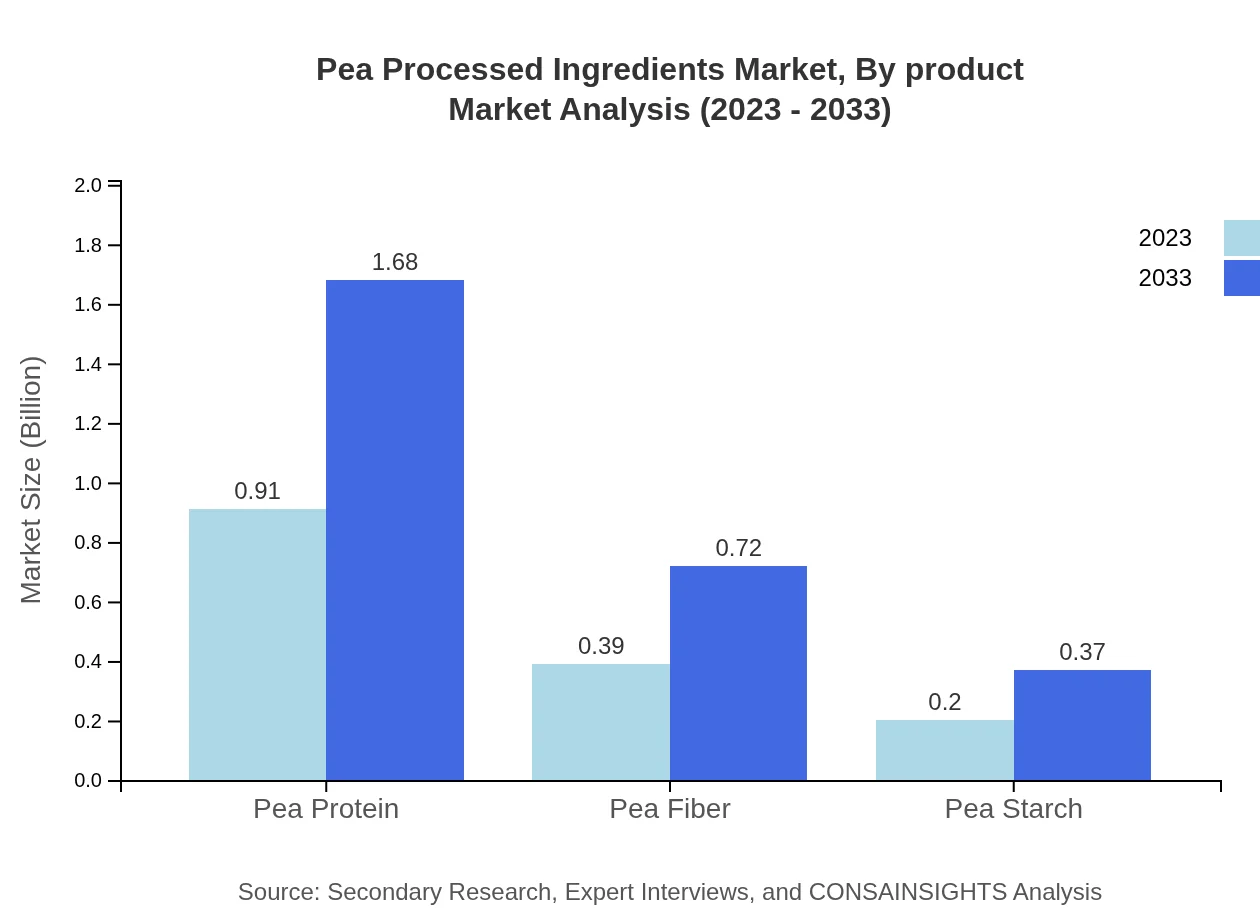
Pea Processed Ingredients Market Analysis By Product
The Pea Processed Ingredients market is segmented into various products including pea protein, pea starch, and pea fiber. As of 2023, the market size for pea protein is approximately $0.91 billion, expected to reach $1.68 billion by 2033. Pea starch and fiber are also growing segments, with sizes of $0.20 billion and $0.39 billion respectively in 2023, which are projected to grow significantly in the coming years.
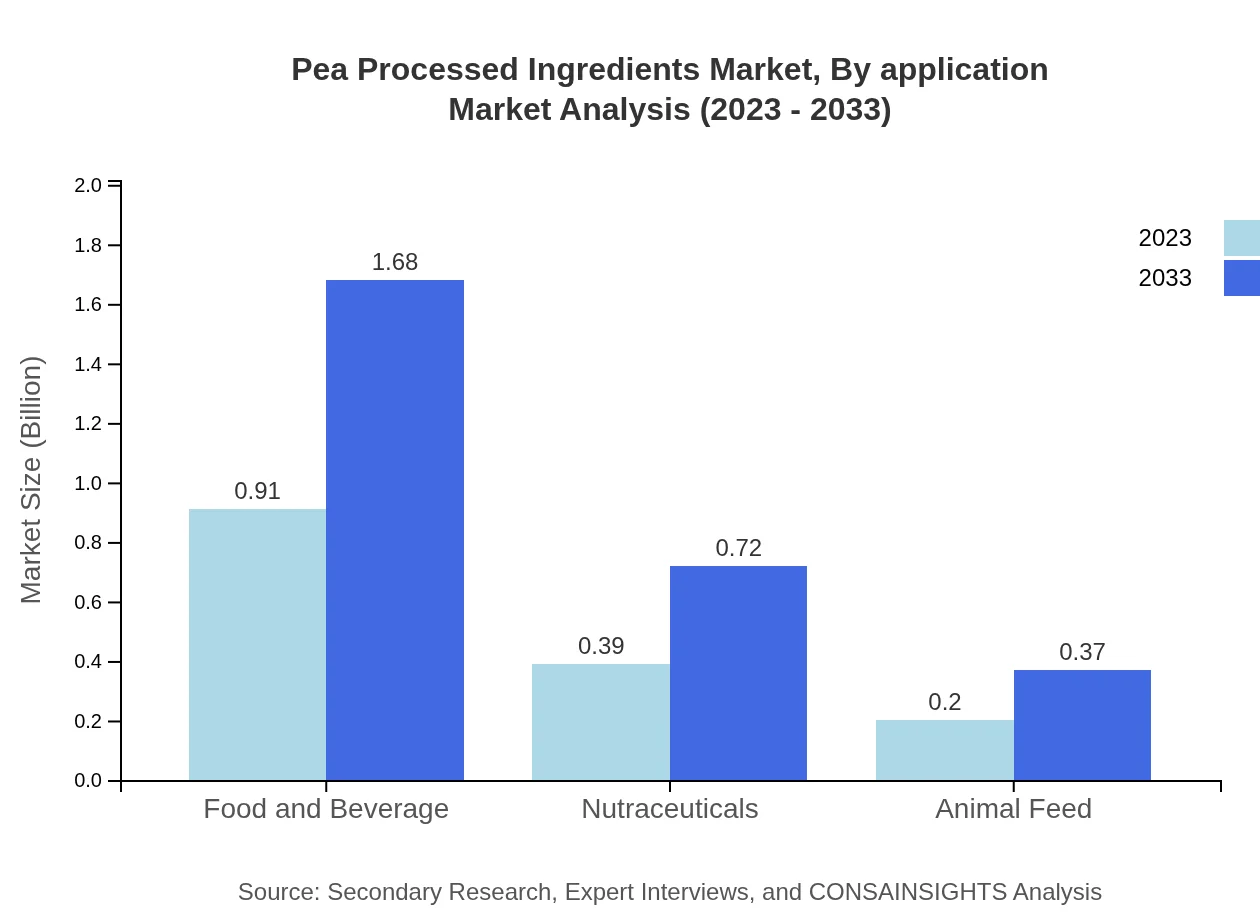
Pea Processed Ingredients Market Analysis By Application
In terms of applications, the food and beverage segment dominates, accounting for $0.91 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $1.68 billion by 2033, driven by the rising demand for plant-based products. Other applications such as nutraceuticals and animal feed also represent significant market shares, with nutraceuticals growing from $0.39 billion to $0.72 billion in the same period.
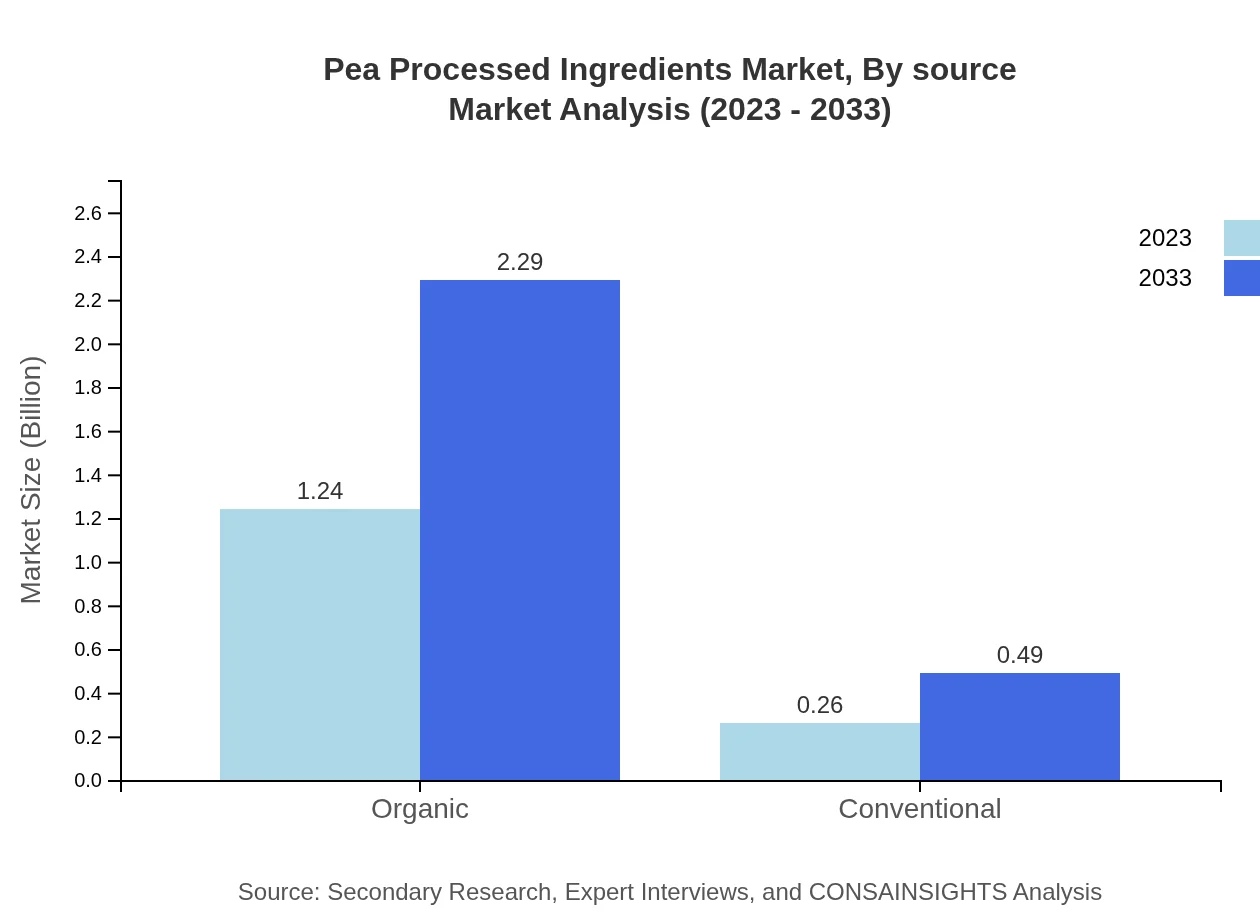
Pea Processed Ingredients Market Analysis By Source
The market segments into organic and conventional sources. The organic segment is significantly larger, with a market size of $1.24 billion in 2023, growing to $2.29 billion by 2033. The trend towards organic products is driven by consumer demand for clean-label and health-conscious options.
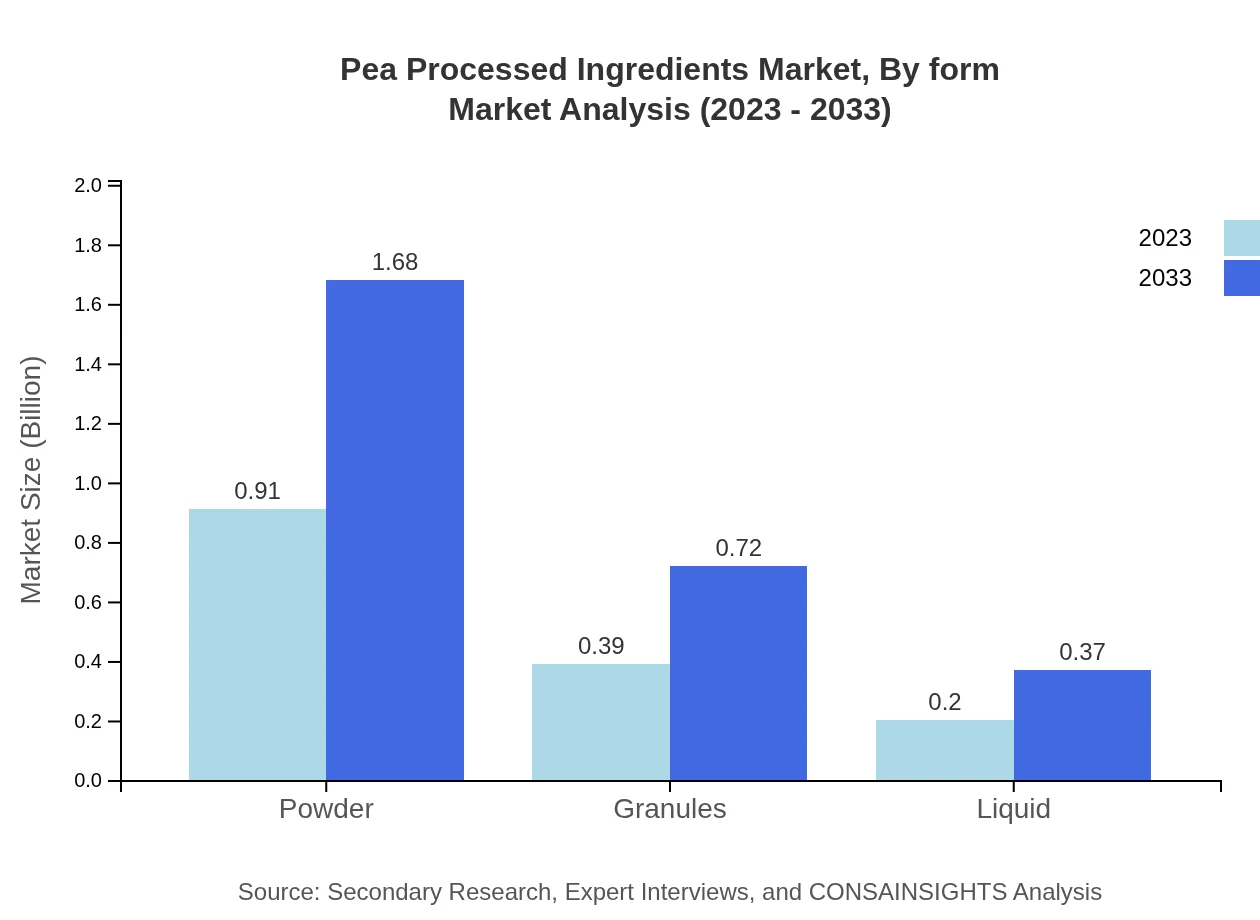
Pea Processed Ingredients Market Analysis By Form
The form of pea ingredients is crucial, with powders dominating the market due to their versatility and ease of use in various applications. The powder market is expected to grow from $0.91 billion in 2023 to $1.68 billion by 2033, while liquids and granules are also emerging segments with marked growth prospects.
Pea Processed Ingredients Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Pea Processed Ingredients Industry
Roquette Frères:
A leading global player in the pea protein market, Roquette specializes in providing high-quality plant-based ingredients and solutions tailored for diverse applications.Ingredion Incorporated:
A prominent ingredient solutions company, Ingredion offers a range of pea-based products designed to enhance food formulations and maintain texture.Pea Protein Co.:
Known for its innovative processing technologies, Pea Protein Co. focuses on producing high-quality pea protein concentrates and isolates.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of pea Processed Ingredients?
The pea-processed ingredients market is valued at approximately $1.5 billion as of 2023, with a projected CAGR of 6.2%. This growth reflects increasing consumer demand for plant-based protein and healthier alternatives.
What are the key market players or companies in this pea Processed Ingredients industry?
Key players in the pea-processed ingredients industry include companies like Ingredion Incorporated, DuPont, and Roquette Frères, which lead the market through innovations in product offerings such as pea protein, starch, and fiber.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the pea Processed Ingredients industry?
The growth in the pea-processed ingredients industry is predominantly driven by the increasing demand for plant-based proteins, health benefits associated with peas, and rising consumer awareness regarding sustainable food sourcing.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the pea Processed Ingredients?
North America is currently the fastest-growing region for pea-processed ingredients, projected to expand from a market size of $0.58 billion in 2023 to $1.07 billion by 2033, indicating a strong demand for plant-based alternatives.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the pea Processed Ingredients industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the pea-processed ingredients industry, tailoring insights according to specific client needs to ensure relevancy and accuracy in market analysis.
What deliverables can I expect from this pea Processed Ingredients market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables such as market size analysis, competitive landscape, growth opportunity assessment, regional forecasts, and segment-specific insights tailored to your business strategy in the pea-processed ingredients market.
What are the market trends of pea Processed Ingredients?
Current market trends in pea-processed ingredients include a rise in organic product offerings, increased innovation in food formulations, and a significant shift towards clean label products, aiming for transparency and health-focused attributes.