Peanut Butter Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: peanut-butter
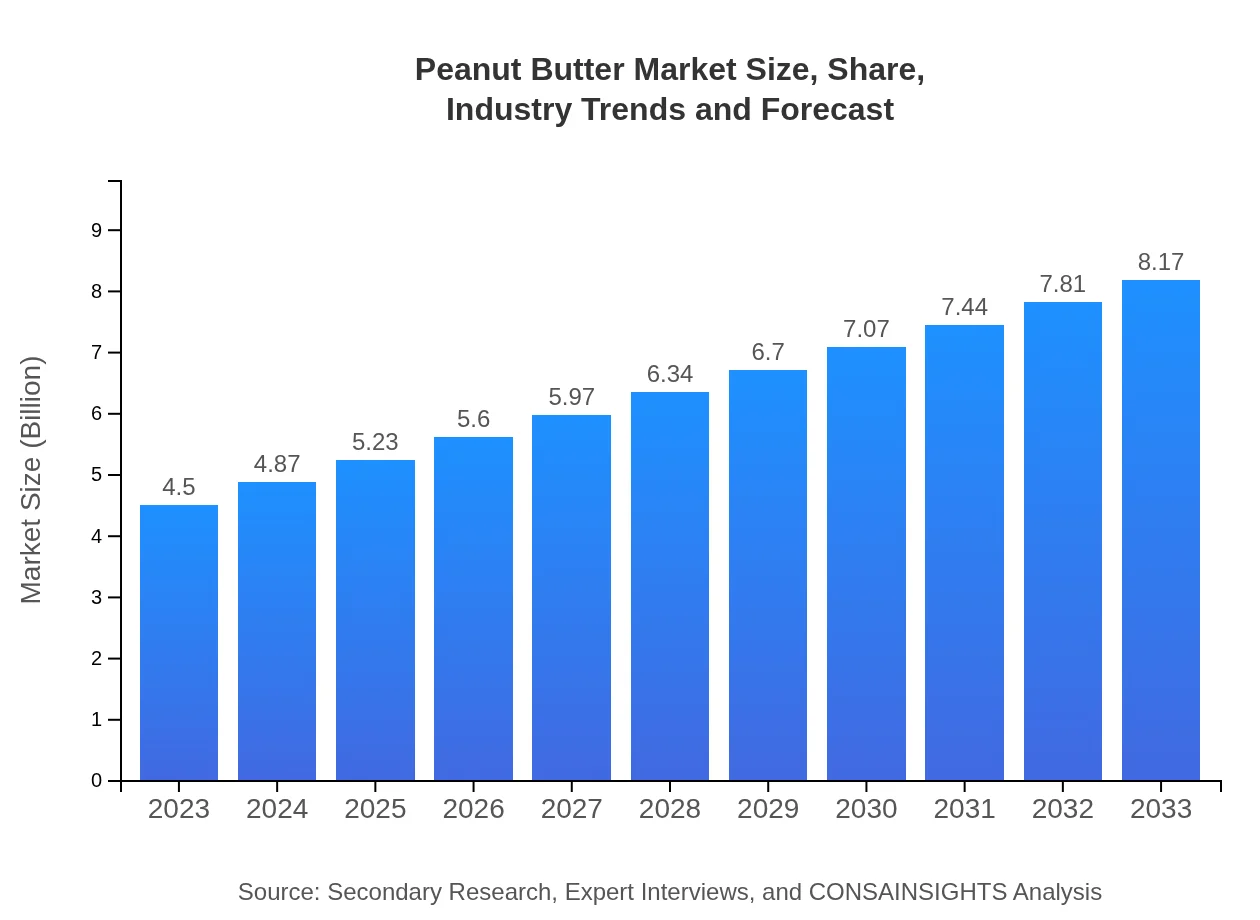
Peanut Butter Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This market report provides a comprehensive overview of the peanut butter industry, including market size, growth forecasts from 2023 to 2033, regional insights, segmentation analysis, and key trends shaping the future of peanut butter consumption globally.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $4.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.0% |
| 2033 Market Size | $8.17 Billion |
| Top Companies | J.M. Smucker Company, Skippy, Peter Pan, SunButter |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Peanut Butter Market Overview
Customize Peanut Butter Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Peanut Butter market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Peanut Butter's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Peanut Butter
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Peanut Butter market in 2023?
Peanut Butter Industry Analysis
Peanut Butter Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Peanut Butter Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Peanut Butter Market Report:
In Europe, the peanut butter market is anticipated to grow substantially from USD 1.24 billion in 2023 to USD 2.25 billion by 2033. Demand is being driven by the increasing health consciousness among consumers and the trend of incorporating peanut butter into a variety of dishes. Furthermore, European consumers are showing a preference for organic and natural peanut butters.Asia Pacific Peanut Butter Market Report:
The Asia Pacific peanut butter market is poised for rapid growth, projected to increase from USD 0.90 billion in 2023 to USD 1.63 billion by 2033. Rising urbanization, an expanding middle class, and growing health consciousness are driving demand for peanut butter products. Additionally, the region is witnessing a surge in popularity for peanut-based snacks and spreads among younger consumers.North America Peanut Butter Market Report:
North America remains the largest market for peanut butter, with revenues expected to rise from USD 1.67 billion in 2023 to USD 3.03 billion by 2033. The dominance of established brands, coupled with the increasing trend toward clean-label products, is accelerating market growth. The rise of innovative peanut butter product lines, including organic and flavored variants, contributes to this trend.South America Peanut Butter Market Report:
The South American market, although smaller, is growing steadily, with a projected increase from USD 0.20 billion in 2023 to USD 0.36 billion by 2033. Growing awareness of nutritional benefits and the rising trend of snacking are key factors contributing to this growth. However, challenges related to sourcing quality peanuts may impact market dynamics.Middle East & Africa Peanut Butter Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa peanut butter market is expected to grow from USD 0.50 billion in 2023 to USD 0.91 billion by 2033. Factors contributing to this growth include growing health awareness, rising disposable incomes, and a shift towards Western dietary habits. However, market penetration remains a challenge due to cultural preferences regarding traditional cuisines.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
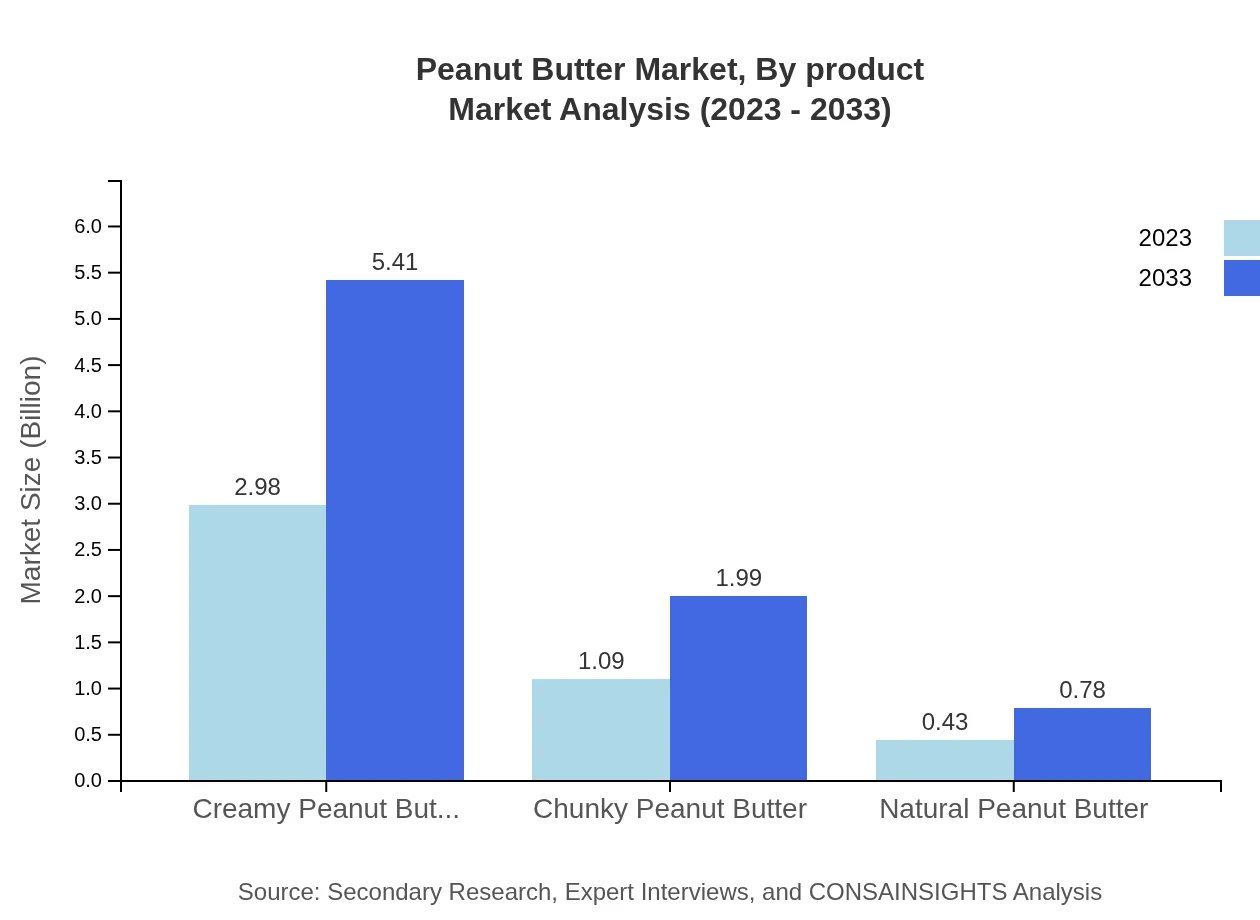
Peanut Butter Market Analysis By Product
In 2023, creamy peanut butter leads the market with a share of approximately 66.18%, valued at USD 2.98 billion, and is projected to reach USD 5.41 billion by 2033. Chunky peanut butter, with a market size of USD 1.09 billion in 2023, is expected to grow to USD 1.99 billion. Natural peanut butter holds a niche, currently valued at USD 0.43 billion, anticipated to grow to USD 0.78 billion by 2033. Special variations, like spreads for other culinary applications, contribute to overall market diversity.
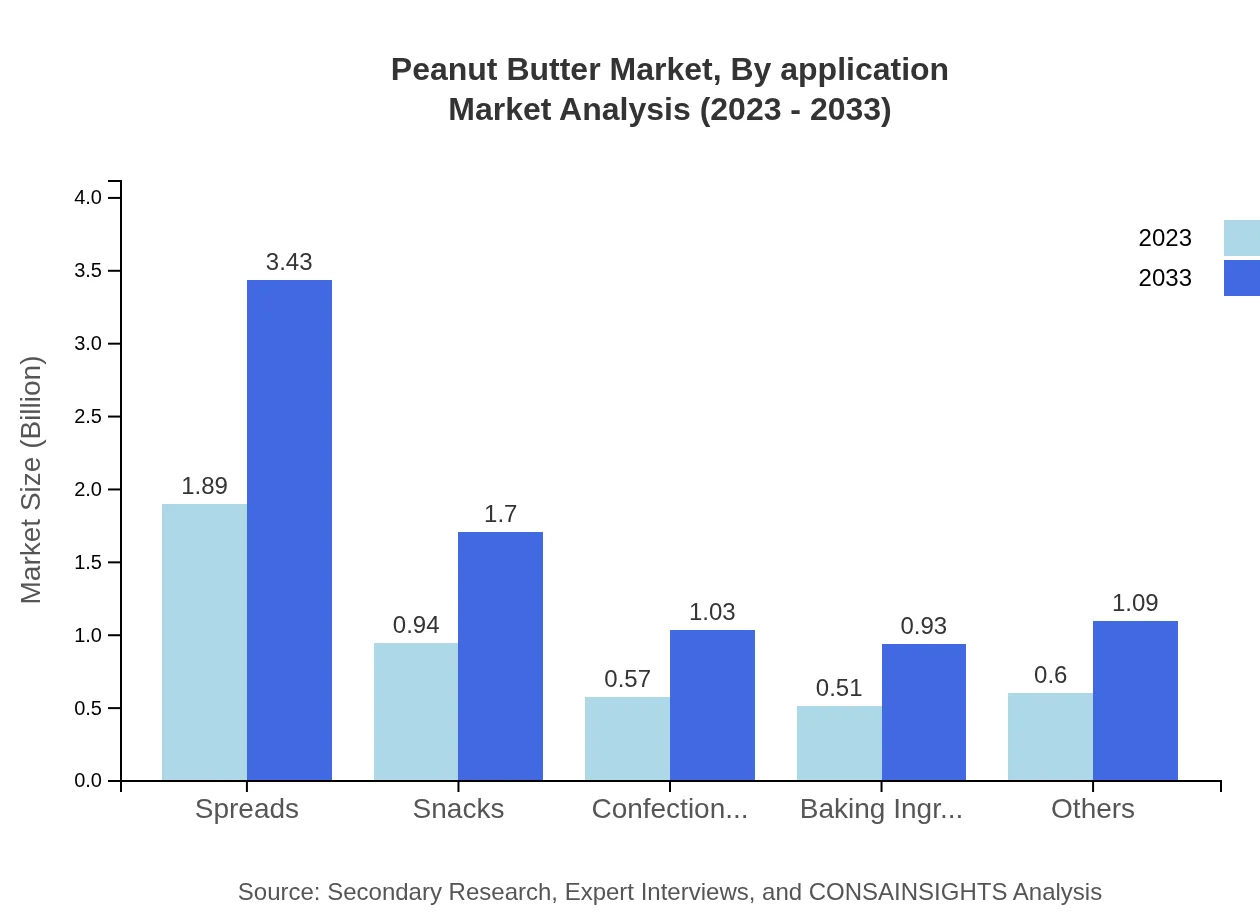
Peanut Butter Market Analysis By Application
The market is segmented into household use, food service industry, and baking ingredients. Households dominate, representing about 66.18% of the market and expected to grow from USD 2.98 billion to USD 5.41 billion by 2033. The food service industry, currently valued at USD 1.09 billion, is projected to grow to USD 1.99 billion, indicating increasing use in restaurants and cafes.
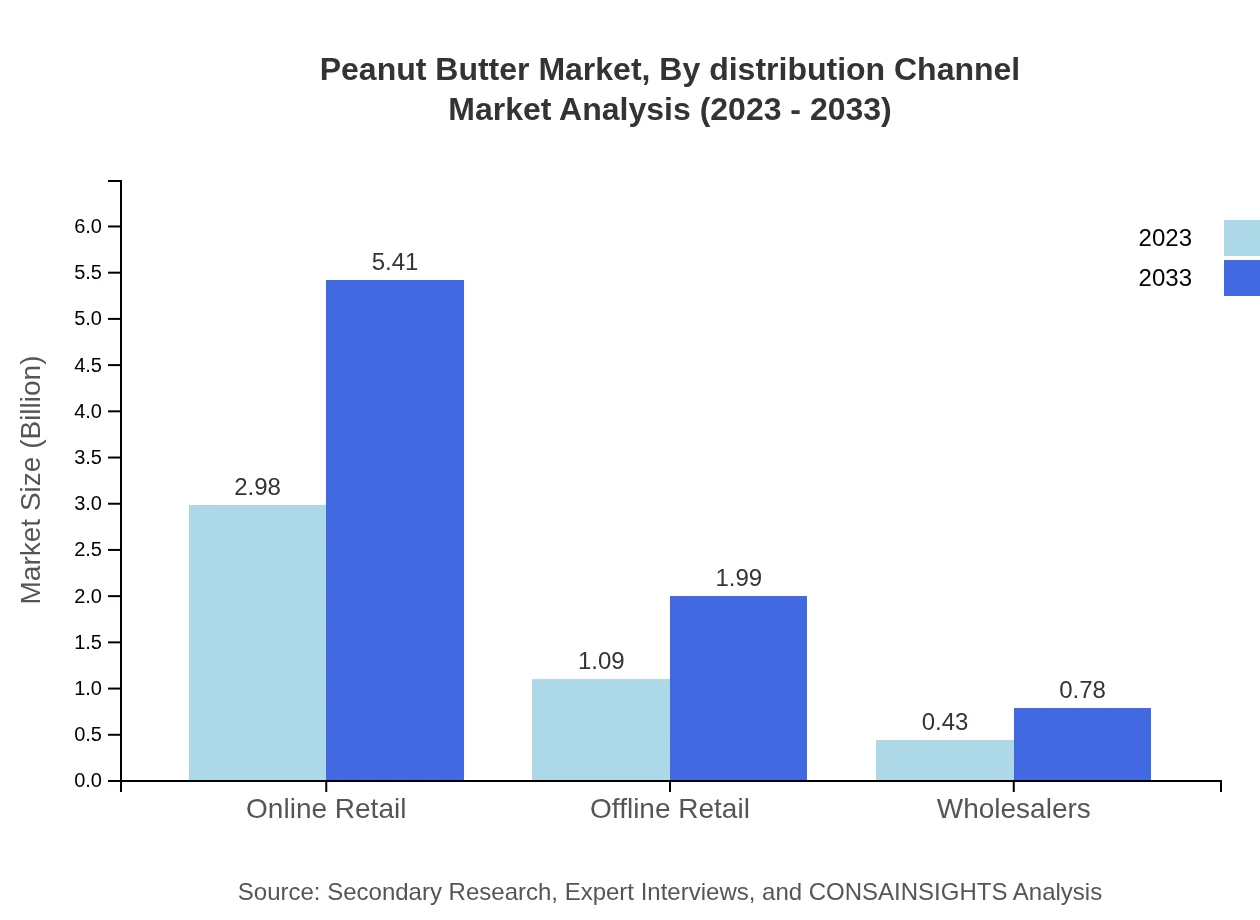
Peanut Butter Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Distribution channels for peanut butter comprise online and offline retail. Online retail is expected to dominate, growing from USD 2.98 billion in 2023 to USD 5.41 billion by 2033. Offline retail is also significant, with expected growth from USD 1.09 billion to USD 1.99 billion as consumers value the convenience of both online shopping and traditional retail experiences.
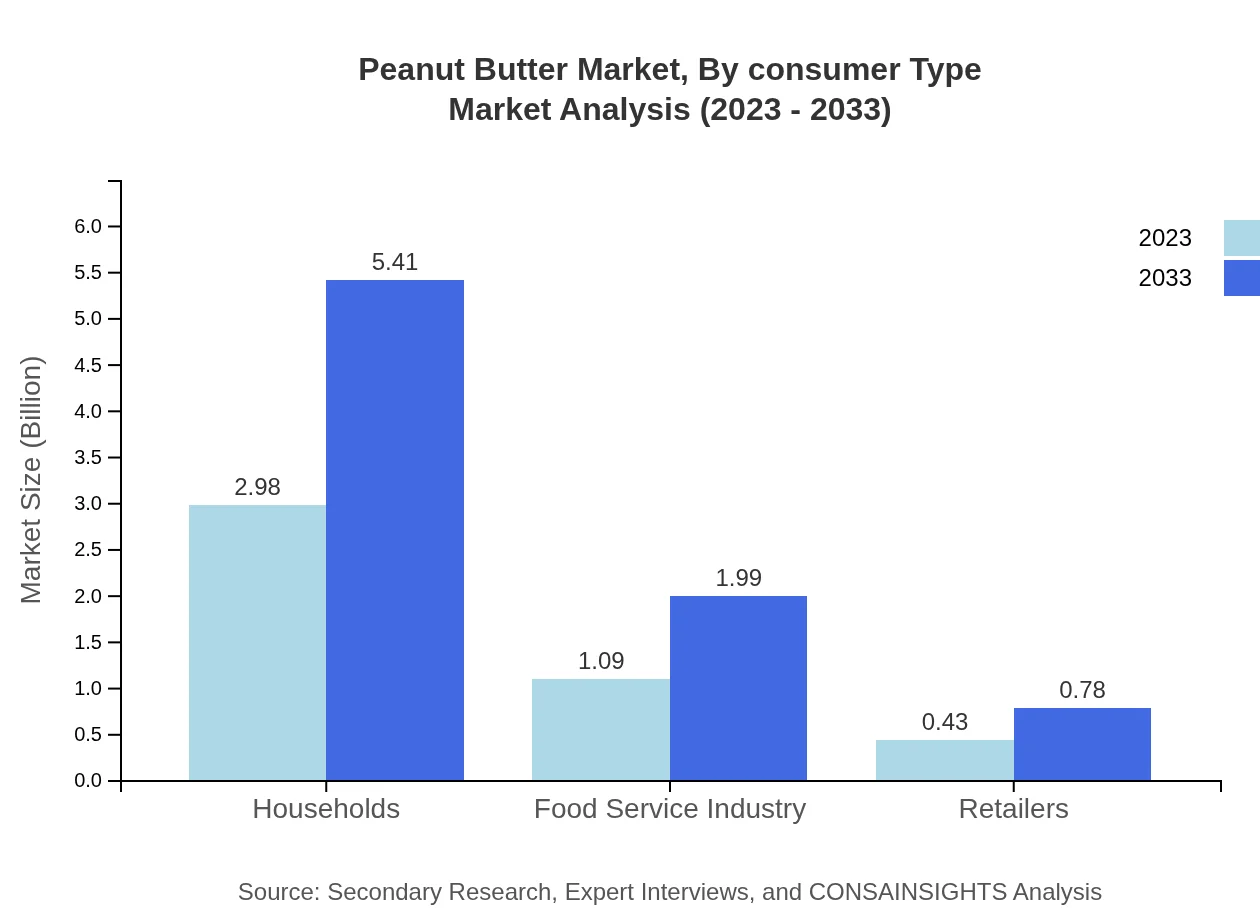
Peanut Butter Market Analysis By Consumer Type
The peanut butter market is analyzed through consumer type segments including households, health-conscious individuals, and children. Households remain the dominant consumer segment. The health-conscious are increasingly adopting peanut butter for its nutritional benefits, while children’s preferences drive the demand for flavored varieties.
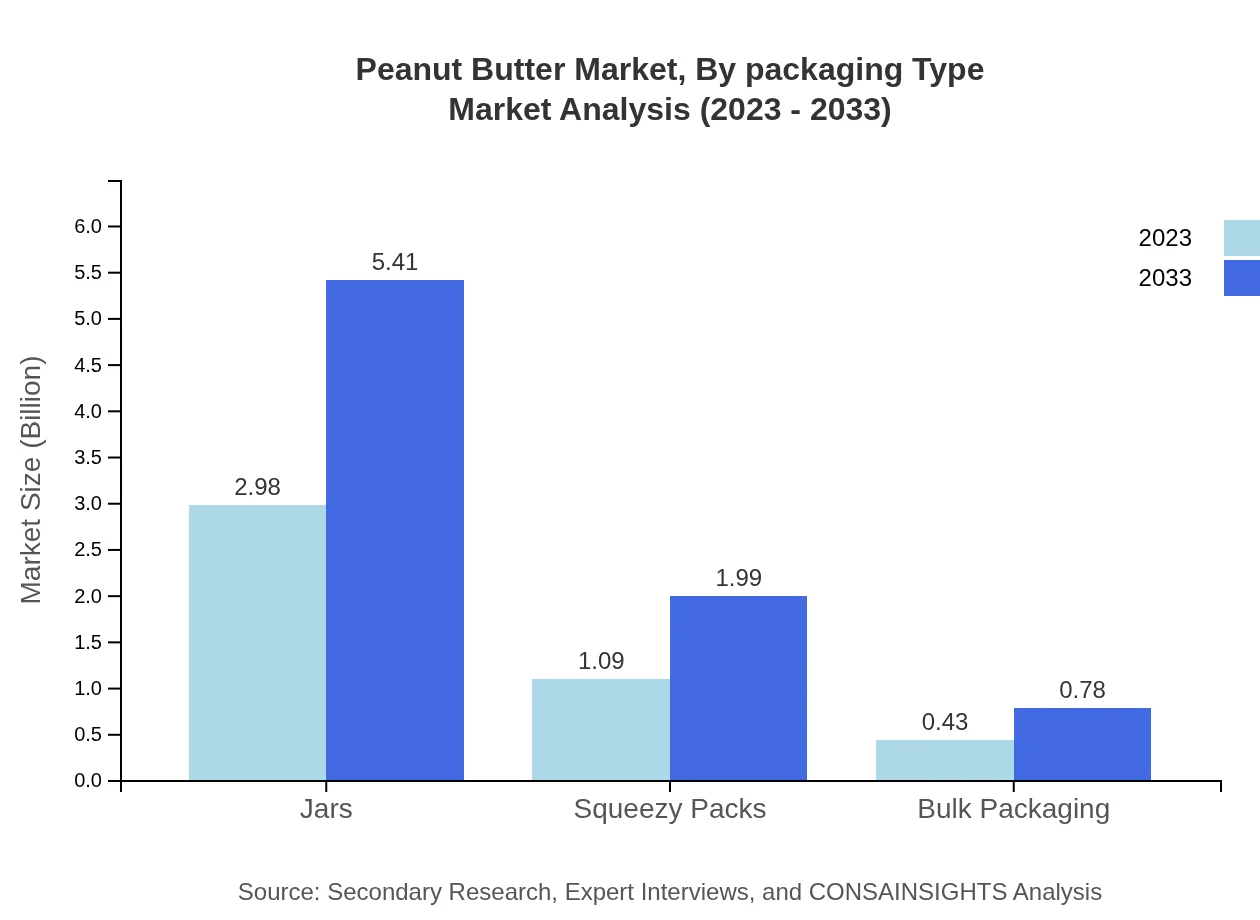
Peanut Butter Market Analysis By Packaging Type
Packaging options include jars, squeezy packs, and bulk packaging. Jars lead the market with a size of USD 2.98 billion in 2023, expected to reach USD 5.41 billion by 2033. Squeezy packs are valued at USD 1.09 billion, projected to grow to USD 1.99 billion as their convenience appeals to on-the-go consumers.
Peanut Butter Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Peanut Butter Industry
J.M. Smucker Company:
A leading player in the peanut butter market, J.M. Smucker Company is known for its wide range of peanut butter products, including natural and organic varieties, catering to health-conscious consumers.Skippy:
Owned by Hormel Foods, Skippy is one of the most recognized peanut butter brands globally, offering various products from creamy to chunky options, focusing on affordability and accessibility.Peter Pan:
Peter Pan is known for its rich taste and multiple product lines, including reduced-fat and natural versions, appealing to a broad consumer base.SunButter:
Specializing in sunflowers seeds, SunButter provides peanut butter alternatives, targeting health-conscious and allergy-sensitive consumers.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of peanut Butter?
The peanut butter market size is projected to reach approximately $4.5 billion in 2023, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.0% anticipated through 2033. This robust growth indicates a strong demand and expanding consumer base for peanut butter globally.
What are the key market players or companies in the peanut Butter industry?
Key players in the peanut butter industry include notable brands like J.M. Smucker Company, Skippy, and Kraft. These companies have established strong market presence and continue to innovate their products to meet consumer preferences and health trends.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the peanut butter industry?
Growth in the peanut butter industry is driven by rising health consciousness among consumers, increasing popularity of plant-based diets, and innovative product offerings. Additionally, the expanding use of peanut butter in various culinary applications contributes significantly to market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the peanut butter market?
The North America region is expected to experience the fastest growth, with its market size projected to increase from $1.67 billion in 2023 to $3.03 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by high consumer demand and a growing trend toward convenient and healthy snacks.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the peanut butter industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights provides customizable market reports tailored specifically for the peanut butter industry. Clients can request tailored data and insights to meet their unique research needs, allowing businesses to make informed strategic decisions.
What deliverables can I expect from this peanut butter market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables from the peanut butter market research project, including detailed market analysis, trends, competitive landscape, regional insights, and growth forecasts, allowing companies to navigate the market effectively and enhance their decision-making processes.
What are the market trends of peanut butter?
Current market trends for peanut butter include a shift toward natural and organic varieties, increasing demand for flavored options, and a growing preference for convenience packaging. Additionally, there is an evident rise in peanut butter usage in health-oriented food products and snacks.