Peas Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: peas
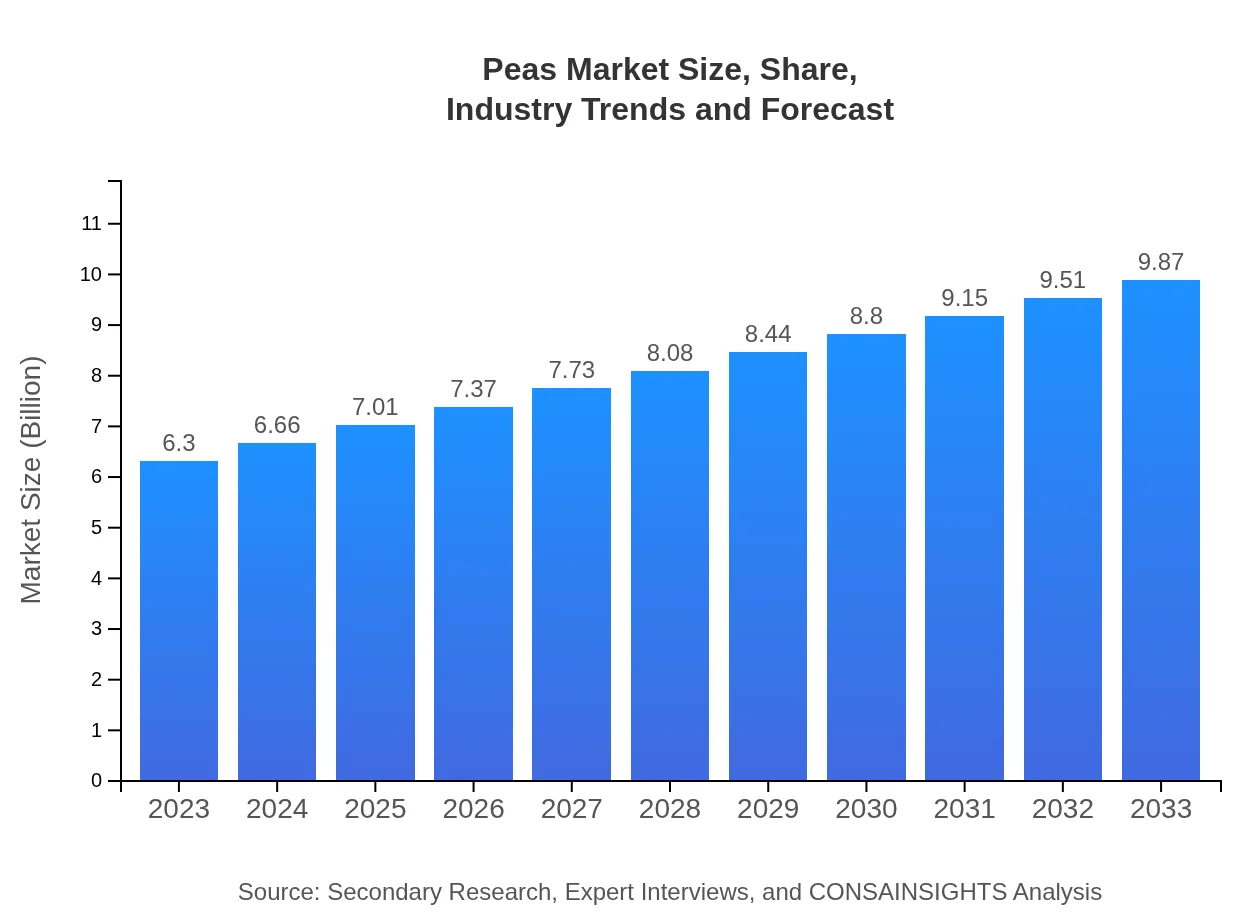
Peas Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Peas market, covering insights on market size, segmentation, regional performance, and industry trends from 2023 to 2033. It aims to present a detailed overview for stakeholders and potential investors.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $6.30 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $9.87 Billion |
| Top Companies | Green Giant, Bonduelle, Pioneer Seeds, Breyers, Horizon Organic |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Peas Market Overview
Customize Peas Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Peas market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Peas's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Peas
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Peas market in 2023?
Peas Industry Analysis
Peas Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Peas Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Peas Market Report:
In Europe, the peas market is projected to grow from 1.52 billion USD in 2023 to 2.38 billion USD by 2033. The region shows a significant shift towards organic and sustainable agriculture practices, supported by government policies favoring environmental sustainability. Countries such as the UK, France, and Germany are at the forefront, promoting pea consumption as part of healthy diets.Asia Pacific Peas Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the peas market is expected to expand from 1.20 billion USD in 2023 to 1.88 billion USD by 2033. This growth is driven by the rising consumption of peas in countries like India and China, where they are integral to traditional diets. Additionally, the increasing focus on sustainable agriculture practices is expected to further boost cultivation in this region.North America Peas Market Report:
North America, with a market size of 2.08 billion USD in 2023, is forecasted to reach 3.26 billion USD by 2033. The region is characterized by a strong processing industry and a growing trend towards organic products. The United States and Canada lead in terms of production and consumption, largely driven by food manufacturers and consumer preferences for healthy ingredients.South America Peas Market Report:
The South American market for peas is anticipated to grow from 0.62 billion USD in 2023 to 0.97 billion USD by 2033. Countries like Brazil and Argentina are witnessing an increase in pea cultivation due to favorable climatic conditions. Rising health awareness is fueling the demand for nutritious food sources across the region.Middle East & Africa Peas Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is expected to increase from 0.88 billion USD in 2023 to 1.38 billion USD by 2033. The growth is driven by an increase in food consumption patterns and a push for self-sustainability in agricultural production. Countries in this region are beginning to recognize the nutritional value and versatility of peas, further stimulating market expansion.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
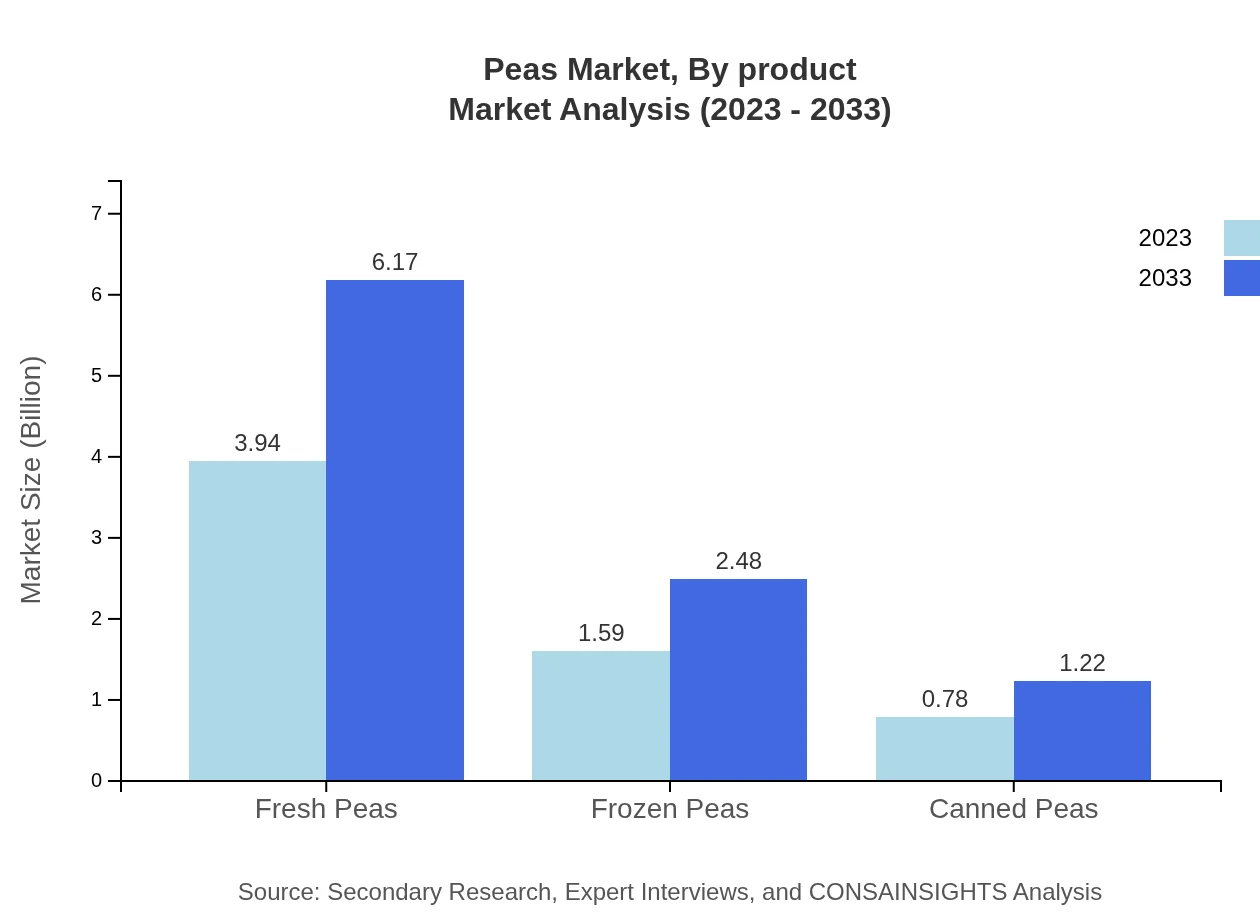
Peas Market Analysis By Product
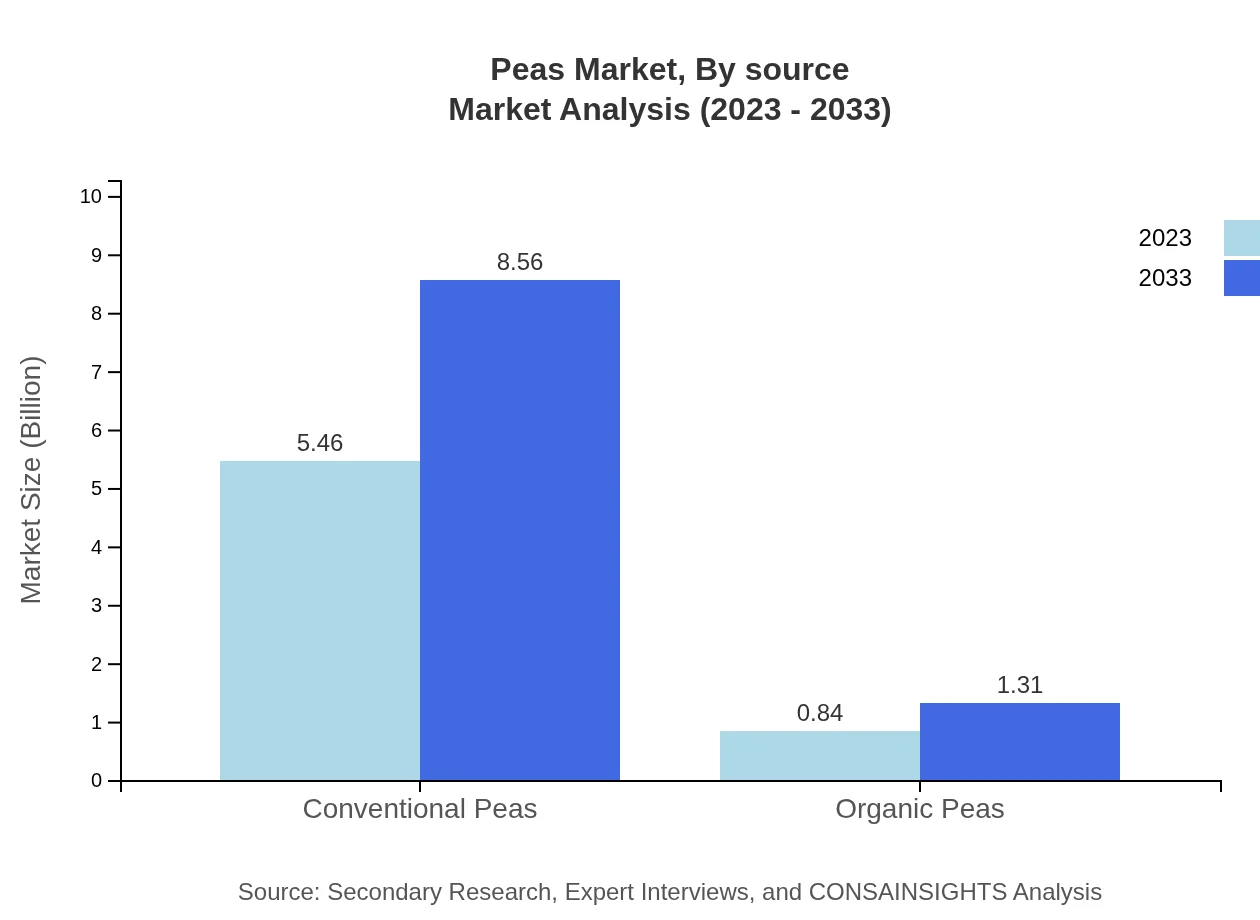
The Peas market is primarily divided into conventional peas and organic peas. Conventional peas dominate the market due to their widespread availability and lower cost, valued at 5.46 billion USD in 2023, expected to rise to 8.56 billion USD by 2033. In contrast, organic peas, while smaller in share, are rapidly gaining popularity, with a growth from 0.84 billion USD in 2023 to 1.31 billion USD in 2033.
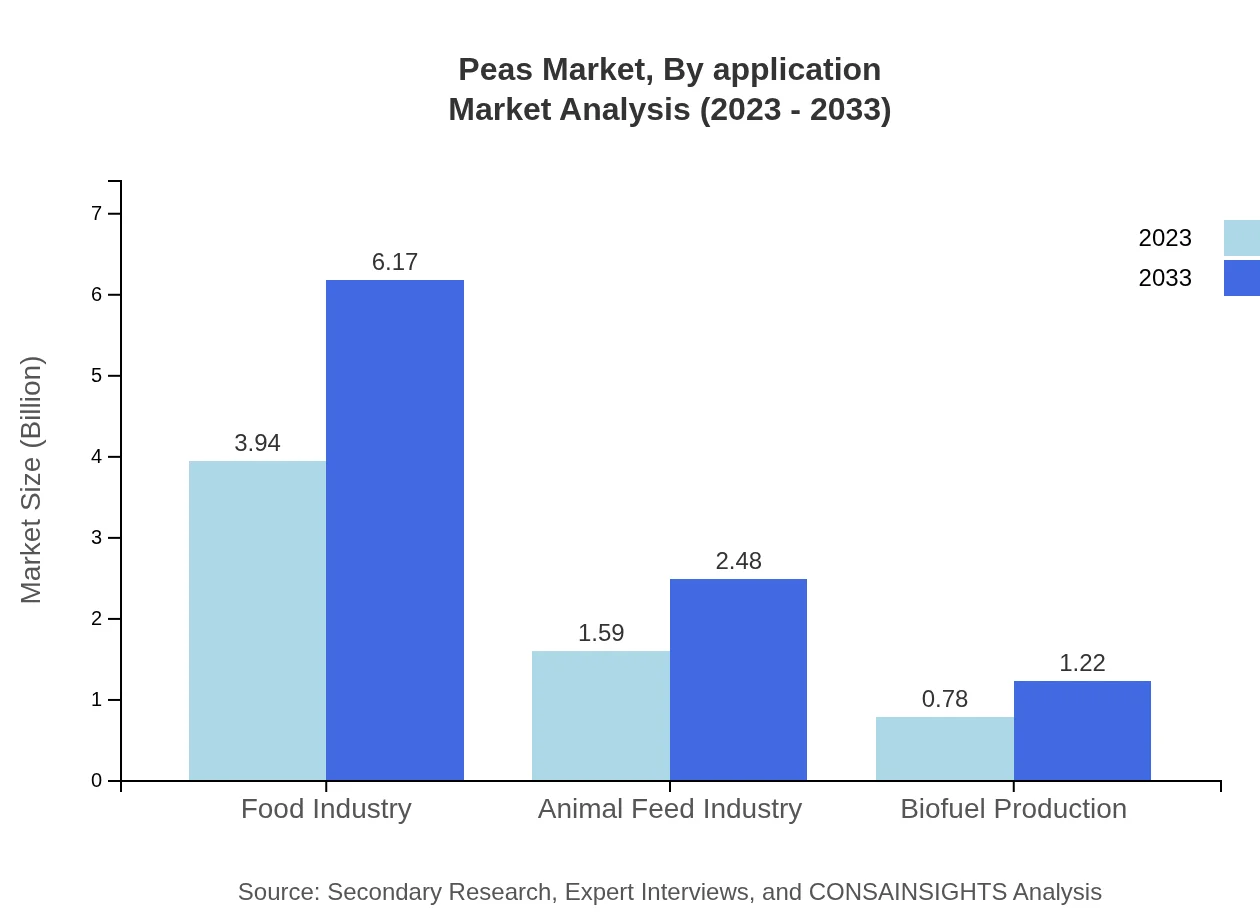
Peas Market Analysis By Application
Applications for peas include food for households, food processors, animal feed, and biofuel production. The food industry holds a significant share, valued at 3.94 billion USD in 2023, forecast to reach 6.17 billion USD by 2033. Animal feed, currently valued at 1.59 billion USD, is anticipated to grow to 2.48 billion USD, showcasing robust growth across sectors.
Peas Market Analysis By Source
The Peas market features both genetically modified and non-genetically modified sources. The non-GMO segment is preferred for its perceived health benefits and safety. This segment reflects a larger market demand, especially in health-conscious consumer demographics.
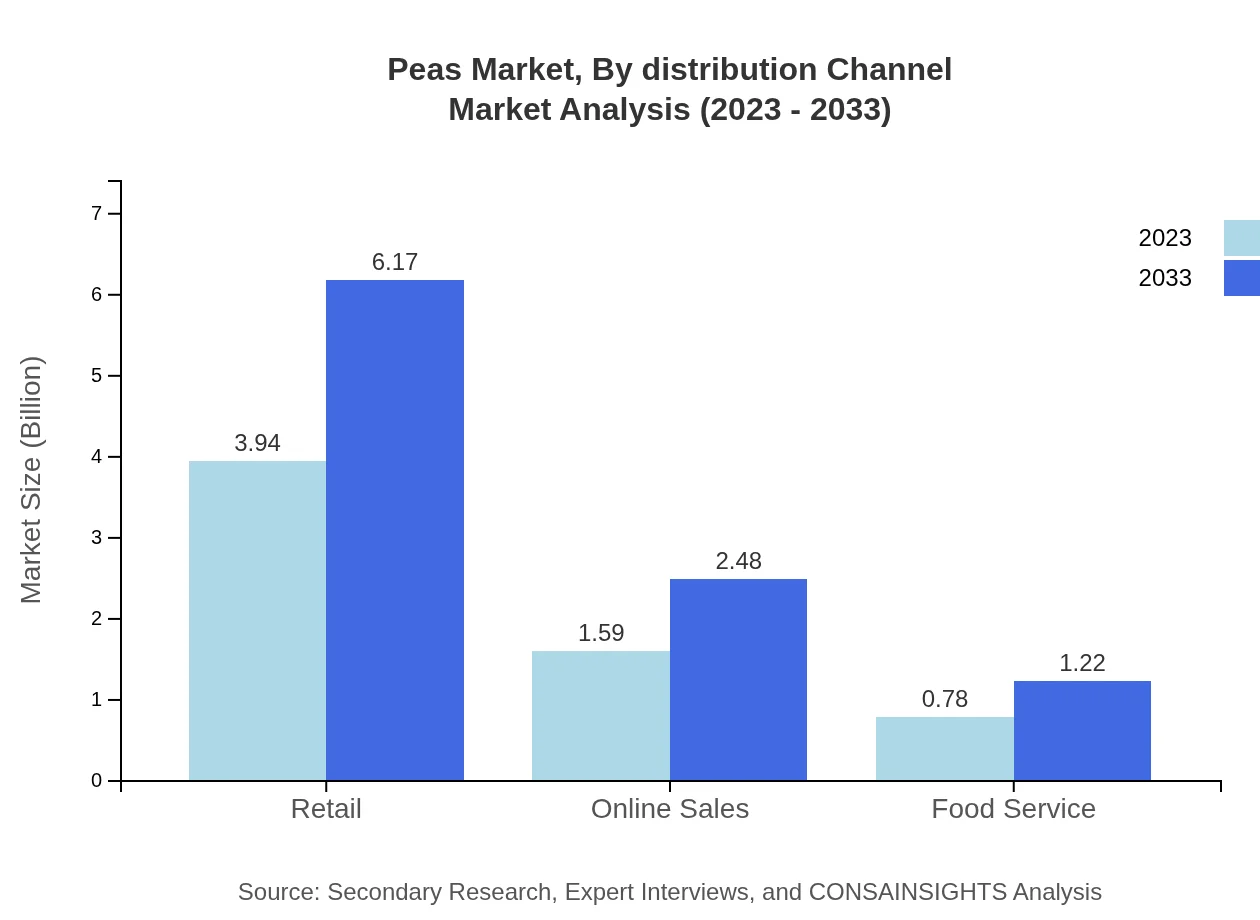
Peas Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Distribution channels for peas include retail, online sales, and food service. Retail remains the dominant channel, expected to grow from 3.94 billion USD in 2023 to 6.17 billion USD by 2033, while online sales are also seeing increasing traction, valued at 1.59 billion USD and anticipated to reach 2.48 billion USD.
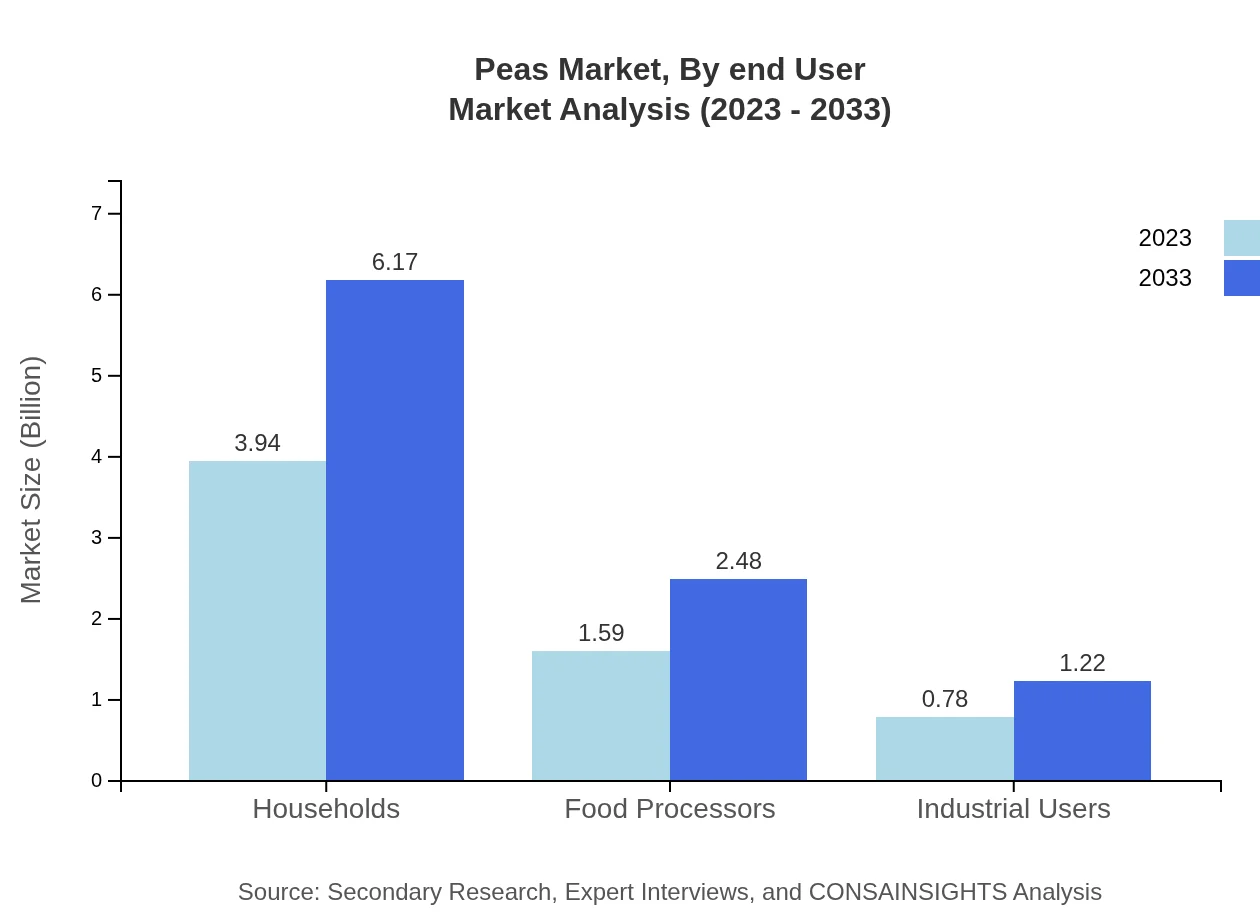
Peas Market Analysis By End User
End-users of peas primarily include households, food processors, and industrial users. Households account for a significant share, expected to maintain robust growth through 2033 alongside food processors, who utilize peas in various processed food products.
Peas Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Peas Industry
Green Giant:
Green Giant is a well-known brand in the frozen food sector, offering a range of frozen peas and vegetables. Their commitment to quality and sustainability has made them a leader in the market.Bonduelle:
Bonduelle is a global leader in the vegetable processing industry, known for its canned and frozen pea products. Their extensive distribution network and focus on health-oriented products drive their market presence.Pioneer Seeds:
Pioneer Seeds specializes in seed development and agronomy to enhance crop yields, including peas. Their innovations have significantly impacted pea cultivation standards.Breyers:
Breyers offers a variety of frozen peas, appealing to health-conscious consumers with a focus on non-GMO and organic products.Horizon Organic:
Horizon Organic is dedicated to providing organic and sustainable food products that cater to health-centric consumers looking for nutritious options.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of peas?
The global peas market is currently valued at approximately $6.3 billion, with a projected CAGR of 4.5% from 2023 to 2033. This growth reflects increasing demand for peas in food products and other applications.
What are the key market players or companies in the peas industry?
The peas market includes several significant players, such as Greenyard, Bonduelle, and Seneca Foods. These companies drive innovation and market penetration with diverse offerings in processing and distribution.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the peas industry?
Key growth factors for the peas industry include rising health consciousness, demand for plant-based proteins, increasing applications in food processing, and expanding consumer bases in emerging markets.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the peas market?
North America and Europe are currently leading regions in the peas market. North America is projected to grow from $2.08 billion in 2023 to $3.26 billion by 2033, showcasing significant expansion opportunities.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the peas industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the peas industry, featuring detailed insights and projections for particular segments and geographies.
What deliverables can I expect from this peas market research project?
Expect comprehensive market analysis reports, trend assessments, segment breakdowns, competitive landscape reviews, and tailored data visualization tools to support strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of peas?
Current trends in the peas market include increased consumer interest in organic and fresh variants, growth in eco-friendly packaging solutions, and the rise of online sales channels, highlighting evolving shopping behaviors.