Photonics Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: photonics
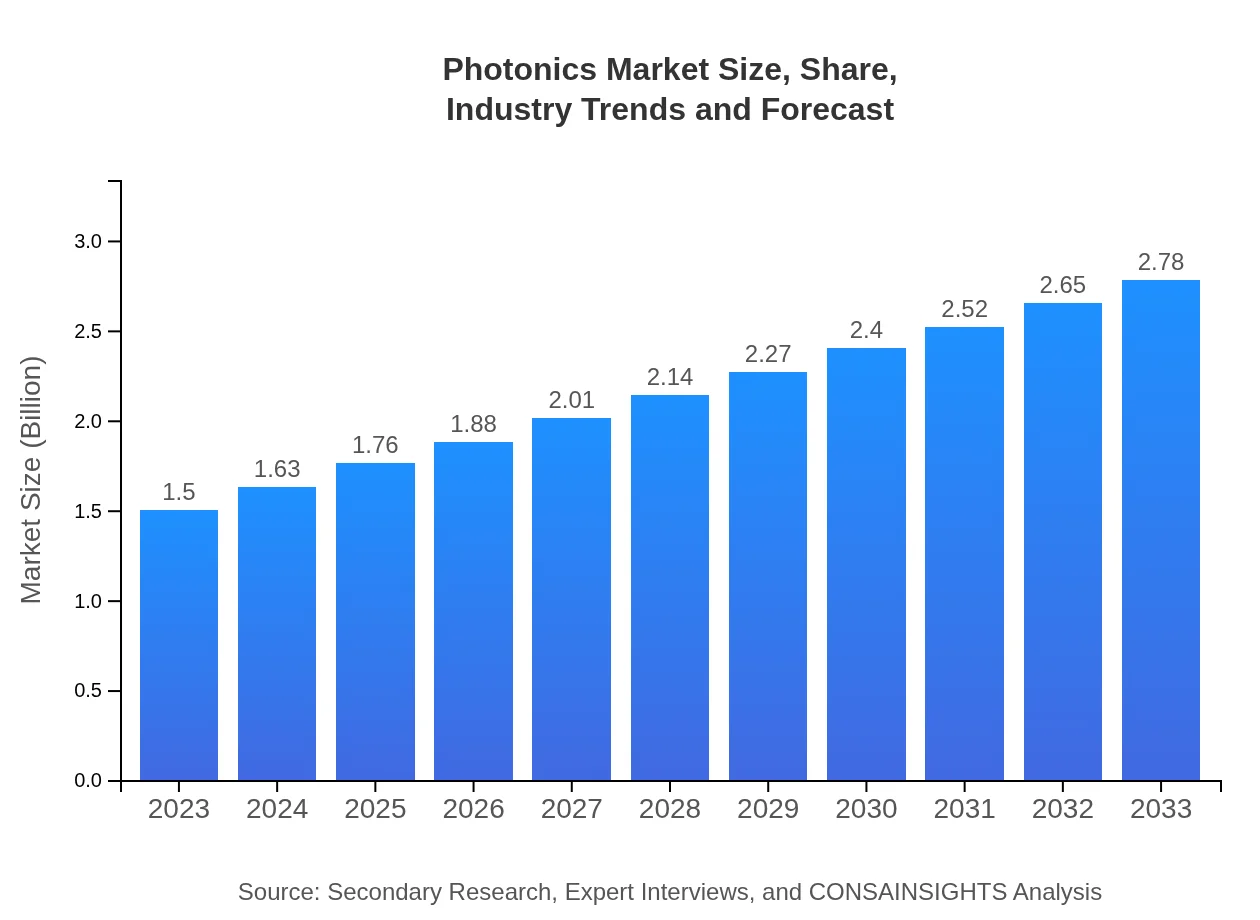
Photonics Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an extensive analysis of the Photonics market, covering insights on market size, trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033, with detailed breakdowns by region and industry applications.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $1.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $2.78 Billion |
| Top Companies | Thorlabs, Inc., Coherent Inc., IPG Photonics Corporation, NKT Photonics |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Photonics Market Overview
Customize Photonics Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Photonics market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Photonics's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Photonics
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Photonics market in 2023 and 2033?
Photonics Industry Analysis
Photonics Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Photonics Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Photonics Market Report:
The European photonics market accounted for $0.46 billion in 2023, anticipated to reach $0.84 billion by 2033. Europe's focus on sustainability and energy-efficient solutions is driving the adoption of photonic devices, supported by robust regulatory frameworks.Asia Pacific Photonics Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region's photonics market was valued at $0.29 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to $0.53 billion by 2033, driven by increasing electronic component manufacturing and telecommunications demands. Countries like China and Japan are at the forefront of integrating photonic technologies into their manufacturing processes and telecommunications infrastructures.North America Photonics Market Report:
North America dominates the photonics market with a market size of $0.50 billion in 2023, expanding to $0.93 billion by 2033. The region's leadership is due to significant investments in research and development, primarily in the U.S., fostering innovations in photonic applications across various sectors.South America Photonics Market Report:
In South America, the photonics market is small but growing, with a market size of $0.10 billion in 2023 expected to rise to $0.18 billion by 2033. Growth is attributed to initiatives aimed at improving communication infrastructures and the increasing adoption of healthcare technologies.Middle East & Africa Photonics Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa photonics market is expected to grow from $0.16 billion in 2023 to $0.29 billion by 2033. The growth is fueled by increasing investments in telecommunications and infrastructure development initiatives in the region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
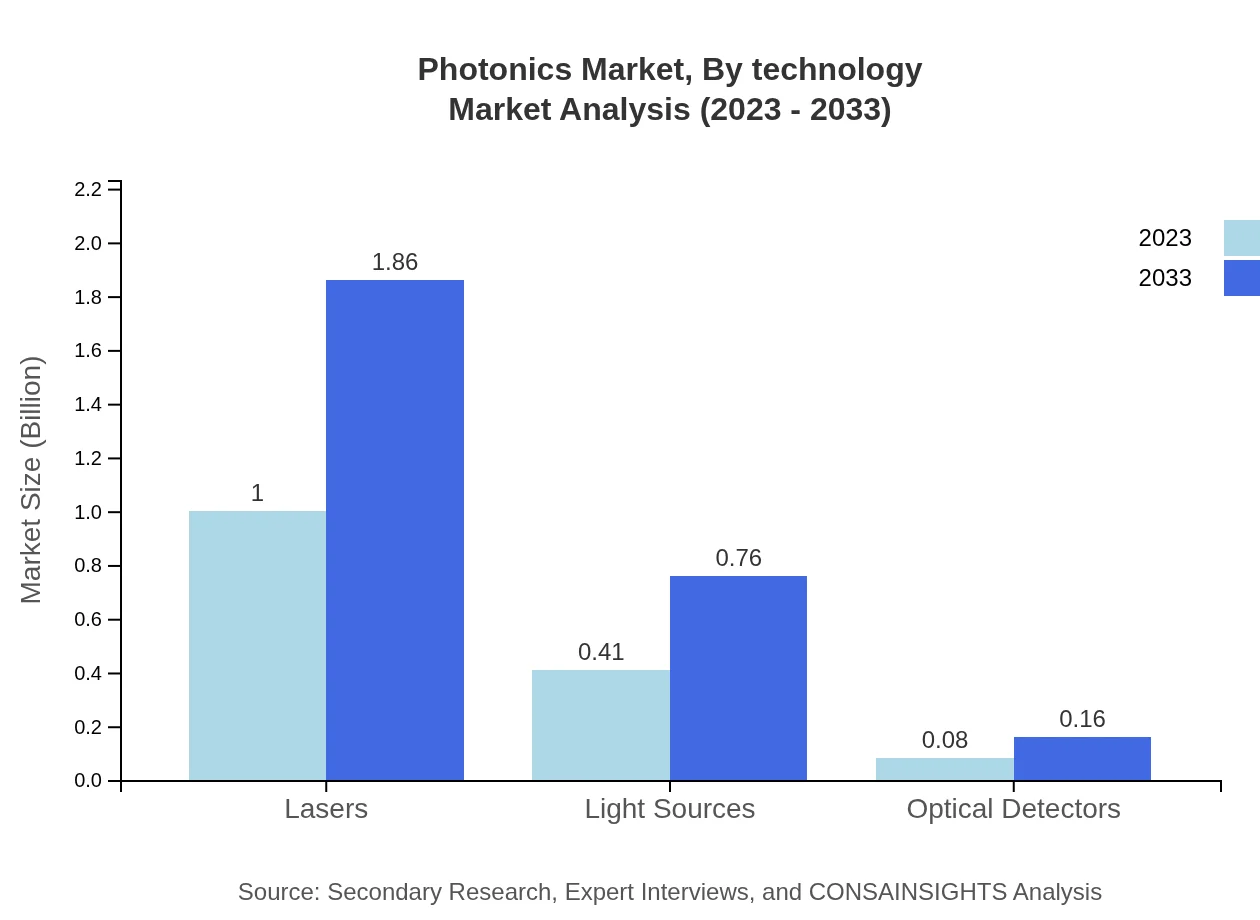
Photonics Market Analysis By Technology
The photonics market by technology features various advanced applications including optical fibers, lasers, and light sources. The optical fibers segment accounts for a commanding share, reaching a market size of $1.00 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $1.86 billion by 2033, due to rising demands for data transmission. Lasers are also a critical technology, with market growth from $1.00 billion to $1.86 billion forecasted in the same timeframe. Emerging technologies, including advances in quantum dots and organic photonic materials, are also contributing to future growth.
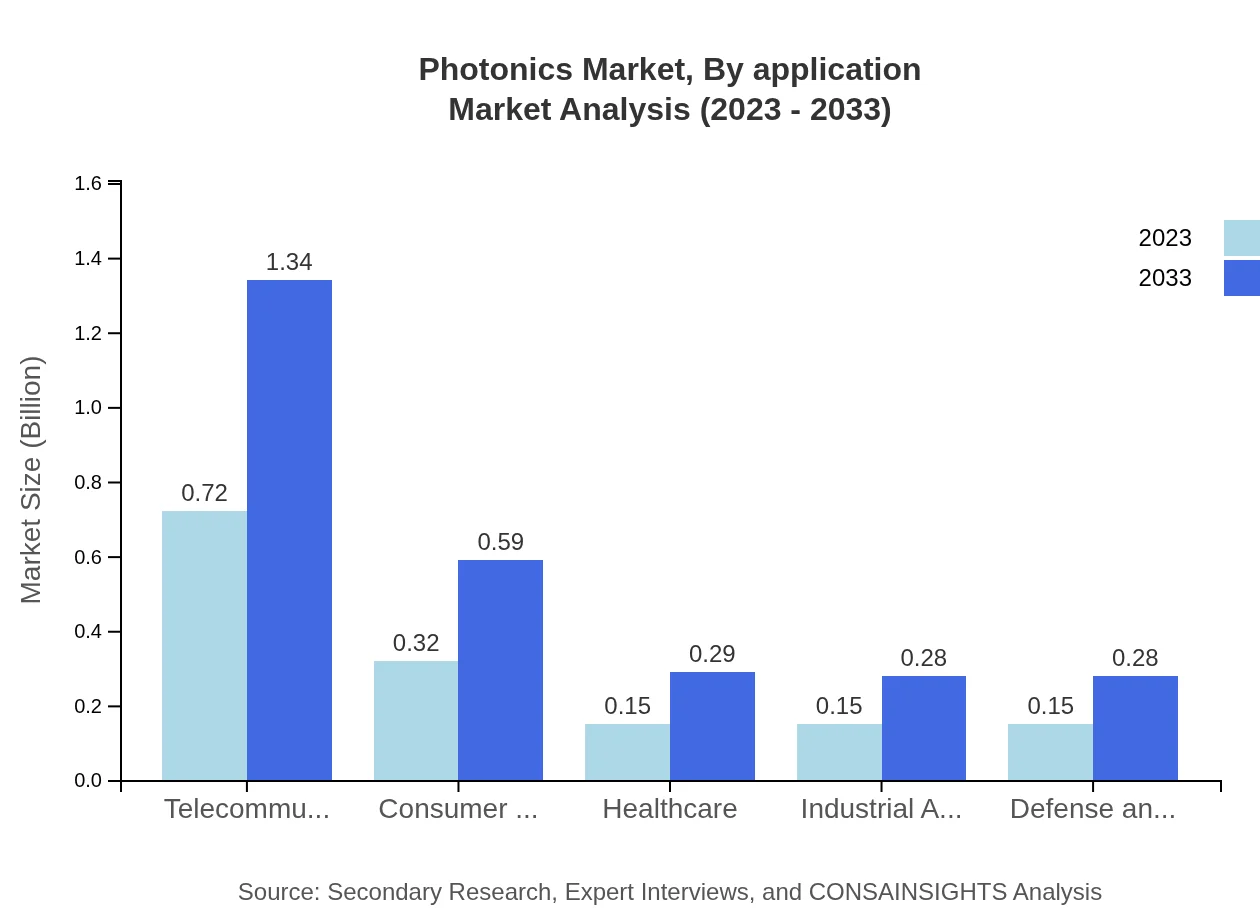
Photonics Market Analysis By Application
In the applications segment, telecommunications dominates with an anticipated market size increase from $0.72 billion in 2023 to $1.34 billion in 2033. Other significant applications include healthcare, growing from $0.31 billion to $0.58 billion, and consumer electronics, expected to rise from $0.32 billion to $0.59 billion. Industrial applications are also on the rise, driven by the integration of smart technologies into production processes.
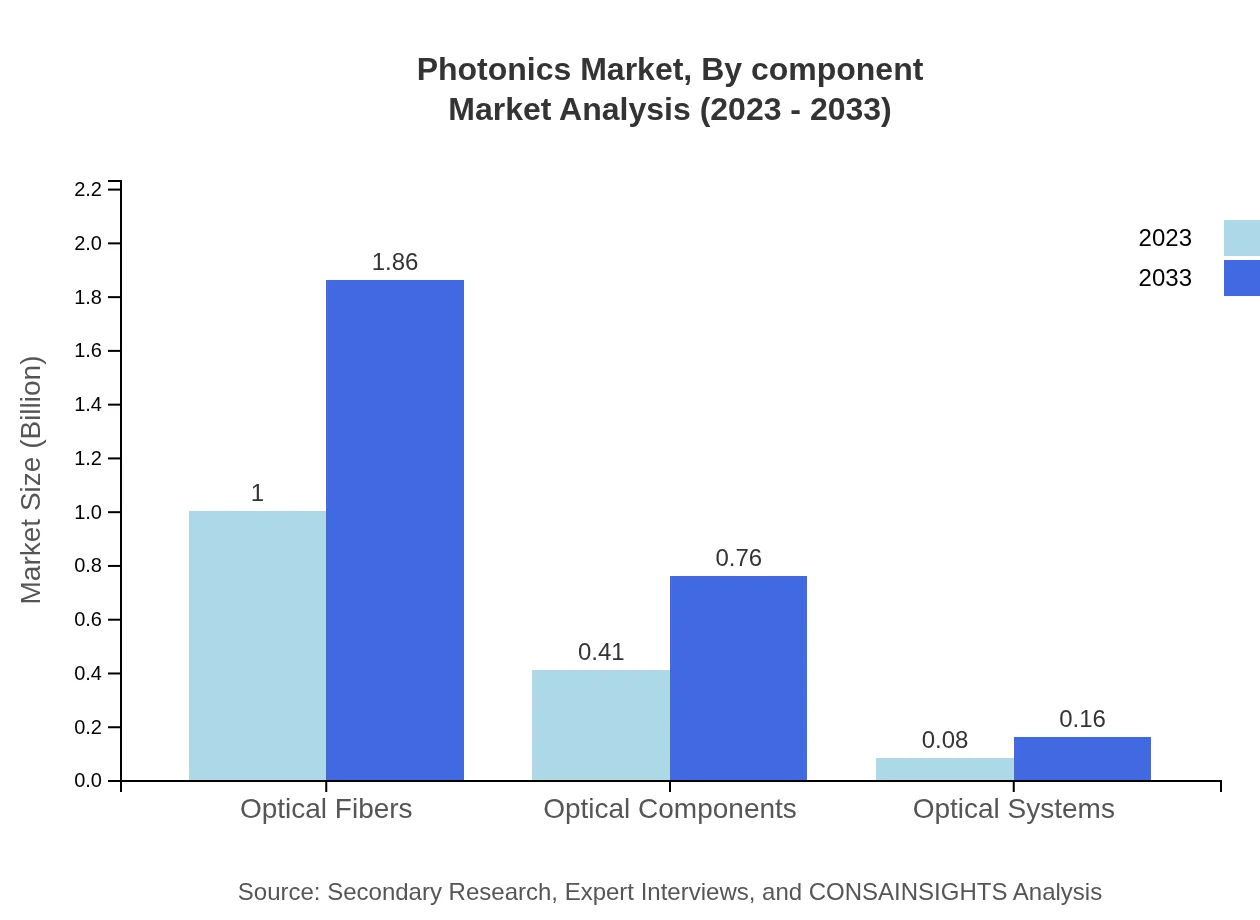
Photonics Market Analysis By Component
Components such as optical fibers and lasers significantly shape the Photonics market dynamics. Optical fibers maintain the largest market share at $1.00 billion in 2023 with growth to $1.86 billion by 2033, while laser systems also showcase a positive growth trend. Optical components and systems are gaining traction, thanks to their use in applications across various sectors.
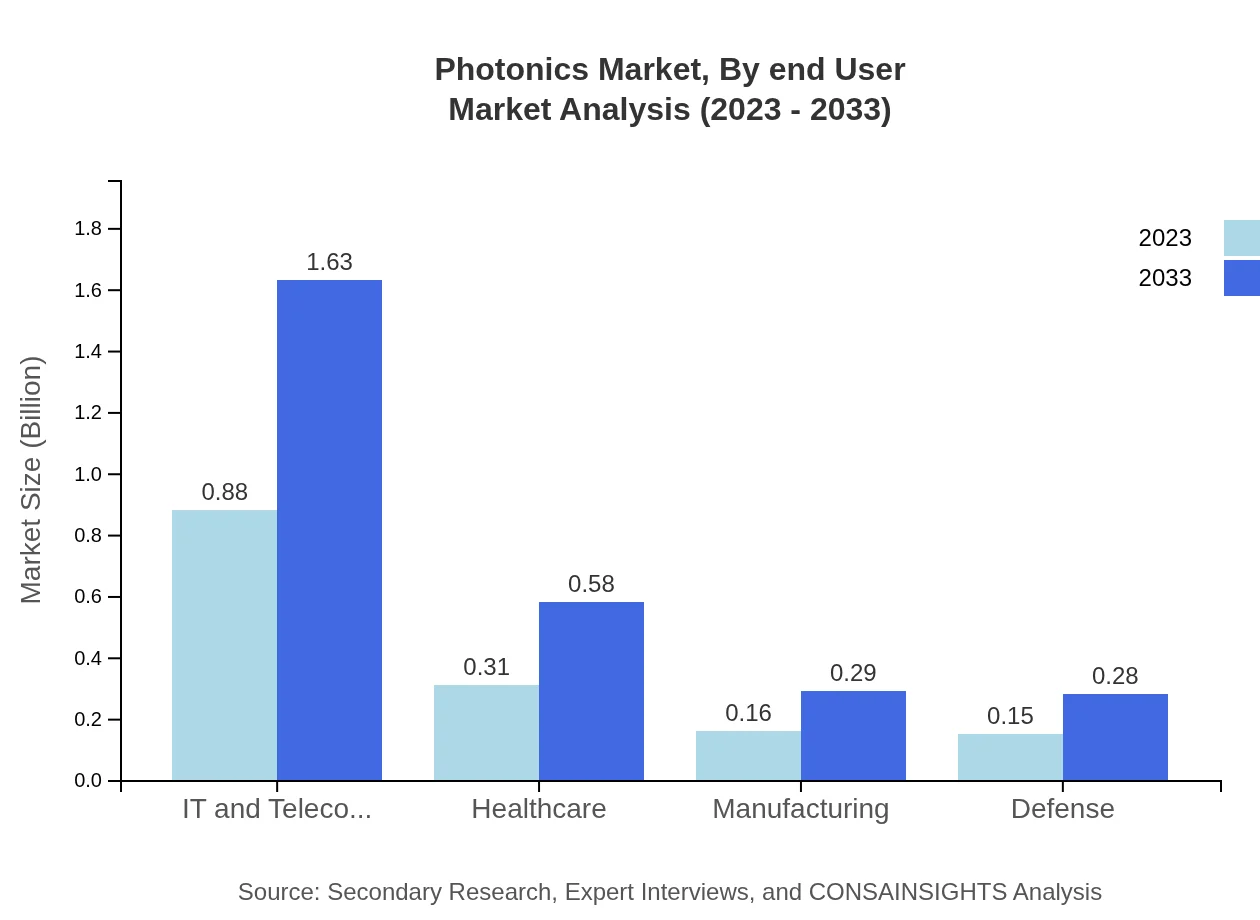
Photonics Market Analysis By End User
The end-user industry for photonics can be segmented into several important categories, including IT and telecommunications, having the highest share at approximately 58.66% in 2023 and expected to remain constant. The healthcare and defense sectors also exhibit substantial growth opportunities, highlighting the technology's utility across diverse domains.
Photonics Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Photonics Industry
Thorlabs, Inc.:
Thorlabs is a leading provider of photonics equipment, offering a wide range of products including lasers, optical components, and systems for various applications in research and industry.Coherent Inc.:
Coherent provides laser-based solutions, including solid-state lasers and laser systems that cater to markets such as materials processing, scientific research, and medical diagnostics.IPG Photonics Corporation:
IPG Photonics is a leader in fiber laser technology, known for its innovative laser solutions that enhance production processes and support medical applications.NKT Photonics:
NKT Photonics develops advanced photonic technologies, specializing in high-performance optical fibers and light sources that cater to industrial, medical, and scientific needs.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of photonics?
The photonics market size is projected to reach $1.5 billion in 2023, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% through 2033. This growth reflects the increasing adoption of photonic technologies across various industries.
What are the key market players or companies in this photonics industry?
Key players in the photonics industry include companies focused on optical components and systems, telecommunications, automotive technologies, and healthcare applications. They significantly influence product innovation and market growth through strategic partnerships and new product developments.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the photonics industry?
Growth in the photonics industry is primarily driven by advancements in optical technologies, increasing demand for telecommunications services, and the rising use of light-based devices in healthcare and manufacturing. Societal shifts towards automation and AI also contribute significantly.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the photonics market?
The fastest-growing region in the photonics market is North America, expected to grow from $0.50 billion in 2023 to $0.93 billion by 2033. Following closely, Europe also shows notable growth, rising from $0.46 billion to $0.84 billion.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the photonics industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports for the photonics industry. These tailored insights focus on specific market segments, technologies, and regional data to meet the unique requirements of clients, ensuring they receive the most relevant information.
What deliverables can I expect from this photonics market research project?
From the photonics market research project, clients can expect comprehensive reports including market size and forecasts, segment analysis, competitive landscape insights, and trends. Additionally, detailed data visualizations and strategic recommendations will be provided.
What are the market trends of photonics?
Current trends in the photonics market include increasing integration of photonic devices in consumer electronics and telecommunications, expansion in healthcare applications, and a surge in research surrounding laser technologies. These trends indicate a robust and evolving market landscape.