Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: photovoltaic-solar-panel
Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Photovoltaic Solar Panel market, offering insights into its current state, future forecasts, technological advancements, and regional dynamics from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
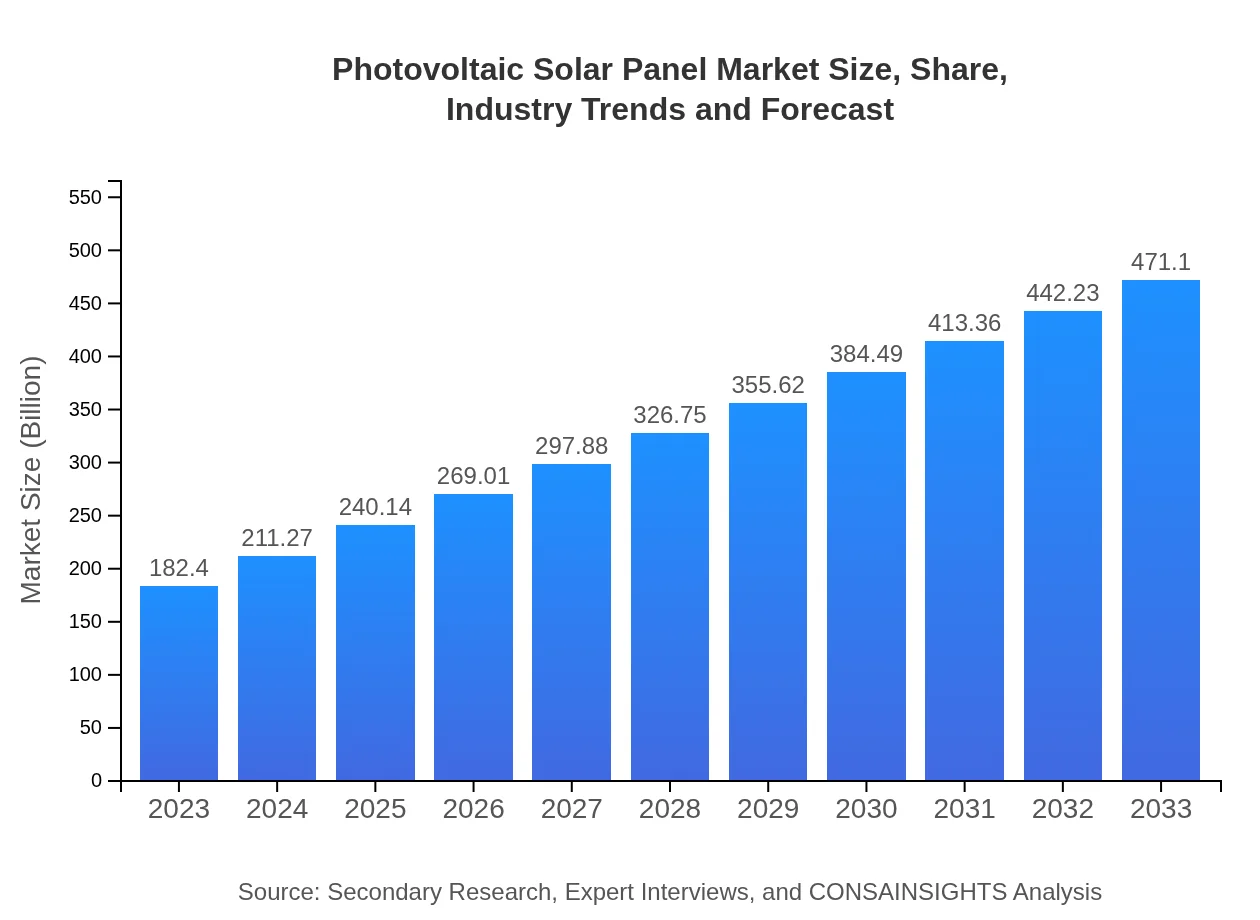
| 2023 Market Size | $182.40 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.6% |
| 2033 Market Size | $471.10 Billion |
| Top Companies | First Solar, Inc., Trina Solar Limited, Canadian Solar Inc., JinkoSolar Holding Co., Ltd., SunPower Corporation |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Overview
Customize Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Photovoltaic Solar Panel market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Photovoltaic Solar Panel's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Photovoltaic Solar Panel
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Photovoltaic Solar Panel market in 2023?
Photovoltaic Solar Panel Industry Analysis
Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Report:
Europe exhibited a market value of $48.92 billion in 2023, expected to skyrocket to $126.35 billion by 2033. The EU’s commitment to sustainability and climate neutrality by 2050 pushes considerable investments in solar technologies.Asia Pacific Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Report:
In Asia Pacific, the market was valued at $39.64 billion in 2023, with projections reaching $102.37 billion by 2033. Rapid industrialization and urbanization, along with government initiatives promoting renewable energy adoption, are driving this growth.North America Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Report:
North America demonstrates a significant market potential, valued at $61.16 billion in 2023 and projected at $157.96 billion by 2033. The U.S. leads in solar energy adoption, supported by favorable policies and energy policies aimed at diversification.South America Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Report:
The South American market is on the rise, with a size of $11.58 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $29.91 billion by 2033. Countries like Brazil and Chile are spearheading solar initiatives, focusing on utility-scale projects to meet energy demands.Middle East & Africa Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market started at $21.10 billion in 2023 and aims for $54.51 billion by 2033. Investment in solar projects is proliferating, driven by the region's vast solar potential and energy demands.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Analysis By Technology
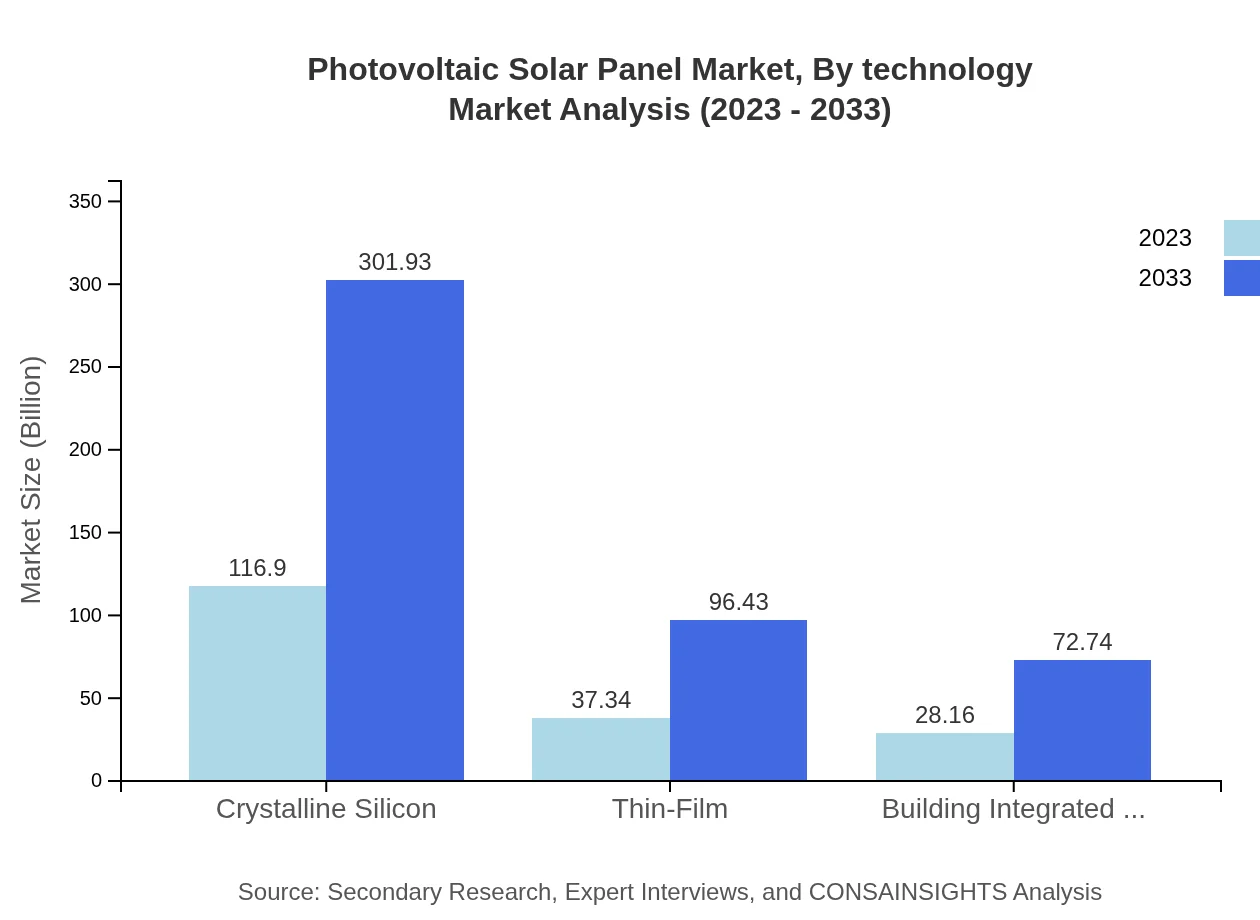
The technology segment encompasses Crystalline Silicon, Thin-Film, and Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV). Crystalline Silicon dominates with a market share of 64.09% in 2023, projected to increase as efficiency improves. Meanwhile, Thin-Film shows rising interest with a market share of 20.47%, particularly in applications demanding flexible solar panel solutions. BIPV, with its unique integration capabilities, constitutes 15.44%, highlighting a shift towards multifunctional solar applications.
Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Analysis By End User
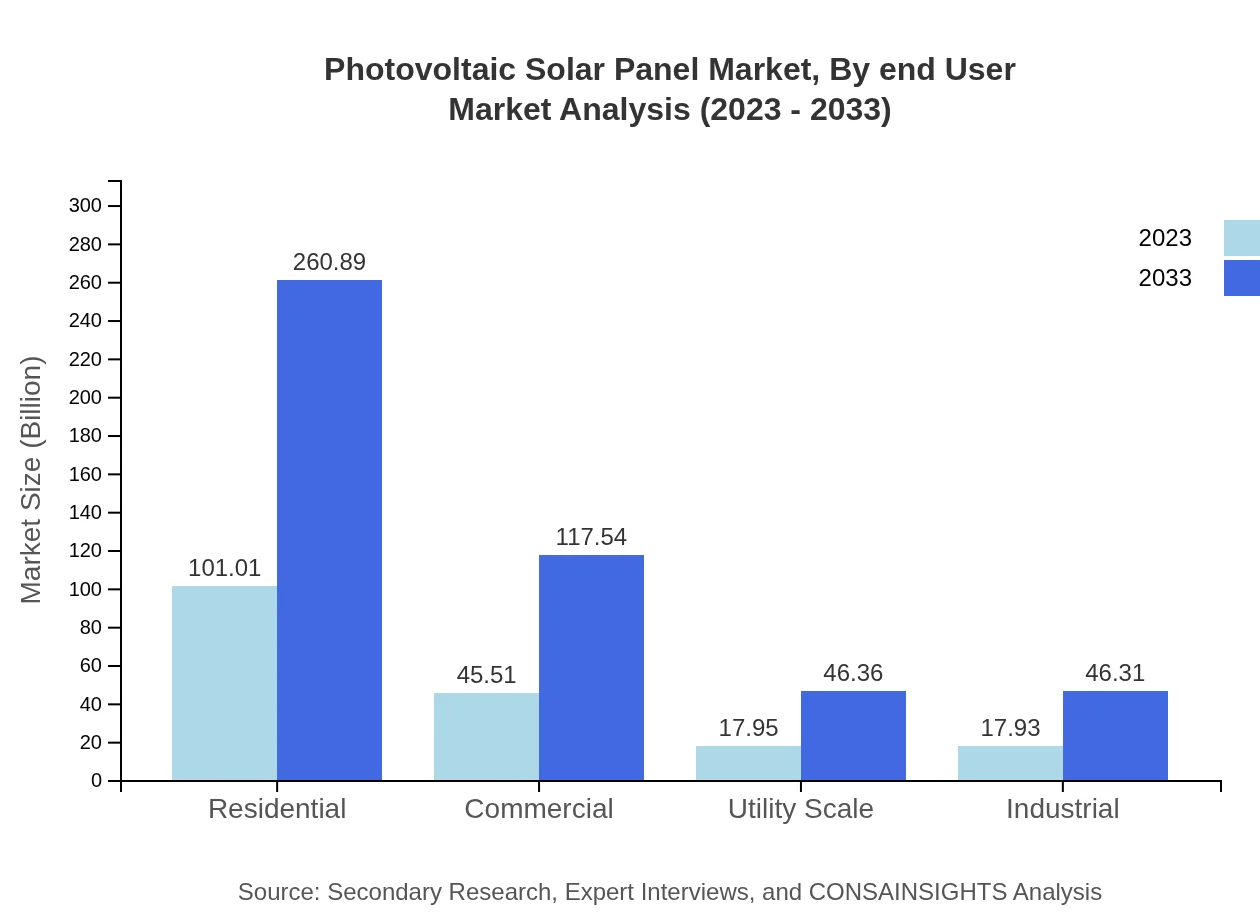
The end-user segments include Residential, Commercial, Industrial, and Utility Scale installations. The Residential sector features significant growth, accounting for a market size of $101.01 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $260.89 billion by 2033. The Commercial sector is anticipated to grow from $45.51 billion to $117.54 billion, while Industrial and Utility Scale segments are progressively gaining traction as more businesses seek sustainable energy solutions.
Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Analysis By Installation Type
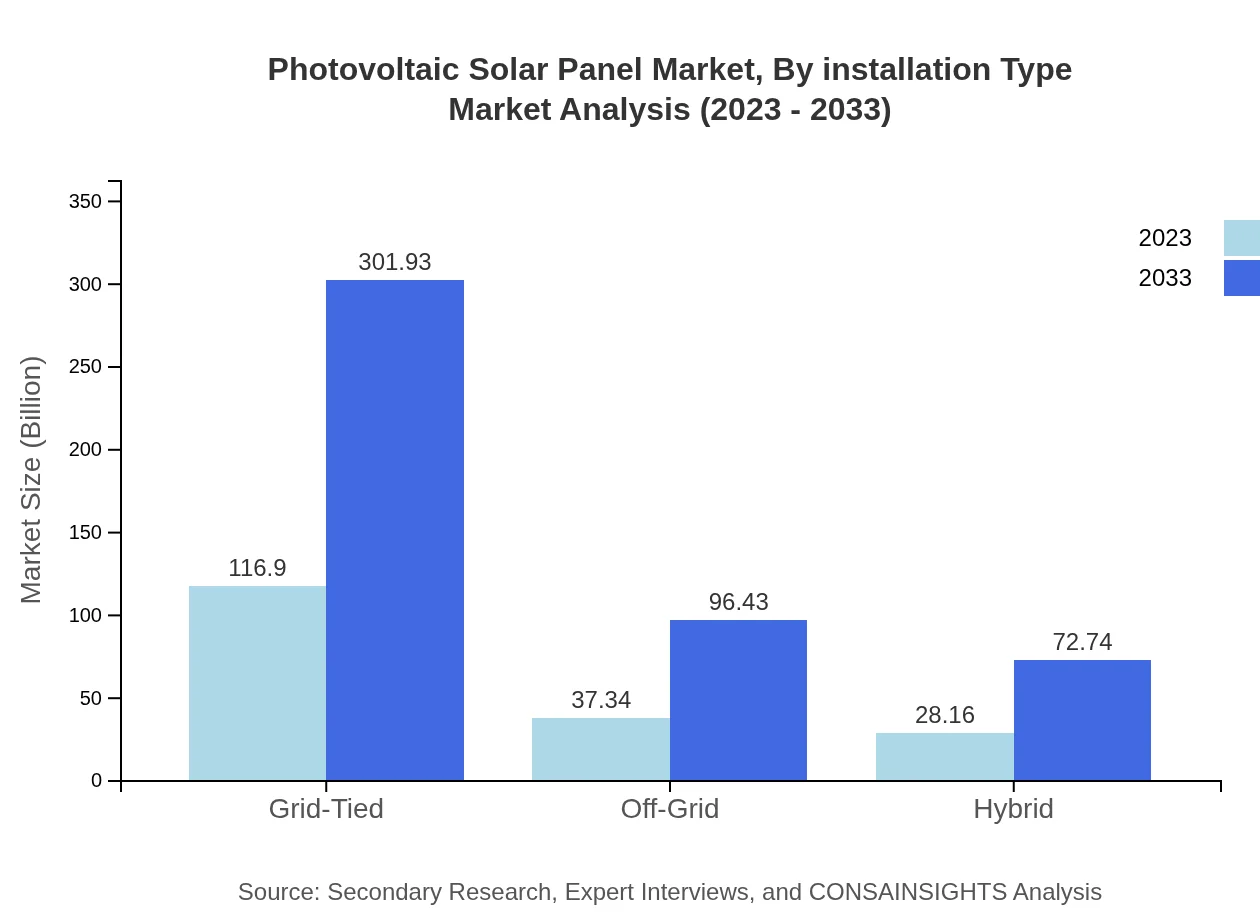
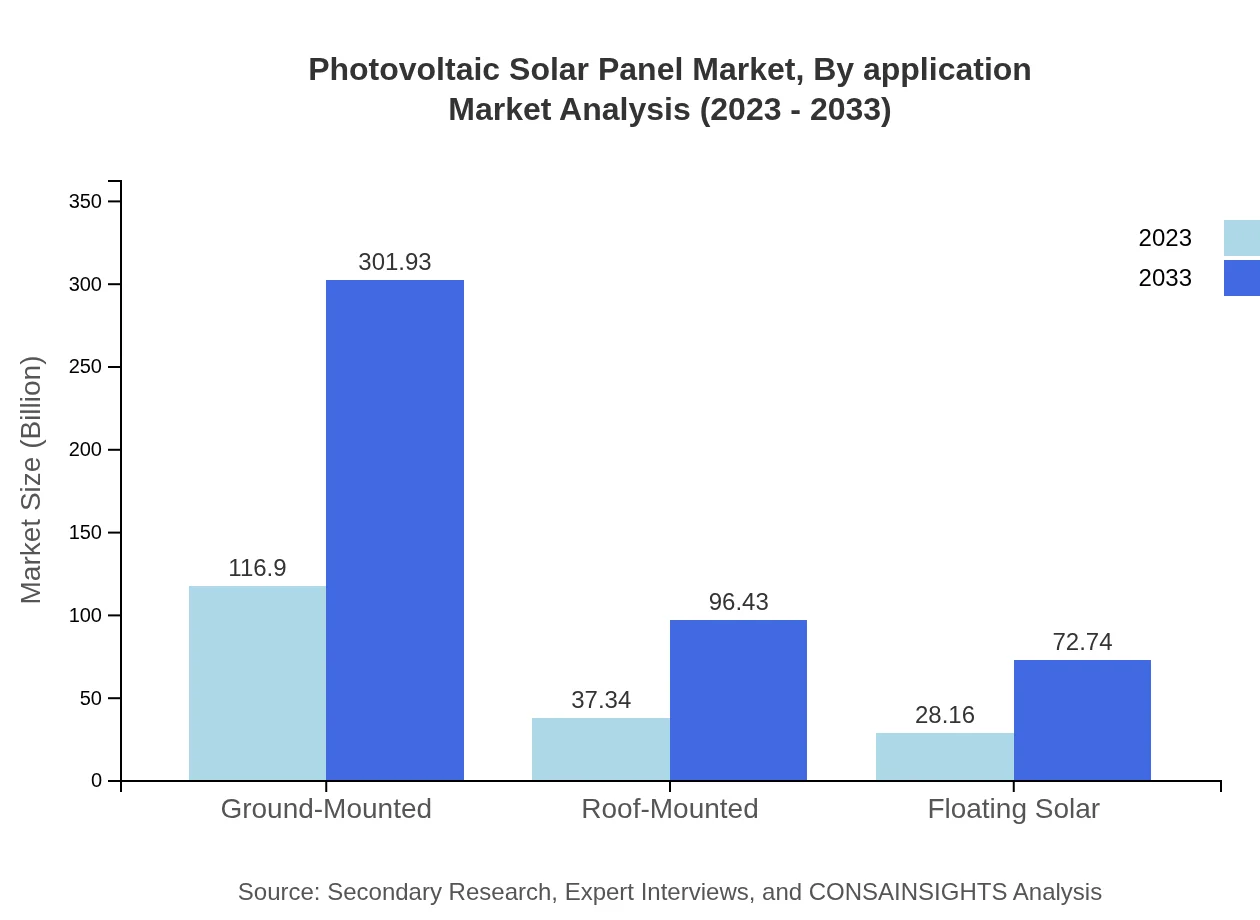
The market is segmented by installation type: Ground-Mounted, Roof-Mounted, and Floating Solar. Ground-Mounted solar panels represent a substantial portion of the market, with a size of $116.90 billion in 2023 and projected growth to $301.93 billion. Roof-Mounted installations, increasingly favored for urban settings, are set to grow from $37.34 billion to $96.43 billion. Floating Solar is an emerging segment, offering solutions for limited land availability.
Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Analysis By Application
Applications for photovoltaic panels span multiple sectors, including residential, commercial, utility, and off-grid systems. The residential application leads with an increasing move towards solar rooftops. The commercial application contributes significantly to market growth, driven by businesses seeking cost-effective, renewable energy solutions. Utility applications will see increased investments as countries continue to build large-scale solar plants.
Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Analysis By Region Global Trends
Global trends shaping the Photovoltaic Solar Panel market include increasing efficiency through technology advancements, a move towards decentralized energy solutions, and heightened environmental regulations demanding reduced carbon footprints. The rise in demand for energy storage solutions, alongside integration with smart grids, enhances the utility of solar energy, presenting further growth opportunities for market stakeholders.
Photovoltaic Solar Panel Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Photovoltaic Solar Panel Industry
First Solar, Inc.:
A leader in photovoltaic (PV) solar energy solutions, First Solar specializes in utility-scale solar power plants and is recognized for its innovative thin-film technology.Trina Solar Limited:
Trina Solar is one of the largest manufacturers of solar PV modules globally, dedicated to solar energy solutions and sustainable energy innovations.Canadian Solar Inc.:
Canadian Solar is a leading global provider of solar modules and a manufacturer of solar PV solutions, focusing on innovation and sustainability.JinkoSolar Holding Co., Ltd.:
JinkoSolar is another top-tier supplier known for its high-efficiency modules and extensive presence in the global solar market.SunPower Corporation:
SunPower designs and manufactures high-efficiency solar technologies, emphasizing quality and performance in the residential and commercial markets.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of photovoltaic Solar Panel?
The global photovoltaic solar panel market is valued at approximately $182.4 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 9.6%, forecasted to reach significant growth by 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the photovoltaic Solar Panel industry?
Key players in the photovoltaic solar panel industry include First Solar, JinkoSolar, Trina Solar, Canadian Solar, and SunPower, among others, driving innovation and market growth.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the photovoltaic Solar Panel industry?
Growth drivers include increasing demand for renewable energy, government incentives and policies promoting solar adoption, technological advancements improving panel efficiency, and rising environmental concerns.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the photovoltaic Solar Panel?
The Asia Pacific region is expected to see rapid expansion, with market growth from $39.64 billion in 2023 to $102.37 billion by 2033, fueled by increased investments and government support.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the photovoltaic Solar Panel industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the photovoltaic-solar-panel industry, tailored to specific needs and business objectives to help clients make informed decisions.
What deliverables can I expect from this photovoltaic Solar Panel market research project?
Expect comprehensive market analysis reports, segment insights, competitive landscape assessments, regional data, and growth forecasts to support strategic planning and investment decisions.
What are the market trends of photovoltaic Solar Panel?
Current trends include rising adoption of BIPV solutions, advancements in thin-film technology, increased demand for off-grid systems, and the integration of energy storage solutions with solar technologies.