Pigeon Peas Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: pigeon-peas
Pigeon Peas Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Pigeon Peas market, detailing insights regarding market size, trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It encompasses industry analysis, segmentation, and region-specific insights, along with technological advancements and key market players.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
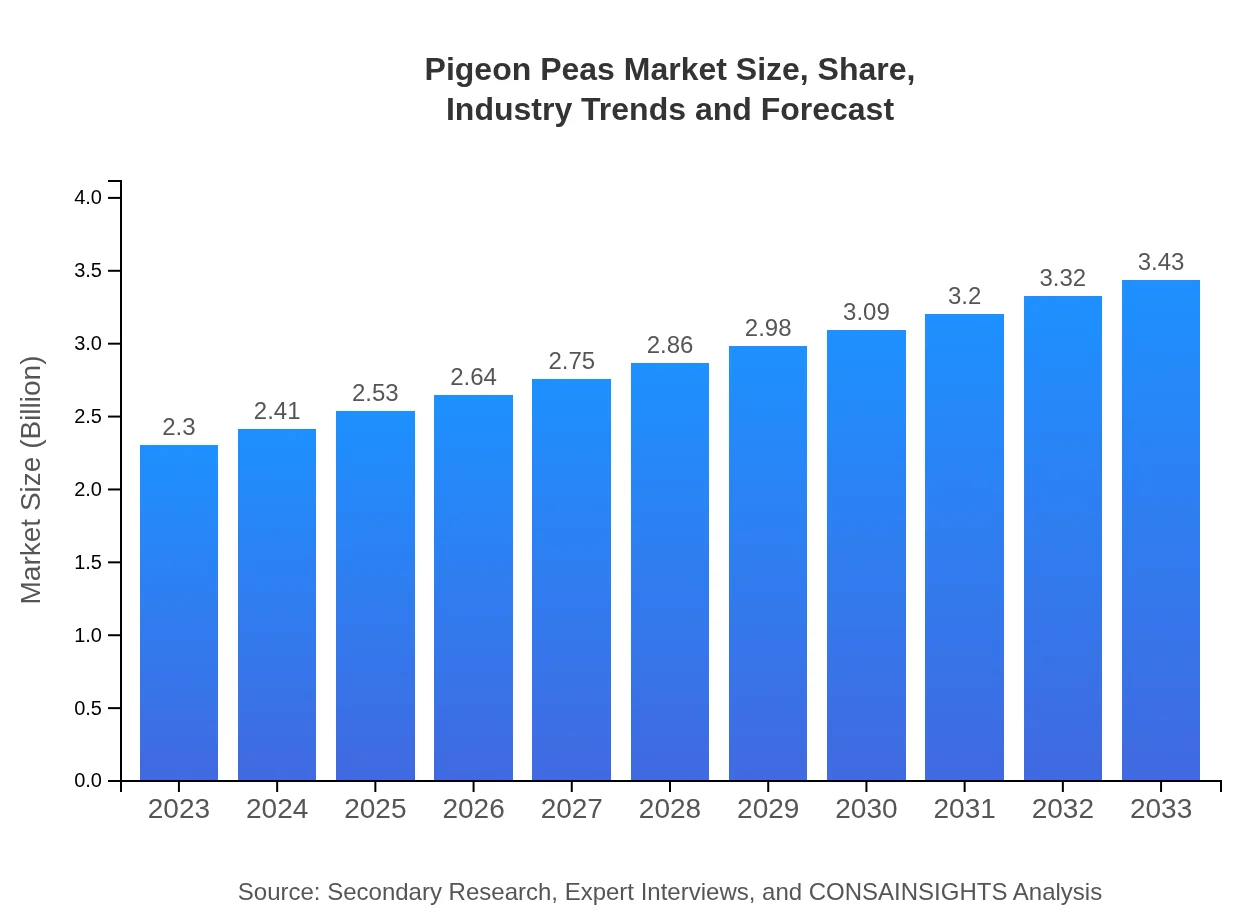
| 2023 Market Size | $2.30 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.0% |
| 2033 Market Size | $3.43 Billion |
| Top Companies | Agro Products and Agencies, Lamb Weston, Trinity Foods |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Pigeon Peas Market Overview
Customize Pigeon Peas Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Pigeon Peas market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Pigeon Peas's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Pigeon Peas
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Pigeon Peas market in 2023?
Pigeon Peas Industry Analysis
Pigeon Peas Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Pigeon Peas Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Pigeon Peas Market Report:
The European market for Pigeon Peas stood at $0.79 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to expand to $1.18 billion by 2033, benefiting from rising adoption of vegan diets and sustainable sourcing practices.Asia Pacific Pigeon Peas Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Pigeon Peas market is valued at $0.41 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $0.61 billion by 2033. India is the largest producer and consumer, highlighting increased local consumption driven by dietary changes.North America Pigeon Peas Market Report:
In North America, the Pigeon Peas market is currently valued at $0.76 billion and is expected to rise to $1.13 billion by 2033. The growing interest in plant-based diets and veganism is enhancing their market appeal.South America Pigeon Peas Market Report:
South America presents a growing niche for Pigeon Peas, with a market size of $0.02 billion in 2023 expected to reach $0.03 billion by 2033. The focus on sustainable agriculture promotes interest in Pigeon Peas as an alternative crop.Middle East & Africa Pigeon Peas Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market for Pigeon Peas is $0.32 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $0.48 billion by 2033. The region's potential growth is augmented by increasing import activities and local cultivation efforts.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
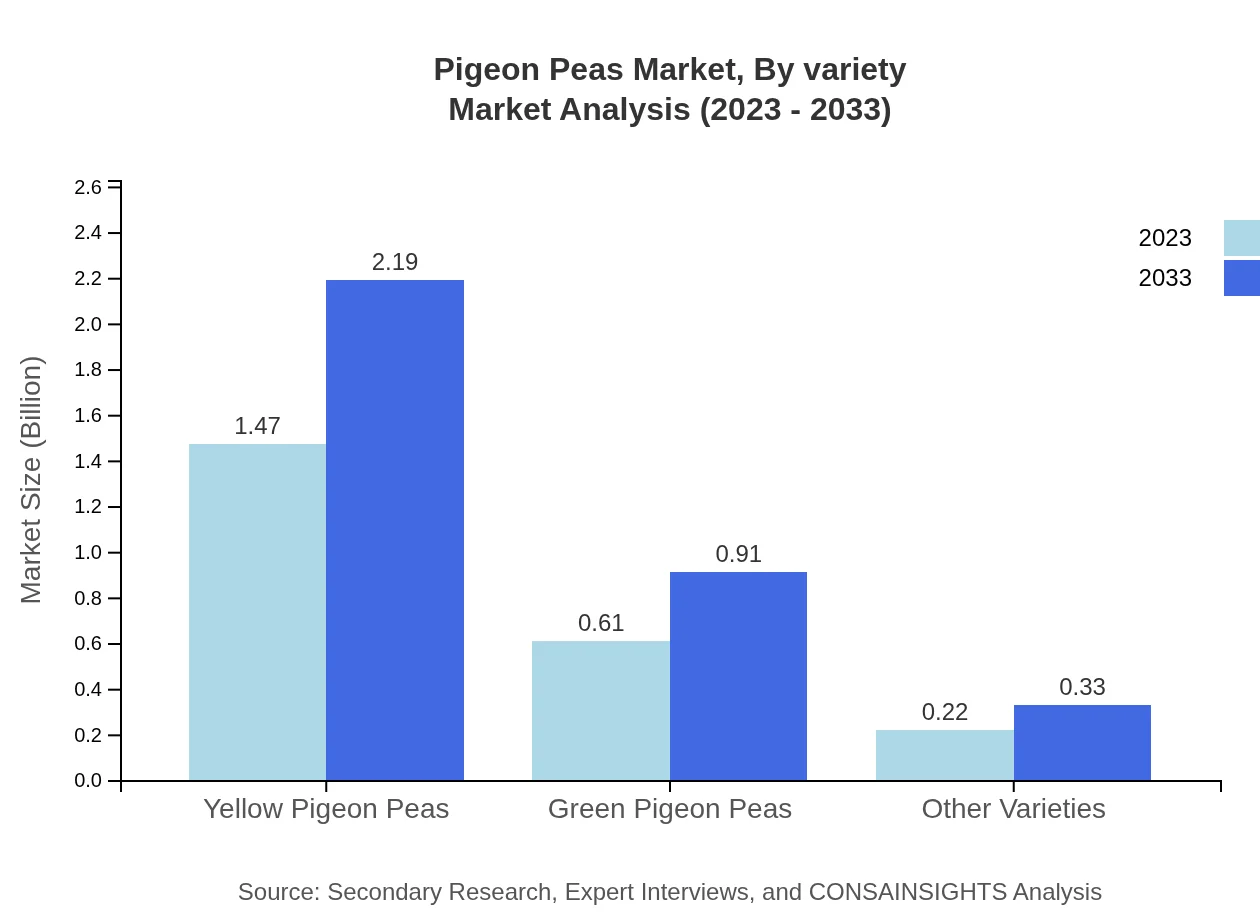
Pigeon Peas Market Analysis By Variety
By variety, the Pigeon Peas market comprises Yellow Pigeon Peas, Green Pigeon Peas, and Other Varieties. Yellow Pigeon Peas dominate with a market size of $1.47 billion in 2023, increasing to $2.19 billion by 2033, holding a share of 63.82%. Green Pigeon Peas follow with $0.61 billion and are expected to reach $0.91 billion, maintaining a 26.53% market share. Other varieties contribute less but are growing as preferences diversify.
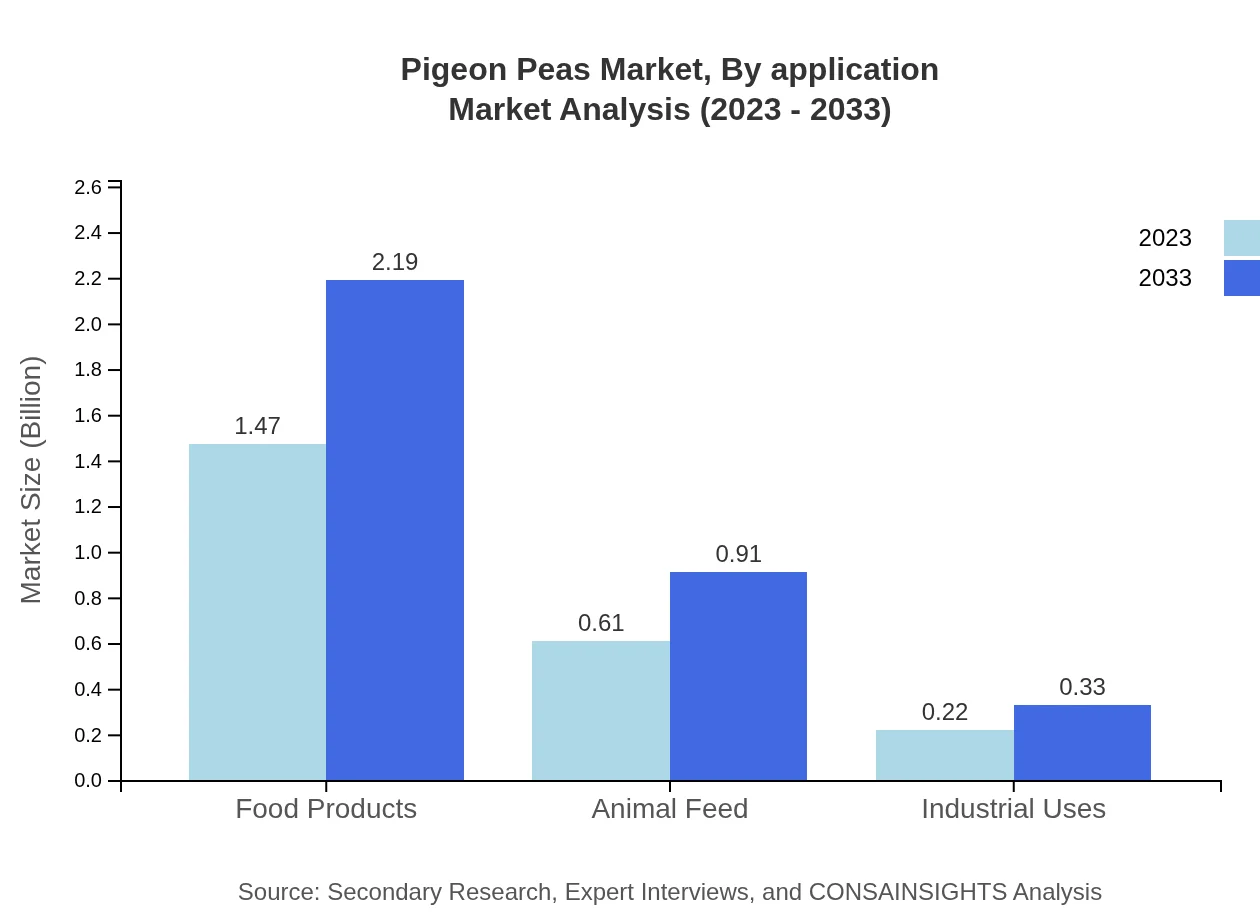
Pigeon Peas Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, Food Products lead the market, representing $1.47 billion in 2023 and expected to grow to $2.19 billion with a 63.82% share. Animal Feed captures $0.61 billion (26.53% share), while Industrial Uses contribute smaller yet notable figures ($0.22 billion in 2023, projecting to $0.33 billion by 2033).
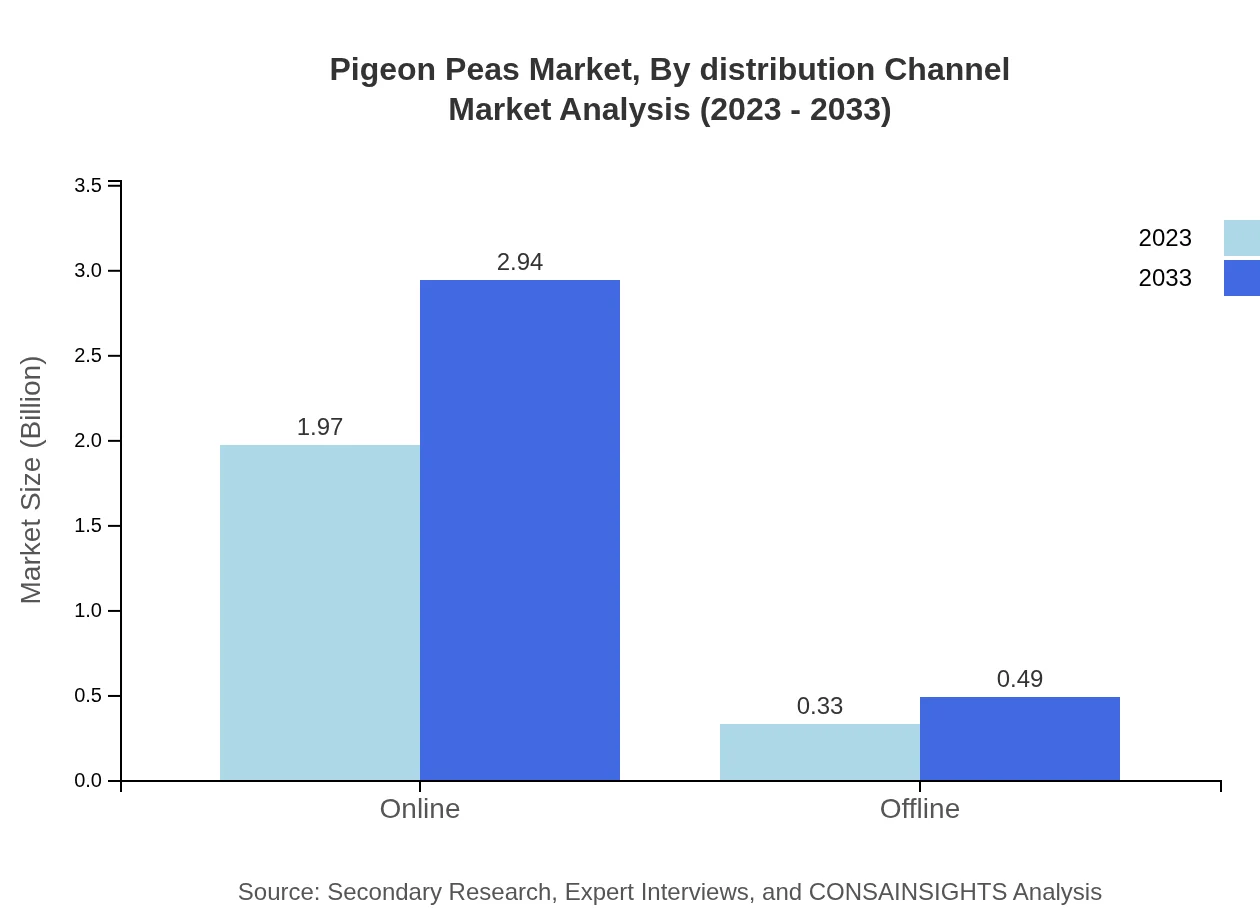
Pigeon Peas Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Distribution channels are segmented into Online and Offline markets. The Online market, valued at $1.97 billion, is projected to grow to $2.94 billion (85.78% share) by 2033, reflecting significant digital purchasing trends. Offline channels are comparatively smaller, with $0.33 billion now, expected to grow to $0.49 billion (14.22% share) during the forecast period.
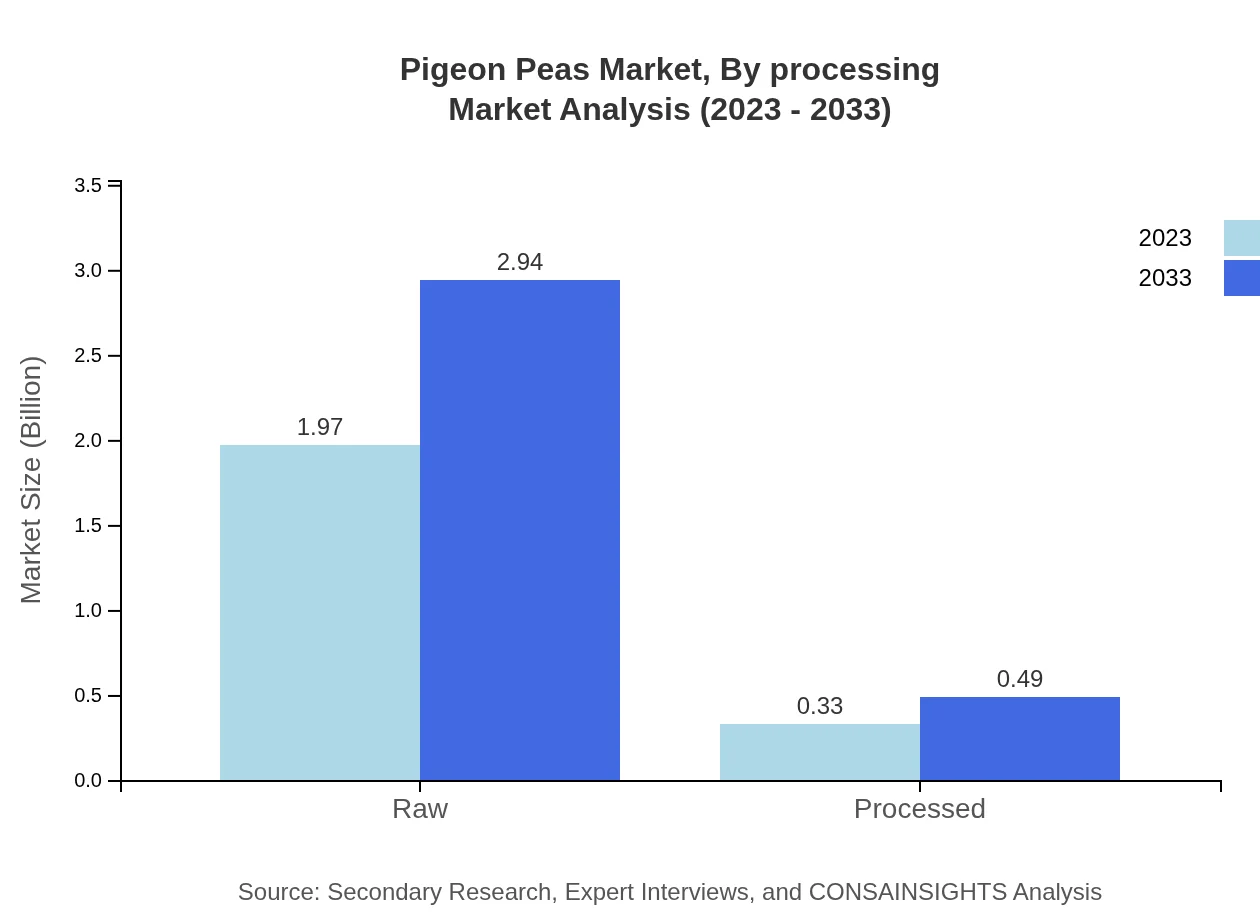
Pigeon Peas Market Analysis By Processing
Regarding processing, Raw Pigeon Peas dominate the market with $1.97 billion currently and a projection of $2.94 billion by 2033, holding an 85.78% share. Processed types, while smaller, are on a growth trajectory from $0.33 billion in 2023 to $0.49 billion (14.22% share).
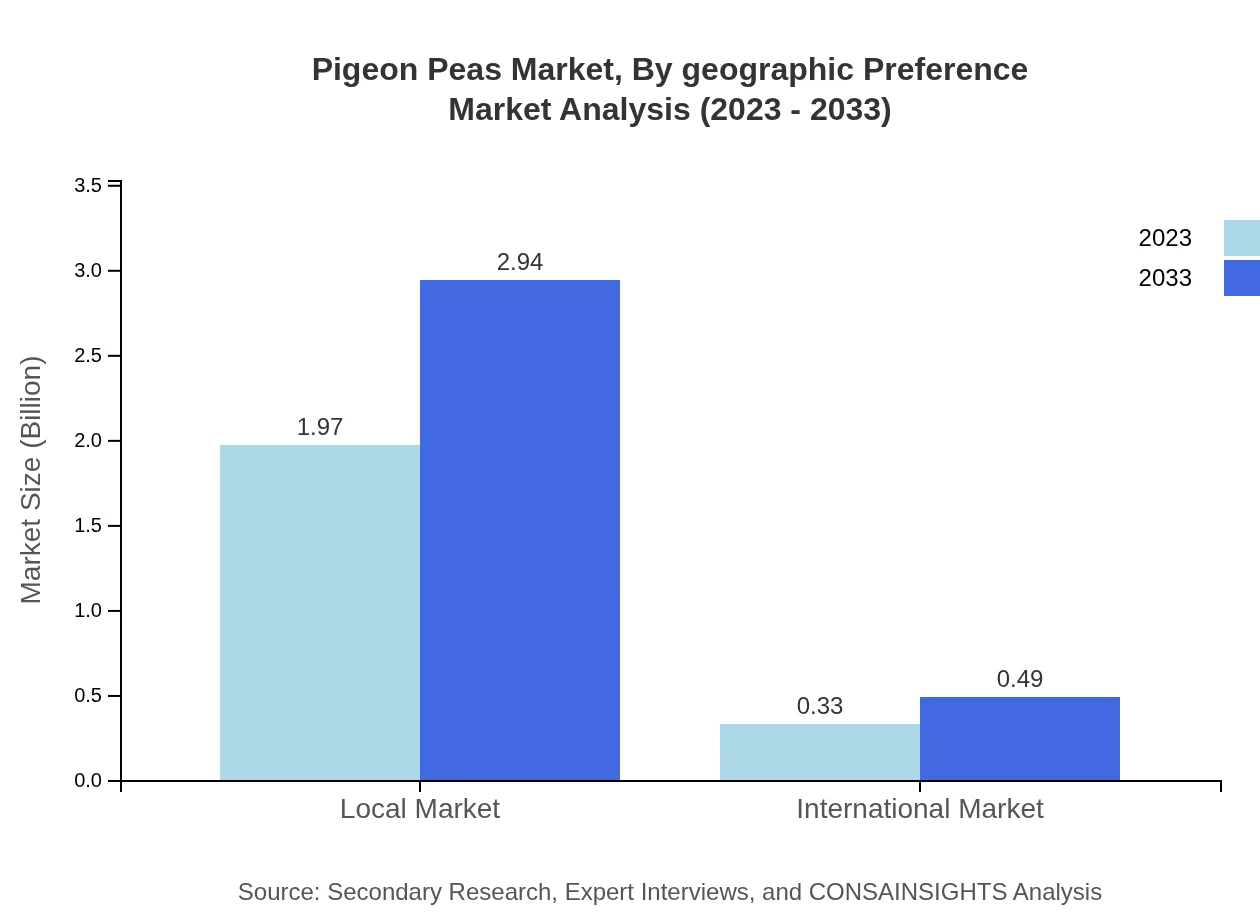
Pigeon Peas Market Analysis By Geographic Preference
By geographic preference, the Local Market emphasizes locally sourced Pigeon Peas, valued at $1.97 billion and expected to rise to $2.94 billion (85.78% share). In contrast, the International Market, valued at $0.33 billion, is anticipated to grow to $0.49 billion (14.22% share), reflecting increasing global trade.
Pigeon Peas Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Pigeon Peas Industry
Agro Products and Agencies:
A leading supplier known for high-quality legumes, including Pigeon Peas, with a strong position in the Asian market.Lamb Weston:
An established player focused on innovative food processing techniques, helping to enhance the appeal of Pigeon Peas in the processed food sectors.Trinity Foods:
Specializes in organic pulses and legumes, making significant strides in promoting sustainability in cultivation and processing.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of pigeon Peas?
The global pigeon peas market size is projected to reach $2.3 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.0%. This growth reflects increased demand for this nutritious legume.
What are the key market players or companies in the pigeon Peas industry?
Key players include major agricultural firms and processors specializing in pulses and legumes, such as ADM, Olam International, and T.H. Seeds. These companies dominate production, processing, and distribution channels.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the pigeon peas industry?
Growth drivers include rising health consciousness leading to increased vegetarian and vegan diets, enhanced agricultural practices increasing yield, and expanding markets in Asia and Africa, contributing to steady demand.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the pigeon peas market?
The fastest-growing region is North America, expected to grow from $0.76 billion in 2023 to $1.13 billion by 2033 due to increased consumption and demand for plant-based proteins.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the pigeon peas industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market research reports tailored to specific requirements in the pigeon peas industry, allowing clients to access detailed insights based on unique market needs.
What deliverables can I expect from this pigeon peas market research project?
Deliverables include an in-depth market analysis report, segmented data insights, trend analysis, competitor landscape overview, and actionable recommendations for strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of pigeon peas?
Market trends show a significant shift towards organic pigeon peas, enhanced agricultural technology adoption for better yields, and increasing interest in sustainable sourcing, reflecting consumer preferences.