Plant Based Protein Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: plant-based-protein
Plant Based Protein Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report examines the Plant-Based Protein market from 2023 to 2033, offering insights into market dynamics, size, growth rates, key players, and regional performance, providing a comprehensive overview for stakeholders and investors.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
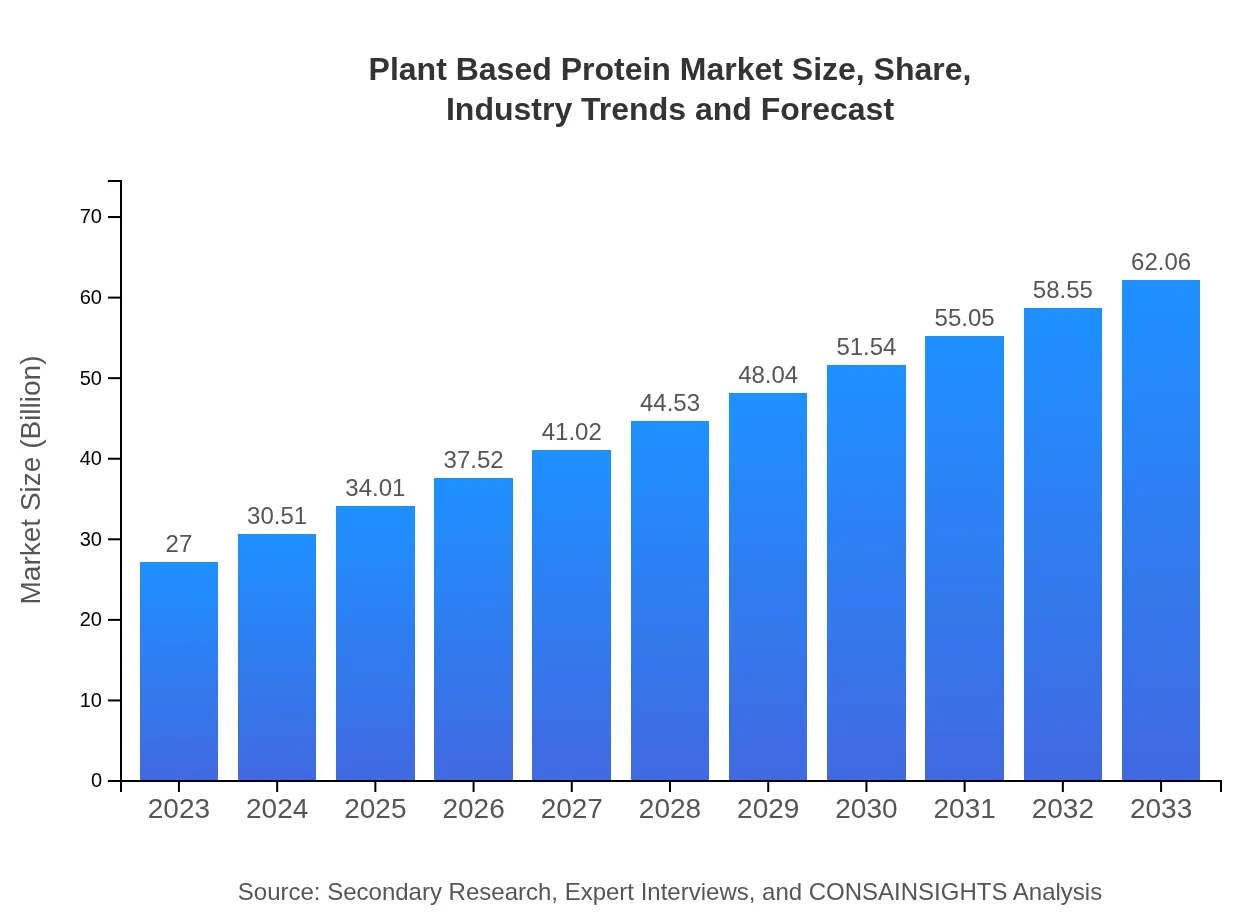
| 2023 Market Size | $27.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 8.4% |
| 2033 Market Size | $62.06 Billion |
| Top Companies | Beyond Meat, Impossible Foods, Nestlé, Oatly, Quorn Foods |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Plant Based Protein Market Overview
Customize Plant Based Protein Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Plant Based Protein market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Plant Based Protein's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Plant Based Protein
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Plant-Based Protein market in 2023 and 2033?
Plant Based Protein Industry Analysis
Plant Based Protein Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Plant Based Protein Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Plant Based Protein Market Report:
The European Plant-Based Protein market stands at 8.37 billion USD in 2023, with projections of reaching 19.24 billion USD by 2033. Europe is witnessing a significant trend towards veganism and flexitarian diets, supported by government regulations promoting sustainable food production.Asia Pacific Plant Based Protein Market Report:
In 2023, the Plant-Based Protein market in the Asia Pacific region was valued at approximately 5.09 billion USD and is expected to reach 11.70 billion USD by 2033, demonstrating a substantial CAGR. Urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and changing dietary habits are driving growth in this region, alongside growing awareness about health and sustainability.North America Plant Based Protein Market Report:
North America is a leading market for Plant-Based Protein, valued at approximately 9.62 billion USD in 2023 and expected to reach 22.12 billion USD by 2033. Strong demand in food and beverage applications combined with a growing base of health-conscious consumers drives this region's robust growth.South America Plant Based Protein Market Report:
The South American Plant-Based Protein market is relatively nascent, estimated at 0.29 billion USD in 2023 and projected to grow to 0.67 billion USD by 2033. The growth is attributed to increasing health consciousness and an inclination towards vegetarianism, albeit at a slower pace compared to other regions.Middle East & Africa Plant Based Protein Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's Plant-Based Protein market, valued at 3.63 billion USD in 2023, is projected to grow to 8.33 billion USD by 2033. Factors influencing this growth include population growth, urbanization, and a shifting dietary pattern among younger consumers.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
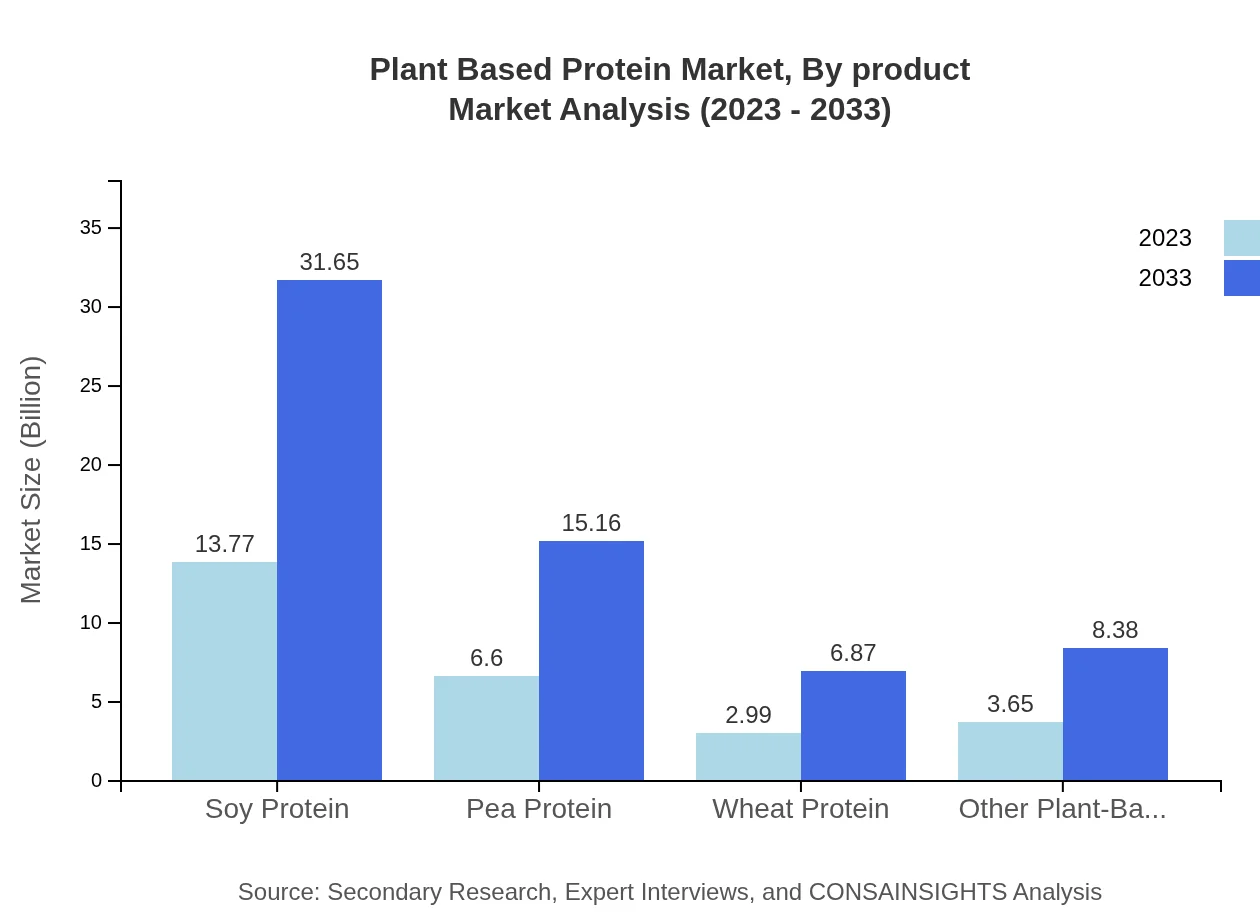
Plant Based Protein Market Analysis By Product
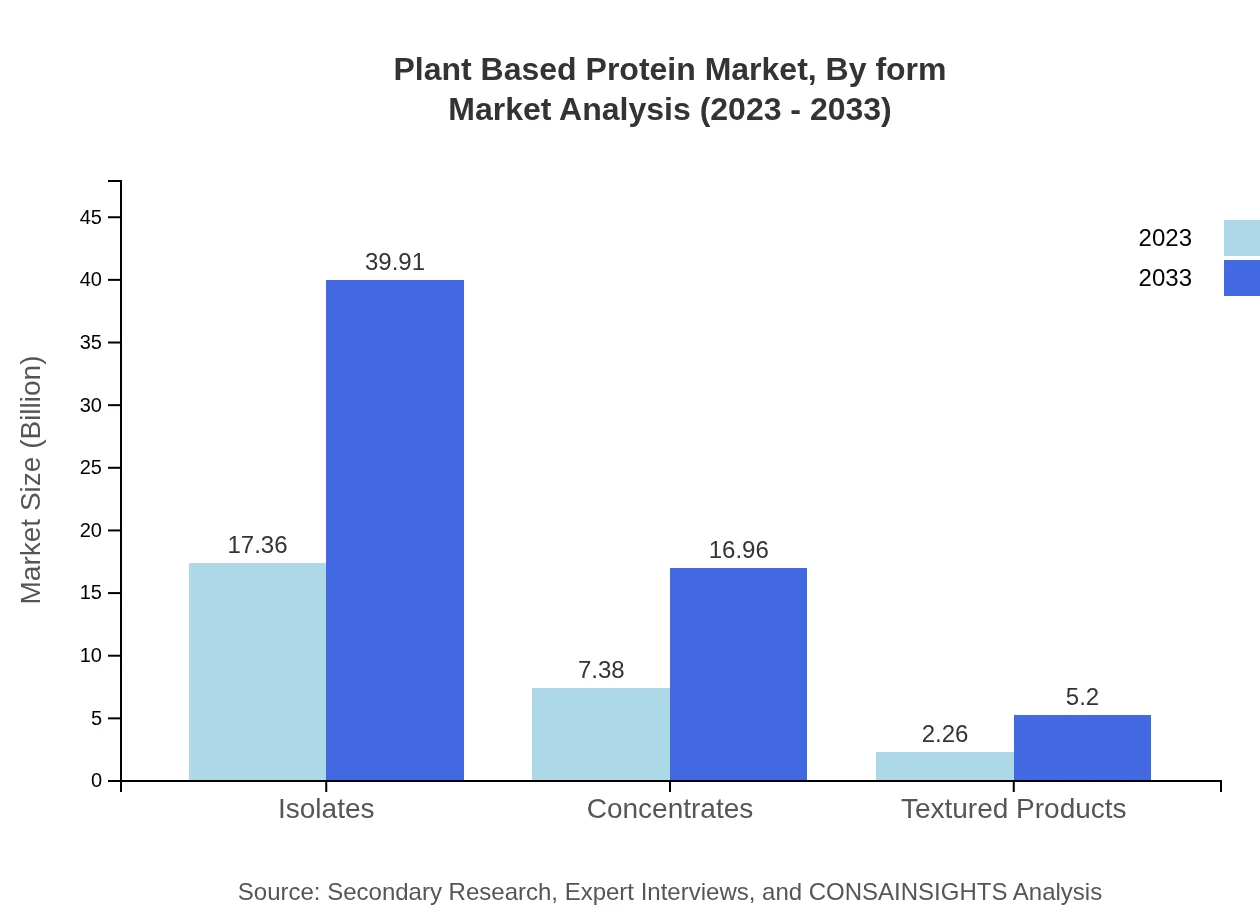
Isolates dominate the market with a valuation of 17.36 billion USD in 2023, expected to reach 39.91 billion USD by 2033, accounting for 64.3% of the market share. Concentrates follow as a significant segment valued at 7.38 billion USD in 2023, projected to rise to 16.96 billion USD. Textured products, legumes, grains, seeds, and various other plant-based proteins collectively broaden the market appeal.
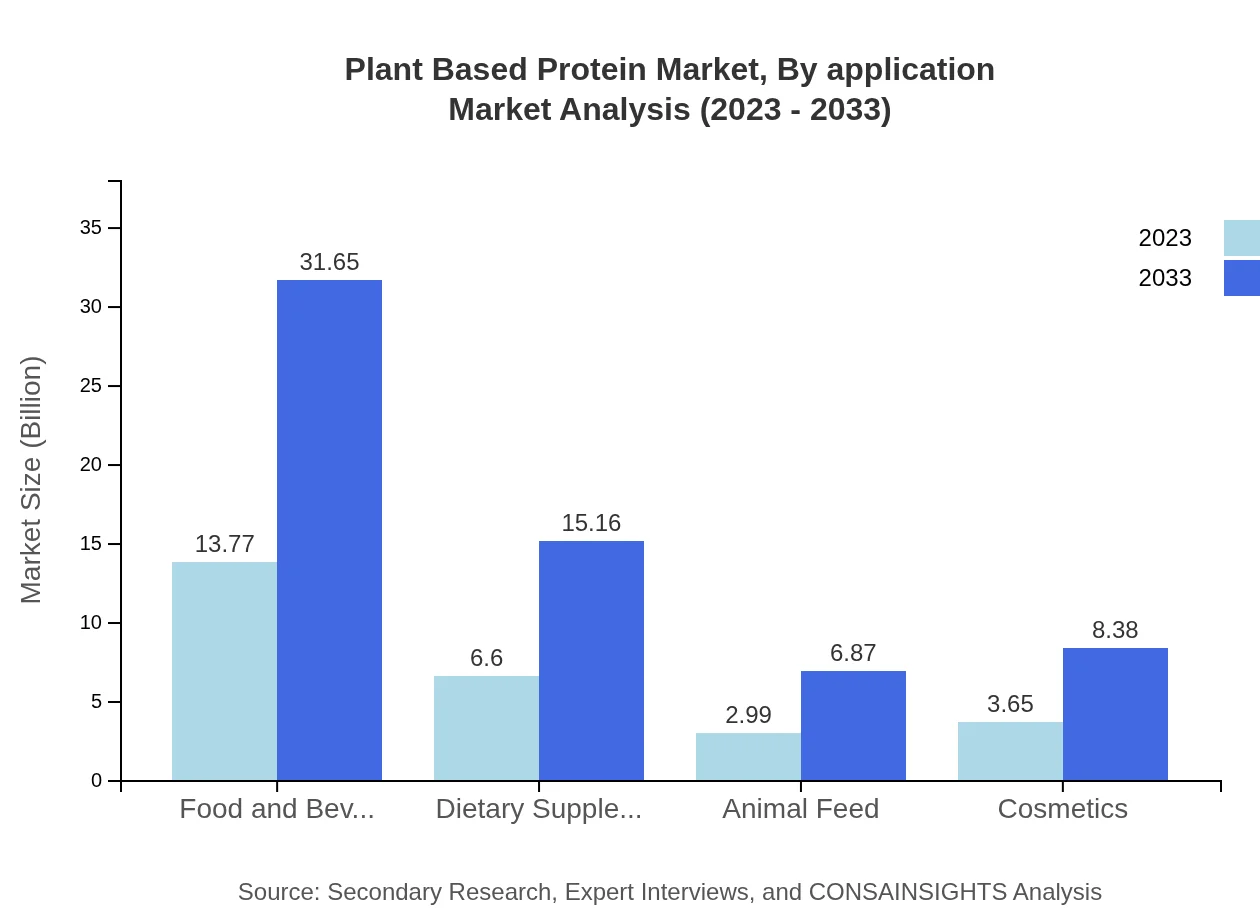
Plant Based Protein Market Analysis By Application
Food and beverages account for a considerable share of the market, estimated at 13.77 billion USD in 2023 and expected to reach 31.65 billion USD by 2033. Dietary supplements are also a crucial segment, valued at 6.60 billion USD in 2023, projected to grow to 15.16 billion USD in 2033, reflecting the growing health trends.
Plant Based Protein Market Analysis By Form
The market can also be segmented based on form, including powders, bars, and ready-to-eat forms, with powders being the most versatile and widely used form in smoothies and baking. Each form meets diverse consumer preferences and facilitates ingredient incorporation across various food products.
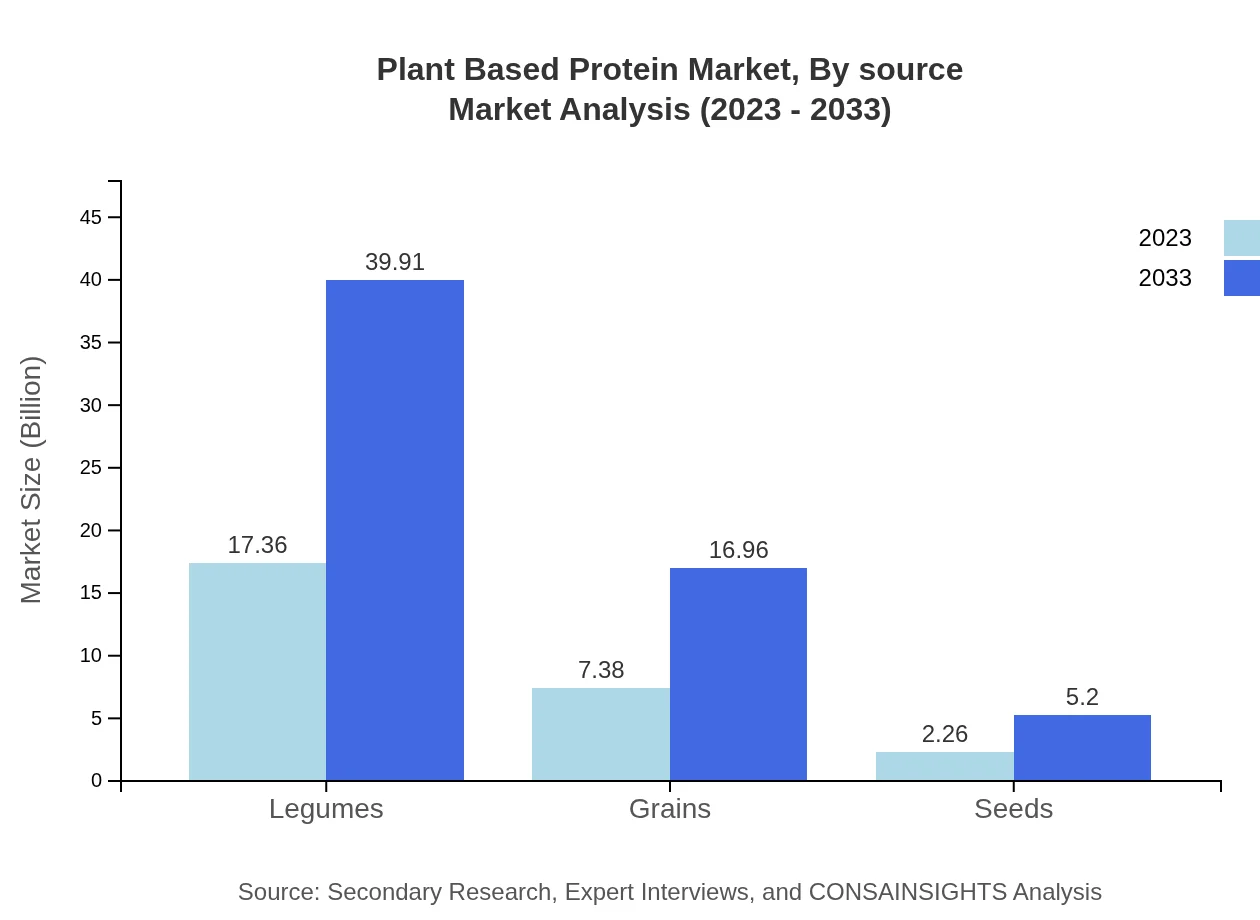
Plant Based Protein Market Analysis By Source
Soy protein remains a leader in the market with 13.77 billion USD in 2023, followed by pea protein at 6.60 billion USD and other sources like wheat, legumes, and seeds. The nutritional properties and functionality of these proteins contribute to their growing adoption in various industries.
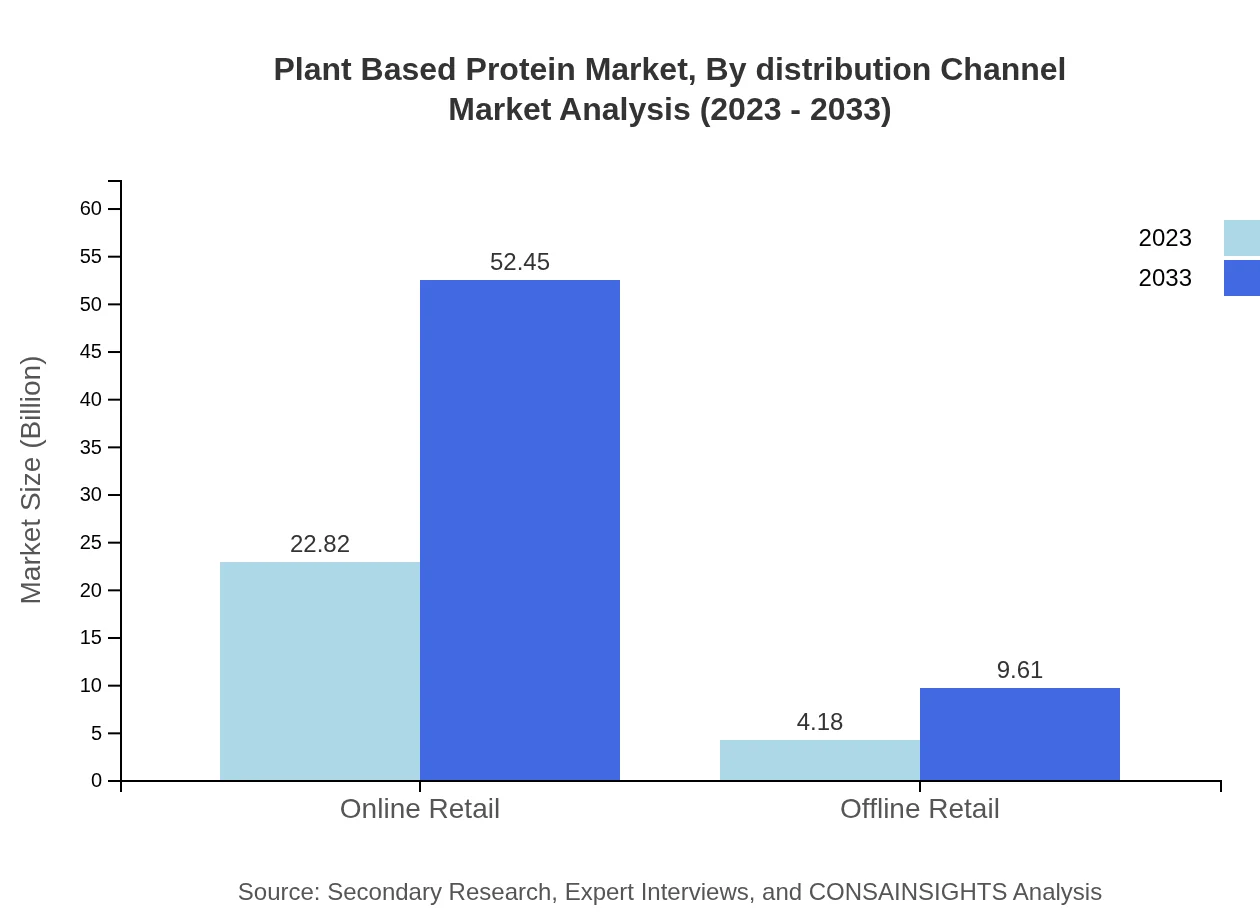
Plant Based Protein Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The distribution channels for Plant-Based Protein include online and offline retail. Online retail accounts for a substantial share, valued at 22.82 billion USD in 2023, highlighting changing consumer shopping habits influenced by convenience and accessibility.
Plant Based Protein Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Plant Based Protein Industry
Beyond Meat:
A leading player specializing in plant-based meat substitutes, Beyond Meat offers innovative products that cater to a diverse consumer base seeking healthier and sustainable meat alternatives.Impossible Foods:
Known for its technology-driven approach, Impossible Foods focuses on creating plant-based products that replicate the taste and texture of meat, gaining significant market traction.Nestlé:
Nestlé has made substantial investments in plant-based proteins and offers various products under its brands, promoting sustainability in food production.Oatly:
A leader in oat-based products, Oatly is known for its innovative dairy alternatives, which have become widely accepted in the plant-based segment.Quorn Foods:
Quorn is recognized for its meat alternatives made from mycoprotein, focusing on sustainability and nutrition to appeal to health-conscious consumers.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of plant Based Protein?
The global market size of plant-based protein is projected to reach approximately $27 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.4%. This growth indicates strong consumer interest in alternatives to animal protein sources.
What are the key market players or companies in the plant Based Protein industry?
Key players in the plant-based protein market include major companies like Beyond Meat, impossible Foods, and Pea Protein Co. These businesses drive innovation and product development in the sector, contributing to market growth.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the plant Based Protein industry?
The growth of the plant-based protein industry is driven by increased health consciousness, rising demand for sustainable food sources, and changing consumer preferences towards plant-based diets, which are viewed as healthier alternatives.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the plant Based Protein?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the plant-based protein market, with market size projected to increase from $9.62 billion in 2023 to $22.12 billion by 2033, reflecting a growing trend towards plant-based diets.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the plant Based Protein industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to client needs within the plant-based protein industry, providing insights into trends, market size, and forecasts specific to various segments and regions.
What deliverables can I expect from this plant Based Protein market research project?
Clients can expect detailed deliverables, including comprehensive market analysis reports, data visualizations, trend forecasts, competitor analysis, and actionable insights tailored to their strategic needs within the plant-based protein sector.
What are the market trends of plant Based Protein?
Current market trends in plant-based protein include a strong shift towards health-focused products, innovative food formulations, growing online retail avenues, and increased adoption in culinary applications driven by environmental sustainability.