Plant Genomics Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: plant-genomics
Plant Genomics Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Plant Genomics market from 2023 to 2033, encompassing market size, growth rates, and industry trends. Insights on segmentation, regional dynamics, and key players are included, aiming to support stakeholders in making informed decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
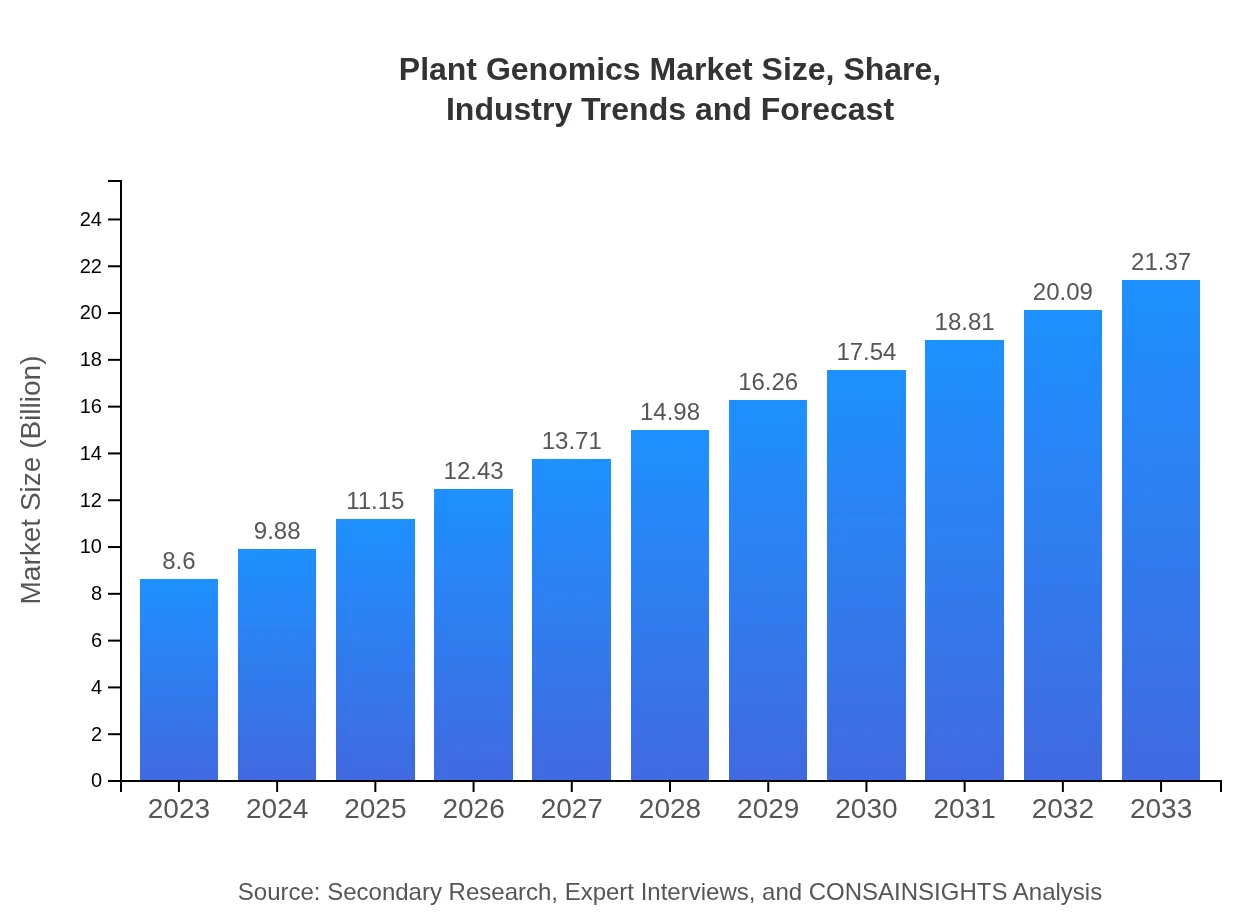
| 2023 Market Size | $8.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $21.37 Billion |
| Top Companies | Monsanto Company, Syngenta AG, DuPont de Nemours, Inc., Corteva Agriscience, Illumina, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Plant Genomics Market Overview
Customize Plant Genomics Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Plant Genomics market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Plant Genomics's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Plant Genomics
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Plant Genomics market in 2023?
Plant Genomics Industry Analysis
Plant Genomics Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Plant Genomics Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Plant Genomics Market Report:
Europe’s Plant Genomics market is anticipated to expand from $2.54 billion in 2023 to $6.31 billion by 2033, driven by stringent regulations promoting sustainable agriculture and food safety. The European Union's investments in genomic research contribute to the region's growth, alongside public acceptance of genetically modified crops. Collaborative efforts between governments and agricultural entities are essential for advancing innovations in the plant genomics field.Asia Pacific Plant Genomics Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is projected to witness significant growth in the Plant Genomics market, with a market size increasing from $1.87 billion in 2023 to $4.64 billion by 2033. Countries like India and China are driving innovations in agriculture through genomic research, focusing on high-yield varieties and pest-resistant crops. The escalating need for food production amid population growth is a significant factor propelling this region's investment in plant genomics.North America Plant Genomics Market Report:
North America stands as a leader in the Plant Genomics market, with the market size climbing from $2.78 billion in 2023 to $6.92 billion by 2033. The U.S. showcases a strong focus on research and development in biotechnology, supported by favorable regulatory frameworks and investments in agricultural innovations. The presence of major biotech firms and research institutions enhances the region's dominance.South America Plant Genomics Market Report:
In South America, the Plant Genomics market is expected to grow from $0.63 billion in 2023 to $1.56 billion by 2033. The agricultural sector in countries like Brazil and Argentina is increasingly adopting genomics to enhance crop yields and manage pests, which is crucial in a region heavily dependent on agriculture. The emphasis on sustainable farming practices is also spurring the adoption of genomic technologies.Middle East & Africa Plant Genomics Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region’s market is poised to grow from $0.78 billion in 2023 to $1.94 billion by 2033. Though this region currently experiences slower growth compared to others, there is a growing recognition of the importance of plant genomics in overcoming challenges such as drought and food scarcity. Investments in research initiatives aimed at improving crop resilience are gradually increasing, reflecting a shift towards sustainable agricultural practices.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Plant Genomics Market Analysis By Technology
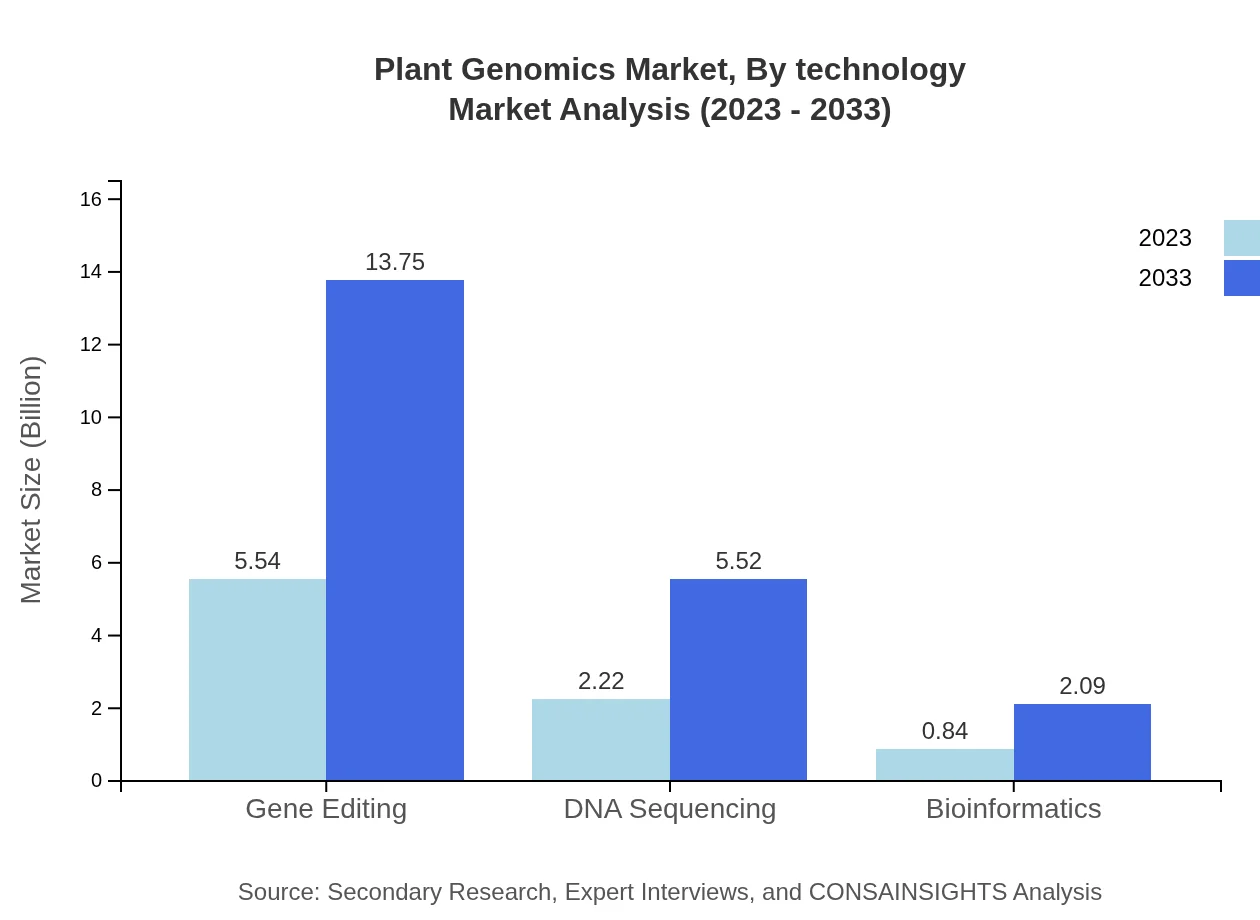
The technological segment of the Plant Genomics market encompasses key areas such as Gene Editing, DNA Sequencing, and Bioinformatics. Gene Editing holds a substantial market size, projected to grow from $5.54 billion in 2023 to $13.75 billion by 2033, representing a 64.37% market share. Similarly, DNA Sequencing is set to expand from $2.22 billion to $5.52 billion, capturing approximately 25.85% of the market share during the forecast period. Innovations in these technologies are crucial for enhancing crop traits, increasing global food security, and addressing climate-related challenges.
Plant Genomics Market Analysis By Application
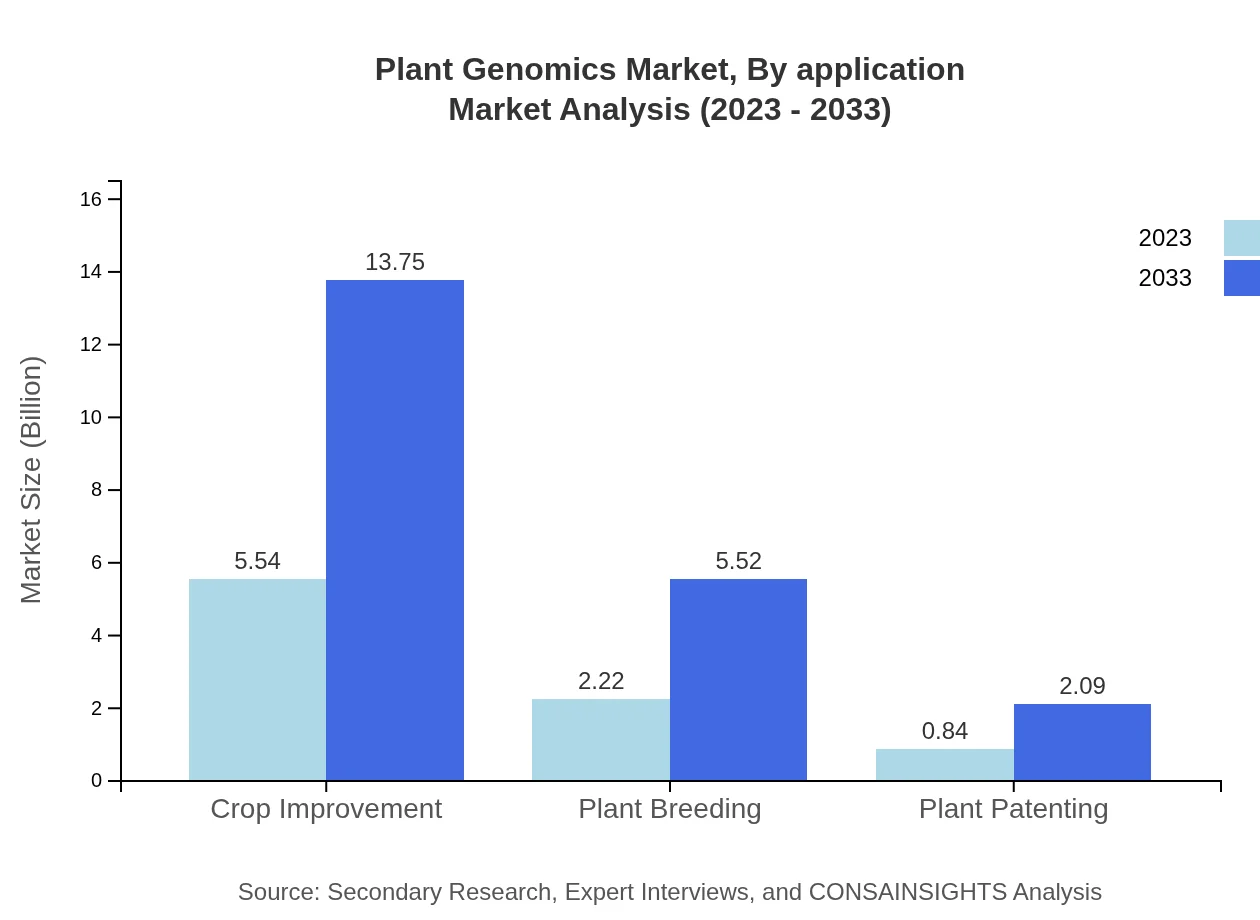
Applications of Plant Genomics are primarily found in Agriculture, Biotechnology, and the Food Industry. The Agriculture segment dominates the market, with a size projected to grow from $5.54 billion in 2023 to $13.75 billion by 2033, holding 64.37% of the market share. The Biotechnology segment also plays a vital role, growing from $2.22 billion to $5.52 billion, representing 25.85% of the market. The Food Industry, though smaller, is expected to rise from $0.84 billion to $2.09 billion, emphasizing the importance of genomics in food security and quality.
Plant Genomics Market Analysis By End User
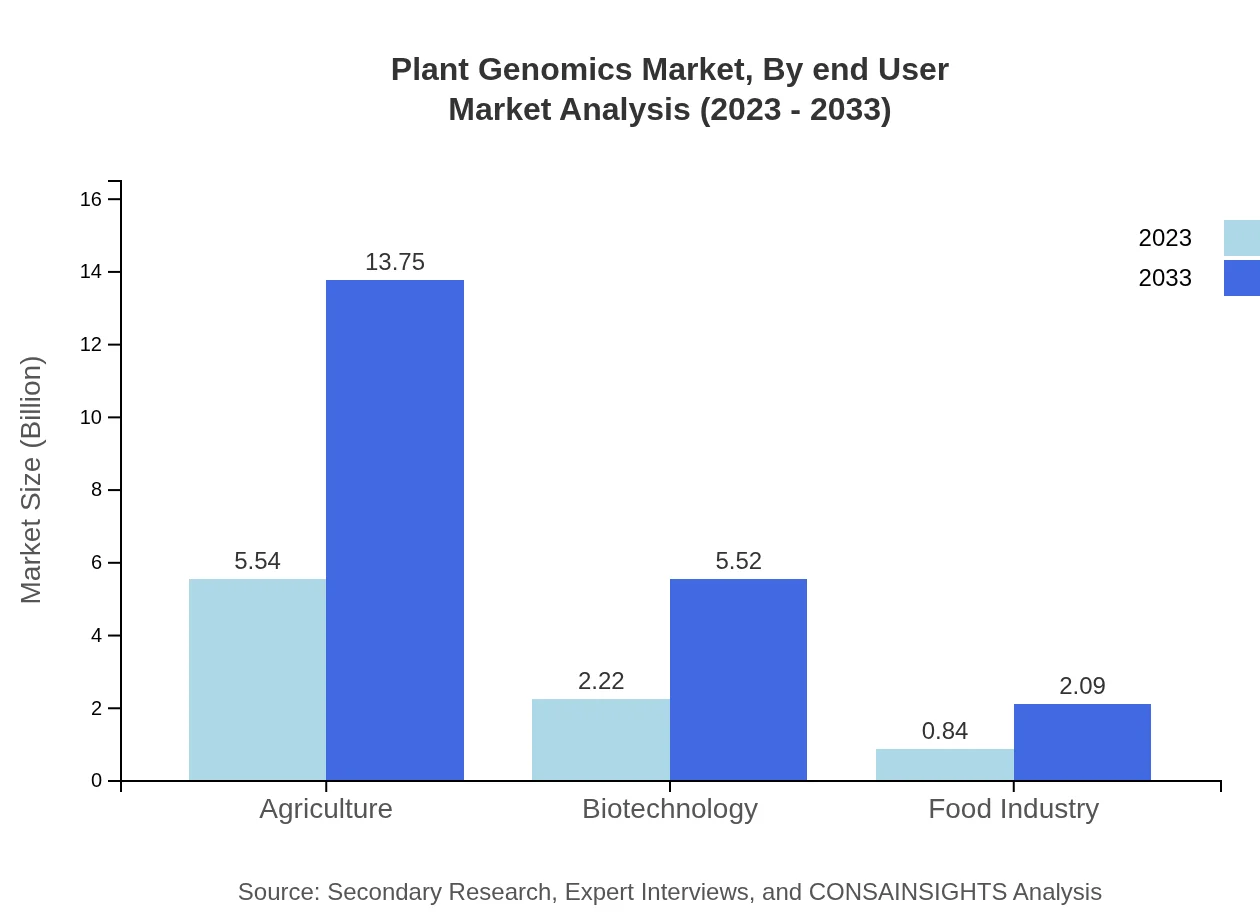
End-users of the Plant Genomics market include agricultural firms, research institutions, and food producers. Agricultural firms are the largest share holders, utilizing genomic technologies to enhance productivity and sustainability. Research institutions are increasingly involved in developing innovative solutions, while food producers leverage genomics to ensure quality and safety in plant-based products. This ecosystem is critical in driving advancements and ensuring that the agricultural sector meets the demands of a growing global population.
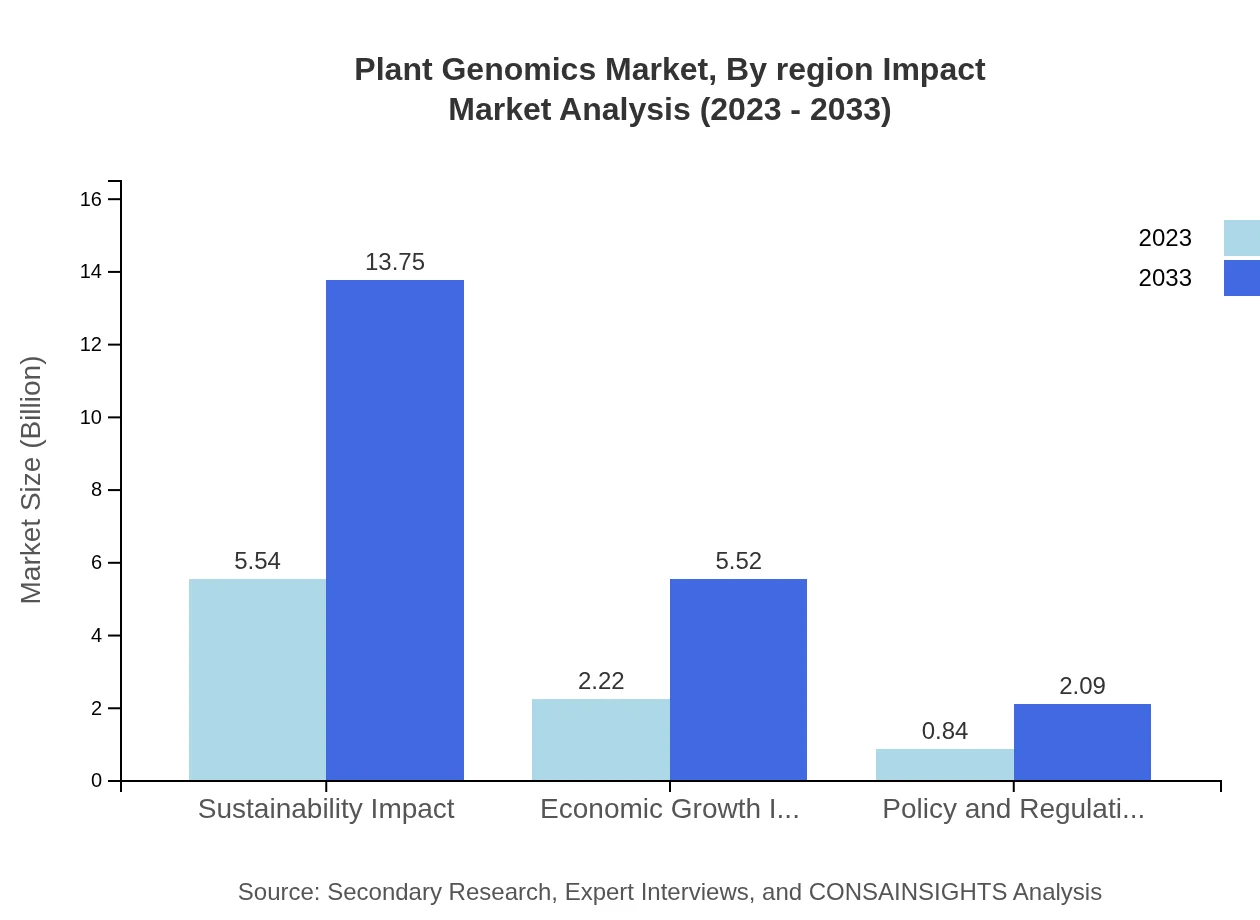
Plant Genomics Market Analysis By Region Impact
Regional dynamics significantly impact the Plant Genomics market. North America leads due to strong R&D efforts and advanced agricultural practices, while Europe enforces stringent regulations that foster sustainable innovations. The Asia Pacific region is rapidly growing, capitalizing on population demands and technological advancements. South America's reliance on agriculture drives adoption, and the Middle East and Africa are beginning to embrace plant genomics as a solution to environmental challenges. Each region contributes uniquely to the global momentum of plant genomics.
Plant Genomics Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Plant Genomics Industry
Monsanto Company:
A leading agricultural company focused on biotechnology, known for its innovations in genetically modified organisms and sustainable farming practices.Syngenta AG:
A global agribusiness that provides various products and technologies, aimed at enhancing crop yields and advancing agricultural solutions.DuPont de Nemours, Inc.:
Involved in biotechnology and agriculture, DuPont focuses on developing hybrid crops and agricultural products to meet global food demands.Corteva Agriscience:
A major player in providing advanced agricultural solutions and seed technologies, focusing on sustainable farming practices and crop protection.Illumina, Inc.:
Leaders in genetic sequencing technologies, Illumina provides tools that are vital for research in plant genomics and agricultural development.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of plant Genomics?
The plant genomics market is valued at $8.6 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 9.2% from 2023 to 2033, indicating robust industry growth driven by technological advancements and increased agricultural demand.
What are the key market players or companies in this plant Genomics industry?
Key players in the plant genomics market include major biotech companies and research institutions specializing in agricultural innovation, biotechnology, and genetic research, which significantly contribute to the industry's development and technological advancements.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the plant Genomics industry?
Growth in the plant genomics industry is driven by technological advancements in gene editing and DNA sequencing, increasing demand for food security, crop resilience, and sustainable agriculture, as well as supportive government policies promoting biotechnological research.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the plant Genomics?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing in the plant genomics market, with a market growth from $1.87 billion in 2023 to $4.64 billion in 2033, driven by advancements in technology and increased agricultural investments.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the plant Genomics industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the plant genomics industry, enabling businesses to gain insights and make informed decisions based on their unique market requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this plant Genomics market research project?
Deliverables from the plant genomics market research project include comprehensive reports detailing market size, growth trends, competitive analysis, regional insights, and segment data, all providing actionable insights crucial for strategic planning.
What are the market trends of plant Genomics?
Current market trends in plant genomics show an increasing focus on gene editing techniques, advancements in bioinformatics, and rising investments in sustainable agricultural practices, reflecting the industry's shift towards enhanced productivity and environmental sustainability.