Power Electronics Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: power-electronics
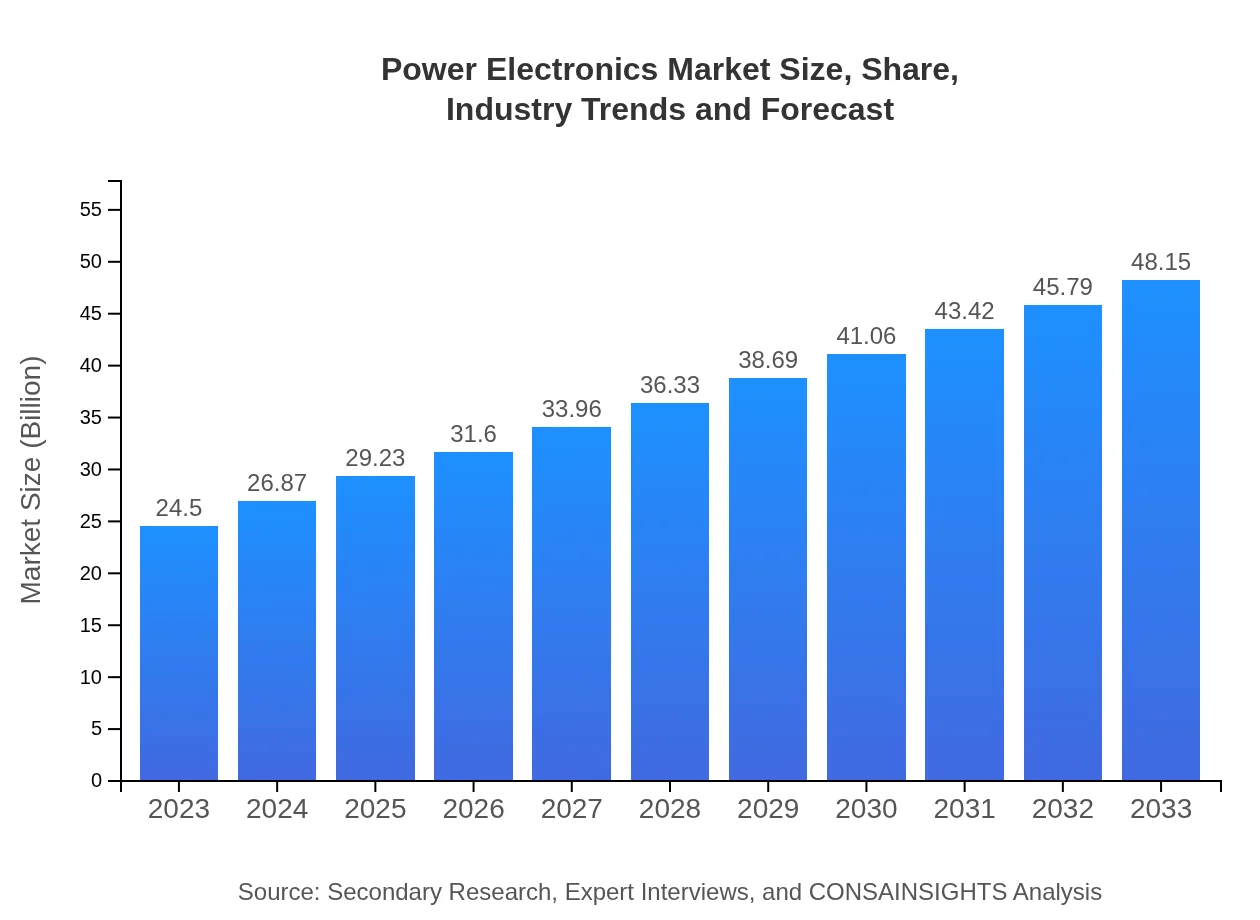
Power Electronics Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Power Electronics market, covering key trends, market size projections, regional performance, and industry dynamics from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $24.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $48.15 Billion |
| Top Companies | Infineon Technologies, Texas Instruments, Toshiba Corporation, STMicroelectronics, NXP Semiconductors |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Power Electronics Market Overview
Customize Power Electronics Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Power Electronics market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Power Electronics's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Power Electronics
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Power Electronics market in 2023?
Power Electronics Industry Analysis
Power Electronics Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Power Electronics Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Power Electronics Market Report:
The European market is anticipated to rise from $6.89 billion to $13.54 billion, largely due to stringent regulations on energy efficiency and a shift towards sustainable energy practices.Asia Pacific Power Electronics Market Report:
The Asia Pacific market is projected to grow from $4.87 billion in 2023 to $9.58 billion in 2033, mainly driven by industrial advancements and rising demand for consumer electronics.North America Power Electronics Market Report:
North America will see growth from $7.98 billion in 2023 to $15.68 billion by 2033, influenced by the expansion of electric vehicles and smart grid technologies.South America Power Electronics Market Report:
In South America, the market is expected to increase from $1.79 billion to $3.51 billion during the same period, spurred by investments in renewable energy and infrastructure development.Middle East & Africa Power Electronics Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market will develop from $2.97 billion to $5.85 billion, thanks to increasing adoption of renewable energy solutions and government initiatives to diversify energy resources.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
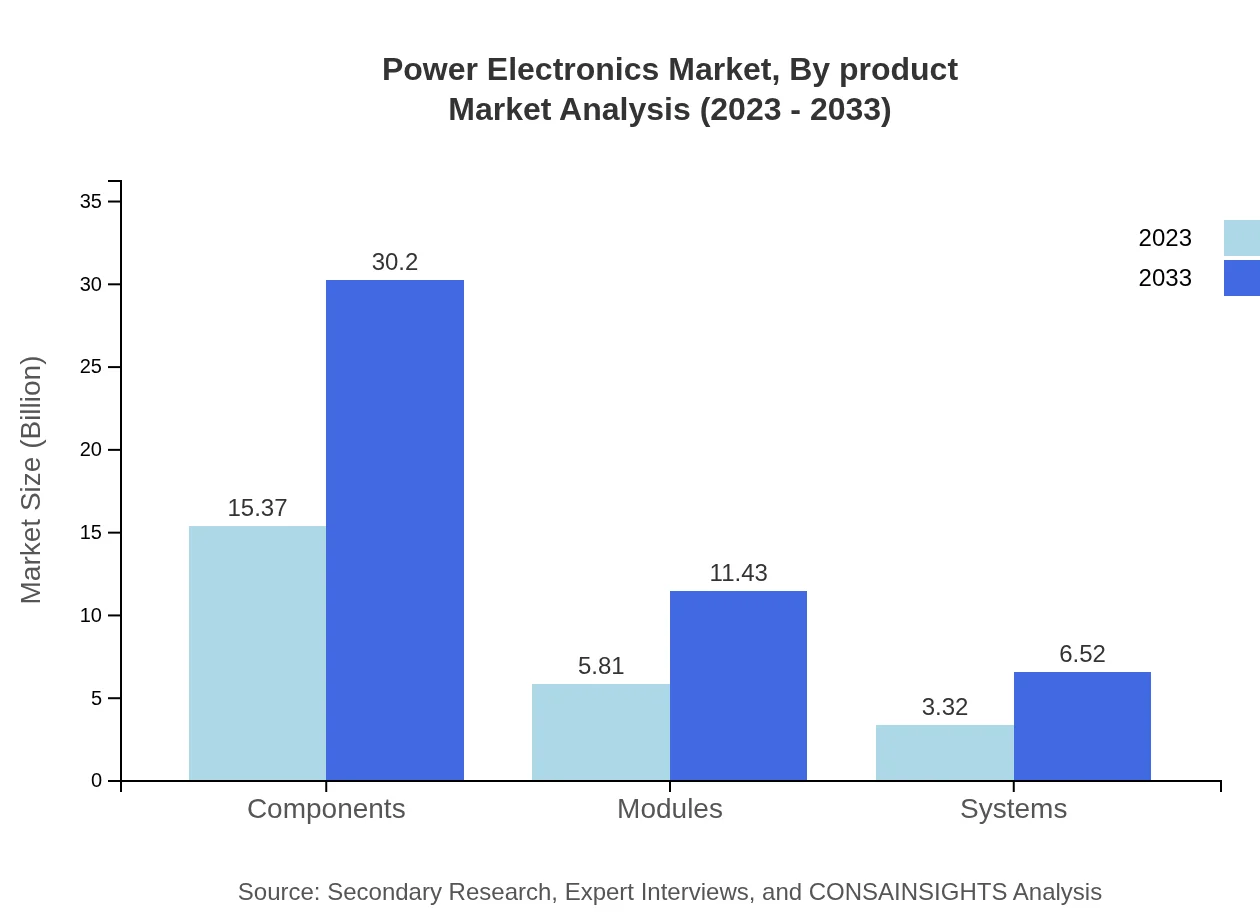
Power Electronics Market Analysis By Product
The product segment is a significant driver for market growth, focusing primarily on components, modules, and systems. The component segment is projected to grow from $15.37 billion in 2023 to $30.20 billion in 2033, maintaining a market share of 62.72%. Modules and systems are also important, growing to $11.43 billion and $6.52 billion, respectively, by 2033.
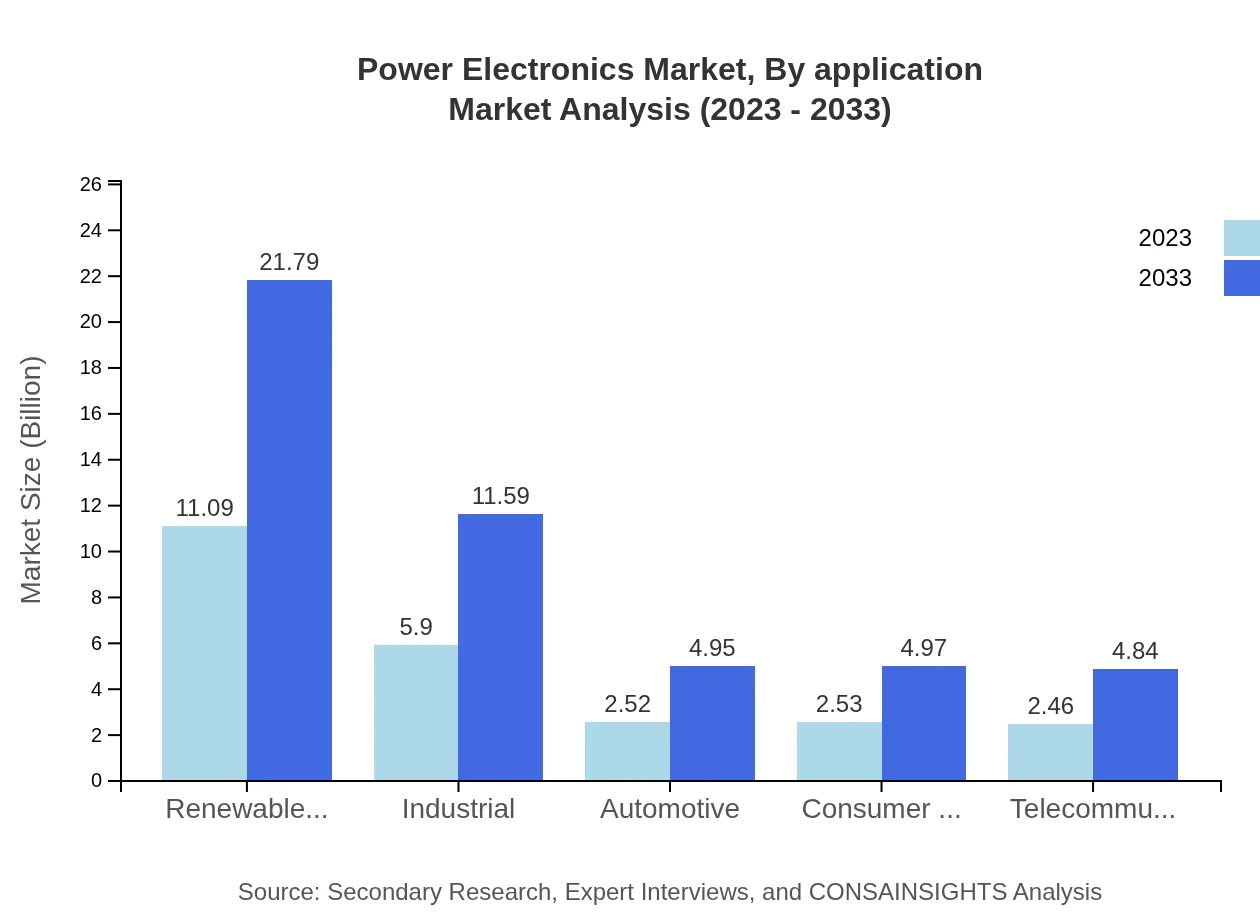
Power Electronics Market Analysis By Application
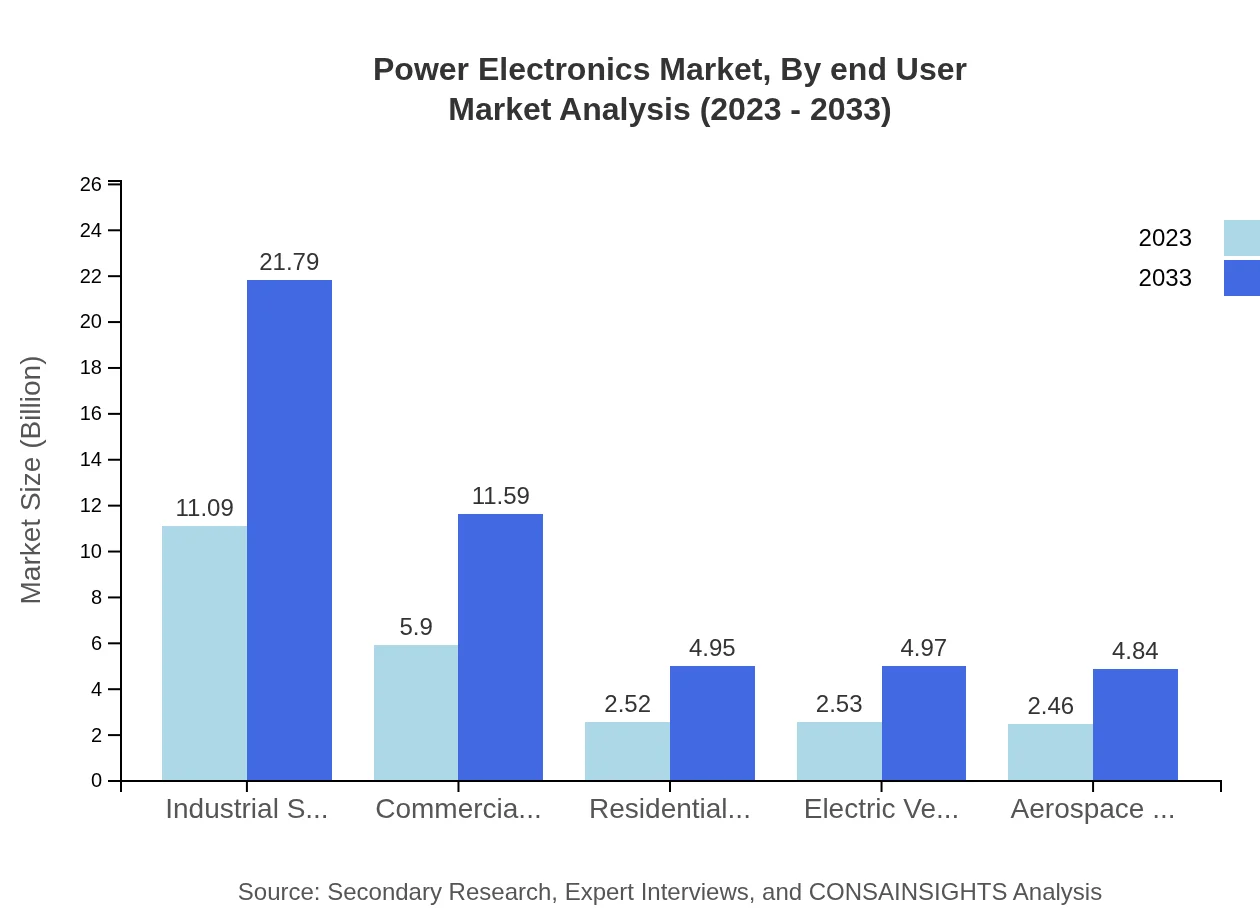
The market by application reveals noteworthy insights, especially within the industrial sector, which is projected to escalate from $11.09 billion to $21.79 billion by 2033. Other sectors, including commercial and residential applications, will also see substantial growth, highlighting the essential role of power electronics in enhancing energy efficiency in various domains.
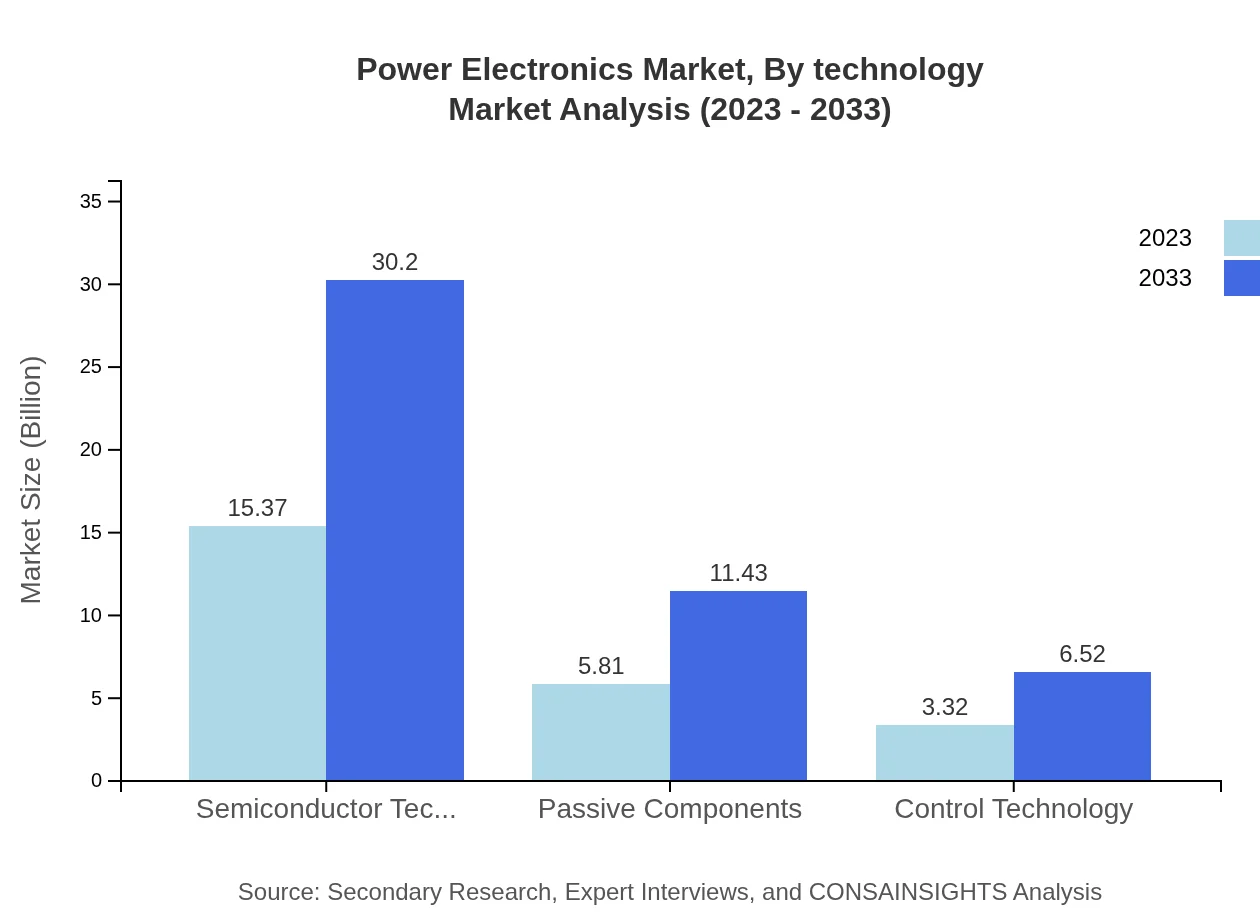
Power Electronics Market Analysis By Technology
Key technologies driving the Power Electronics market include semiconductor technology with a significant share of 62.72% in 2023, and control technology that will expand from $3.32 billion to $6.52 billion by 2033. Continuous advancements in semiconductor materials, such as SiC and GaN, are set to innovate market offerings.
Power Electronics Market Analysis By End User
End-user analysis shows robust demand across various sectors, especially in industrial applications, which maintain a 45.26% market share. The automotive segment, driven by electric vehicles, is expected to grow substantially, indicating a major shift toward sustainable transportation and energy solutions.
Power Electronics Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Power Electronics Industry
Infineon Technologies:
A leader in semiconductor solutions, Infineon is at the forefront of developing power electronic components for automotive and industrial applications.Texas Instruments:
Known for its analog and embedded processing products, Texas Instruments plays a crucial role in providing innovative power management solutions.Toshiba Corporation:
Toshiba is heavily invested in power electronics, offering advanced semiconductor products essential for energy-efficient applications.STMicroelectronics:
STMicroelectronics specializes in multi-market solutions, providing innovative products and solutions in power management for diverse applications.NXP Semiconductors:
NXP is a key player focusing on high-performance mixed-signal and standard product solutions, with significant contributions to automotive and industrial sectors.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Power Electronics?
The global Power Electronics market was valued at approximately $24.5 billion in 2023, with an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8%. By 2033, the market is projected to grow significantly, reflecting increasing demand across various sectors.
What are the key market players or companies in the Power Electronics industry?
Key players in the Power Electronics sector include global giants such as Texas Instruments, Infineon Technologies, Mitsubishi Electric, STMicroelectronics, and NXP Semiconductors. These companies dominate through innovation in technology, extensive product portfolios, and strong market presence.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Power Electronics industry?
The growth of the Power Electronics industry is driven by factors such as the increasing demand for electric vehicles, advancements in renewable energy technologies, consumer electronics proliferation, and the need for energy-efficient systems across various sectors.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Power Electronics market?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing market for Power Electronics, projected to rise from $4.87 billion in 2023 to $9.58 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by rapid industrialization, technological advancements, and rising demand for electric vehicles.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Power Electronics industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data specifically tailored to the needs of clients in the Power Electronics industry. This includes personalized insights and detailed analysis based on unique client requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this Power Electronics market research project?
Deliverables from the Power Electronics market research project include comprehensive reports with market size data, growth forecasts, competitive analyses, segments breakdown, and regional insights to aid strategic decision making.
What are the market trends of Power Electronics?
Current trends in the Power Electronics market include a surge in energy efficiency demand, increased adoption of semiconductor technologies, a shift towards renewable energy solutions, and expanding applications in automotive and consumer electronics sectors.