Power Management System Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: power-management-system
Power Management System Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Power Management System market, covering market trends, segmentation, regional insights, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It aims to equip stakeholders with valuable data and insights to guide their business decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
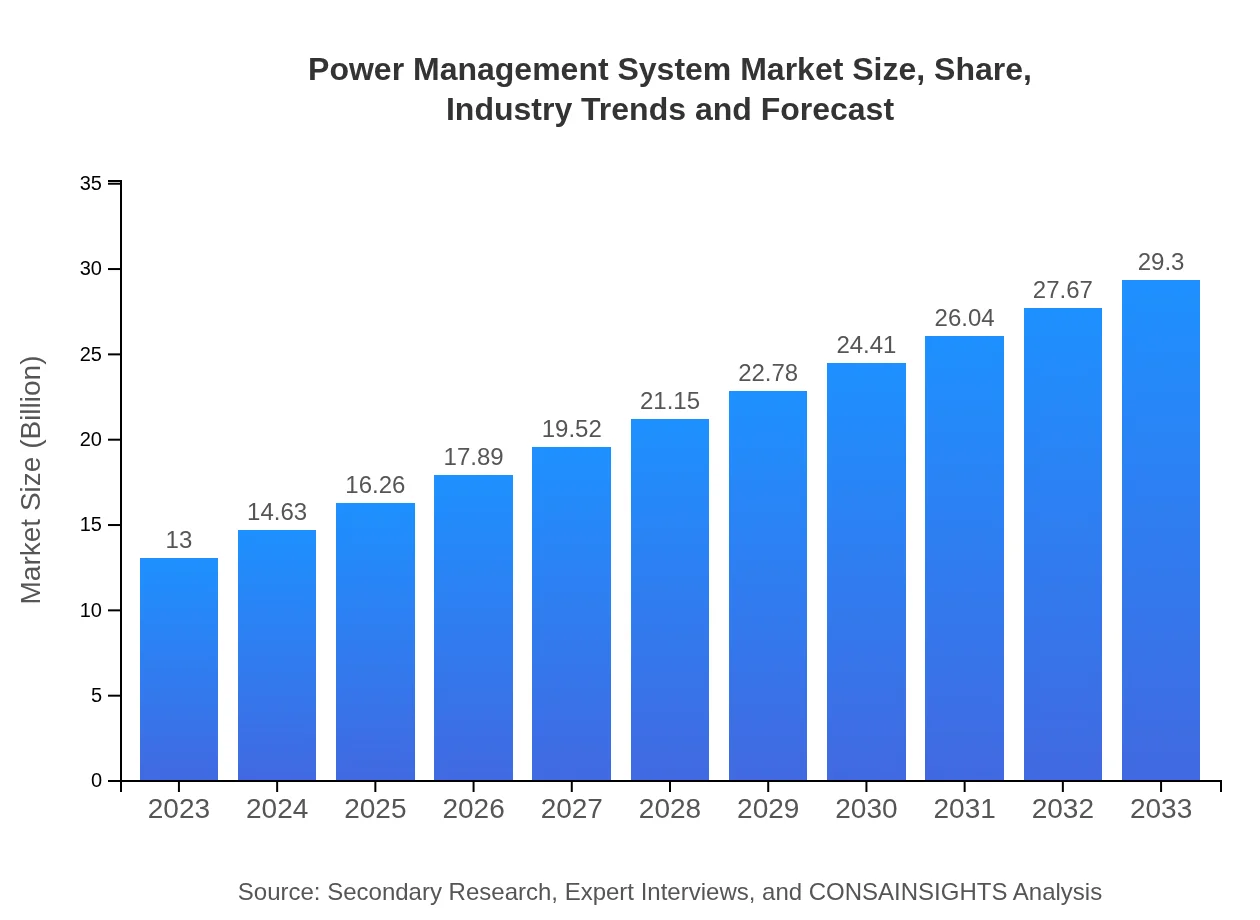
| 2023 Market Size | $13.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 8.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $29.30 Billion |
| Top Companies | Texas Instruments, Analog Devices, NXP Semiconductors, Infineon Technologies, STMicroelectronics |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Power Management System Market Overview
Customize Power Management System Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Power Management System market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Power Management System's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Power Management System
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Power Management System market in 2023?
Power Management System Industry Analysis
Power Management System Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Power Management System Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Power Management System Market Report:
In Europe, the PMS market is projected to grow from $4.26 billion in 2023 to $9.61 billion by 2033. The European Union's stringent energy regulations and initiatives aimed at reducing carbon footprints have catalyzed significant investments in power management solutions.Asia Pacific Power Management System Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region dominates the Power Management System market, accounting for a substantial share due to rapid industrialization and urbanization. In 2023, the market in this region is valued at $2.40 billion and is expected to grow to $5.42 billion by 2033. The booming electronics and automotive industries, coupled with government initiatives promoting energy efficiency, are significant factors driving this growth.North America Power Management System Market Report:
North America is a significant market for Power Management Systems, with a size of $4.53 billion in 2023, expected to climb to $10.21 billion by 2033. The presence of numerous technology companies and a strong emphasis on innovation and sustainable practices drive growth in this region.South America Power Management System Market Report:
South America is a developing market for Power Management Systems, with a market value of $1.15 billion in 2023, projected to reach $2.58 billion by 2033. The rising focus on sustainable energy solutions and increased investment in renewable energy sources are key trends ensuring steady market growth.Middle East & Africa Power Management System Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa show potential for growth in the Power Management System market, with valuations starting from $0.66 billion in 2023 and projected to reach $1.49 billion by 2033. Growing investments in infrastructure and energy efficiency solutions are expected to boost market development.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
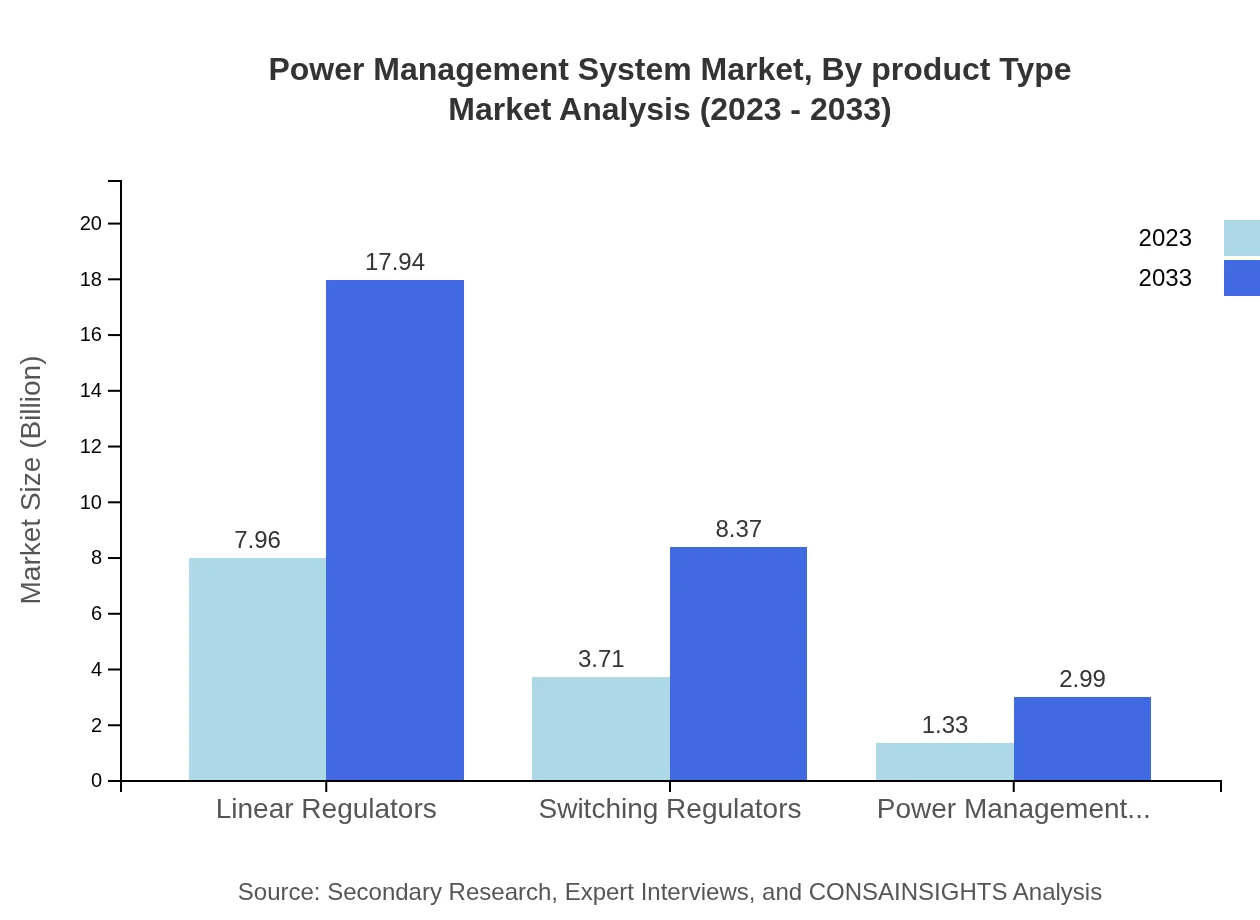
Power Management System Market Analysis By Product Type
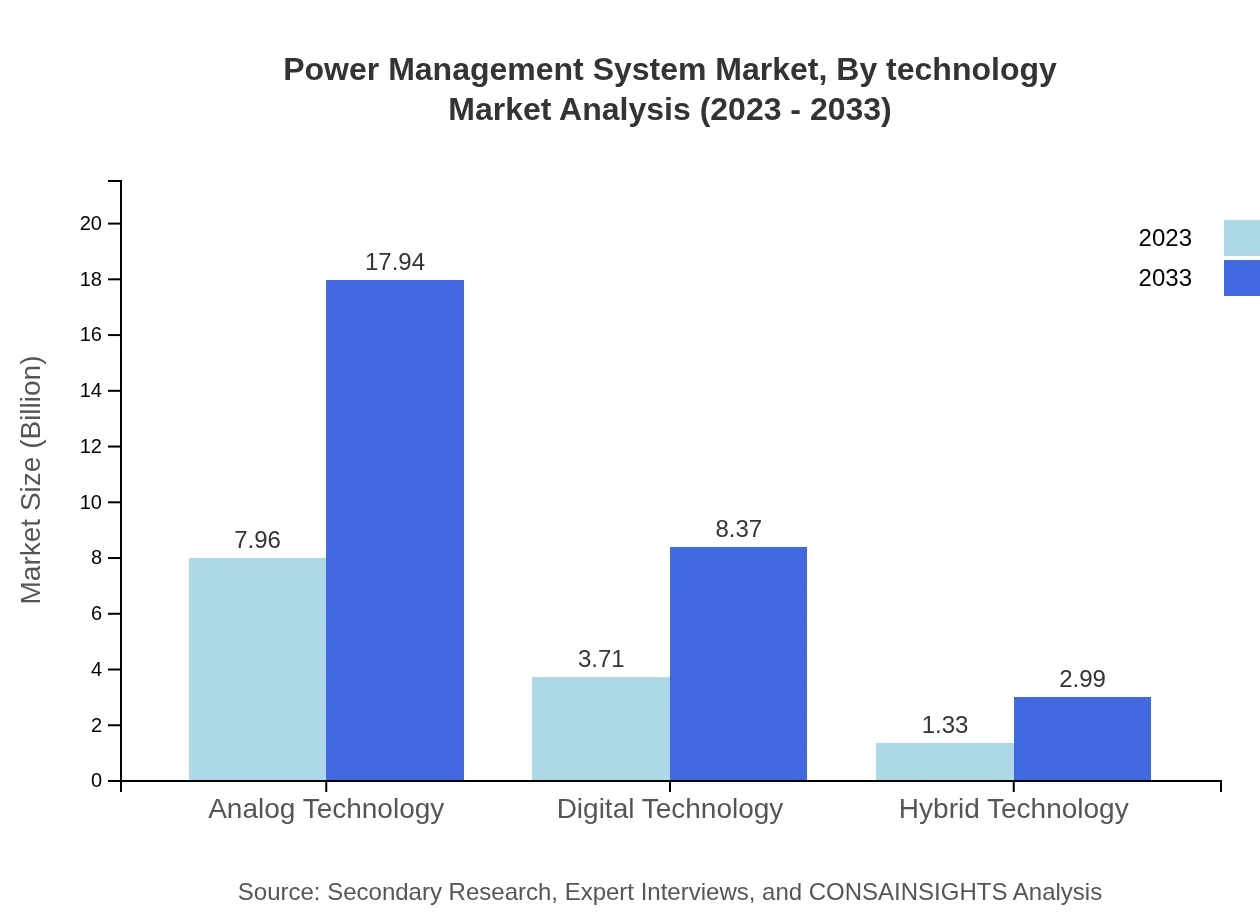
The Power Management System market is segmented by product type into Analog Technology, Digital Technology, Hybrid Technology, and Power Management ICs. In 2023, the Analog Technology segment holds the largest market share of $7.96 billion, expected to grow to $17.94 billion by 2033. Digital Technology stands at $3.71 billion, with expectations to reach $8.37 billion. Hybrid Technology, valued at $1.33 billion in 2023, projects to $2.99 billion by 2033. Lastly, Power Management ICs will grow from $1.33 billion to $2.99 billion in the same timeframe.
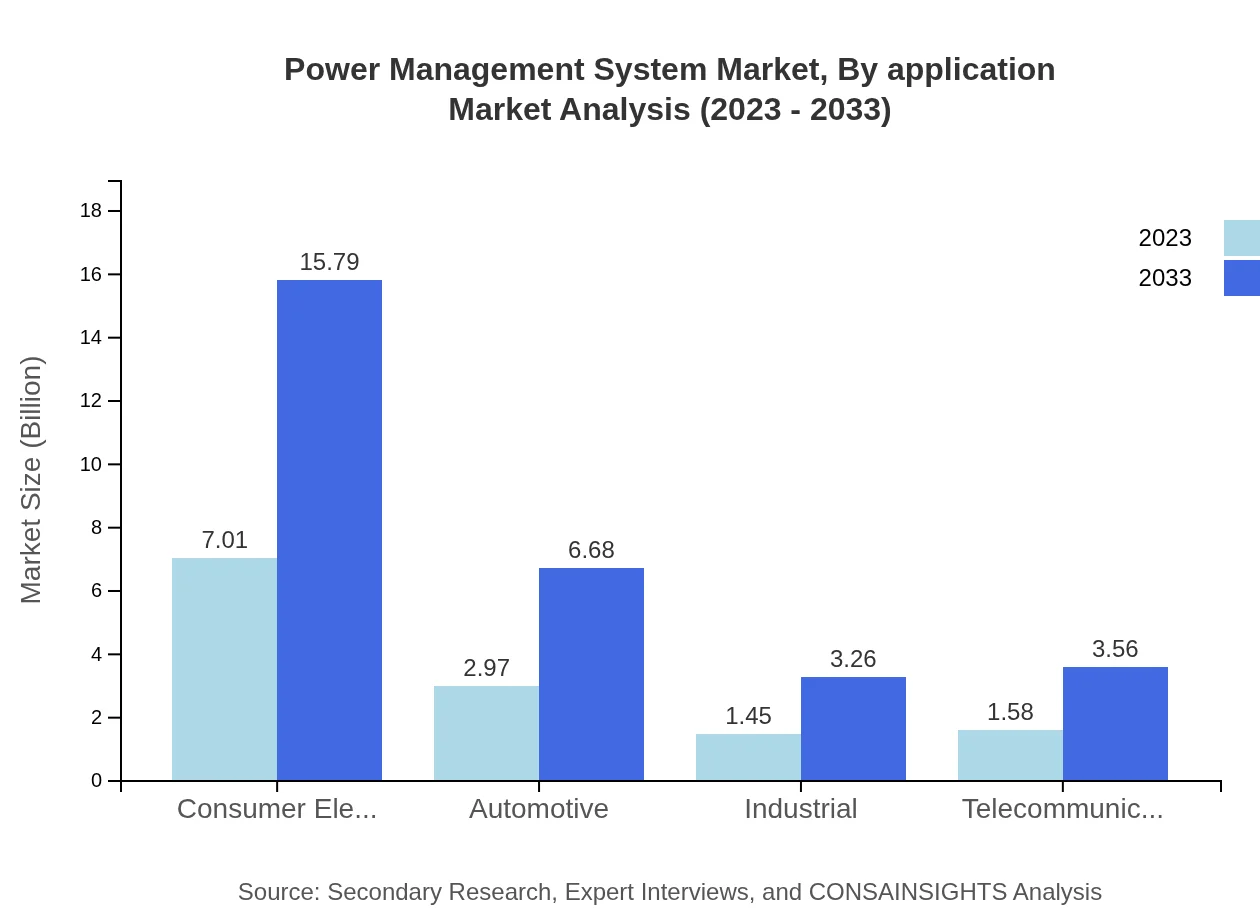
Power Management System Market Analysis By Application
By application, the Power Management System market is segmented into Consumer Electronics, Automotive, Industrial, Telecommunications, Healthcare, and Energy & Utilities. Consumer Electronics contributes significantly with a size of $7.01 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $15.79 billion by 2033. The Automotive sector, currently valued at $2.97 billion, is projected to grow to $6.68 billion, while Telecommunications is expected to grow from $1.58 billion to $3.56 billion over the same period.
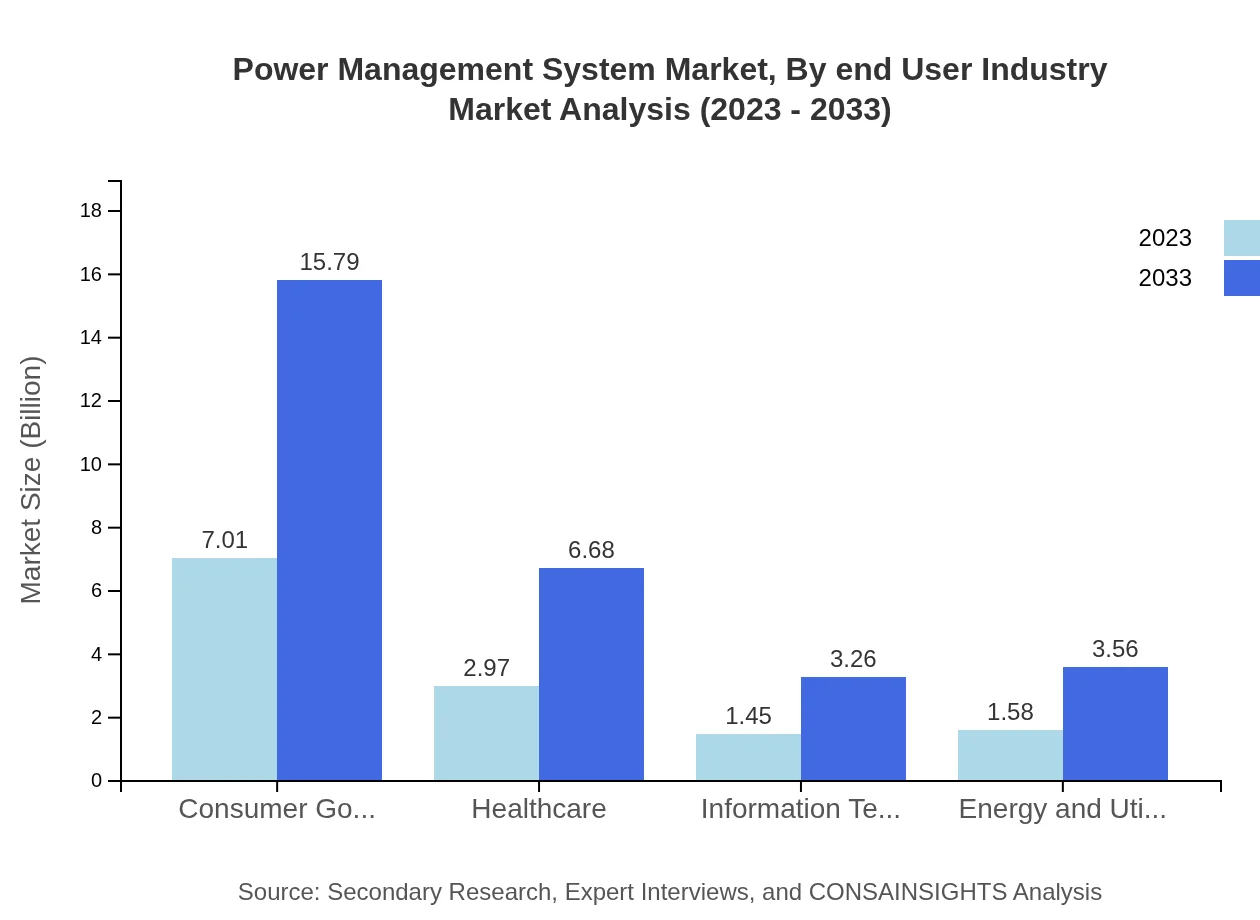
Power Management System Market Analysis By End User Industry
The market by end-user industry features significant segments like Consumer Goods, Healthcare, IT, and Energy Sector. Consumer Goods presently holds a valued market size of $7.01 billion, growing to $15.79 billion by 2033. The Healthcare market is anticipated to increase from $2.97 billion to $6.68 billion. In the Energy and Utilities sector, the market is projected to evolve from $1.58 billion to $3.56 billion between 2023 and 2033.
Power Management System Market Analysis By Technology
The technology segment includes analog, digital, and hybrid technologies. Analog Technology currently dominates the market with a share of 61.23% in 2023, maintaining the same through to 2033. Digital Technology holds a smaller, but significant share of 28.56%, and shows potential for growth over the coming years. Hybrid technology's share is projected to remain stable around 10.21%.
Power Management System Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Power Management System Industry
Texas Instruments:
A leading innovator in the field of power management solutions, Texas Instruments develops a broad range of analog technologies that enhance energy efficiency across industries.Analog Devices:
Analog Devices specializes in high-performance power management ICs, delivering advanced energy management solutions that enable cutting-edge technology applications.NXP Semiconductors:
NXP provides secure connections and infrastructure for a smarter world, with significant contributions to power management in the automotive and industrial sectors.Infineon Technologies:
Infineon is a top player in power management technologies, investing heavily in R&D to push boundaries in energy efficiency and sustainability.STMicroelectronics:
STMicroelectronics is at the forefront of power management solutions, particularly in adaptive control technologies that optimize energy consumption and enhance effectiveness across applications.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of power Management System?
The global power management system market is projected to reach approximately $13 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.2% from 2023. This growth reflects increasing energy efficiency demands and the shift towards smart grid technologies.
What are the key market players or companies in this power Management System industry?
Key players in the power management system market include major companies like Siemens AG, Schneider Electric, General Electric, and ABB Ltd. These companies are pivotal in shaping the industry's direction by providing advanced technological solutions.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the power Management System industry?
The growth in the power management system industry is driven by the rising demand for energy efficiency, integration of renewable energy sources, advancements in smart technologies, and regulations promoting sustainability. These factors collectively enhance system reliance and functionality.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the power Management System market?
The North American region is the fastest-growing market for power management systems, expected to expand from $4.53 billion in 2023 to $10.21 billion by 2033, fueled by technological advancements and significant investments in energy infrastructure.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the power Management System industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the power management system industry. Clients can leverage in-depth analyses and customized insights to inform strategic decisions and planning.
What deliverables can I expect from this power Management System market research project?
From the power management system market research project, clients can expect comprehensive reports including market size data, competitive analysis, segment insights, regional breakdowns, and trend analyses to effectively guide their strategic decisions.
What are the market trends of power Management System?
Current trends in the power management system market include the shift towards digital technologies, increasing adoption of IoT in energy management, and rising consumer preference for renewable energy solutions. These trends signal a significant transformation in energy consumption practices.