Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: precious-metals-e-waste-recovery
Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery market from 2023 to 2033, detailing size, growth trends, key players, and industry insights to inform strategic decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
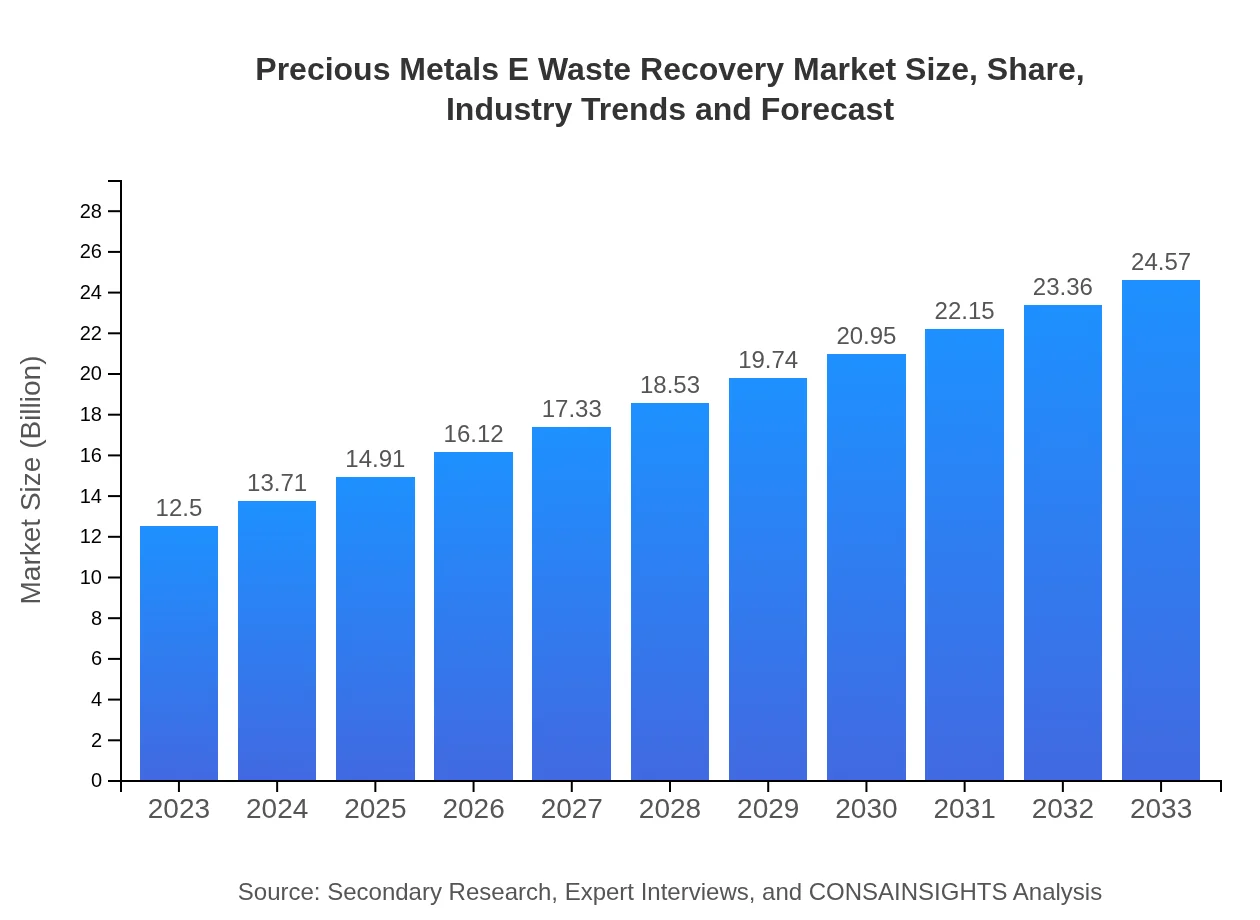
| 2023 Market Size | $12.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $24.57 Billion |
| Top Companies | Umicore, Sims Recycling Solutions, Boliden Group, Dowa Holdings |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Overview
Customize Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Precious Metals E Waste Recovery market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Precious Metals E Waste Recovery's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Precious Metals E Waste Recovery
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Precious Metals E Waste Recovery market in 2023?
Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Industry Analysis
Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Report:
The European market is notably strong, starting at $3.27 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $6.43 billion by 2033. Europe leads in e-waste recycling efforts due to strong regulatory frameworks and high consumer awareness regarding sustainability.Asia Pacific Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific region's market is valued at $2.66 billion, expected to grow to $5.23 billion by 2033, driven by rapid urbanization and electronic consumption. This region embraces innovative recovery technologies, contributing substantially to overall e-waste recycling efforts.North America Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Report:
North America's market, sitting at $4.09 billion in 2023, is anticipated to reach $8.03 billion by 2033. The region benefits from stringent e-waste regulations that encourage manufacturers and recyclers to adopt effective recovery strategies.South America Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Report:
With a market size of $0.95 billion in 2023 and a forecast of $1.86 billion by 2033, South America is emerging in precious metals recovery. Enhanced governmental policies aimed at environmental sustainability are beginning to support industry growth.Middle East & Africa Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region will grow from $1.53 billion in 2023 to approximately $3.02 billion by 2033. Increasing focus on sustainable development and the establishment of e-waste management frameworks are expected to boost market growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
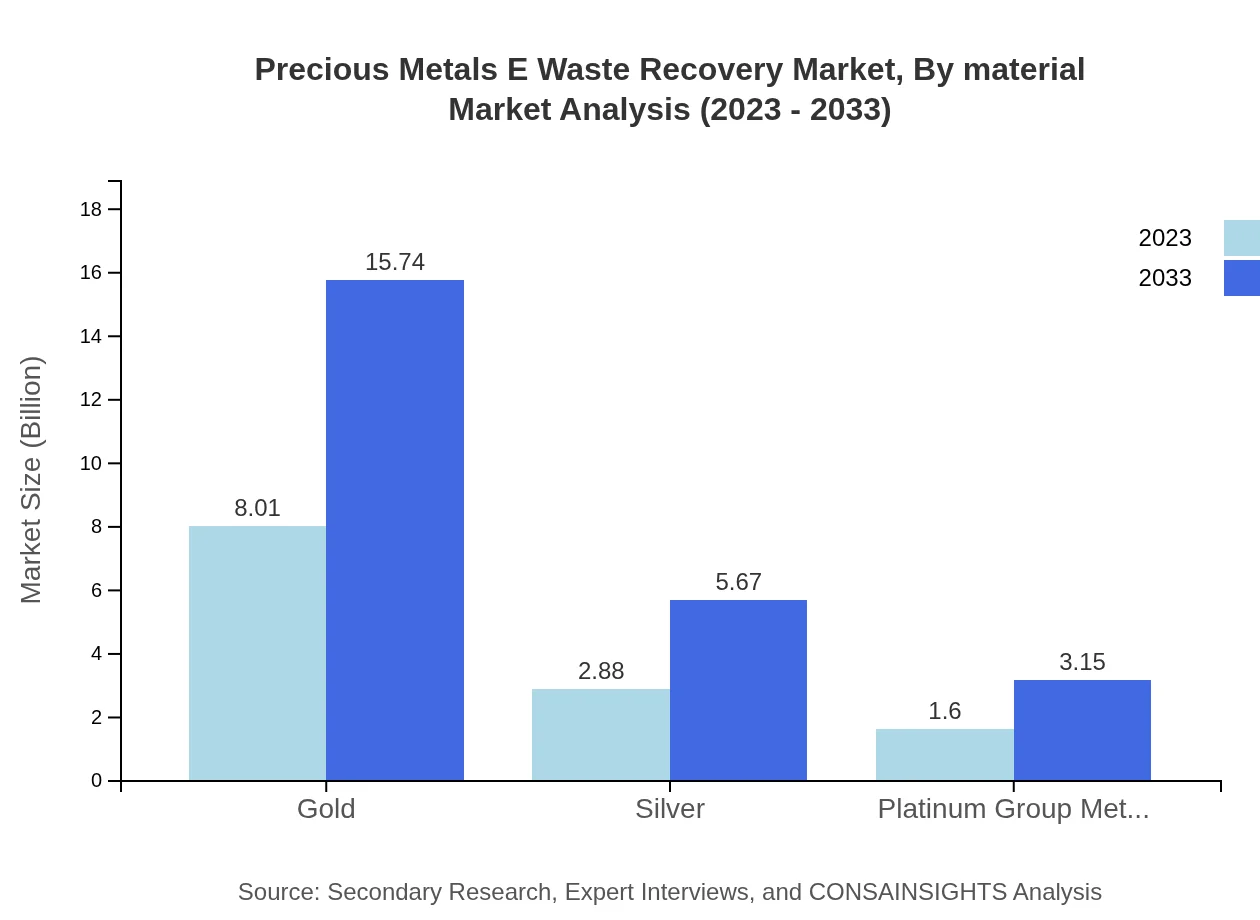
Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Analysis By Material
Significant materials in the precious metals recovery market include gold, silver, and platinum group metals. In 2023, gold recovery generated approximately $8.01 billion with a share of 64.08%. By 2033, this segment is forecasted to reach $15.74 billion, still capturing a dominant share of the market. Silver and platinum group metals also contribute to market growth, reflecting increasing consumer demand for recovered metals.
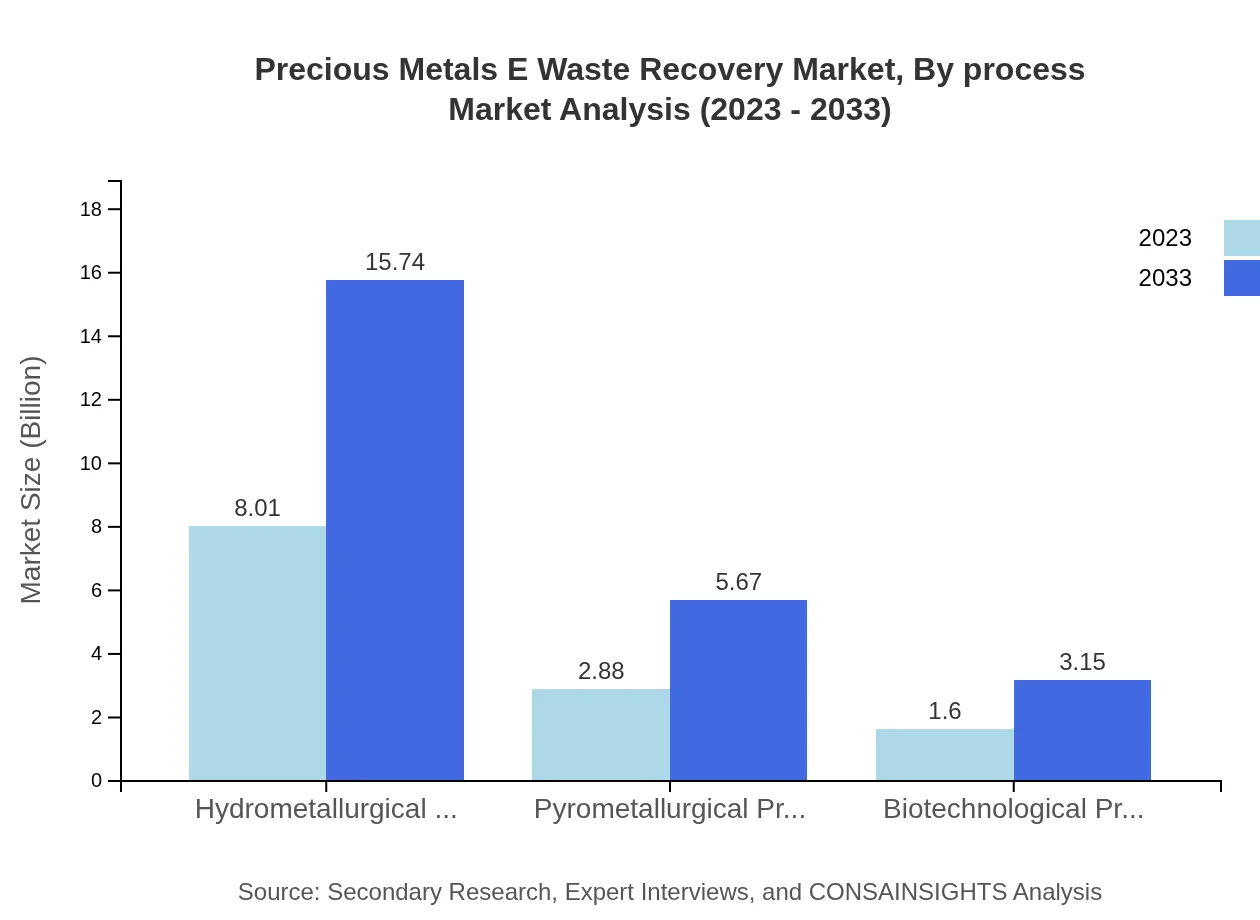
Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Analysis By Process
The market is segmented by recovery processes: hydrometallurgical processes lead with a market size of $8.01 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $15.74 billion by 2033. This method is favored for its efficiency. Meanwhile, pyrometallurgical processes account for a significant share at $2.88 billion in 2023 and expected to rise to $5.67 billion by 2033. Biotechnological processes are also emerging, offering promising recovery solutions with a market size of $1.60 billion in 2023 and a forecast of $3.15 billion by 2033.
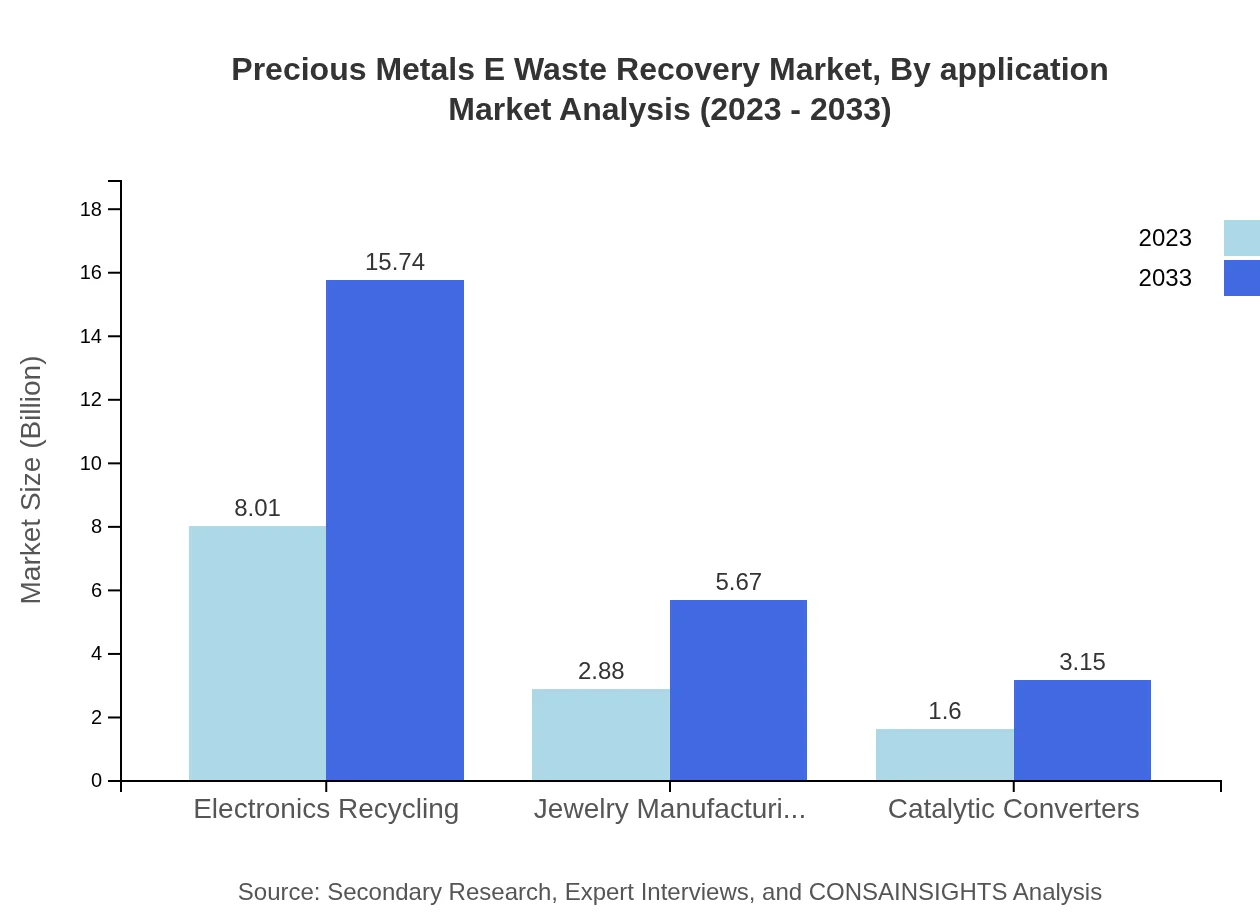
Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Analysis By Application
Applications for recovered precious metals include electronics recycling, jewelry manufacturing, and catalytic converters. Electronics recycling dominates with a market size of $8.01 billion in 2023, poised to grow to $15.74 billion by 2033. The jewelry manufacturing market, meanwhile, will account for $2.88 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $5.67 billion by 2033.
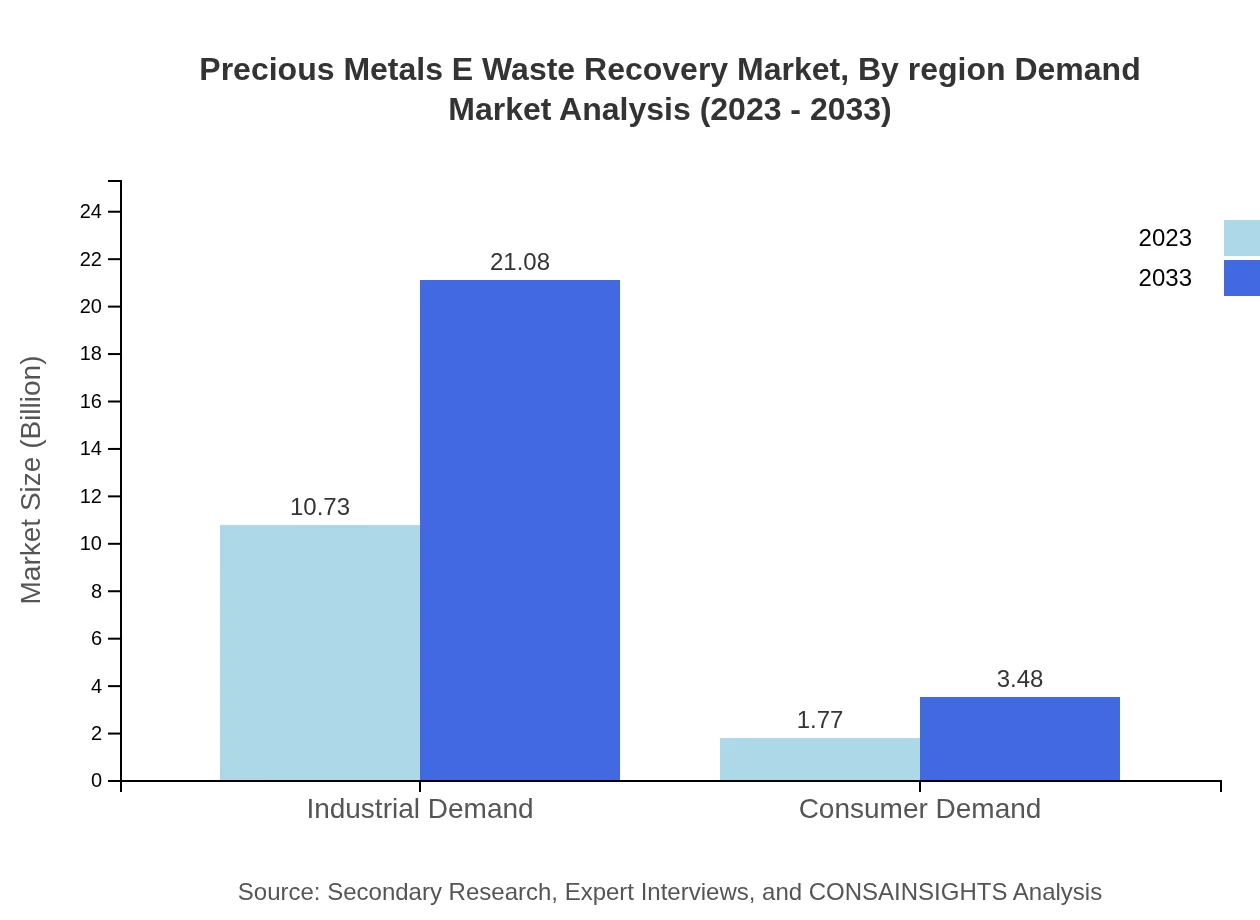
Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Analysis By Region Demand
Demand for recovered precious metals is categorized between industrial and consumer markets. Industrial demand remains robust, reaching $10.73 billion in 2023 and forecasted to double by 2033. In contrast, consumer demand stands at $1.77 billion in 2023 with anticipated growth to $3.48 billion by 2033, demonstrating rising consumer interest in sustainable products.
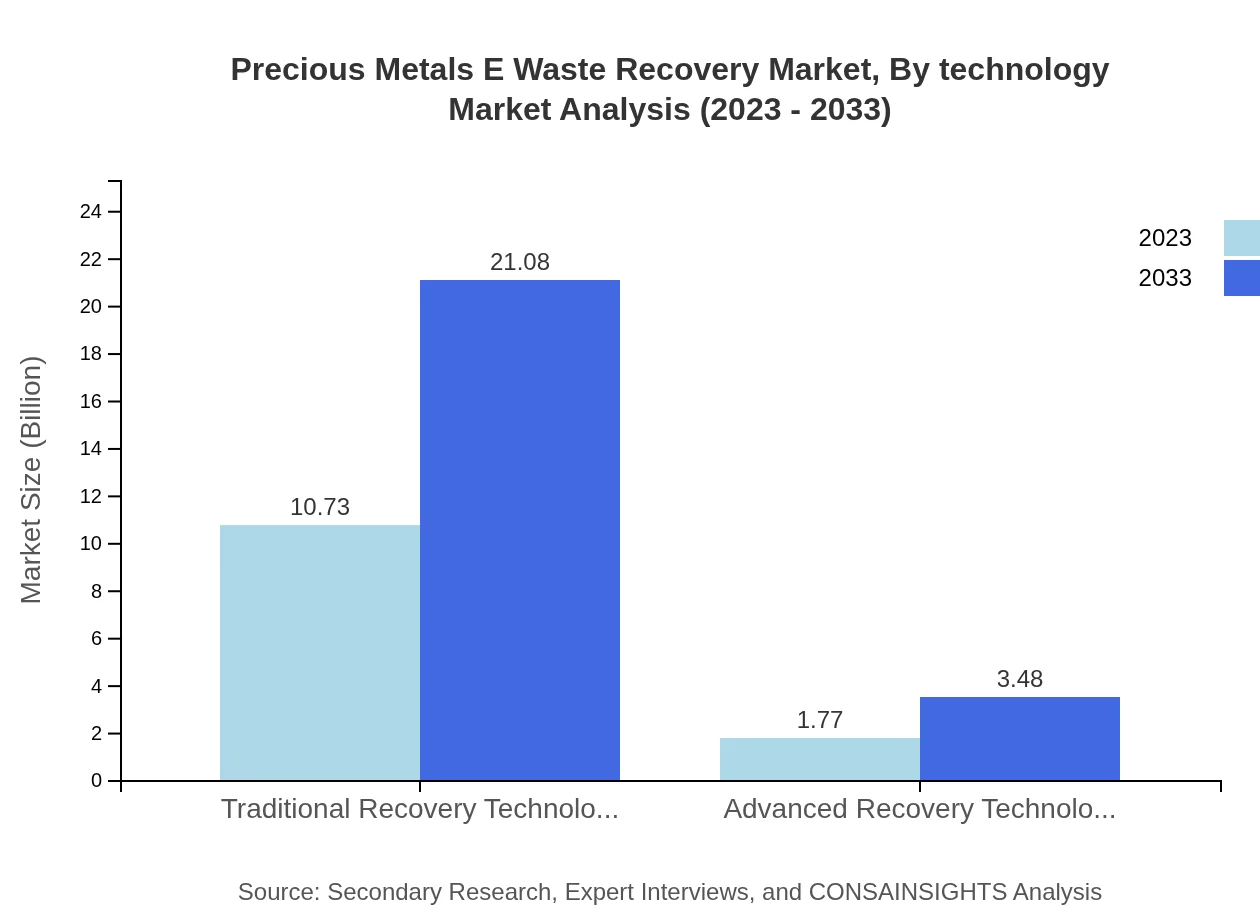
Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements drive the Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery market forward. Traditional recovery technologies dominate the market at $10.73 billion in 2023 and projected growth to $21.08 billion by 2033. However, advanced recovery technologies, although smaller in market share at $1.77 billion in 2023, are gaining traction with a forecast growth to $3.48 billion by 2033.
Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Precious Metals E Waste Recovery Industry
Umicore:
Umicore is a global leader in materials technology and recycling, specializing in the recovery and recycling of precious metals from e-waste.Sims Recycling Solutions:
Sims Recycling Solutions is a prominent player in the electronic waste recycling space, focusing on sustainable recovery solutions for precious metals.Boliden Group:
Boliden Group operates as one of the largest metal recyclers, recovering significant quantities of precious metals from electronic waste.Dowa Holdings:
Dowa Holdings engages in the comprehensive recovery of precious metals from waste products, emphasizing sustainable practices in recycling.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery?
The Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery market is currently valued at approximately $12.5 billion, with a projected CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2033. This growth reflects increasing demand for e-waste recycling and recovery of precious metals.
What are the key market players or companies in this Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery industry?
Key players in the Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery industry include major recycling companies and technology innovators. Specific companies are not named here but generally include those involved in electronics recycling and precious metal recovery.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery industry?
The growth in the Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery industry is driven by increased environmental regulations, the rising value of precious metals, and growing consumer awareness of sustainable practices, all pushing for effective recycling methods.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery market, with projected growth from $4.09 billion in 2023 to $8.03 billion by 2033, followed by significant growth in Europe and Asia Pacific.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery industry, allowing clients to access relevant insights and analysis.
What deliverables can I expect from this Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis, trend identification, segmentation data, competitive landscape, and tailored recommendations based on the latest research findings in the Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery market.
What are the market trends of Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery?
Key trends in the Precious Metals E-Waste Recovery market include increased adoption of advanced recovery technologies, growth in consumer electronics recycling, and a shift towards sustainable practices in industries reliant on precious metals.