Prefabricated Buildings Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: prefabricated-buildings
Prefabricated Buildings Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This detailed market report explores the Prefabricated Buildings sector, covering insights into market size, growth trends, and forecasts for the period from 2023 to 2033. It provides a comprehensive analysis of various segments, regional insights, and the competitive landscape.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
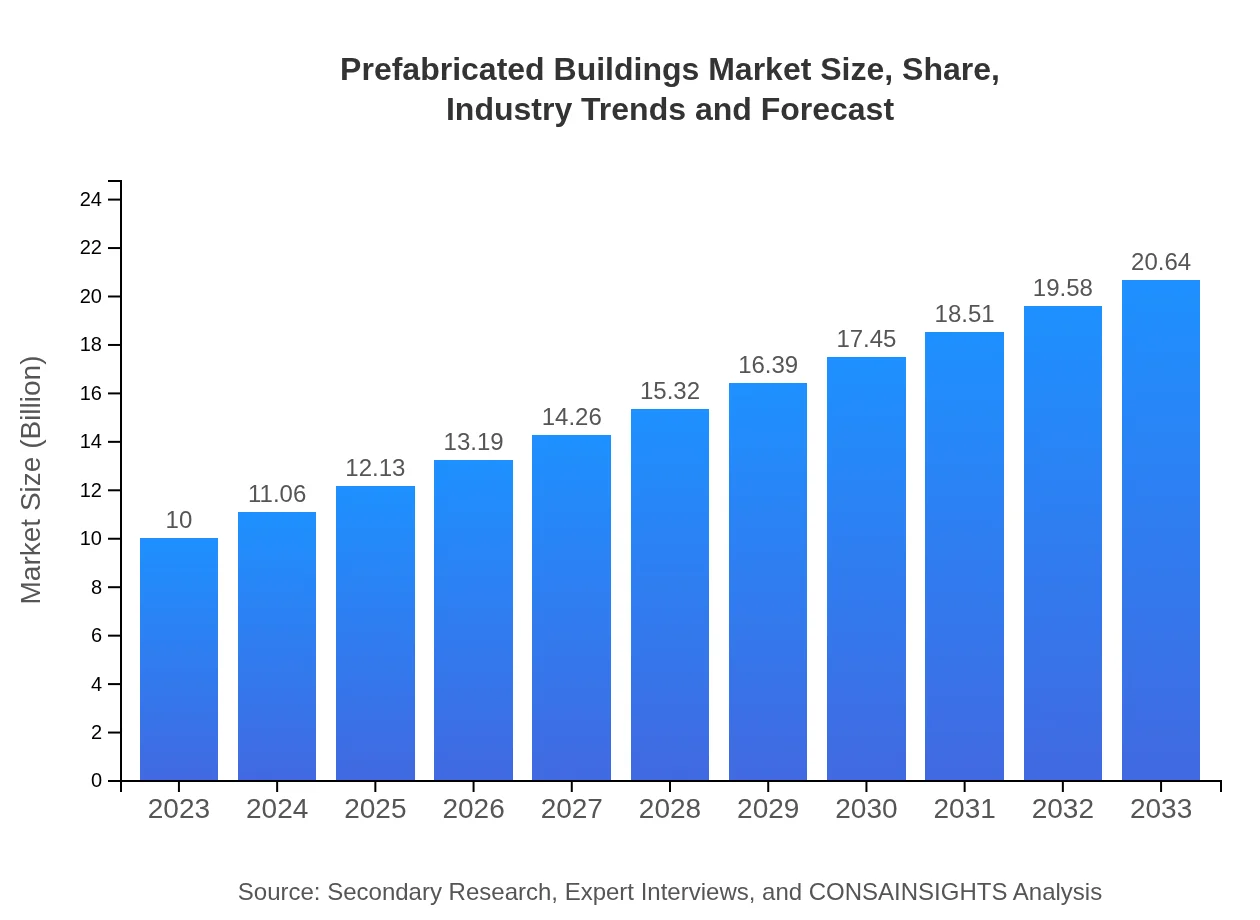
| 2023 Market Size | $10.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $20.64 Billion |
| Top Companies | Modular Space Corporation, Katerra Inc., Lendlease Group, Guerdon Enterprises LLC |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Prefabricated Buildings Market Overview
Customize Prefabricated Buildings Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Prefabricated Buildings market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Prefabricated Buildings's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Prefabricated Buildings
What is the Market Size & CAGR of the Prefabricated Buildings market in 2023?
Prefabricated Buildings Industry Analysis
Prefabricated Buildings Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Prefabricated Buildings Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Prefabricated Buildings Market Report:
European markets will see significant growth from USD 3.32 billion in 2023 to USD 6.85 billion by 2033, as countries emphasize sustainability and regulatory support for innovative building techniques. The widespread adoption of modular construction is particularly evident here.Asia Pacific Prefabricated Buildings Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the prefabricated buildings market is projected to grow from USD 1.88 billion in 2023 to USD 3.87 billion by 2033. Key drivers include rapid urbanization, a growing middle class, and increased investment in infrastructure projects, particularly in countries like China and India.North America Prefabricated Buildings Market Report:
North America's prefabricated buildings market is anticipated to expand from USD 3.36 billion in 2023 to USD 6.93 billion by 2033, driven by heightened demand for affordable housing, commercial spaces, and eco-friendly construction solutions in the United States and Canada.South America Prefabricated Buildings Market Report:
In South America, the market size is expected to rise from USD 0.70 million in 2023 to USD 1.44 million by 2033. The region's growth is supported by ongoing urban expansion and increasing government initiatives aimed at improving housing availability.Middle East & Africa Prefabricated Buildings Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is projected to grow from USD 0.76 billion in 2023 to USD 1.56 billion by 2033. The region's market is fueled by increased infrastructure developments and a growing trend toward prefabrication in the construction sector.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
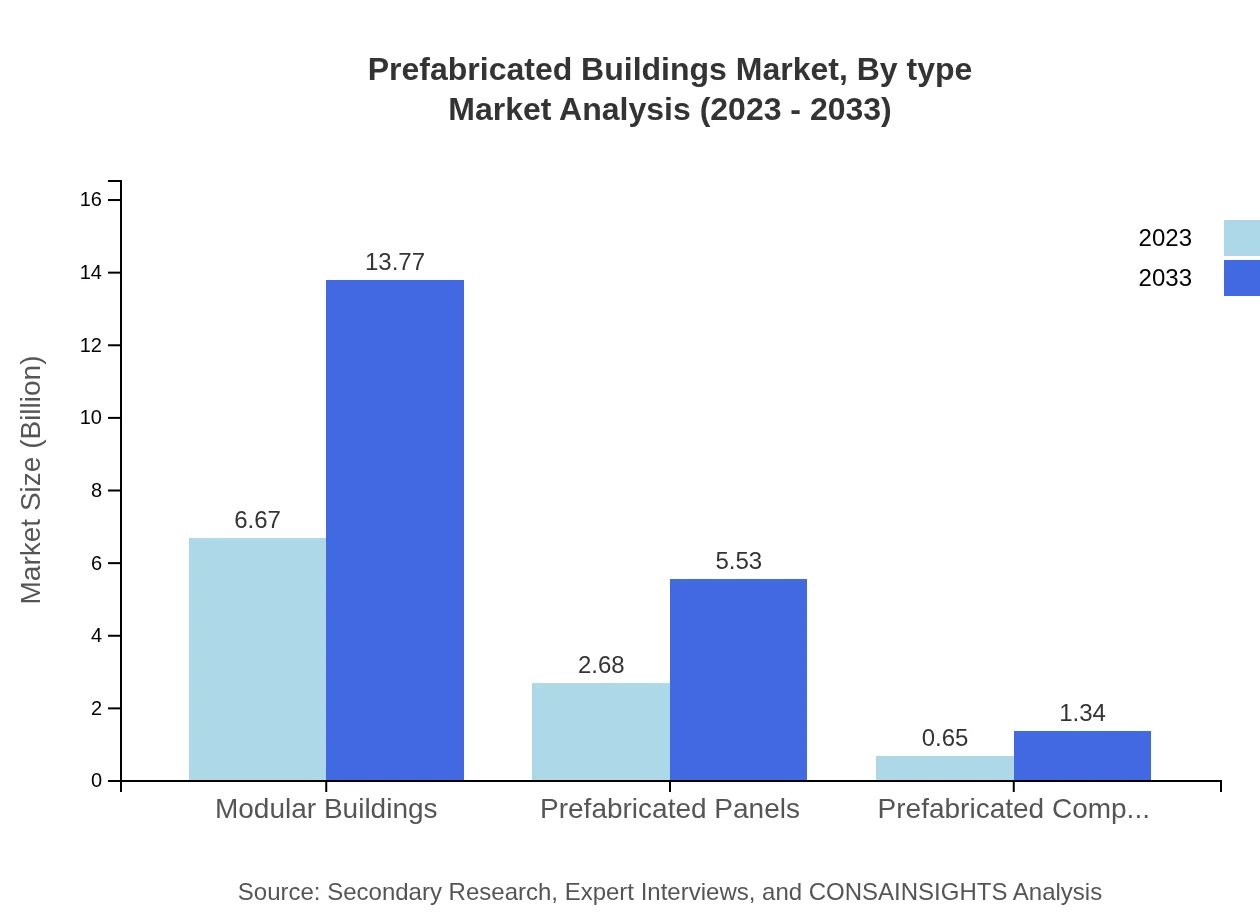
Prefabricated Buildings Market Analysis By Type
The modular buildings segment dominates the prefabricated buildings market, with a size of USD 6.67 billion in 2023 and projected to reach USD 13.77 billion in 2033, marking a consistent 66.7% share. Prefabricated panels follow, expected to grow from USD 2.68 billion to USD 5.53 billion. Prefabricated components and various construction type segments also show growth potential, driven by their applications across diverse building projects.
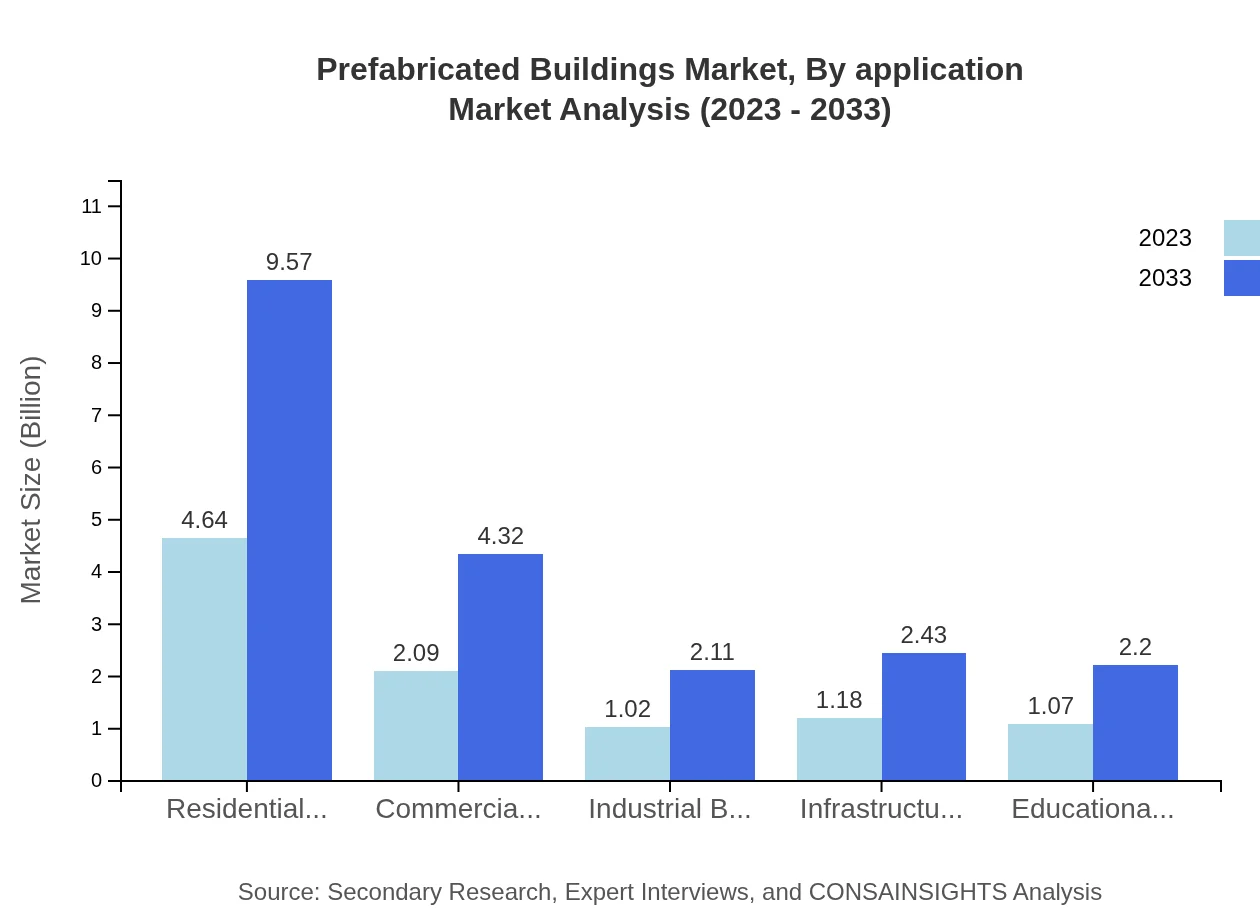
Prefabricated Buildings Market Analysis By Application
Residential buildings account for the largest application segment, valued at USD 4.64 billion in 2023, projected to reach USD 9.57 billion by 2033. Commercial and industrial buildings also contribute significantly, driven by rising demand for workspace and logistical efficiencies. Infrastructure projects are expanding as governments prioritize rapid construction solutions to meet growing demands.
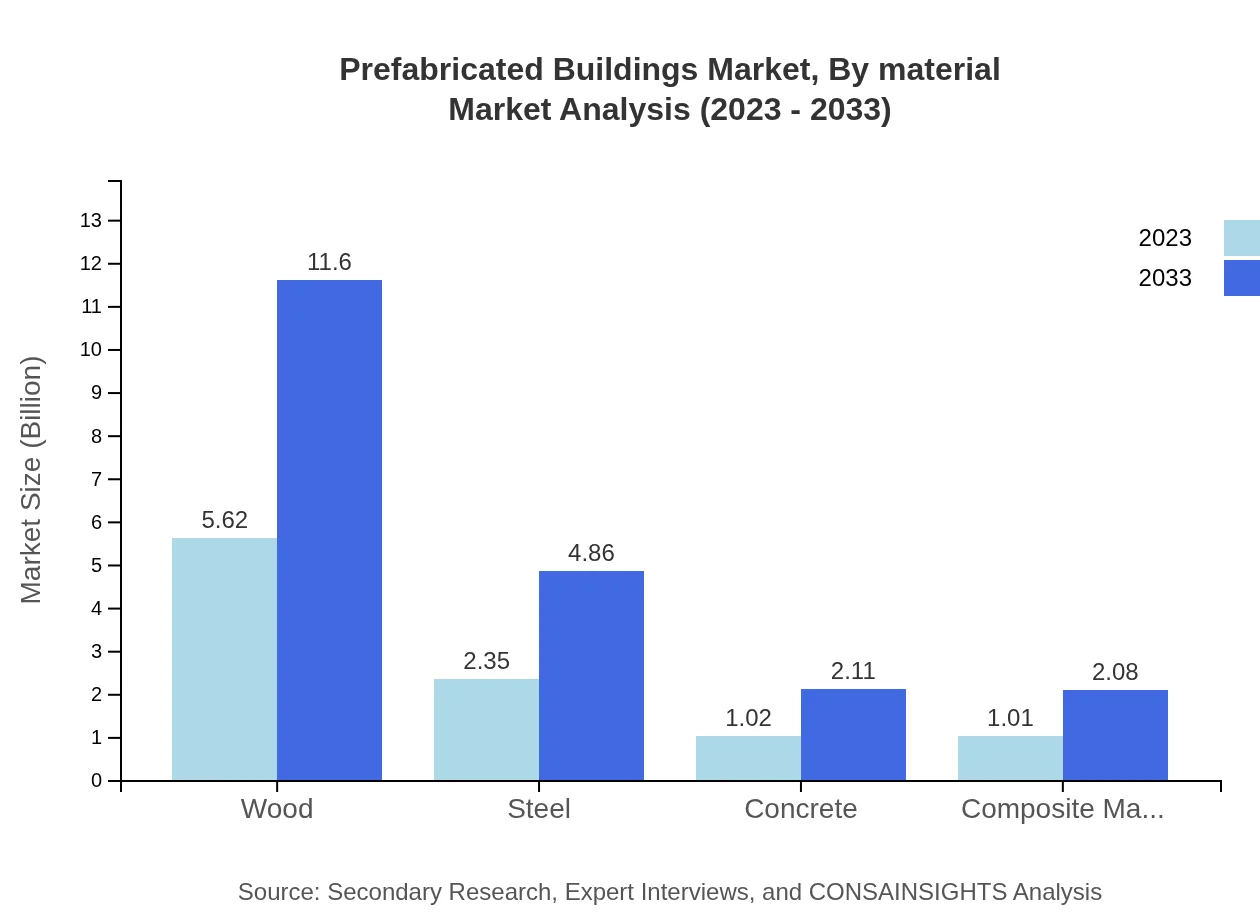
Prefabricated Buildings Market Analysis By Material
Wood remains the leading material in the prefabricated buildings market, with a significant share of 56.2% and projected growth from USD 5.62 billion to USD 11.60 billion. Steel follows with a solid performance, while concrete and composite materials are also gaining traction as development in construction technology evolves.
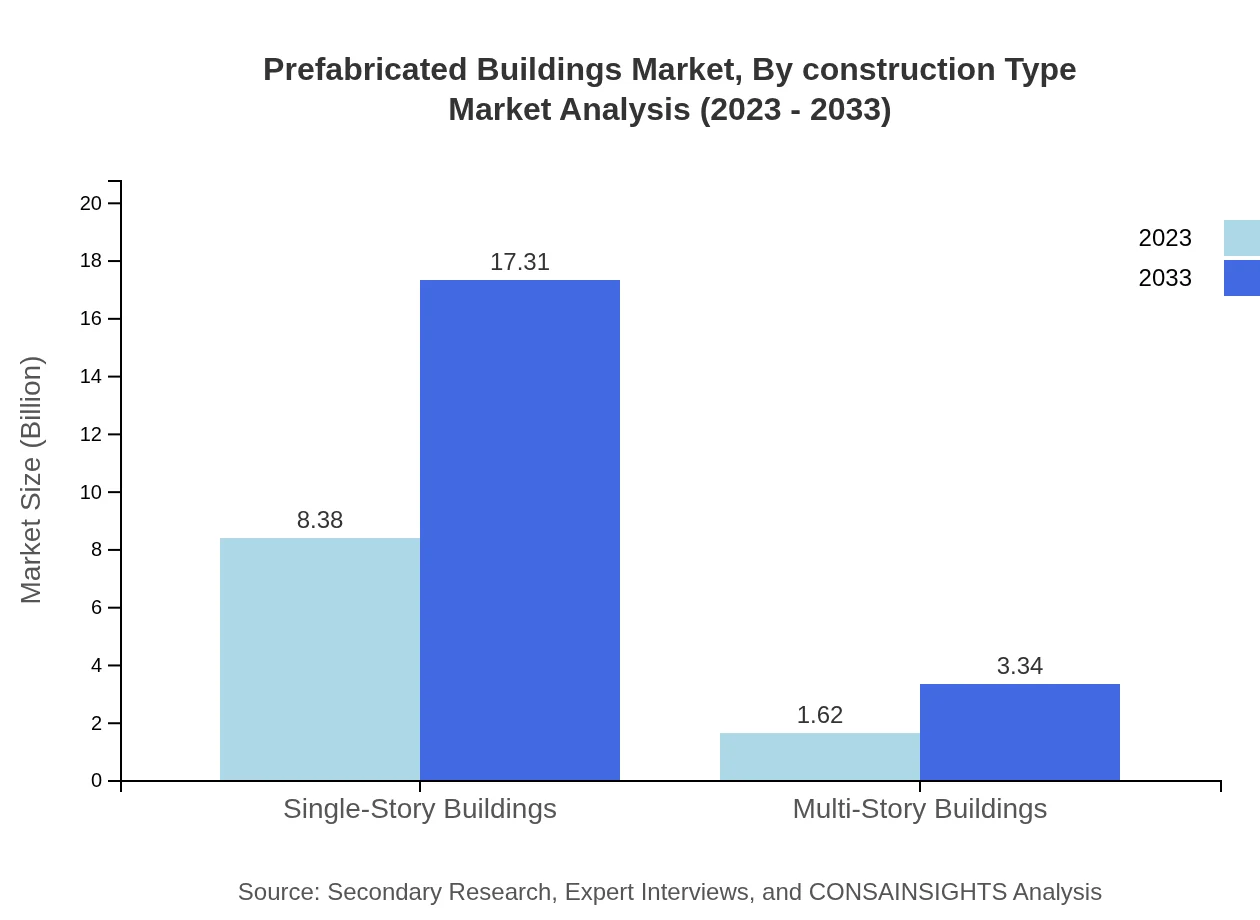
Prefabricated Buildings Market Analysis By Construction Type
Single-story buildings represent the predominant construction type, valued at USD 8.38 billion in 2023 with consistent growth to USD 17.31 billion by 2033. Multi-story buildings, while smaller in size, show growth potential as urban areas continue to expand and require space-efficient solutions.
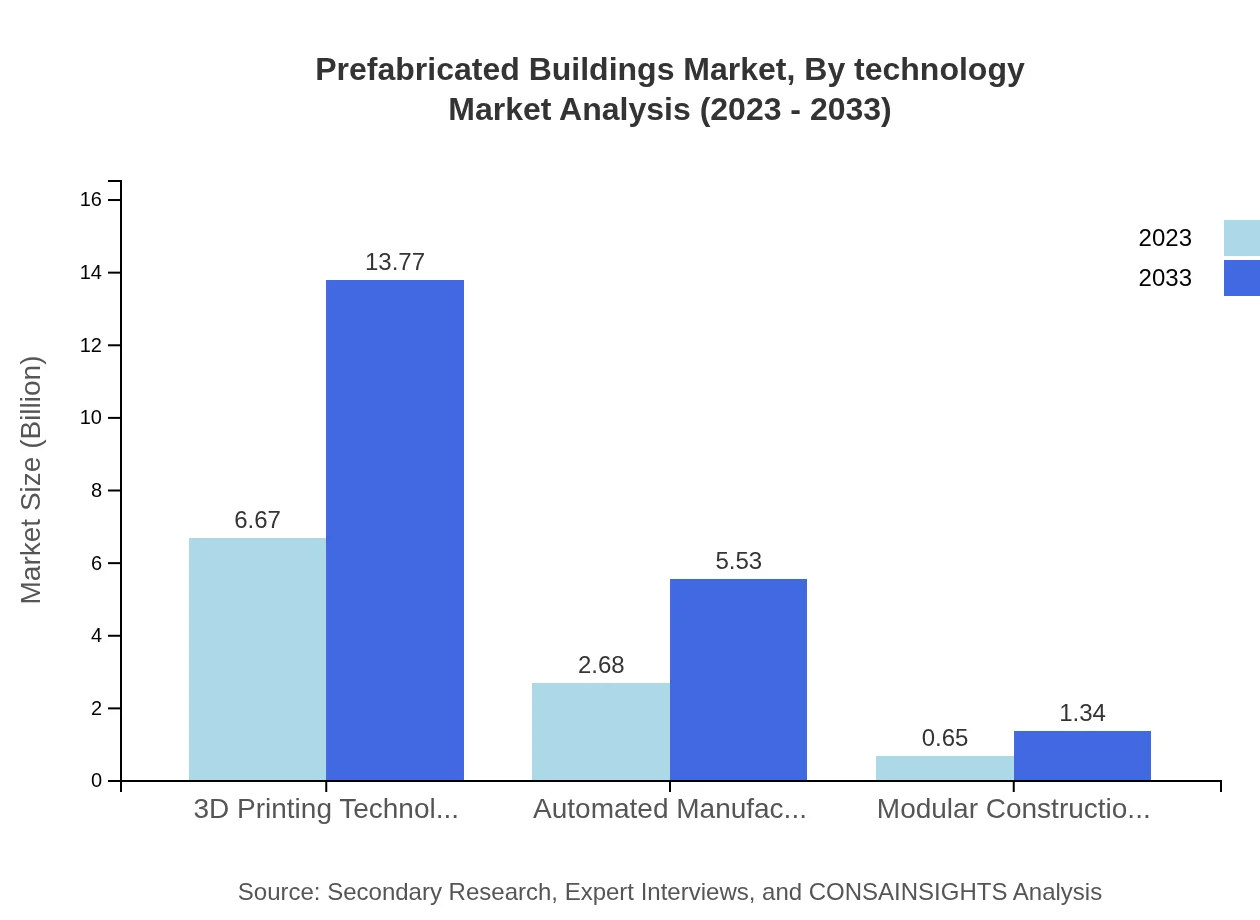
Prefabricated Buildings Market Analysis By Technology
Innovative technologies, including modular construction and automated manufacturing, dominate market trends. The advent of 3D printing technology is increasingly applied, contributing to efficiency and customization in prefabricated solutions, with both segments forecasted to see substantial growth through 2033.
Prefabricated Buildings Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in the Prefabricated Buildings Industry
Modular Space Corporation:
A leader in the modular building industry, offering innovative, flexible solutions for commercial and educational sectors.Katerra Inc.:
A technology-driven construction firm specializing in prefabricated components and sustainable building practices.Lendlease Group:
An international property and infrastructure group known for its commitment to sustainability and high-quality prefabricated buildings.Guerdon Enterprises LLC:
A leading manufacturer of modular buildings, focusing on residential solutions and large commercial projects.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of prefabricated buildings?
The prefabricated buildings market size is projected to reach approximately $10 billion by 2033, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% from 2023 to 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the prefabricated buildings industry?
Key players in the prefabricated buildings industry include major construction firms, modular building manufacturers, and engineering companies specializing in prefabrication technology. These firms are driving innovation and expanding market presence.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the prefabricated buildings industry?
Growth is driven by increasing demand for affordable housing, advancements in manufacturing technologies, sustainability trends, and the need for rapid construction solutions to meet urbanization challenges.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the prefabricated buildings market?
The Asia Pacific region is anticipated to be the fastest-growing market, with projected growth from $1.88 billion in 2023 to $3.87 billion by 2033, showcasing rising urbanization and infrastructure development.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the prefabricated buildings industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the specific needs of clients within the prefabricated buildings industry, allowing for detailed insights into market trends and dynamics.
What deliverables can I expect from this prefabricated buildings market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis reports, segmented data, growth forecasts, competitive landscape assessment, and valuable insights tailored to inform strategic business decisions.
What are the market trends of prefabricated buildings?
Key market trends include the rise of modular construction, increased adoption of sustainable materials, advancements in automation, and growing demand for urban development solutions that allow for quicker and cost-effective building solutions.