Private Equity Market Report
Published Date: 24 January 2026 | Report Code: private-equity
Private Equity Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Private Equity market, covering trends, market size, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It examines key segments, regional insights, and industry leaders, offering valuable data for investors and stakeholders.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
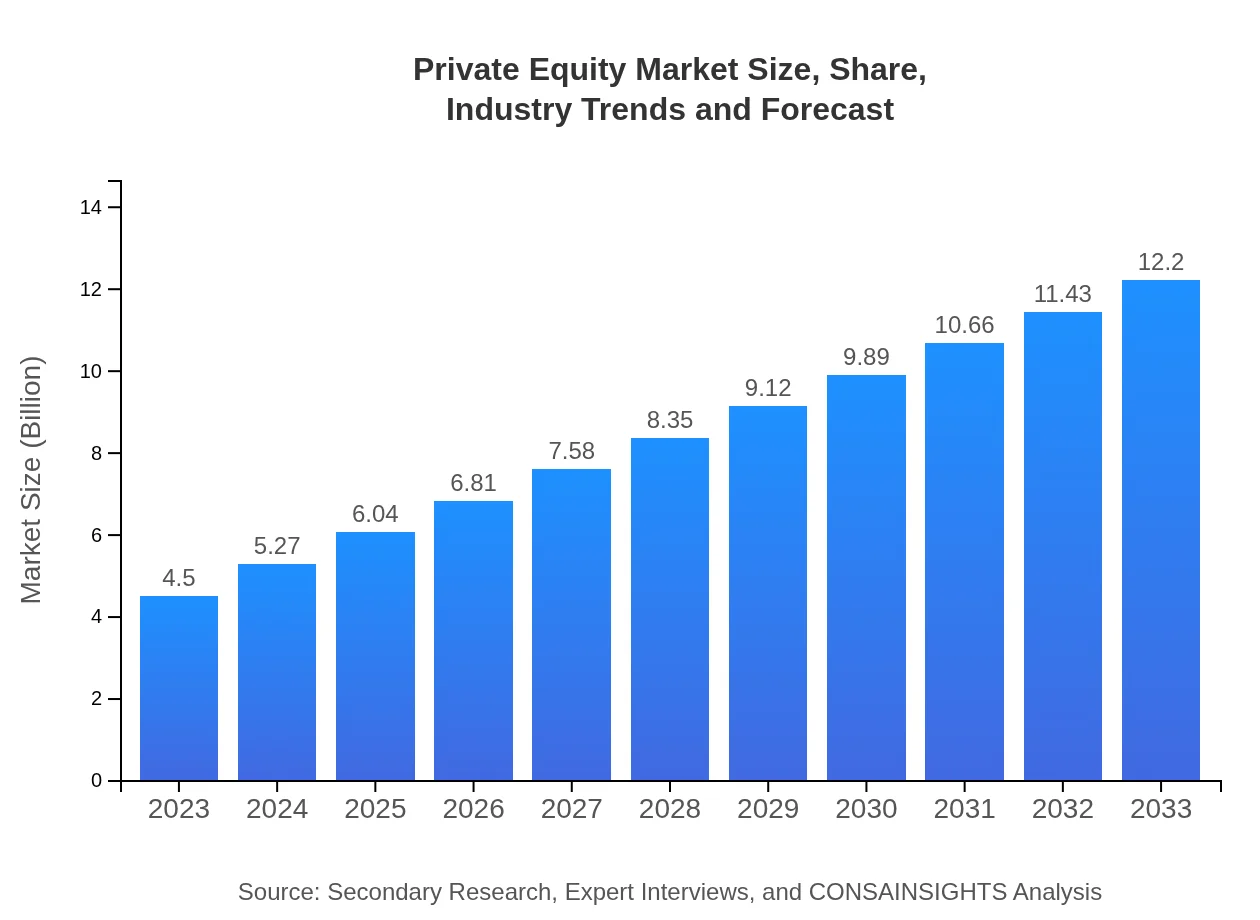
| 2023 Market Size | $4.50 Trillion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 10.1% |
| 2033 Market Size | $12.20 Trillion |
| Top Companies | Blackstone Group, Carlyle Group, KKR, Bain Capital |
| Last Modified Date | 24 January 2026 |
Private Equity Market Overview
Customize Private Equity Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Private Equity market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Private Equity's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Private Equity
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Private Equity market in 2023?
Private Equity Industry Analysis
Private Equity Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Private Equity Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Private Equity Market Report:
The European Private Equity market is expected to grow from $1.34 trillion in 2023 to $3.63 trillion by 2033. The region benefits from a diverse economic landscape and strong institutional support for PE investments. Factors such as economic recovery post-COVID-19, increased venture funding, and regulatory support contribute to this positive trajectory.Asia Pacific Private Equity Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Private Equity market is estimated to grow from $0.85 trillion in 2023 to $2.30 trillion by 2033. This growth is attributed to the rapidly expanding economies, increasing consumer markets, and a rise in tech startups attracting substantial investments. Furthermore, regulatory reforms and an increasing acceptance of PE as a viable investment option contribute positively to this trend.North America Private Equity Market Report:
North America remains the largest market for Private Equity, expected to rise from $1.65 trillion in 2023 to $4.48 trillion by 2033. Key factors driving this growth include the strong performance of technology and healthcare sectors, a favorable fundraising climate, and sustained private equity interest in acquisitions. The US remains the powerhouse, with many firms established in this region pursuing diverse strategies.South America Private Equity Market Report:
South America's Private Equity market is projected to increase from $0.28 trillion in 2023 to $0.76 trillion in 2033. Though smaller compared to other regions, this market presents considerable opportunities in infrastructure and consumer sectors. The region has seen increasing interest from global investors, spurred by improving political stability and economic recovery.Middle East & Africa Private Equity Market Report:
The Private Equity market in the Middle East and Africa is anticipated to expand from $0.38 trillion in 2023 to $1.03 trillion by 2033. The growth is driven by economic diversification strategies in Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries and increasing private equity penetration in African markets, made possible by attractive sectors such as fintech and natural resources.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
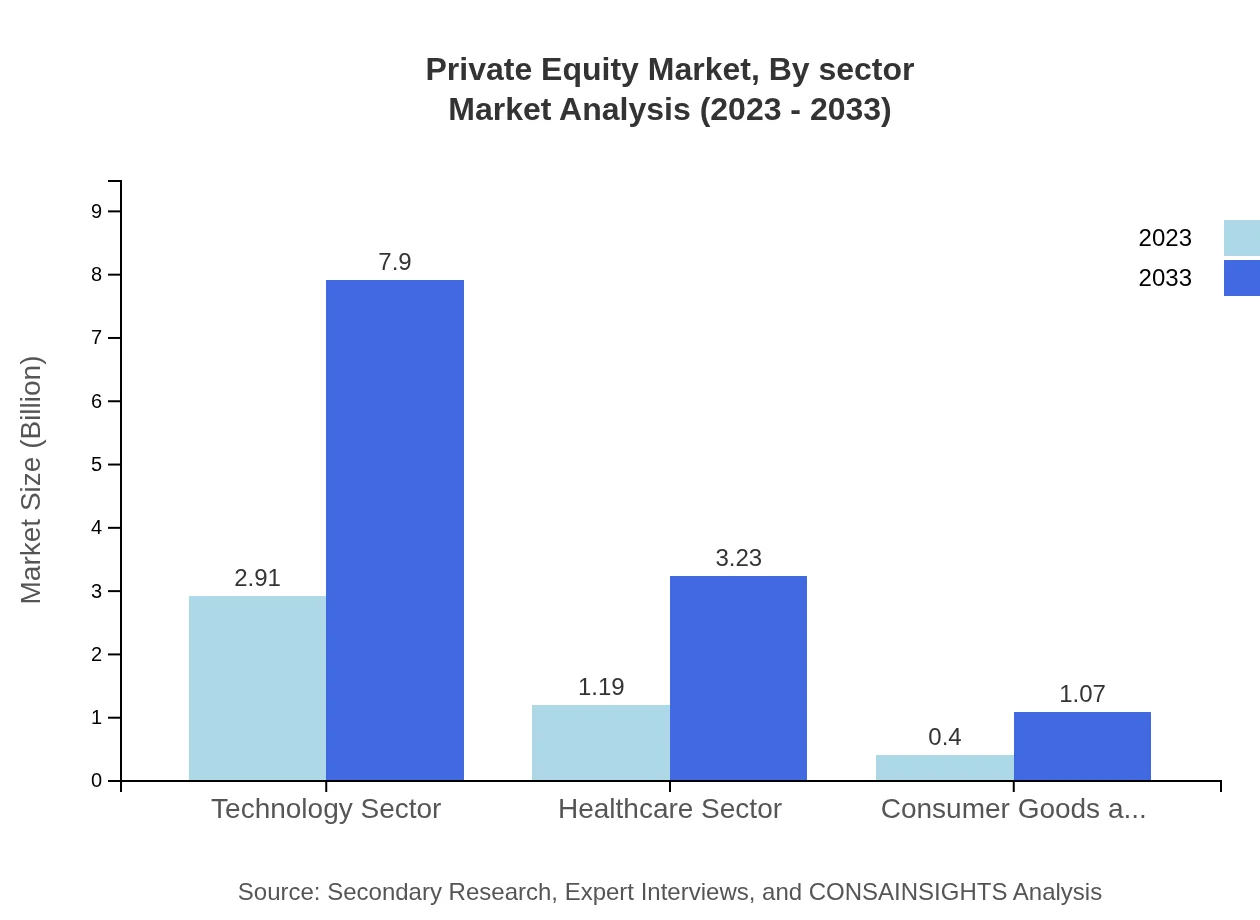
Private Equity Market Analysis By Sector
The sector analysis indicates that technology remains the largest segment, with a market size of $2.91 trillion in 2023, set to reach $7.90 trillion by 2033. The healthcare sector follows with a projected growth from $1.19 trillion to $3.23 trillion, driven by innovative healthcare solutions and expanded services. Consumer goods also show an upward trend from $0.40 trillion to $1.07 trillion, reflecting changing consumer behaviors.
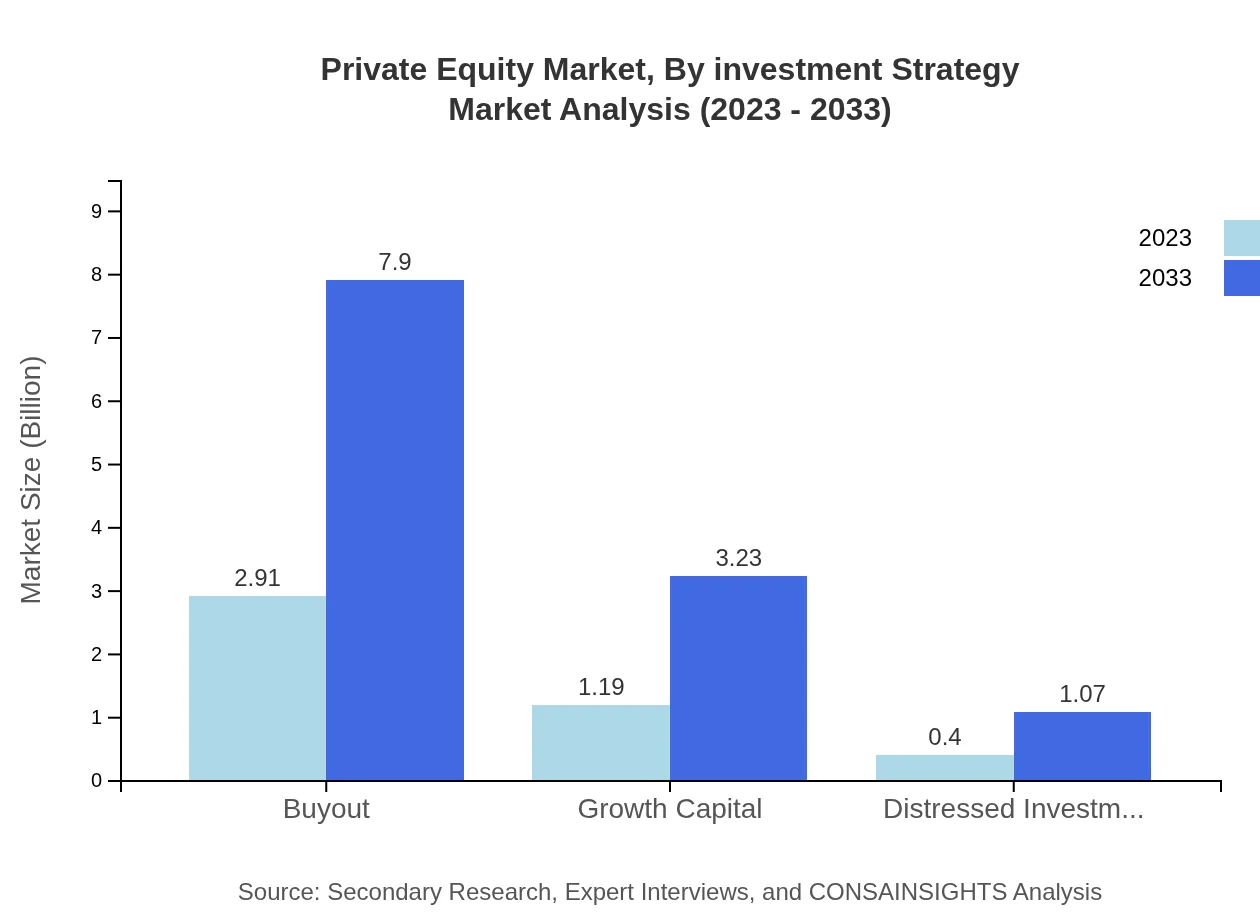
Private Equity Market Analysis By Investment Strategy
Investment strategy segmentation reveals significant potential in buyout funds, forecasting growth from $1.19 trillion in 2023 to $3.23 trillion by 2033. Growth capital, distressed investments, and venture capital are also key components of the landscape, with similar growth patterns reflecting strong investor demand for these strategies.
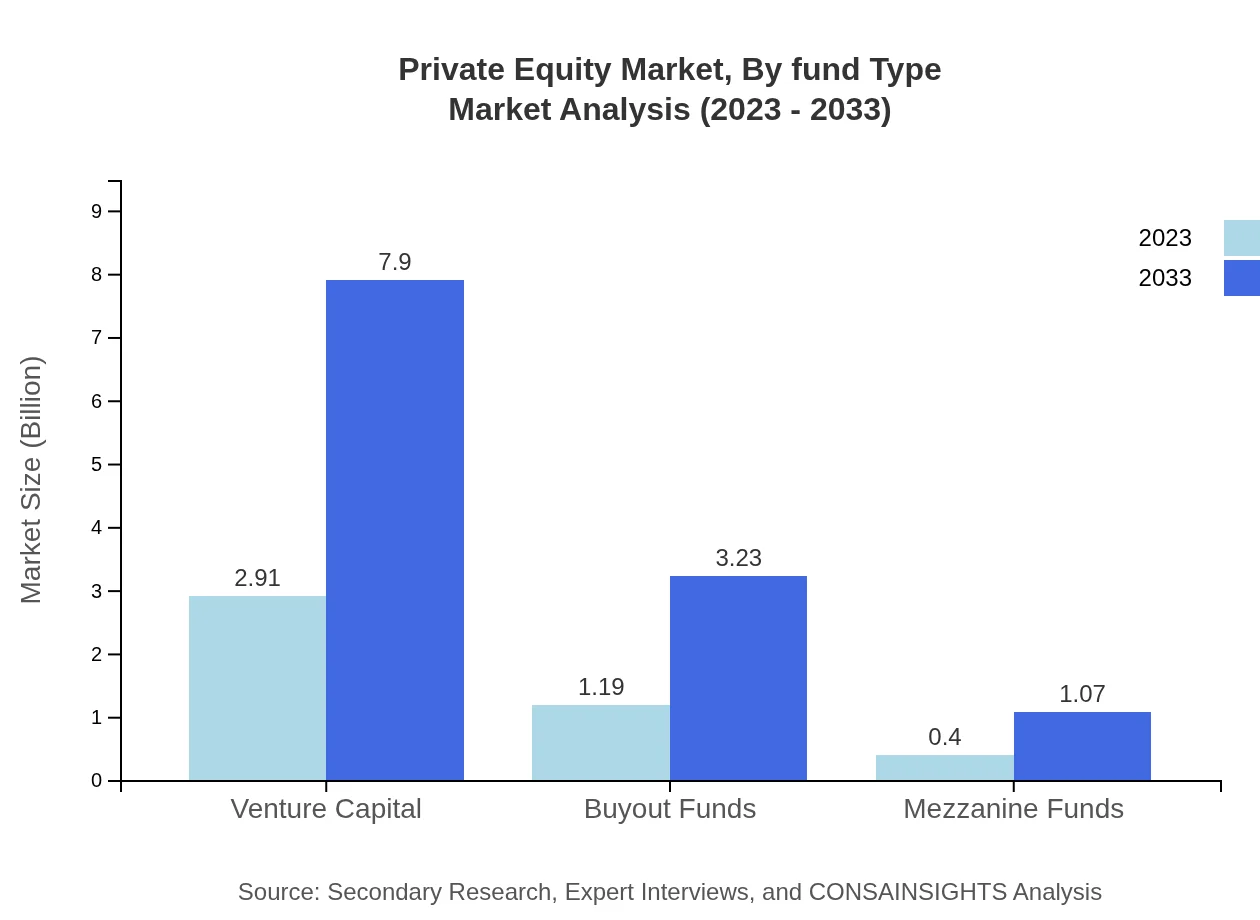
Private Equity Market Analysis By Fund Type
Funds are classified into various types, including mezzanine, growth capital, and buyout funds. Overall, the growth in fund types such as growth capital and buyouts signifies a versatile approach. For instance, growth capital is expected to rise from $1.19 trillion in 2023 to $3.23 trillion by 2033.
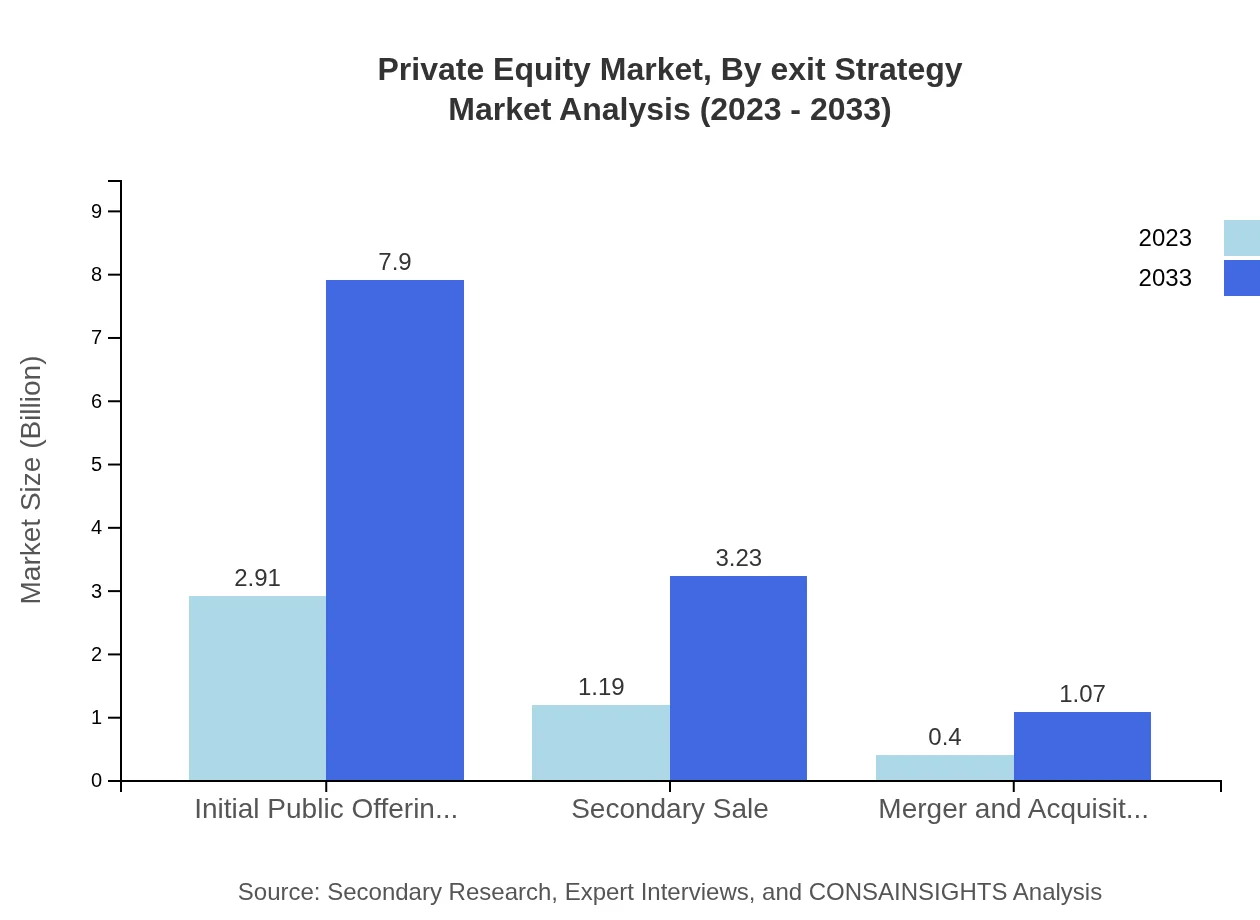
Private Equity Market Analysis By Exit Strategy
The exit strategies drive market dynamics. Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) dominate the exit strategy market, projected to grow from $2.91 trillion in 2023 to $7.90 trillion by 2033. Secondary sales and mergers/acquisitions are also prominent exit strategies for value realization, affecting overall fund performance.
Private Equity Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Private Equity Industry
Blackstone Group:
As one of the largest private equity firms globally, Blackstone specializes in leveraged buyouts and real estate investments, driving substantial returns for its investors.Carlyle Group:
The Carlyle Group is a multinational investment firm focusing on private equity, real assets, and private credit, known for its wide range of investment portfolios across various sectors.KKR:
KKR operates as a global investment firm and is notable for its advanced strategies in private equity and leveraged buyouts while actively investing in sustainable companies.Bain Capital:
Bain Capital partners with its portfolio companies to unlock growth potential and drive improvements in operations with a focus on delivering long-term success.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of private Equity?
The global private equity market is currently valued at approximately $4.5 trillion, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.1% over the next decade, which indicates robust growth and increasing investments in this sector.
What are the key market players or companies in this private Equity industry?
Key players in the private equity landscape include firms like Blackstone Group, Carlyle Group, KKR & Co., Apollo Global Management, and Bain Capital, each contributing significantly to capital deployment and market dynamics.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the private Equity industry?
Growth in private equity is driven by factors such as increased institutional investments, favorable market conditions for buyouts, and rising demand for alternative asset classes as investors seek higher returns and diversification.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the private Equity?
The North America region is the fastest-growing in the private equity market, projected to expand from $1.65 trillion in 2023 to $4.48 trillion by 2033, supported by a strong ecosystem for venture capital and innovation.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the private Equity industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers tailored market report data for private equity, catering to specific client needs and providing in-depth analysis of market trends, segments, and strategic opportunities in the industry.
What deliverables can I expect from this private Equity market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables such as detailed market analysis reports, strategic insights, trend forecasts, regional and segment breakdowns, and actionable recommendations tailored to your specific business requirements.
What are the market trends of private Equity?
Market trends in private equity include increased focus on technology investments, growth in sustainable and impact investing, as well as diversification strategies, reflecting shifting investor preferences towards higher-impact ventures.