Process Control Automation Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: process-control-automation
Process Control Automation Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Process Control Automation market, including detailed insights, competitive landscape, and forecasts for the period 2023-2033. The report covers various segments, applications, technologies, and regional dynamics that shape the current market environment.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
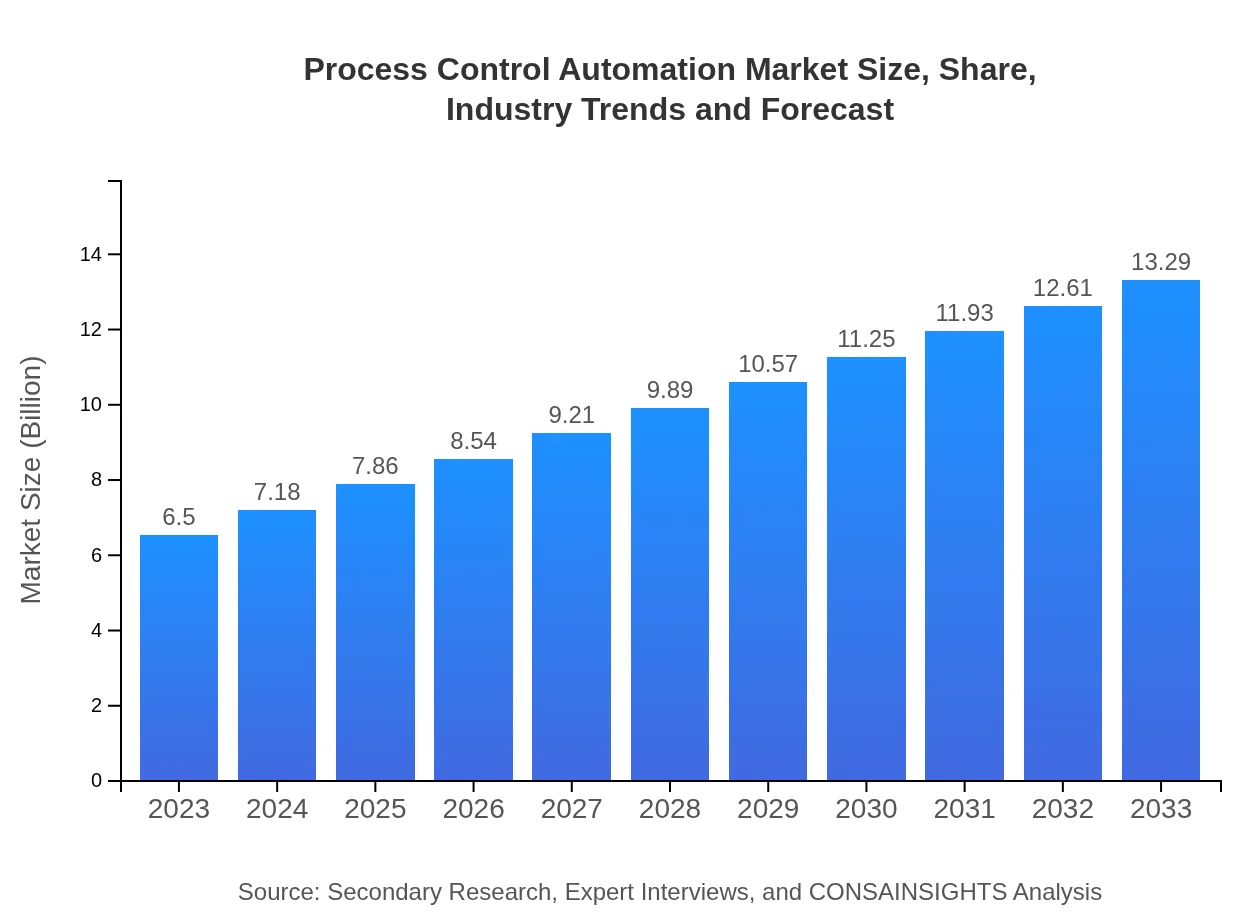
| 2023 Market Size | $6.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $13.29 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Rockwell Automation, Inc., Schneider Electric SE, Emerson Electric Co., Honeywell International Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Process Control Automation Market Overview
Customize Process Control Automation Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Process Control Automation market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Process Control Automation's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Process Control Automation
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Process Control Automation market in 2023?
Process Control Automation Industry Analysis
Process Control Automation Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Process Control Automation Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Process Control Automation Market Report:
Europe is expected to grow from $1.82 billion in 2023 to $3.71 billion by 2033, fueled by stringent regulations promoting process efficiency and the growing emphasis on Industry 4.0, which integrates smart technologies into traditional practices.Asia Pacific Process Control Automation Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is anticipated to experience remarkable growth, with the market expected to rise from $1.33 billion in 2023 to $2.73 billion by 2033. The region's economic expansion, increasing industrialization, and the push towards smart manufacturing technologies are key driving factors.North America Process Control Automation Market Report:
North America remains a dominant market for Process Control Automation, with a projected growth from $2.32 billion in 2023 to $4.74 billion by 2033. The high concentration of manufacturing activities, along with significant investments in technological innovations, drive robust market growth.South America Process Control Automation Market Report:
In South America, the Process Control Automation market is projected to grow from $0.33 billion in 2023 to $0.66 billion by 2033. The region is witnessing a gradual adoption of automation technologies, mainly in the automotive and energy sectors.Middle East & Africa Process Control Automation Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region is set to experience growth from $0.71 billion in 2023 to $1.44 billion by 2033, bolstered by investments in oil and gas, which utilize advanced process automation technologies to enhance operational efficiency.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Process Control Automation Market Analysis By Product Type
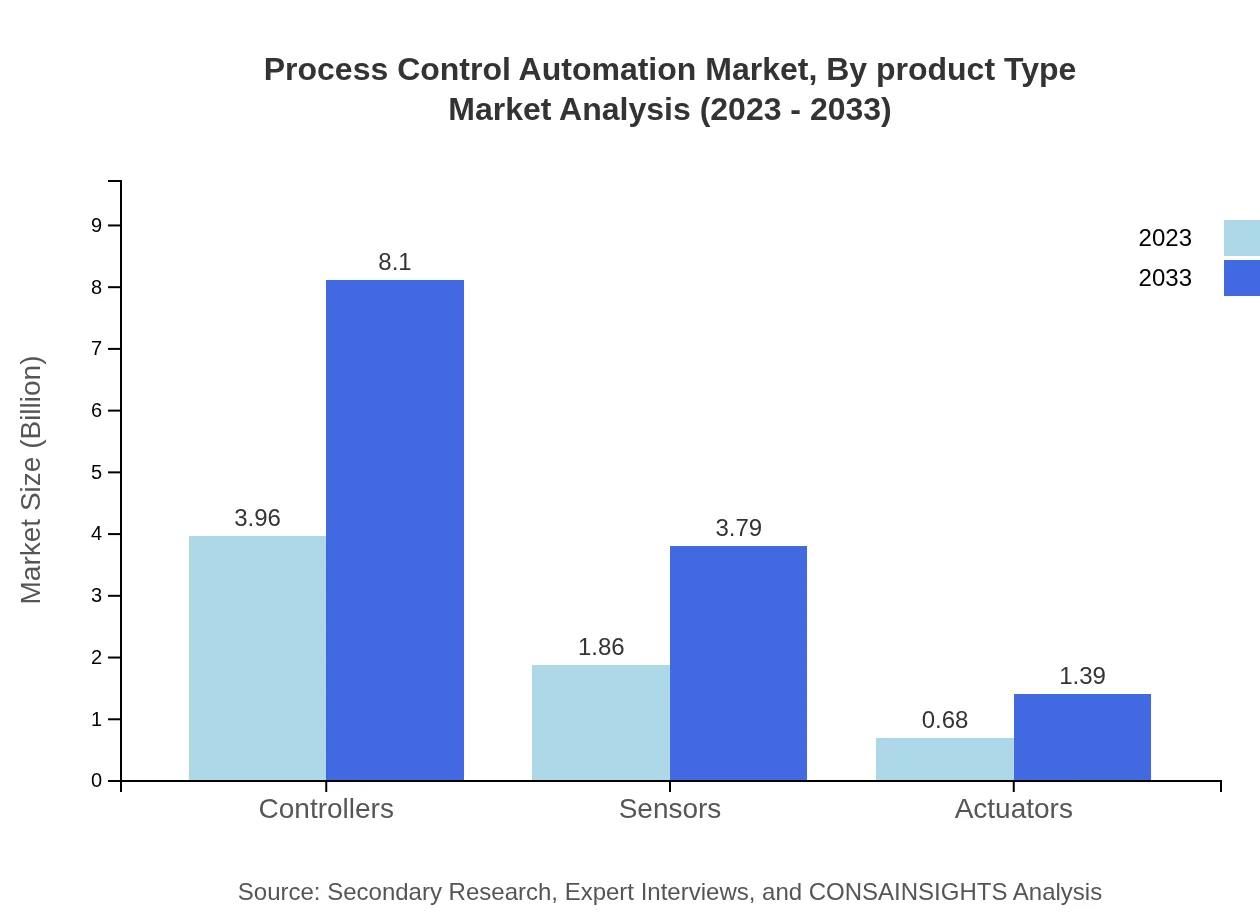
The product types in the Process Control Automation market include controllers, sensors, and actuators. In 2023, controllers lead the market at $3.96 billion (60.98% share), projected to grow to $8.10 billion by 2033. Sensors and actuators show growth trends as critical components in automation processes, with sensors expected to increase from $1.86 billion (28.55% share) to $3.79 billion. Actuators are also experiencing growth, forecasted to rise from $0.68 billion to $1.39 billion, reflecting the increasing demand for automated control in industries.
Process Control Automation Market Analysis By Application
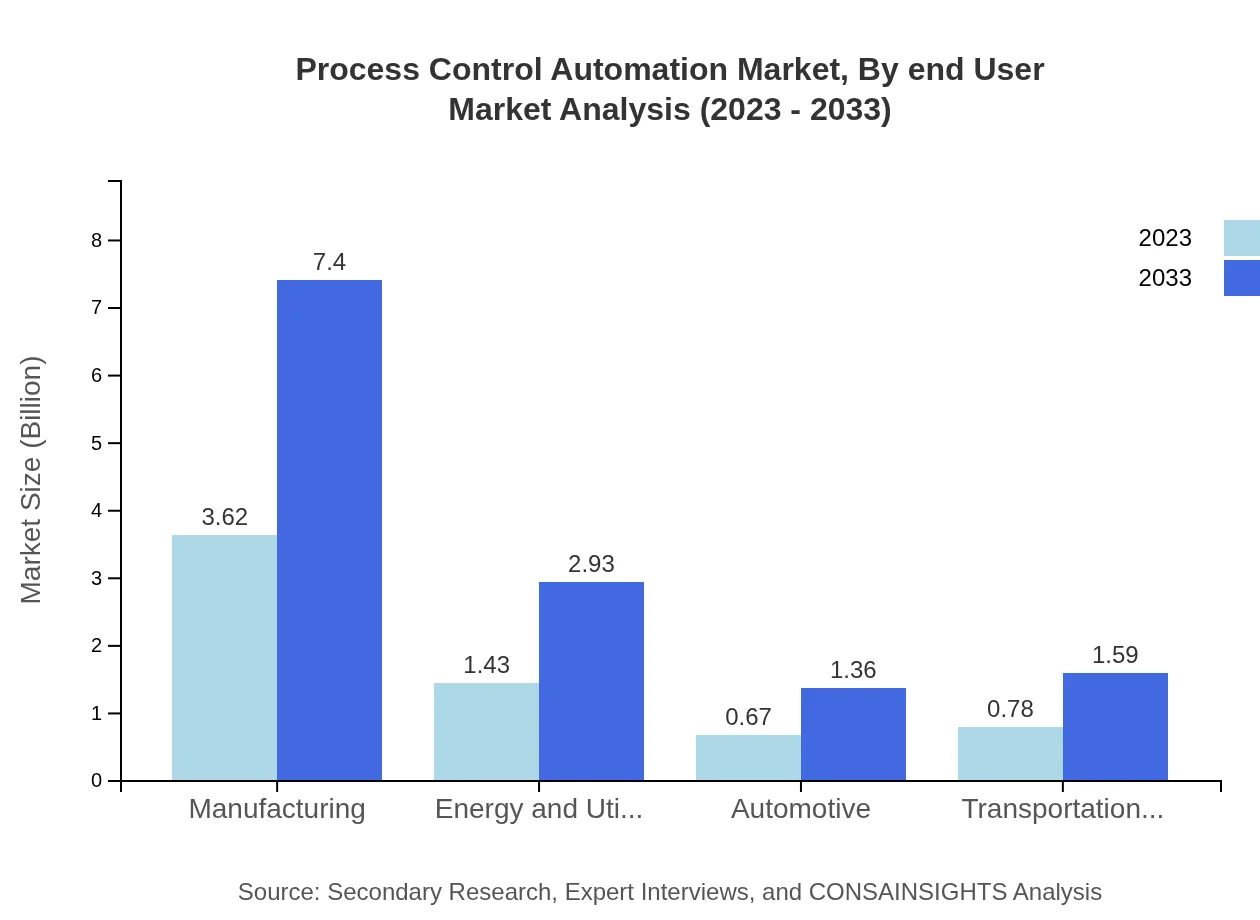
The market is significantly influenced by applications across various industries. Manufacturing comprises the largest segment, valued at $3.62 billion in 2023 (55.71% share), projected to double to $7.40 billion by 2033. Other significant sectors include energy and utilities, showing growth from $1.43 billion to $2.93 billion, and automotive, with expectations to rise from $0.67 billion to $1.36 billion, highlighting the versatility and critical nature of PCA across applications.
Process Control Automation Market Analysis By Technology
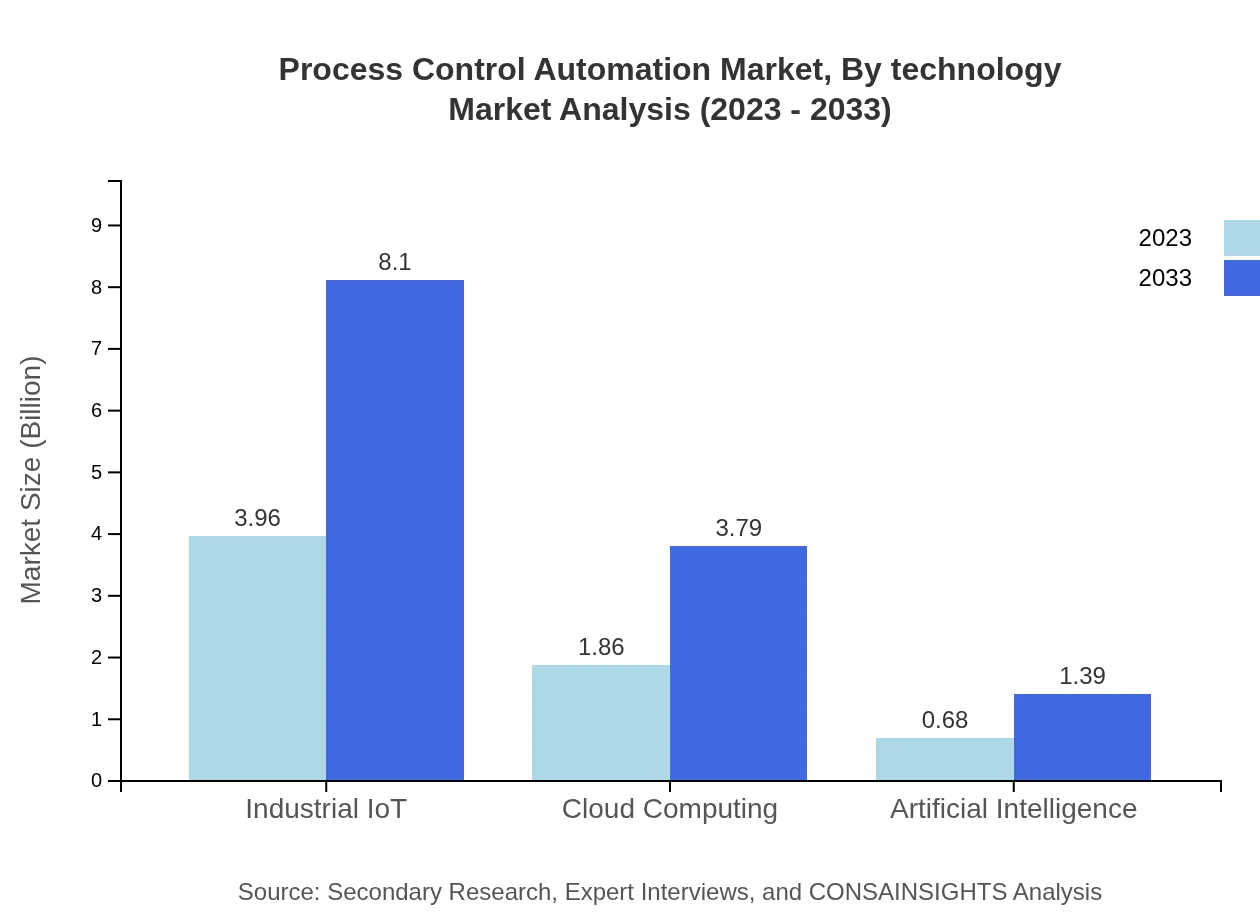
Technology plays a significant role in the Process Control Automation market. The integration of IIoT solutions, projected to grow from $3.96 billion in 2023 (60.98% market share) to $8.10 billion by 2033, shows the trend towards connected devices enhancing automation performance. Meanwhile, cloud computing technologies are expected to expand from $1.86 billion to $3.79 billion, further optimizing data handling and storage capabilities for automation systems.
Process Control Automation Market Analysis By End User
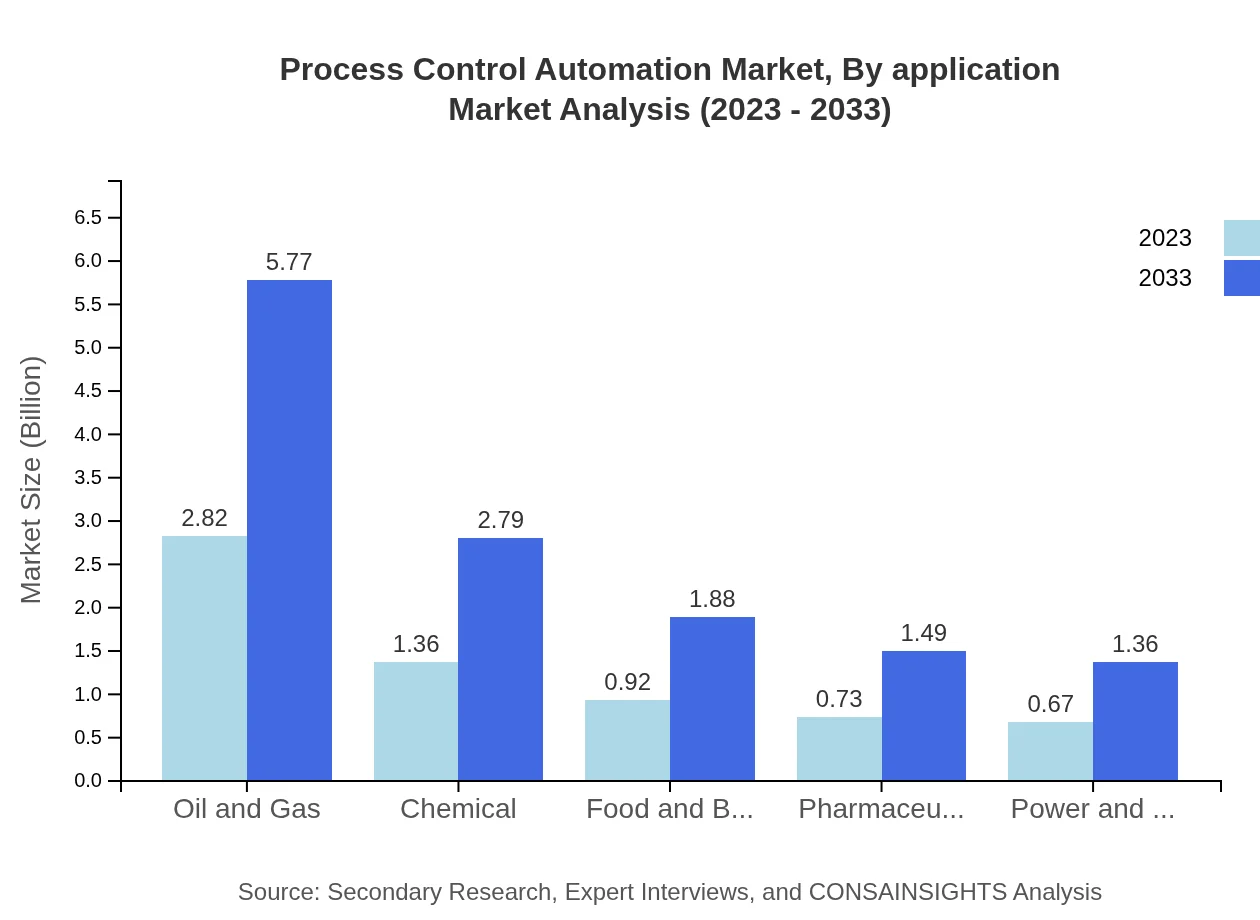
Key end-user industries include oil and gas, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals. The oil and gas segment dominates the space with $2.82 billion in 2023 and projected to reach $5.77 billion by 2033 (43.39% market share), reflecting the sector's significant reliance on automation for efficiency. The chemical industry and food and beverage sectors are also critical, expected to grow steadily, underscoring the expansive nature of automation across diverse industrial applications.
Process Control Automation Market Analysis By Controller Type
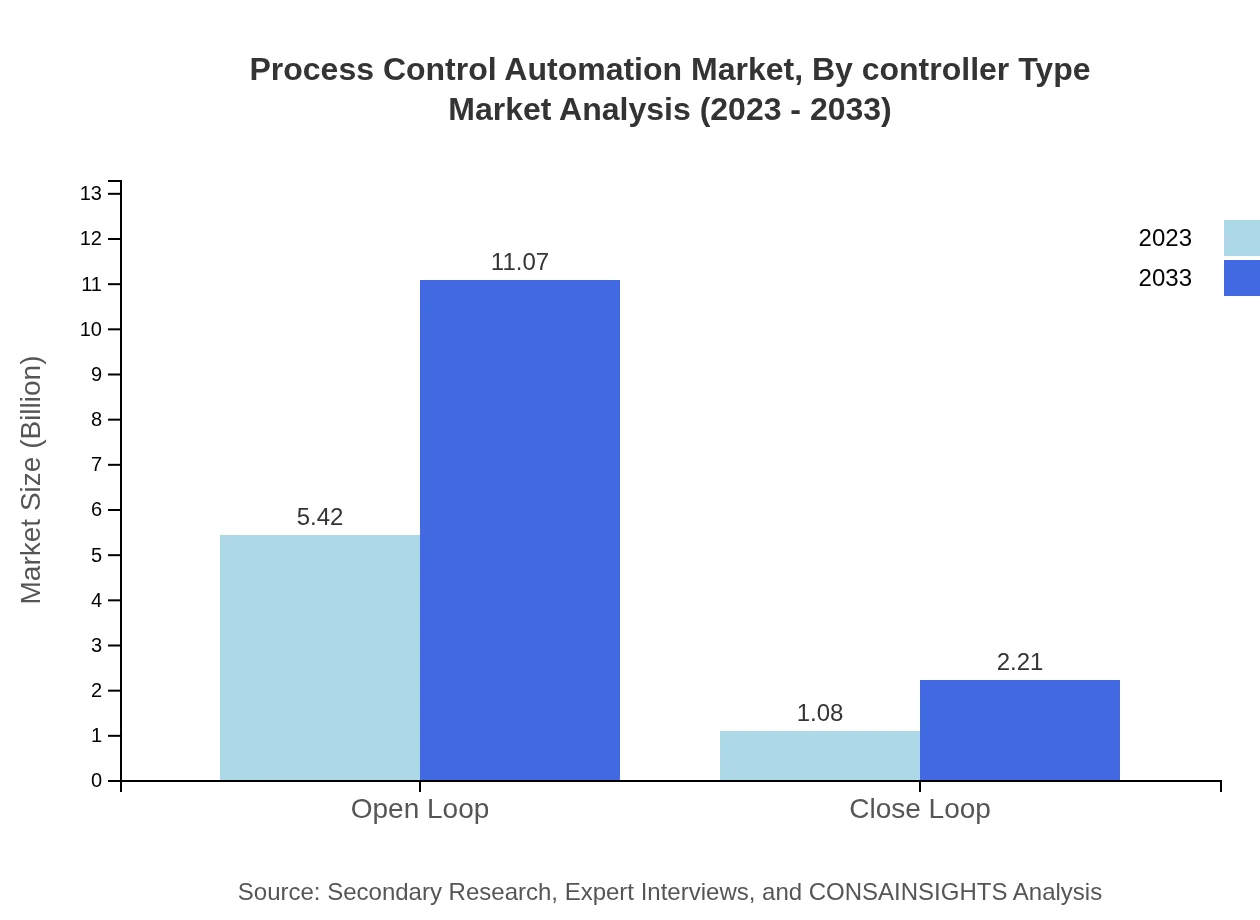
The Process Control Automation market is predominantly driven by open-loop controllers, expected to rise from $5.42 billion in 2023 (83.33% share) to $11.07 billion by 2033. Closed-loop systems, while smaller, are also projected to grow from $1.08 billion to $2.21 billion, emphasizing the increased demand for precision and accuracy in process control systems.
Process Control Automation Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Process Control Automation Industry
Siemens AG:
Siemens AG is a global technology company that provides innovative automation solutions. Their products focus on industrial digitalization and smart manufacturing, making them a leader in the PCA market.Rockwell Automation, Inc.:
Rockwell Automation specializes in providing automation and information solutions. Their offerings enhance productivity and efficiency, making them a key player in the process control sector.Schneider Electric SE:
Schneider Electric is a leading global specialist in energy management and automation. Their advanced automation solutions are pivotal for optimizing industrial processes.Emerson Electric Co.:
Emerson Electric provides process control solutions that enhance operational efficiencies. Their technological innovations support the reliability of industrial processes.Honeywell International Inc.:
Honeywell is renowned for its automation technologies that improve safety, security, and efficiency across various industries, solidifying its position in the PCA market.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Process Control Automation?
The Process Control Automation market is currently valued at approximately $6.5 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% leading to substantial market expansion by 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the Process Control Automation industry?
Key players in the Process Control Automation market include major corporations known for automation solutions and technologies, though specific names and market shares would be detailed in a comprehensive report.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Process Control Automation industry?
Factors driving growth in the Process Control Automation industry include technological advancements, heightened demand for efficiency, regulatory compliance needs, and the integration of AI and IoT technologies.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Process Control Automation?
North America leads as the fastest-growing region in the Process Control Automation market, with a market size expected to rise from $2.32 billion in 2023 to $4.74 billion by 2033.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Process Control Automation industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the Process Control Automation industry, ensuring relevant insights for strategic decisions.
What deliverables can I expect from this Process Control Automation market research project?
Deliverables from the Process Control Automation market research project typically include a comprehensive report, data tables, trends analysis, and insights on market segmentation and forecasts.
What are the market trends of Process Control Automation?
Current trends in the Process Control Automation market include growing adoption of Industrial IoT, AI integration, and increasing investments in smart manufacturing practices.