Propane Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: propane
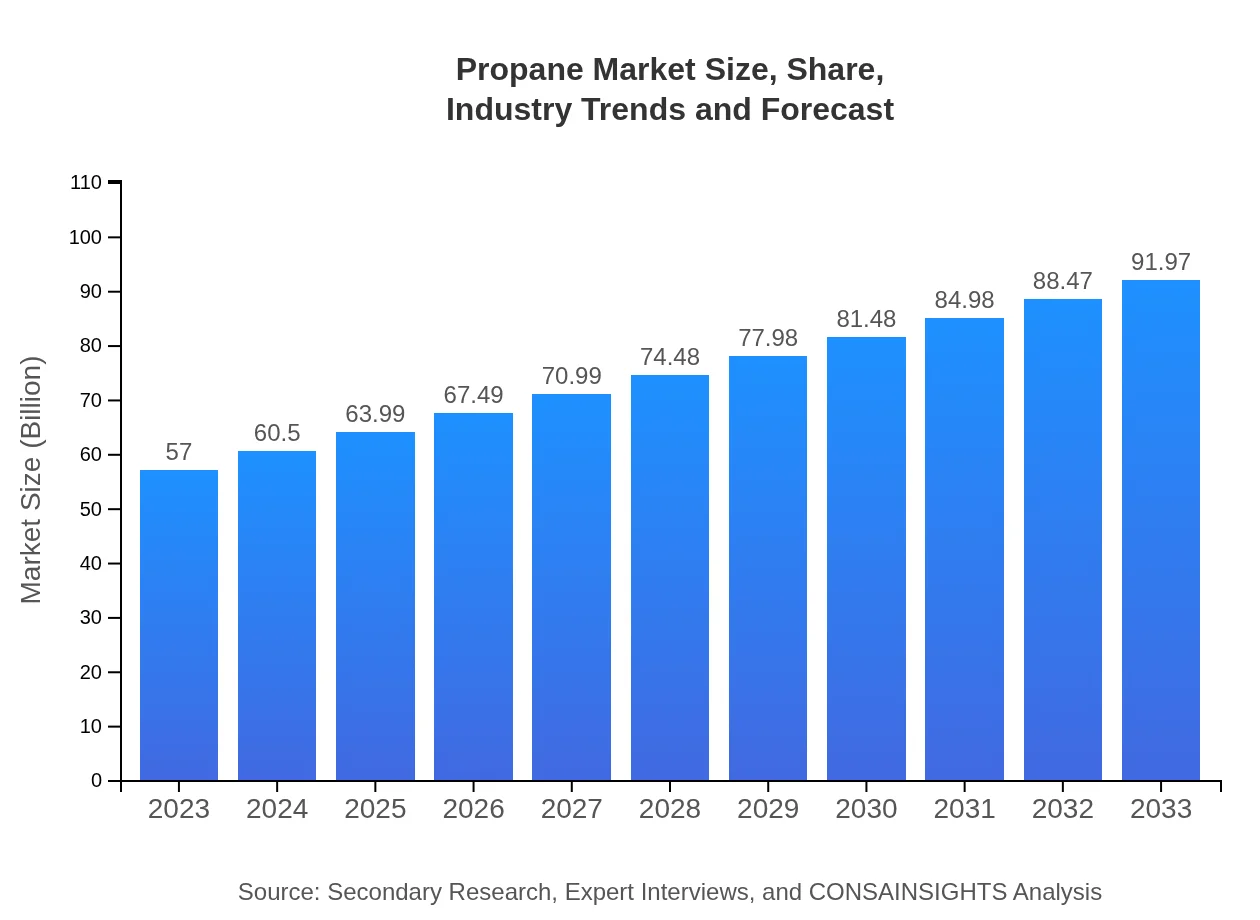
Propane Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report delivers a comprehensive analysis of the propane market, exploring insights, trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. Key highlight areas include market size, industry dynamics, regional performance, and segmentation analysis.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $57.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $91.97 Billion |
| Top Companies | AmeriGas Partners, L.P., U.S. Propane, LLC, Ferrellgas Partners, L.P., Suburban Propane Partners, L.P. |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Propane Market Overview
Customize Propane Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Propane market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Propane's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Propane
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Propane market in 2023?
Propane Industry Analysis
Propane Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
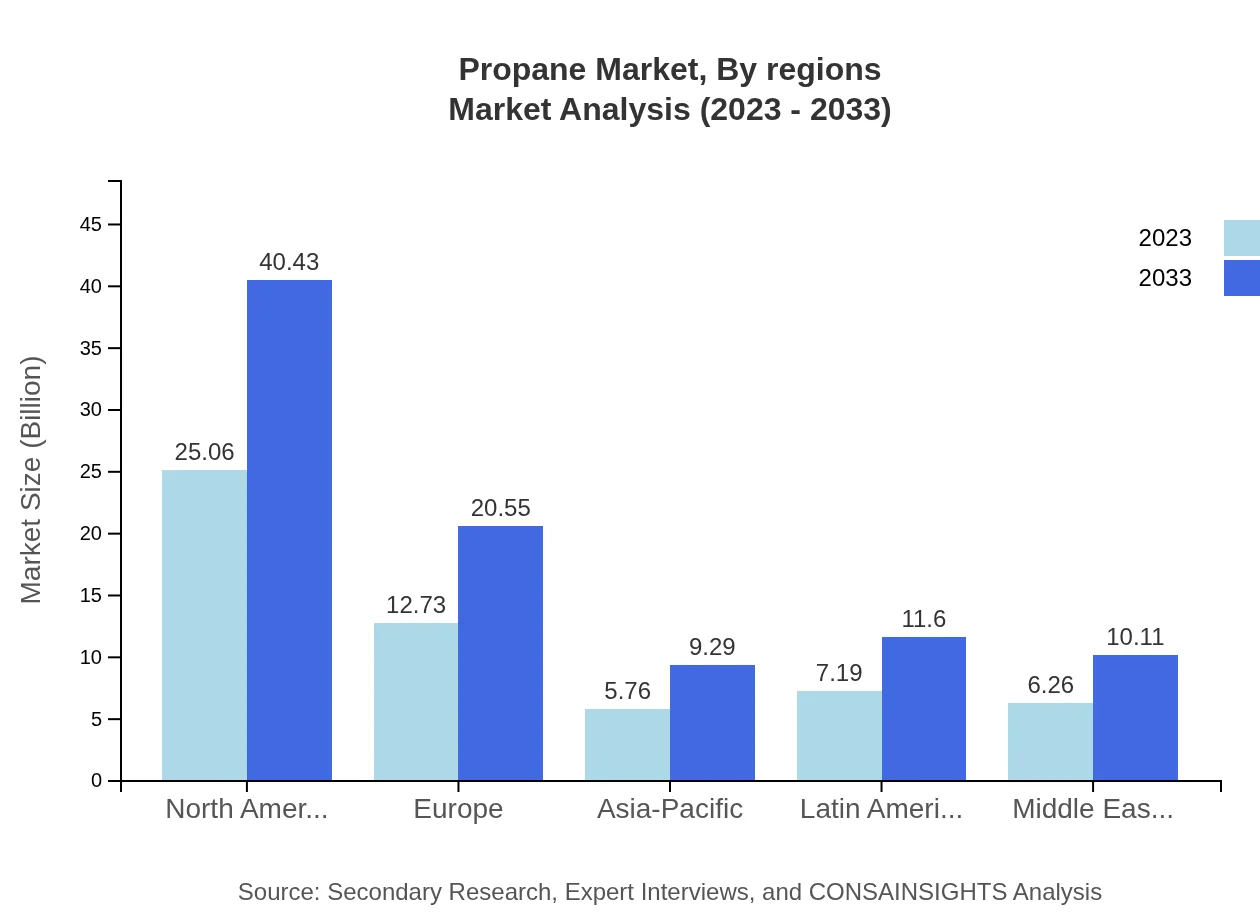
Propane Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Propane Market Report:
The European market for propane is forecasted to expand from USD 14.55 billion in 2023 to USD 23.48 billion by 2033. This growth is largely influenced by stringent environmental regulations favoring cleaner fuels, coupled with an increasing shift away from coal. Countries like Germany and France are at the forefront of this shift.Asia Pacific Propane Market Report:
In the Asia-Pacific region, the propane market is anticipated to grow from USD 11.75 billion in 2023 to USD 18.96 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by increasing industrial activities and a heightened focus on clean energy solutions, particularly in countries like China and India. Propane is favored for its versatility in applications ranging from residential heating to automotive fuel.North America Propane Market Report:
North America dominates the global propane market, with a size of USD 20.67 billion in 2023 expected to grow to USD 33.35 billion by 2033. The U.S. and Canada are leading this trend through increased production from shale gas and robust applications in both residential and industrial sectors, alongside government incentives for propane technologies.South America Propane Market Report:
The South American propane market, valued at USD 4.10 billion in 2023, is projected to reach USD 6.62 billion by 2033, driven by rising energy demands and an increasing preference for liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) as a cleaner energy source. Brazil remains the largest market in the region, driven by economic growth and expanded infrastructure.Middle East & Africa Propane Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the propane market size in 2023 is estimated at USD 5.92 billion and is projected to reach USD 9.56 billion by 2033. The region is witnessing growth due to increased exploration of natural gas resources and its applications in various sectors, alongside favorable government policies promoting natural gas utilization.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
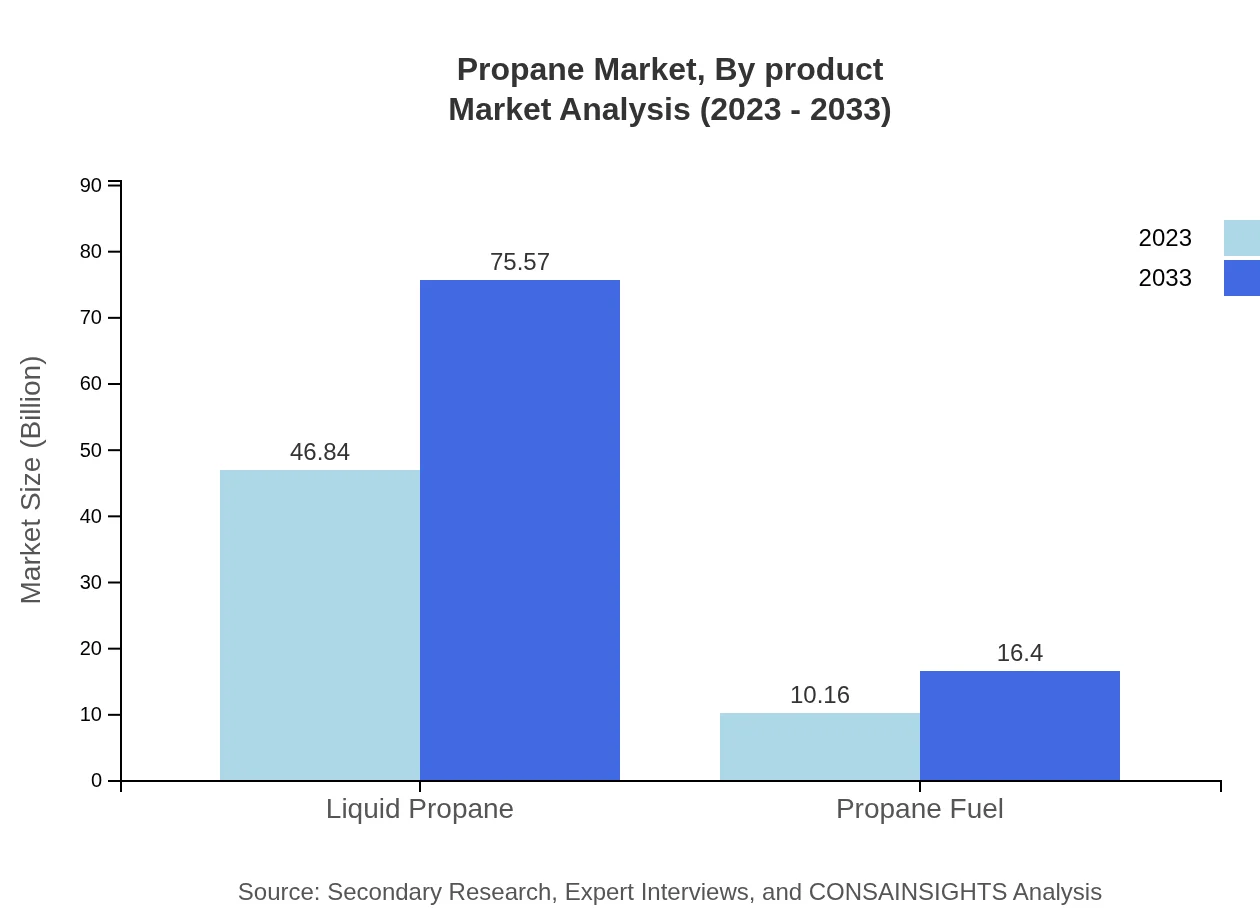
Propane Market Analysis By Product
The liquid propane segment, valued at USD 46.84 billion in 2023, is projected to grow to USD 75.57 billion by 2033, highlighting its significant share in the market. In comparison, propane fuel is valued at USD 10.16 billion in 2023, expected to increase to USD 16.40 billion by 2033. Liquid propane maintains a dominant market position due to its widespread applications in heating, cooking, and as a transportation fuel.
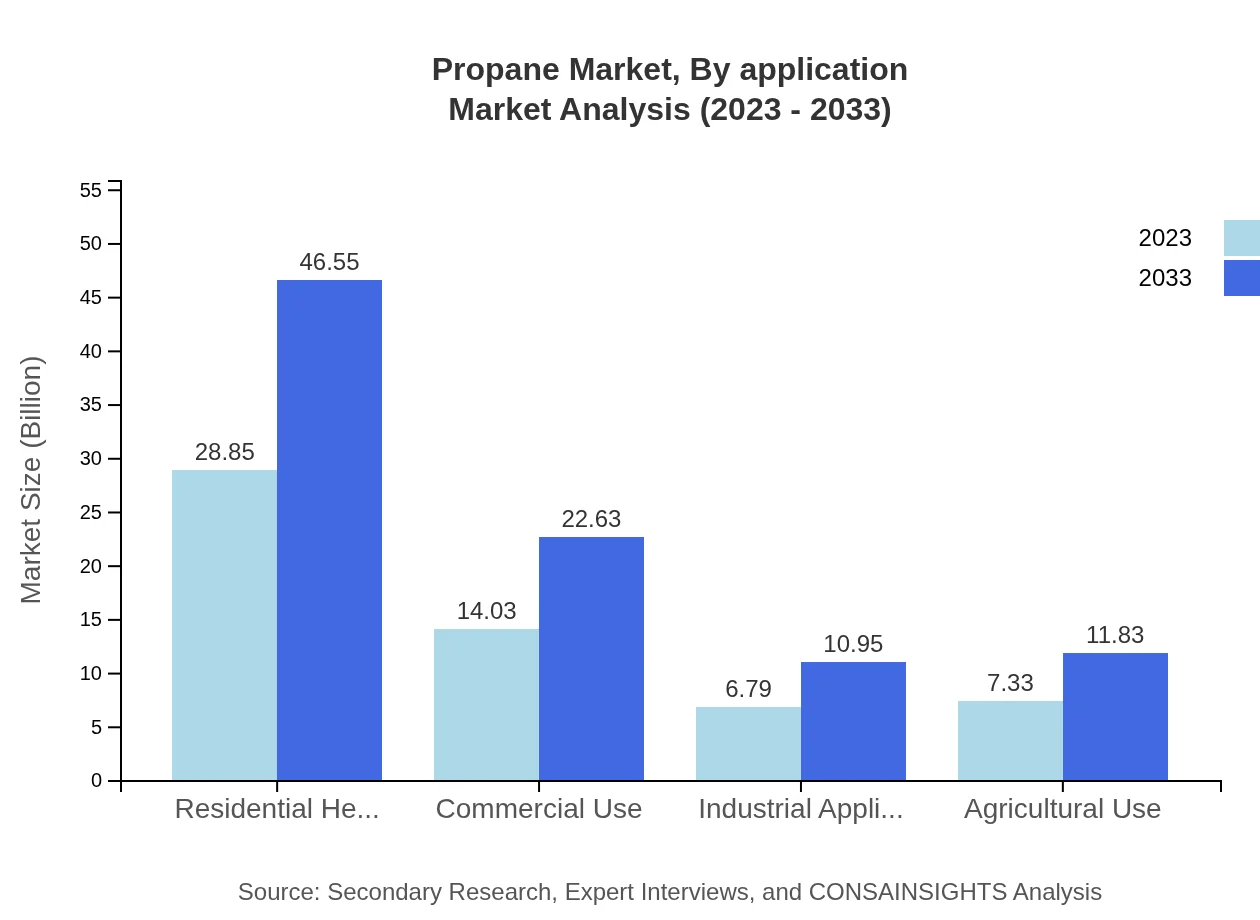
Propane Market Analysis By Application
In terms of applications, the residential sector leads with a size of USD 28.85 billion in 2023, predicted to achieve USD 46.55 billion by 2033, mainly due to increasing energy demands for domestic heating and cooking. The commercial sector is projected to grow significantly from USD 14.03 billion in 2023 to USD 22.63 billion by 2033, driven by the rising adoption of propane in various commercial operations.
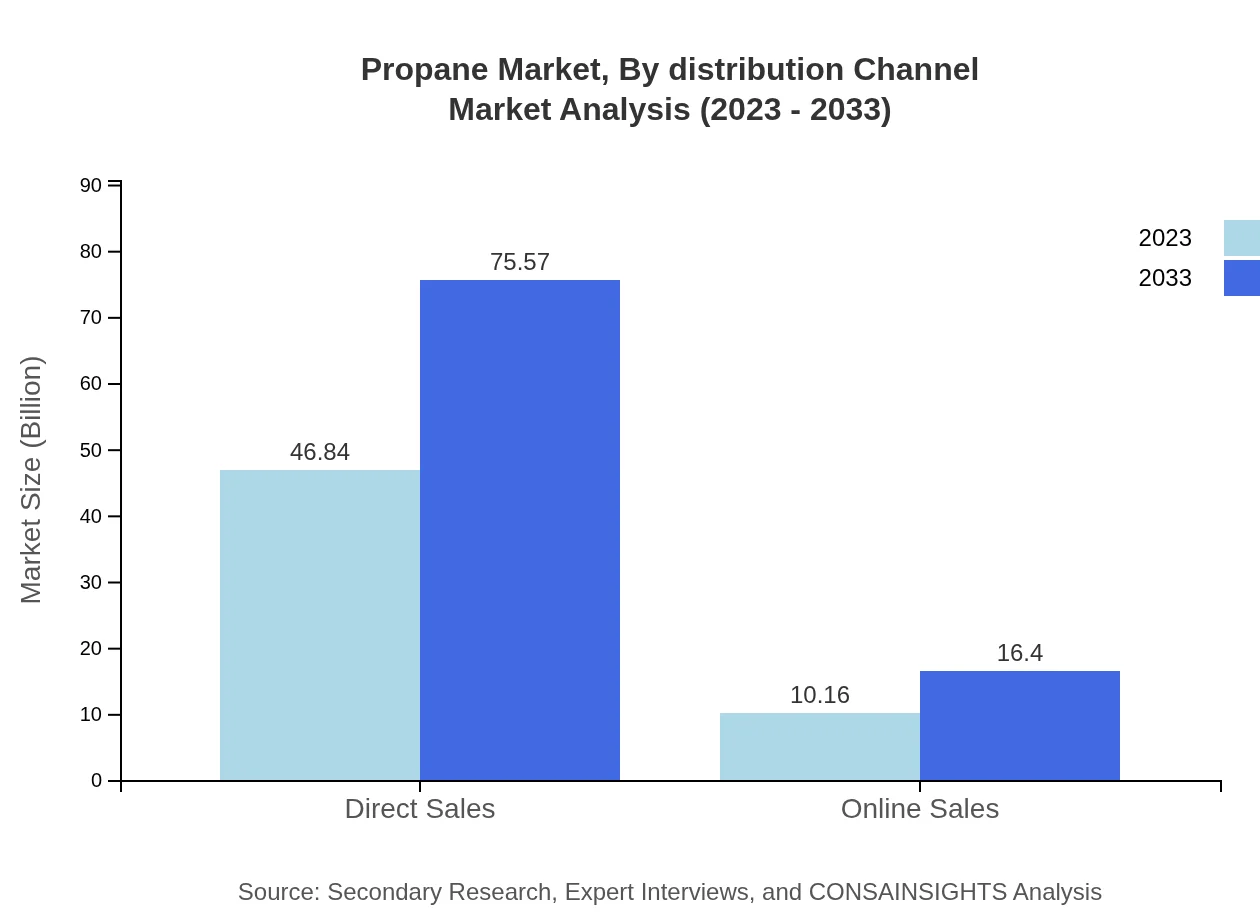
Propane Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Direct sales hold a leading position in the propane market, with sales of USD 46.84 billion expected to rise to USD 75.57 billion by 2033. It represents a significant share due to its established supply chains. Online sales also show promise, increasing from USD 10.16 billion in 2023 to USD 16.40 billion by 2033, driven by changing consumer purchasing behaviors.
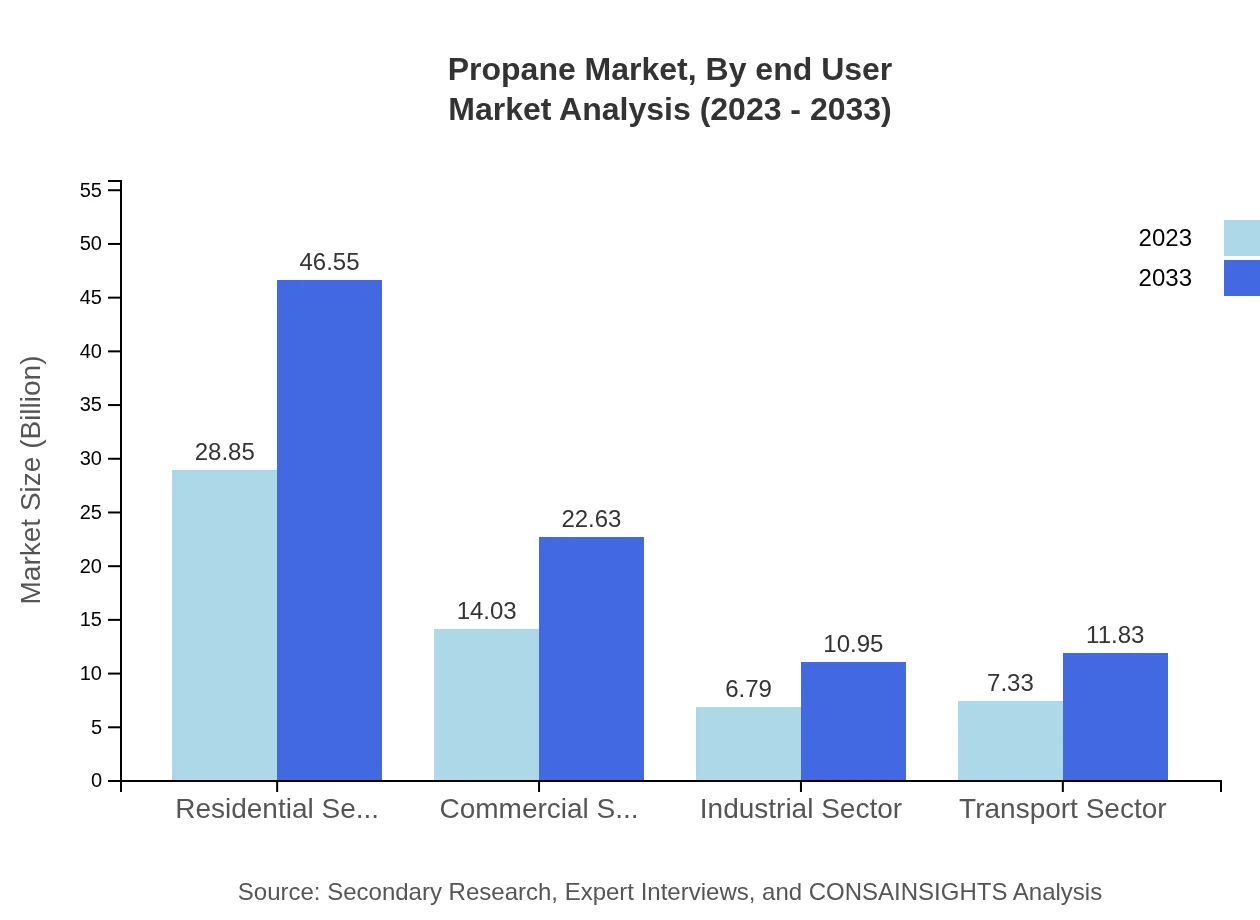
Propane Market Analysis By End User
The residential heating and cooking segment is the largest, estimated to reach USD 28.85 billion in 2023, rising to USD 46.55 billion by 2033, constituting 50.62% market share. Commercial use accounts for USD 14.03 billion in 2023, growing to USD 22.63 billion, signifying a 24.61% share. Industrial applications result in a considerable share as well, indicating diverse utilization across sectors.
Propane Market Analysis By Regions
The segmentation by regions illustrates the distinct market dynamics across North America, Asia-Pacific, Europe, South America, and the Middle East and Africa, highlighting growth opportunities driven by various factors like regional policies, industrial growth, and consumer preferences.
Propane Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Propane Industry
AmeriGas Partners, L.P.:
AmeriGas is the largest propane distribution company in the United States, providing high-quality propane products and services. They focus on residential, commercial, and industrial markets, maintaining a strong commitment to safety and service excellence.U.S. Propane, LLC:
U.S. Propane specializes in providing propane distribution services across various states in the U.S., advocating for safe and reliable propane solutions while also engaging in community and environmental preservation initiatives.Ferrellgas Partners, L.P.:
Ferrellgas offers propane distribution and related services throughout the U.S., focusing on delivering customer-centered experiences and promoting advancements in propane technology.Suburban Propane Partners, L.P.:
Suburban Propane is a nationwide distributor of propane, utilizing modern technology to enhance efficiency and safety in product delivery while investing in renewable propane options.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of propane?
The propane market is projected to reach approximately $57 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8%. This growth reflects increasing demand across various sectors, contributing significantly to its expansion.
What are the key market players or companies in the propane industry?
Key players in the propane industry include major oil and gas companies, such as BP, Shell, and Ferrellgas. Their influence shapes market dynamics, enabling competitive strategies and technological advancements within the propane sector.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the propane industry?
Growth in the propane industry is primarily driven by the rise in residential heating and cooking demand, increased agricultural use, and a shift towards cleaner fuels. These factors collectively bolster market expansion and investment opportunities.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the propane market?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the propane market, projected to scale from $20.67 billion in 2023 to $33.35 billion by 2033. This growth is propelled by rising residential demand and commercial applications.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the propane industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the propane industry. Clients can expect tailored insights and forecasts to support informed decision-making and strategic planning.
What deliverables can I expect from this propane market research project?
Deliverables from the propane market research project typically include detailed market analysis, segmented data reports, regional insights, and forecasts. Clients receive comprehensive insights supporting effective business strategies.
What are the market trends of propane?
Current market trends in propane depict a growing shift towards sustainable energy sources, enhanced usage in transportation, and increasing investments in infrastructure development. These trends indicate a robust trajectory for the propane industry in coming years.