Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: pseudomonas-aeruginosa-infection-treatment
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report delves into the Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection treatment market from 2023 to 2033, providing key insights, data trends, and forecasts regarding market growth, challenges, and emerging technologies within the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
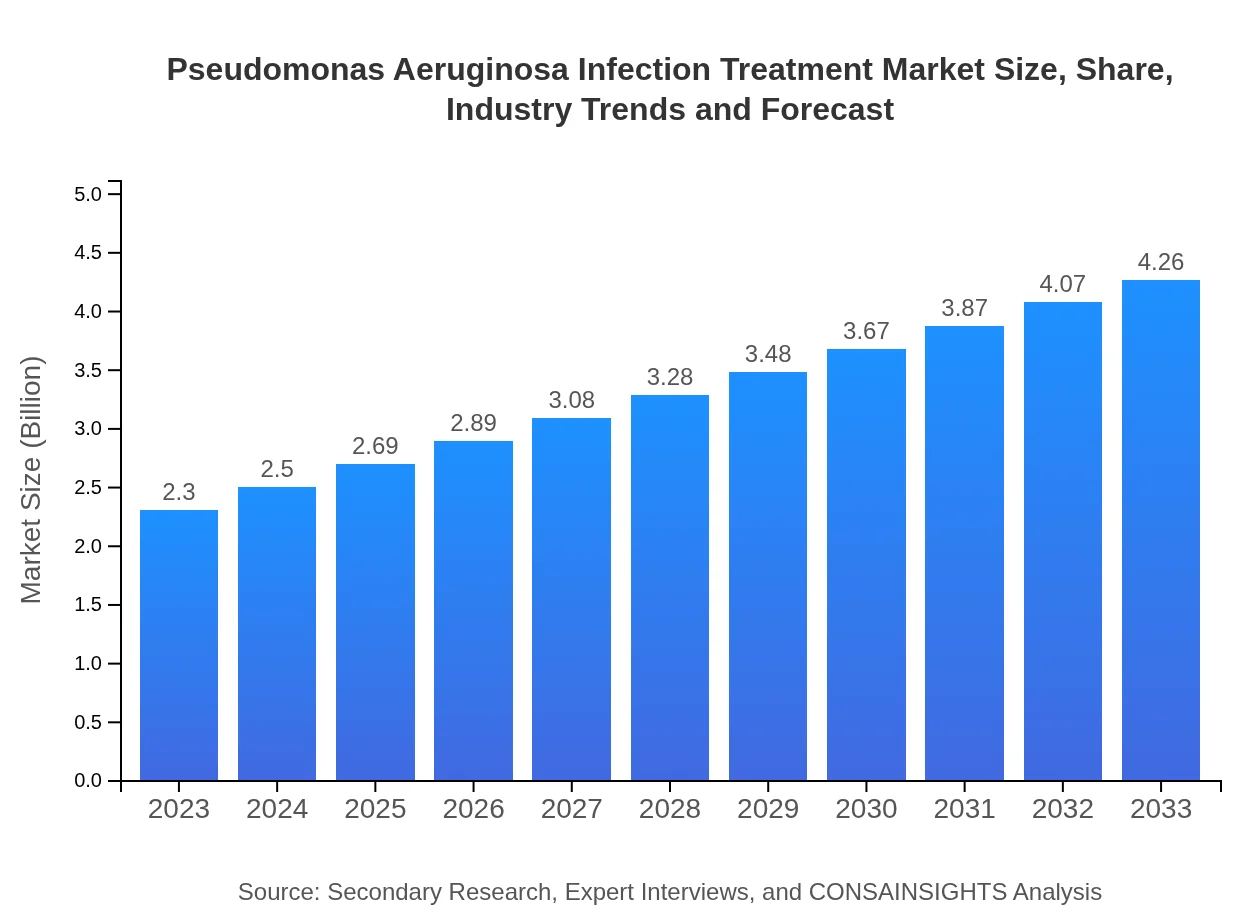
| 2023 Market Size | $2.30 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $4.26 Billion |
| Top Companies | AbbVie Inc., Zynerba Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Gilead Sciences, Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., Pfizer Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Overview
Customize Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment market in 2023?
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Industry Analysis
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Report:
The European market is forecasted to grow from $0.76 billion in 2023 to $1.41 billion by 2033, driven by stringent regulations promoting new antibiotic development and rising cases of hospital-acquired infections.Asia Pacific Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the market for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection treatment is anticipated to grow from $0.41 billion in 2023 to $0.76 billion in 2033. This growth is attributed to an increasing prevalence of bacterial infections and a higher demand for advanced therapeutic options in emerging economies.North America Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Report:
North America is expected to see substantial growth from $0.79 billion in 2023 to $1.47 billion in 2033. Factors such as high healthcare expenditure, advanced research initiatives, and increased focus on combating AMR contribute to this growth.South America Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Report:
South America's market is projected to expand from $0.09 billion in 2023 to $0.17 billion in 2033, supported by rising awareness of antibiotic treatments and improved healthcare infrastructure in the region.Middle East & Africa Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region is estimated to increase from $0.25 billion in 2023 to $0.46 billion in 2033, as healthcare systems in this region evolve and respond to infectious disease outbreaks with better management solutions.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
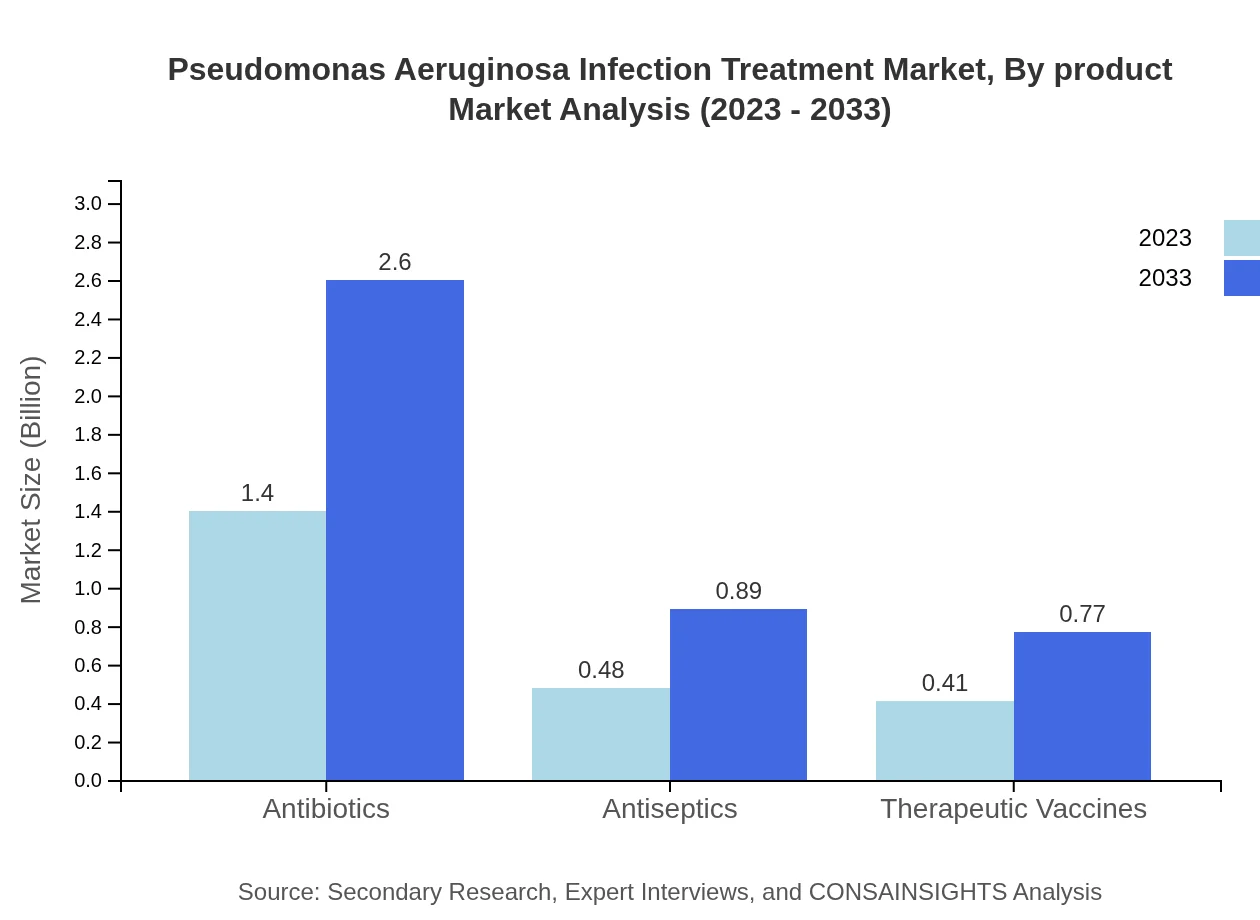
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Analysis By Product
In 2023, the market size for antibiotics is approximately $1.40 billion, growing to $2.60 billion by 2033, capturing a market share of 61.06%. Antiseptics hold a market size of $0.48 billion in 2023, projected to reach $0.89 billion by 2033 (20.97% share). Therapeutic vaccines are anticipated to increase from $0.41 billion in 2023 to $0.77 billion in 2033 (17.97% share).
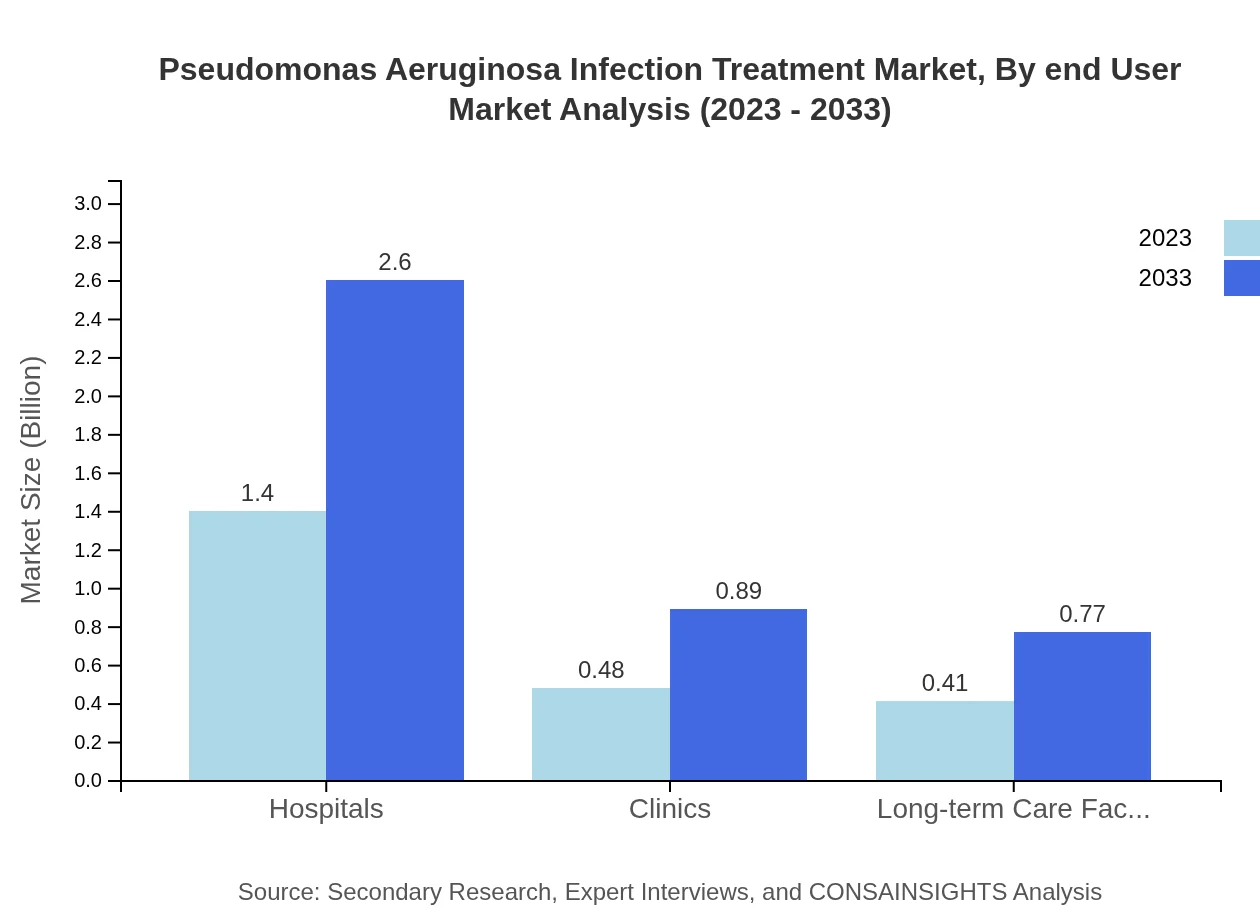
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Analysis By End User
Hospitals currently represent the largest end-user segment, with a market size of $1.40 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $2.60 billion by 2033, maintaining a share of 61.06%. Clinics and long-term care facilities follow, with respective market sizes of $0.48 billion and $0.41 billion in 2023, projected to grow accordingly in the following years.
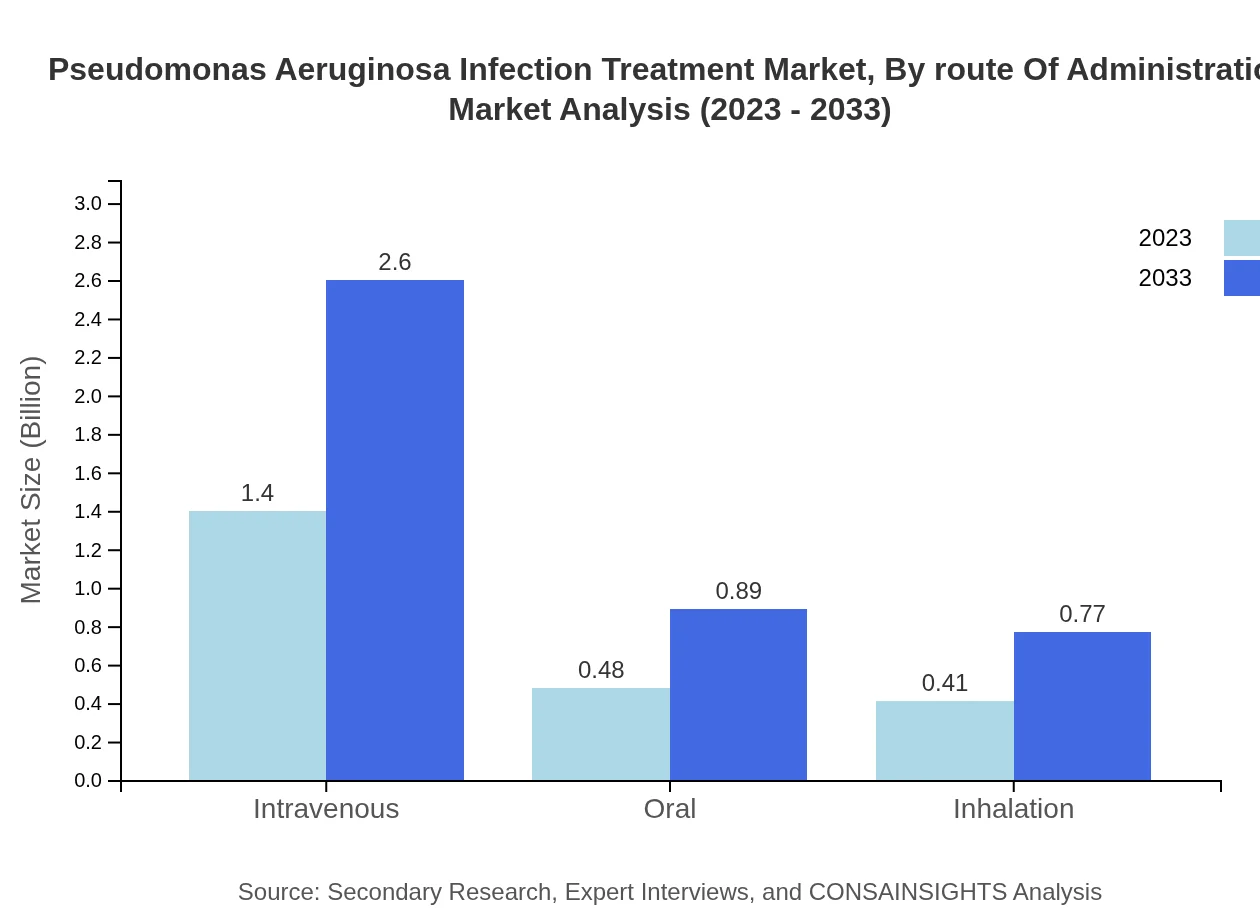
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Analysis By Route Of Administration
Intravenous administration currently dominates the treatment landscape with a market size of $1.40 billion in 2023, forecasted to rise to $2.60 billion by 2033 (61.06% share). Oral and inhalation routes also exhibit growth potential, expanding from $0.48 billion and $0.41 billion to $0.89 billion and $0.77 billion, respectively.
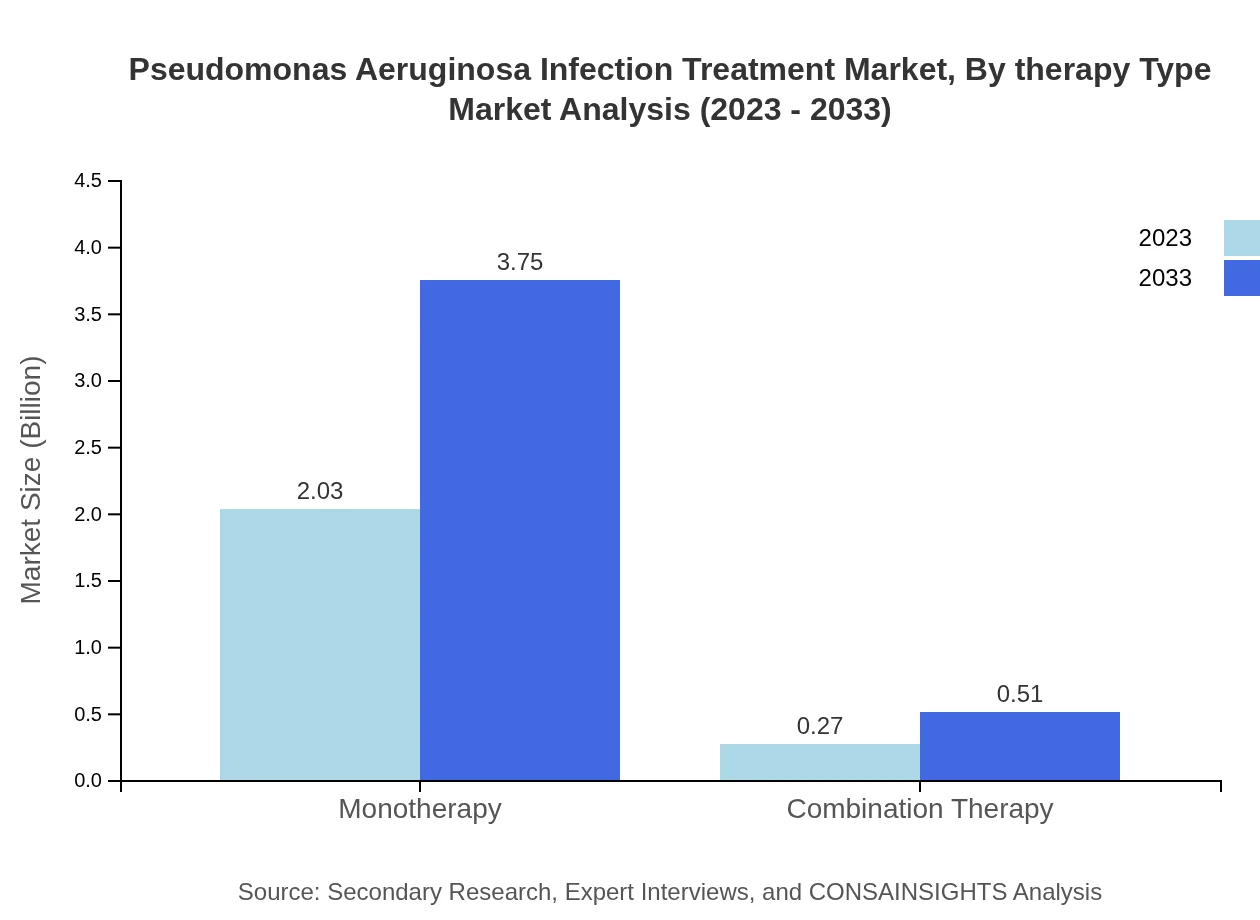
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Analysis By Therapy Type
Monotherapy is a leading therapy type, with a market size of $2.03 billion in 2023 and expected to grow to $3.75 billion by 2033 (88.06% share). Combination therapies, while currently smaller, are anticipated to grow from $0.27 billion to $0.51 billion over the same period (11.94% share).
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment Industry
AbbVie Inc.:
AbbVie focuses on discovering and developing new therapies for complex diseases including infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with a strong portfolio of antibiotics.Zynerba Pharmaceuticals, Inc.:
Zynerba specializes in innovative drug delivery systems, aiming to enhance treatment efficacy for patients suffering from Pseudomonas infections.Gilead Sciences, Inc.:
Gilead is a leading biopharmaceutical company that develops advanced antiviral and antibiotic therapies, including those for drug-resistant bacterial infections.Merck & Co., Inc.:
Merck is well-known for its contributions to antibiotic research, with several products targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa detailed in their extensive evidence-based research.Pfizer Inc.:
Pfizer’s portfolio includes a variety of antibiotics aimed at treating serious infections, particularly in patients at risk of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment?
The global market size for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection treatment is approximately $2.3 billion in 2023, with an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% projected through 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in this pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment industry?
Key players in this industry include pharmaceutical companies specializing in antibiotics and treatment for serious infections, such as Johnson & Johnson, Merck & Co., and Novartis, who dominate the market with diverse treatment offerings.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment industry?
Driving factors include rising antibiotic resistance, increasing prevalence of hospital-acquired infections, and the growing elderly population, enhancing demand for effective treatments and innovative healthcare solutions.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment?
The fastest-growing region is North America, with the market expected to rise from $0.79 billion in 2023 to $1.47 billion by 2033, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure and research investments.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific needs, allowing industries to access detailed insights relevant to their operational focus within the Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection treatment market.
What deliverables can I expect from this pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis, trend reports, competitor assessments, regional market breakdowns, and actionable insights that help inform strategic decision-making and investment opportunities.
What are the market trends of pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Treatment?
Key trends include a shift towards combination therapies, increased focus on intravenous treatments, and growing investments in therapeutic vaccines, with antibiotics remaining a dominant segment in the market.