Railway Cybersecurity Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: railway-cybersecurity
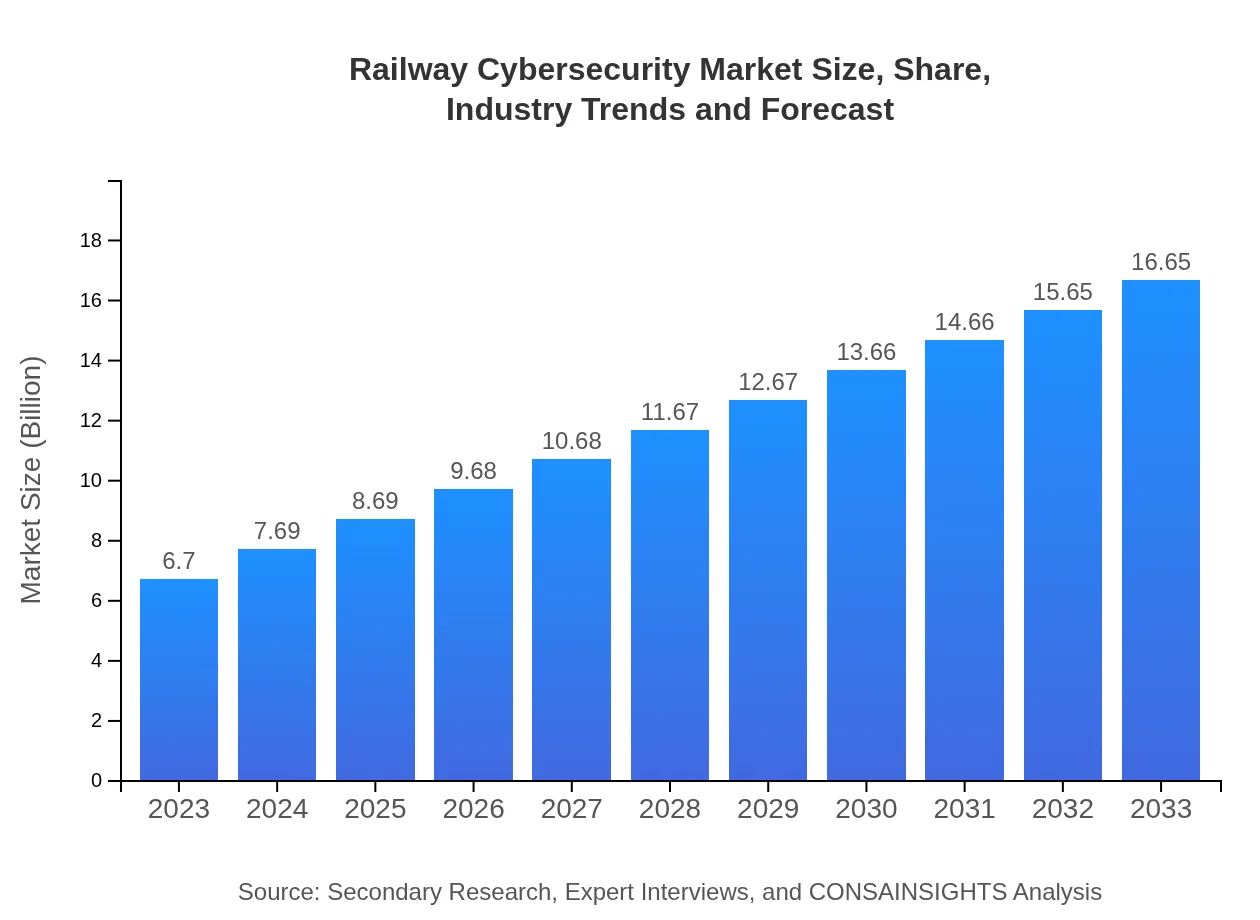
Railway Cybersecurity Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Railway Cybersecurity market, covering key trends, regional insights, competitive landscape, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It offers valuable data for stakeholders to make informed decisions and understand the industry's evolving dynamics.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $6.70 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $16.65 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cisco Systems, Inc., Schneider Electric, Siemens AG, IBM Corporation, Honeywell International Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Railway Cybersecurity Market Overview
Customize Railway Cybersecurity Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Railway Cybersecurity market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Railway Cybersecurity's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Railway Cybersecurity
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Railway Cybersecurity market in 2023?
Railway Cybersecurity Industry Analysis
Railway Cybersecurity Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Railway Cybersecurity Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Railway Cybersecurity Market Report:
The European Railway Cybersecurity market is projected to surge from $1.73 billion in 2023 to $4.30 billion by 2033. The region's commitment to improving cybersecurity frameworks and fostering collaboration among nations will contribute to its growth, particularly in light of rising threats against critical infrastructure.Asia Pacific Railway Cybersecurity Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Railway Cybersecurity market is expected to expand from $1.28 billion in 2023 to approximately $3.19 billion by 2033, reflecting a significant growth trajectory. Countries like China and India are investing heavily in railway infrastructure and modernizing their systems, thereby increasing the demand for cybersecurity solutions to protect these assets.North America Railway Cybersecurity Market Report:
North America holds a substantial share of the Railway Cybersecurity market, expected to grow from $2.45 billion in 2023 to $6.09 billion by 2033. The increasing number of cyber incidents combined with stringent regulations propels rail operators to enhance their cybersecurity strategies, making it a lucrative market.South America Railway Cybersecurity Market Report:
The South American market, although smaller, is anticipated to grow from $0.36 billion in 2023 to $0.89 billion by 2033. The rise in urbanization and railway upgrades in nations like Brazil will drive cybersecurity investments, as operators seek to protect sensitive passenger information and operational integrity.Middle East & Africa Railway Cybersecurity Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is expected to expand from $0.88 billion in 2023 to $2.18 billion by 2033. Emerging economies in the region are focusing on railway development while emphasizing security, thus increasing reliance on cybersecurity solutions.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
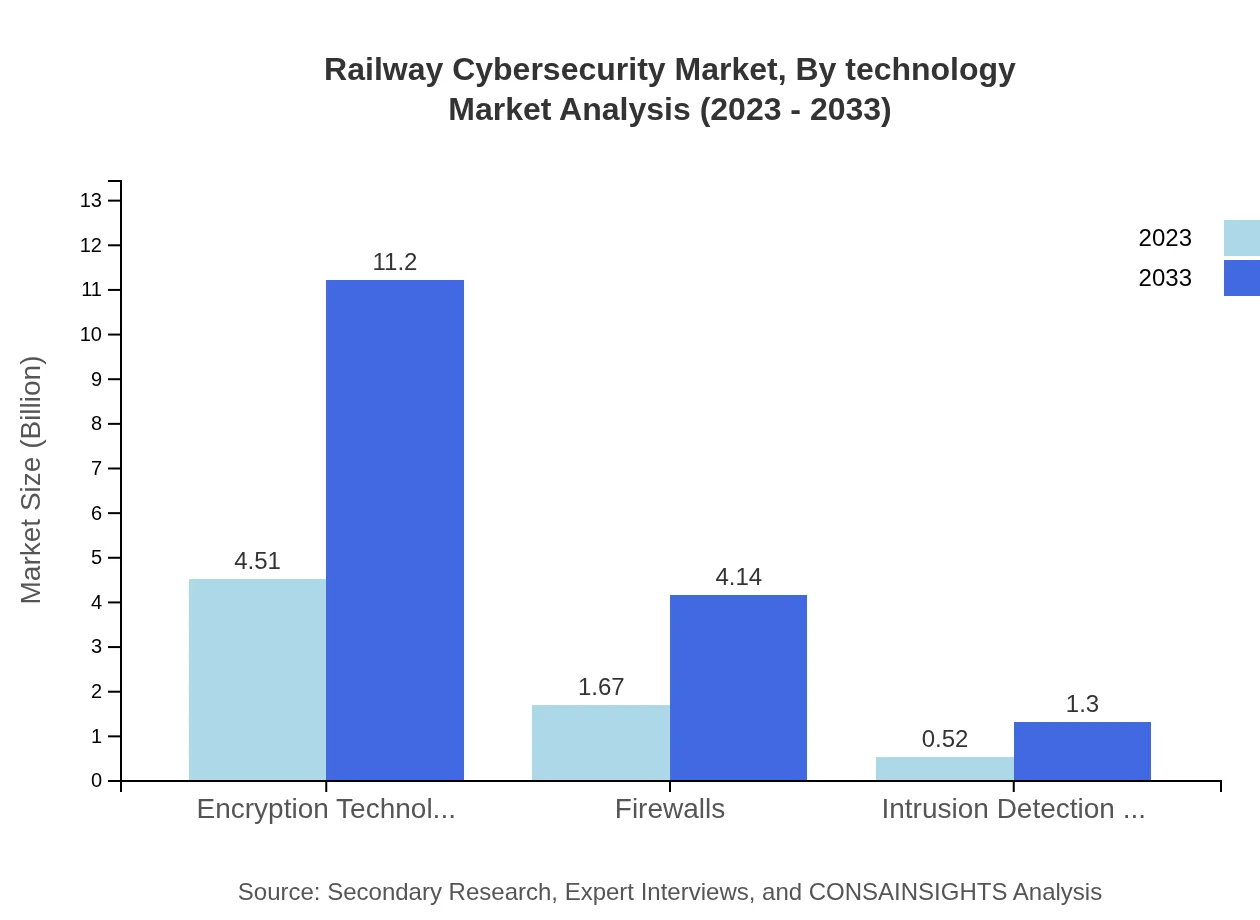
Railway Cybersecurity Market Analysis By Technology
The Railway Cybersecurity market, segmented by technology, showcases significant growth in encryption technologies, which are projected to increase from $4.51 billion in 2023 to $11.20 billion by 2033, maintaining a strong market share. Firewalls are expected to grow from $1.67 billion to $4.14 billion, while intrusion detection systems will see growth from $0.52 billion to $1.30 billion. Each technology plays a vital role in securing railway systems against cyber threats, with encryption being paramount in protecting data integrity.
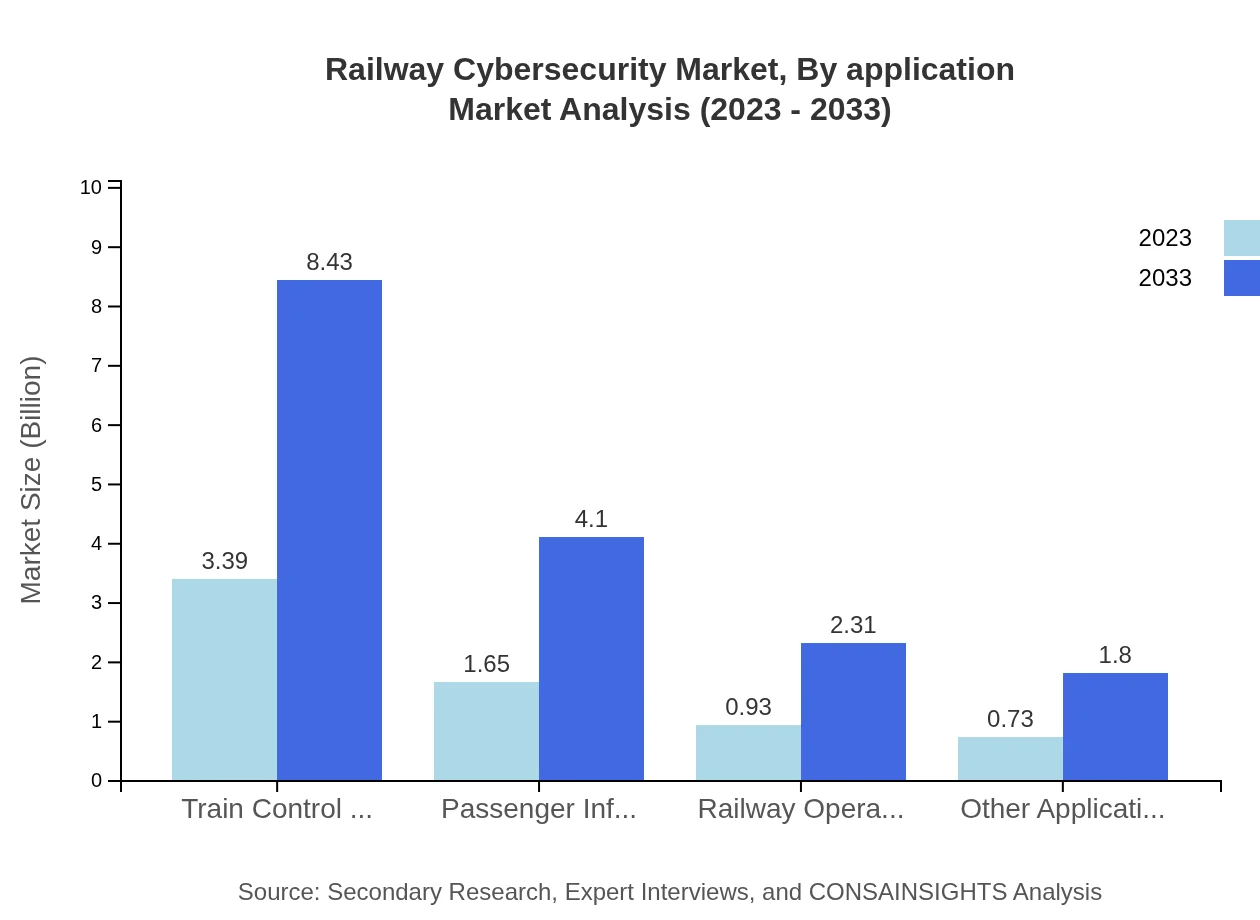
Railway Cybersecurity Market Analysis By Application
In terms of applications, the Railway Cybersecurity market demonstrates robust expansion. Train Control Systems will see growth from $3.39 billion to $8.43 billion. Other significant applications include Passenger Information Systems and Railway Operation Systems, emphasizing the diversity of applications requiring dedicated cybersecurity measures.
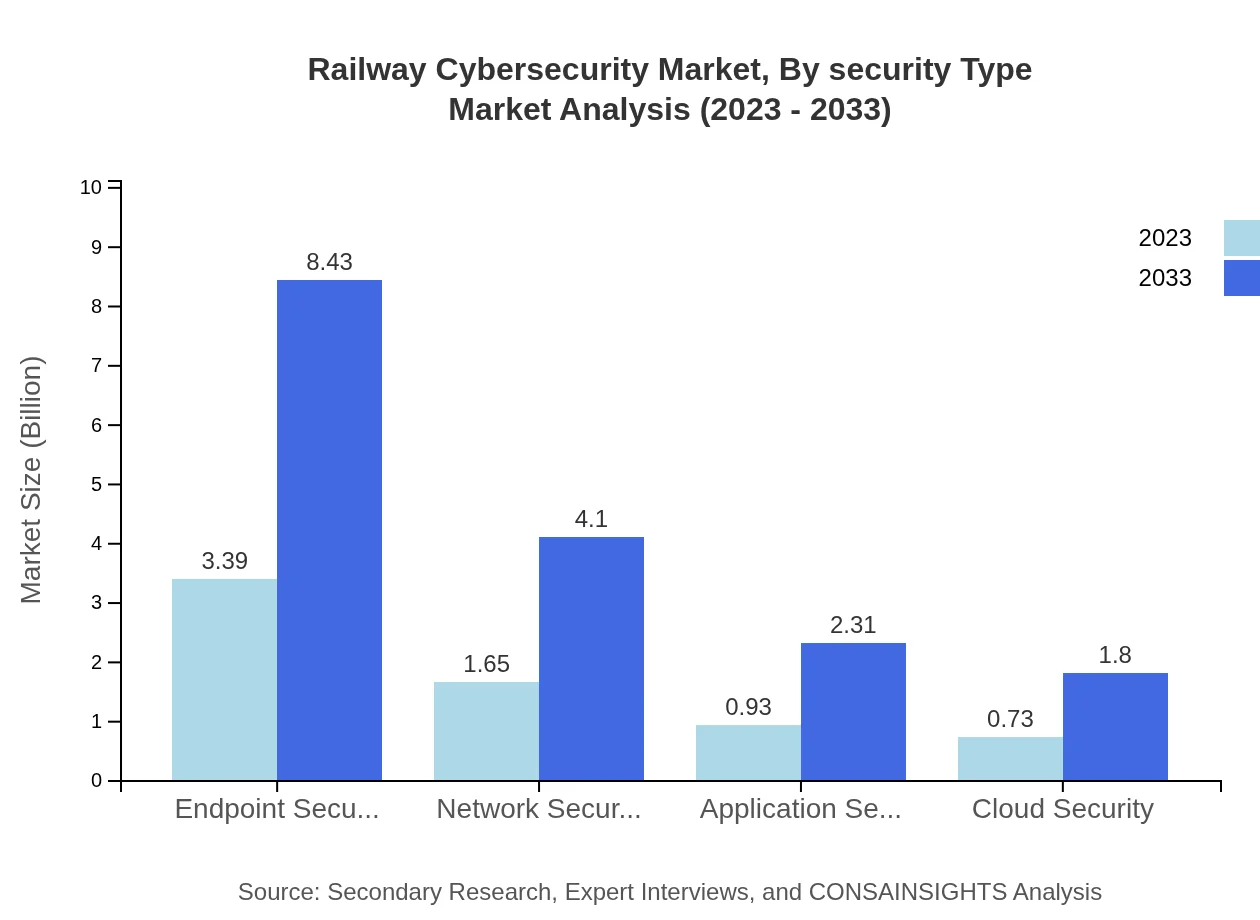
Railway Cybersecurity Market Analysis By Security Type
By security type, endpoint security stands out as a critical area, with projections increasing from $3.39 billion to $8.43 billion by 2033. Network security follows, showcasing similar growth patterns. The focus on endpoint and network security highlights the need for integrated approaches to safeguard railway systems from evolving cyber threats.
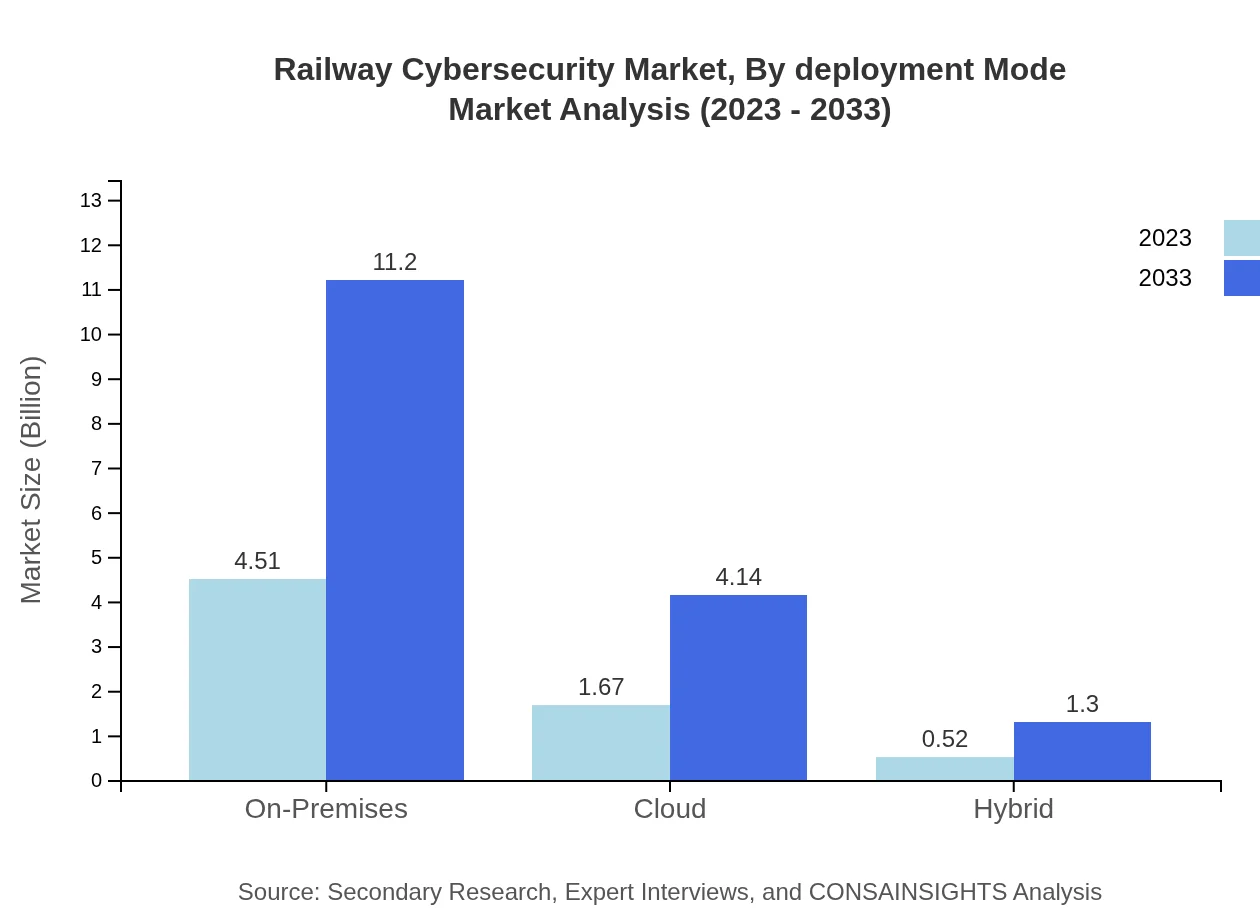
Railway Cybersecurity Market Analysis By Deployment Mode
Market segmentation based on deployment mode indicates a strong preference for on-premises solutions, expected to rise from $4.51 billion to $11.20 billion by 2033. Cloud-based solutions also show notable growth, indicating a shift towards hybrid models that combine both deployment approaches for increased flexibility and security.
Railway Cybersecurity Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Railway Cybersecurity Industry
Cisco Systems, Inc.:
Cisco is a leading provider of networking and cybersecurity solutions, delivering advanced threat detection, secure network infrastructure, and connectivity solutions to the railway sector.Schneider Electric:
Schneider Electric offers cybersecurity solutions aimed at securing critical infrastructure and automation systems within the railway industry, helping to mitigate operational risks.Siemens AG:
Siemens specializes in intelligent mobility solutions, providing cybersecurity services that enhance the protection of railway assets and improve overall system reliability.IBM Corporation:
IBM provides a comprehensive suite of cybersecurity solutions, including AI-driven analytics and incident response services tailored for the complexities of railway operations.Honeywell International Inc.:
Honeywell’s cybersecurity solutions focus on protecting industrial assets within the railway sector, providing integrated defense mechanisms to guard against cyber threats.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of railway cybersecurity?
The railway cybersecurity market is projected to grow from $6.7 billion in 2023 to an estimated size by 2033, with a CAGR of 9.2%. This growth reflects the increasing demand for advanced security solutions within the rail industry.
What are the key market players or companies in the railway cybersecurity industry?
Key players in the railway cybersecurity market include industry leaders specializing in advanced cybersecurity solutions tailored for transportation infrastructure, including major enterprises and technology providers who integrate cutting-edge security measures into railway systems.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the railway cybersecurity industry?
The growth in the railway cybersecurity industry is driven by increasing cyber threats, heightened regulatory requirements for safety, advancements in technology, and the need for improved operational efficiency and data protection within railway systems.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the railway cybersecurity?
North America is the fastest-growing region in railway cybersecurity, projected to expand from $2.45 billion in 2023 to $6.09 billion by 2033, reflecting the region's robust investments in security technologies and infrastructure improvements.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the railway cybersecurity industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the railway cybersecurity industry, allowing clients to obtain tailored insights and analytics suited to specific needs, enabling informed business decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this railway cybersecurity market research project?
Deliverables from the railway cybersecurity market research project typically include comprehensive reports, market analysis segments, forecasts, actionable insights, and recommendations tailored for strategic planning and investment decisions.
What are the market trends of railway cybersecurity?
Market trends in railway cybersecurity indicate growing adoption of encryption technologies, heightened focus on endpoint and network security, along with increasing collaboration between public and private sectors to develop robust security frameworks.