Railway Telematics Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: railway-telematics
Railway Telematics Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report covers the Railway Telematics market, providing insights into current trends, market size, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It includes detailed analyses across various segments, regions, and insights from key market leaders.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
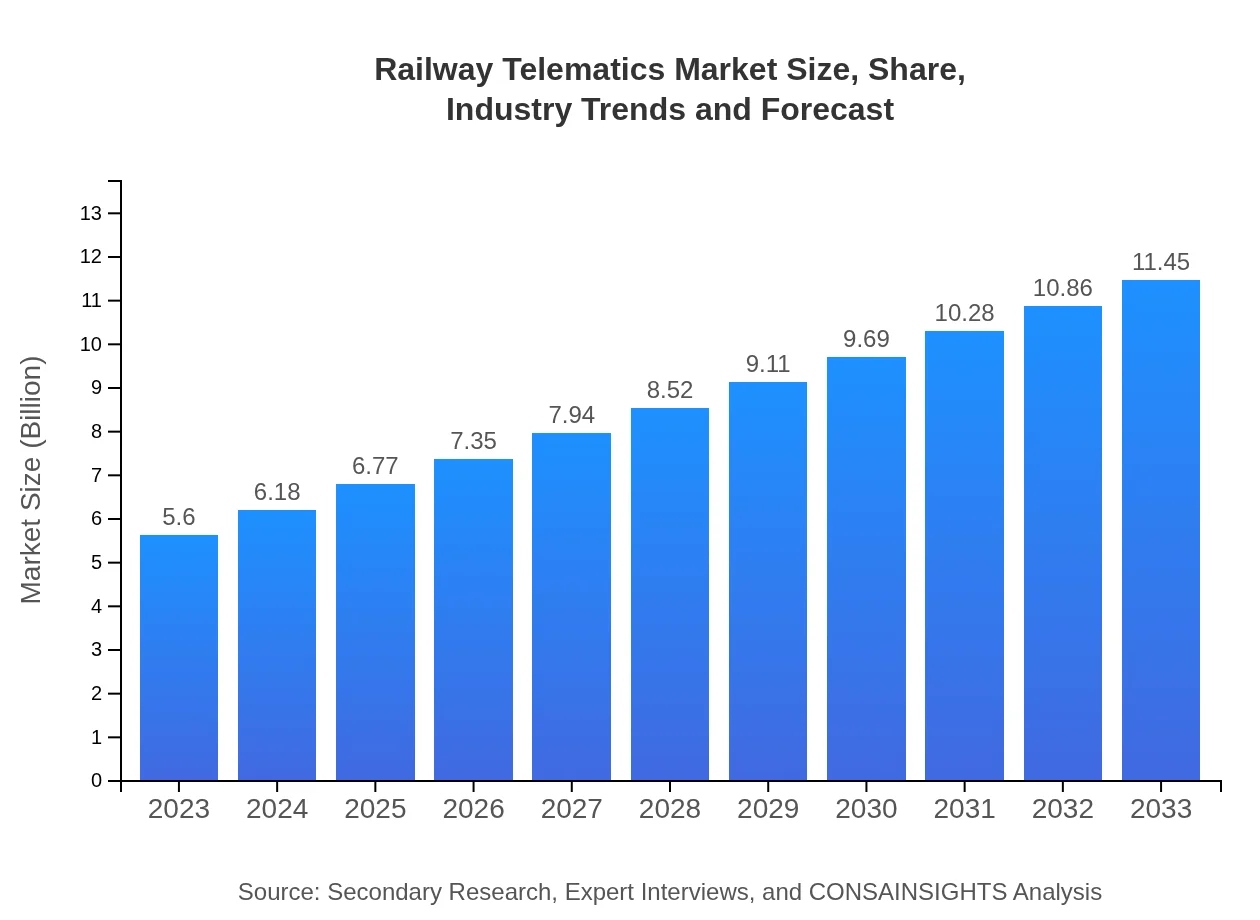
| 2023 Market Size | $5.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $11.45 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Alstom SA, Thales Group, Bombardier Inc., Nokia Networks |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Railway Telematics Market Overview
Customize Railway Telematics Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Railway Telematics market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Railway Telematics's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Railway Telematics
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Railway Telematics market in 2023?
Railway Telematics Industry Analysis
Railway Telematics Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Railway Telematics Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Railway Telematics Market Report:
Europe is anticipated to experience growth in the railway telematics sector, transitioning from $1.47 billion in 2023 to $3.00 billion by 2033. The European Union’s focus on enhancing cross-border rail services and sustainable transport initiatives significantly contributes to this market expansion.Asia Pacific Railway Telematics Market Report:
The Asia Pacific railway telematics market is projected to grow from $1.15 billion in 2023 to $2.35 billion by 2033. Key factors include increasing urbanization, expanding rail networks, and growing investments in smart railway solutions to enhance operational efficiency.North America Railway Telematics Market Report:
North America is a leading region in the Railway Telematics market, projected to grow significantly from $2.05 billion in 2023 to $4.19 billion by 2033. The strong demand for advanced technological solutions in railways, along with stringent safety regulations, drives substantial investment.South America Railway Telematics Market Report:
In South America, the market is set to expand from $0.52 billion in 2023 to $1.06 billion by 2033. The region is experiencing a rise in infrastructure investments and modernization of railway systems, which is poised to elevate the demand for telematics solutions.Middle East & Africa Railway Telematics Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is expected to increase from $0.42 billion in 2023 to $0.85 billion by 2033. The growing emphasis on modernizing rail infrastructure and implementing advanced technology solutions will aid in market growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Railway Telematics Market Analysis By Technology
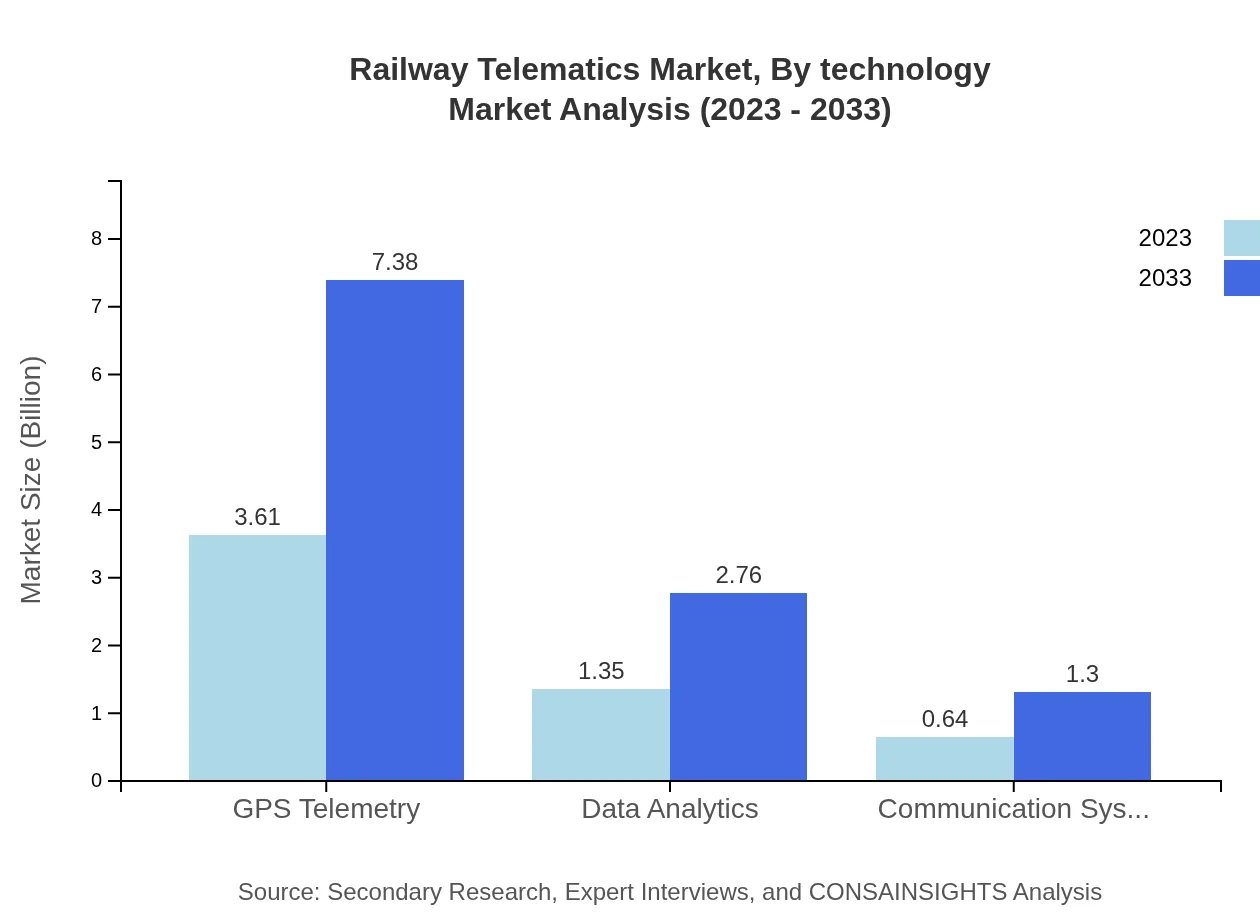
The Railway Telematics market is predominantly driven by GPS telemetry, which commands a significant share due to its critical role in tracking and real-time data provision. Data analytics also plays a major role, with applications analyzing vast amounts of information to enhance decision-making and operational efficiency. Other key technologies include communication systems crucial for inter-vehicle communication, and fleet management systems designed to optimize resource allocation and reduce operational costs.
Railway Telematics Market Analysis By Application
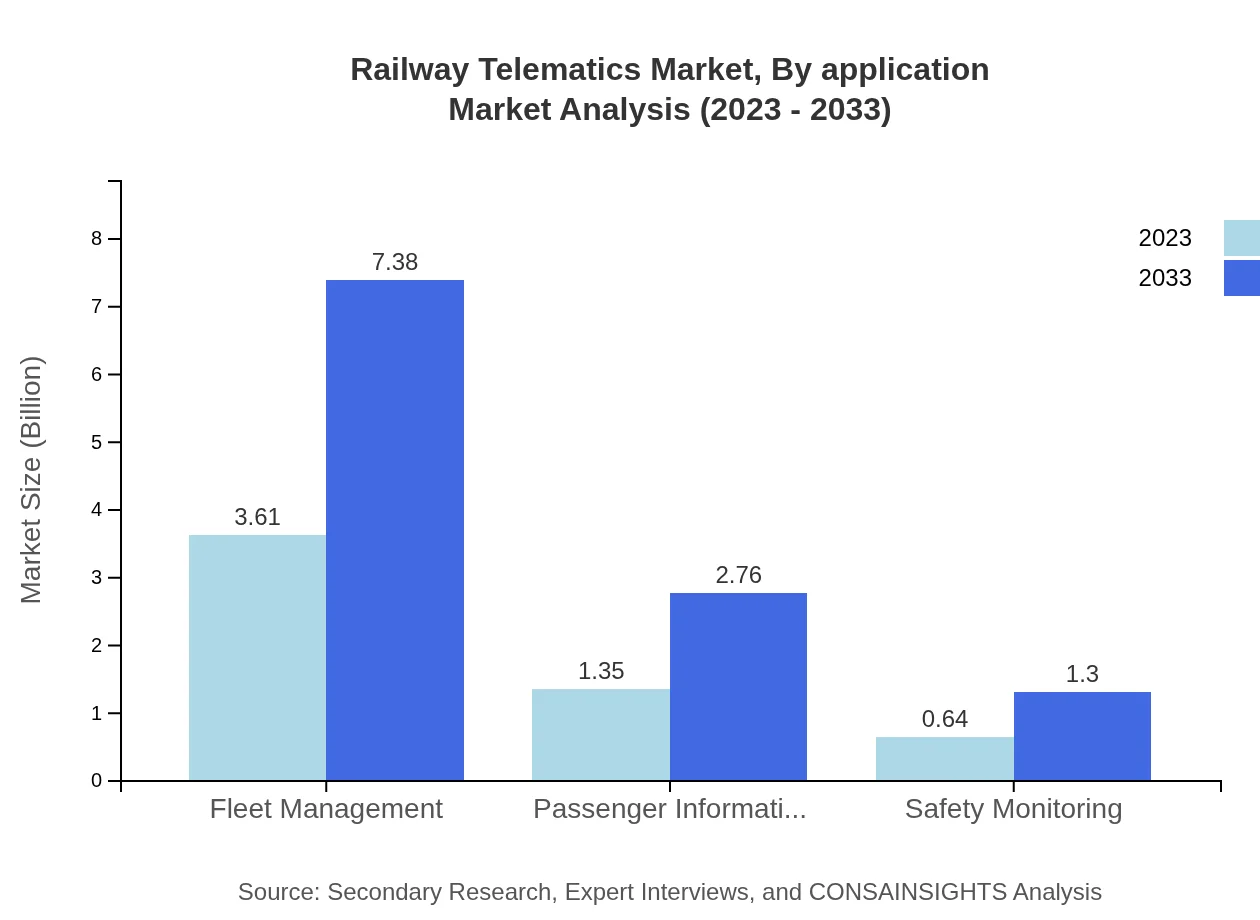
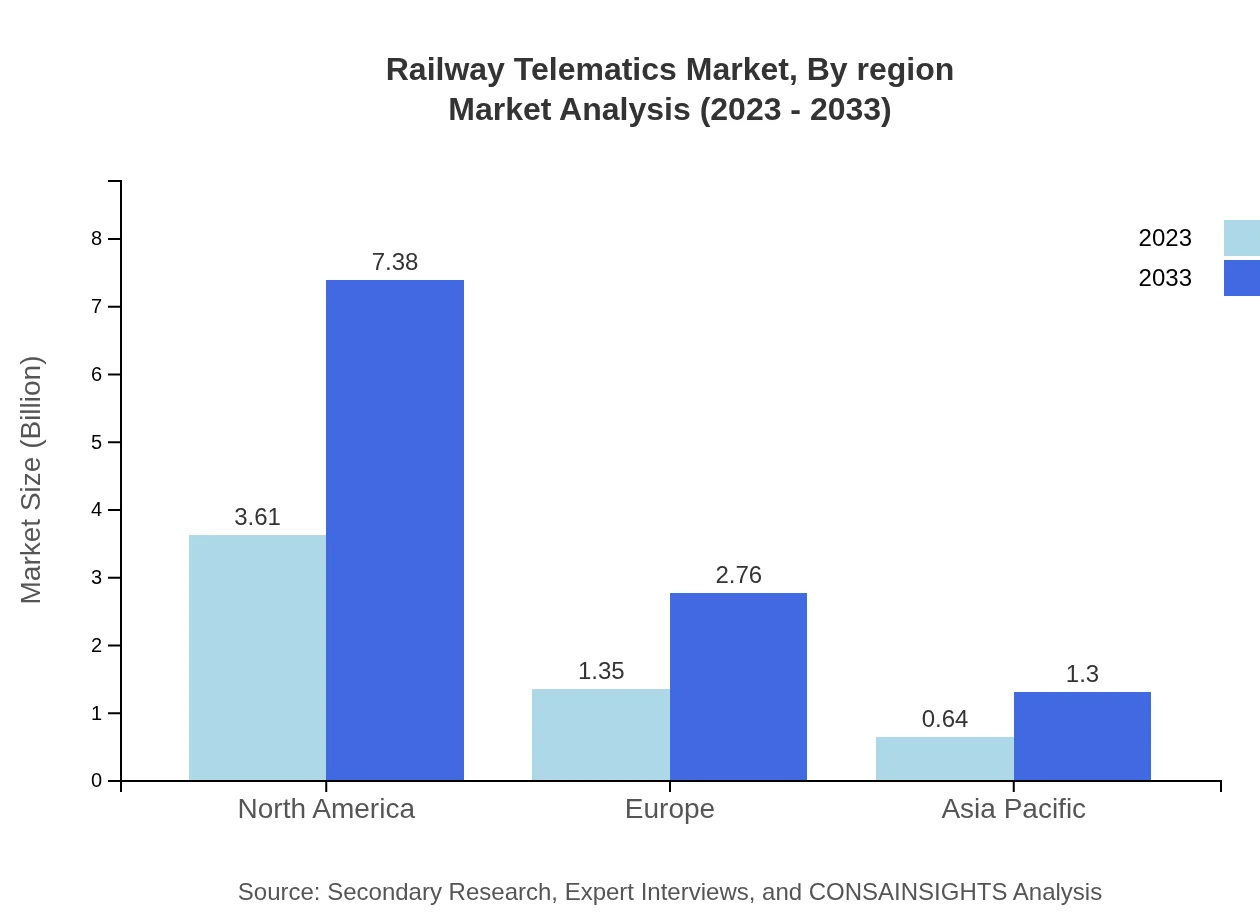
Applications such as fleet management are central to operational efficiency in railway networks, with the fleet management segment forecasted to grow from $3.61 billion in 2023 to $7.38 billion by 2033. Safety monitoring systems are equally vital, aiding in the prevention of accidents and ensuring passenger safety. Passenger information systems leverage telematics technologies to deliver real-time updates and enhance the travel experience.
Railway Telematics Market Analysis By End User
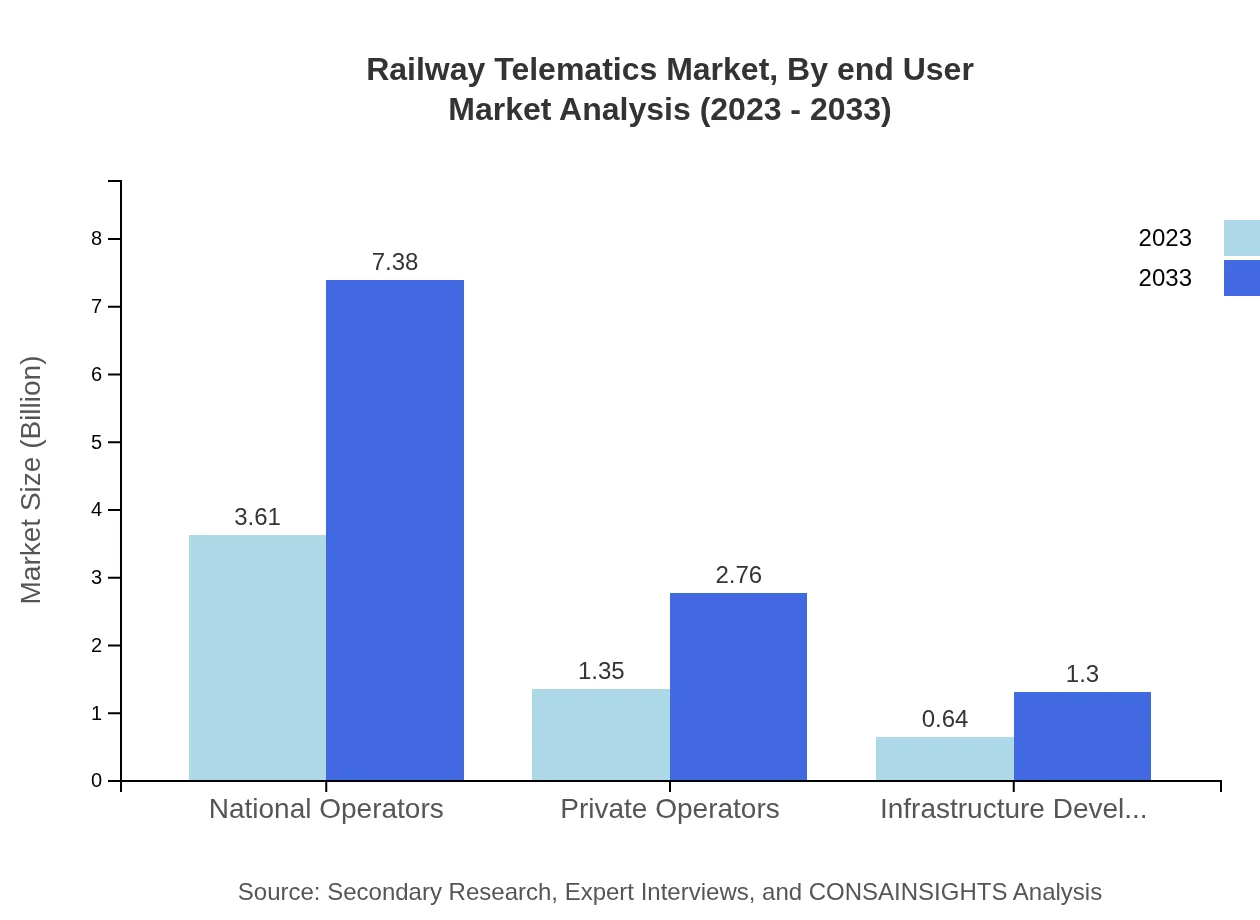
Key end-users in the Railway Telematics market include national and private operators, who are adopting these technologies to improve service delivery and reduce costs. National operators accounted for the majority share in 2023, reflecting their significant investment in telematics to modernize transport networks. Infrastructure developers are also crucial, focusing on implementing telematics for efficient management and maintenance.
Railway Telematics Market Analysis By Region
The Railway Telematics market exhibits significant regional variations, with North America and Europe as frontrunners due to their advanced railway networks and investment in smart technology. The Asia Pacific region, however, is witnessing rapid growth driven by urbanization and substantial infrastructure projects, while South America and the Middle East & Africa are gradually increasing their investments in telematics technology to modernize their existing rail systems.
Railway Telematics Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Railway Telematics Industry
Siemens AG:
Siemens AG is a global powerhouse in electronics and electrical engineering, focusing on industry, infrastructure, transport, and healthcare. In railway telematics, Siemens is known for its leading-edge solutions that enhance operational efficiency and safety through data analytics and smart technology.Alstom SA:
Alstom SA is a multinational company specializing in rail transport and sustainable mobility solutions. They offer innovative telematics solutions aimed at optimizing railway operations, enhancing passenger experiences, and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.Thales Group:
Thales Group provides advanced technology solutions across various domains including aerospace, defense, and transportation. Their presence in railway telematics is marked by a focus on safety systems and innovative communication platforms that facilitate seamless connectivity across networks.Bombardier Inc.:
As a leader in rail technology, Bombardier Inc. specializes in manufacturing, designing, and providing telematics solutions that enhance the effectiveness of railway operations. Their contributions towards smart rail transport are recognized globally.Nokia Networks:
Nokia Networks offers cutting-edge telecommunication and data processing technologies, pivotal in the development of modern railway telematics systems that ensure safety and efficiency on rail networks worldwide.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of railway Telematics?
The railway telematics market is valued at approximately $5.6 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 7.2% through 2033. This growth highlights increasing investment in technology within the rail transport sector.
What are the key market players or companies in the railway Telematics industry?
Key players in the railway telematics industry include major companies such as Siemens, Bombardier, Thales Group, and GE Transportation. These organizations dominate due to their expertise in technology integration and innovative solutions for rail operations.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the railway telematics industry?
Growth in the railway telematics industry is driven by factors such as the need for enhanced operational efficiency, improved safety standards, and the integration of IoT technologies. Additionally, increasing freight transport demand is compelling rail operators to adopt telematics solutions.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the railway telematics sector?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the railway telematics market, projected to grow from $2.05 billion in 2023 to $4.19 billion by 2033. Europe and Asia Pacific also exhibit significant growth trajectories, driven by technological advancements.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the railway telematics industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to the specific needs of clients in the railway telematics industry. This includes detailed analyses of market trends, segments, and forecasts catered to individual business objectives.
What deliverables can I expect from this railway telematics market research project?
From the railway telematics market research project, clients can expect comprehensive market analysis reports, detailed segment insights, forecasts, and identification of potential growth opportunities, all presented in a clear and actionable format.
What are the market trends of railway telematics?
Current market trends in railway telematics include the increasing adoption of GPS telemetry and data analytics technologies, along with enhancements in fleet management and safety monitoring systems, reflecting a broader shift towards digitalization in rail operations.