Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: rare-disease-genetic-testing
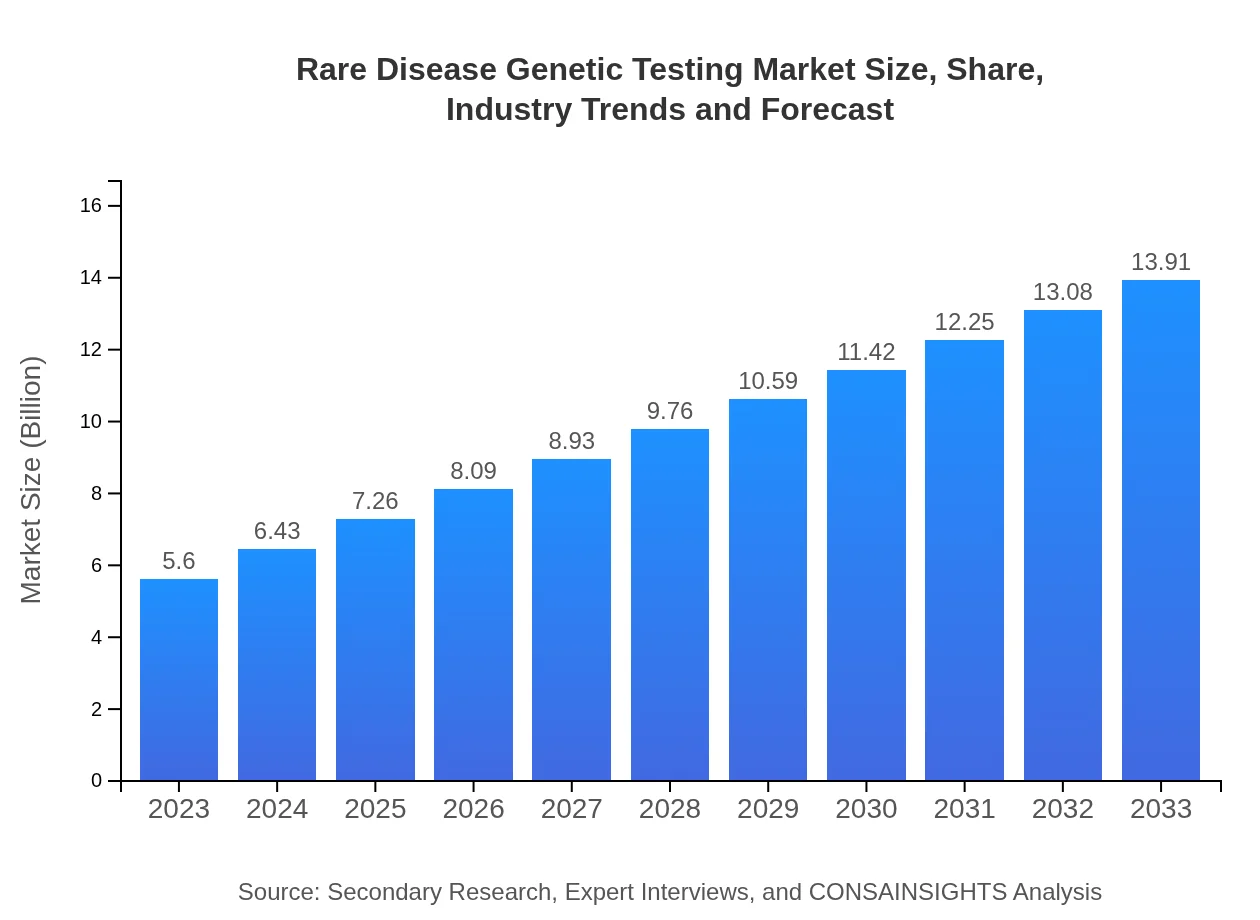
Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report analyzes the Rare Disease Genetic Testing market, providing insights on market trends, size, growth forecasts, regional analysis, and competitive dynamics from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $5.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $13.91 Billion |
| Top Companies | Illumina, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Genomatix, Roche Diagnostics |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Overview
Customize Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Rare Disease Genetic Testing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Rare Disease Genetic Testing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Rare Disease Genetic Testing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Rare Disease Genetic Testing market in 2023?
Rare Disease Genetic Testing Industry Analysis
Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Report:
Europe's Rare Disease Genetic Testing market is projected to expand from $2.05 billion in 2023 to $5.10 billion by 2033, due to favorable regulations and growing investments in genomic research, as health authorities recognize the importance of genetic testing in treating rare diseases.Asia Pacific Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific market is valued at $1.02 billion, growing steadily to $2.53 billion by 2033, driven by increased healthcare expenditure and technological advancements. Countries such as China and India are witnessing a surge in genetic testing services due to improved healthcare infrastructure and rising awareness about rare diseases.North America Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Report:
The North American market is expected to grow from $1.86 billion in 2023 to $4.61 billion by 2033, significantly driven by the increasing prevalence of rare diseases, robust healthcare infrastructure, and a higher adoption rate of advanced genetic testing methodologies.South America Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Report:
The South American market is relatively small, valued at $0.10 billion in 2023 and projected to reach $0.24 billion by 2033. The growth will be fueled by improved healthcare policies and awareness of genetic conditions, although economic challenges may impact growth rates.Middle East & Africa Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Report:
The market in the Middle East and Africa is expected to grow from $0.57 billion in 2023 to $1.43 billion by 2033. Factors contributing to this growth include rising healthcare investments, the increasing prevalence of genetic disorders, and greater emphasis on improving healthcare services.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
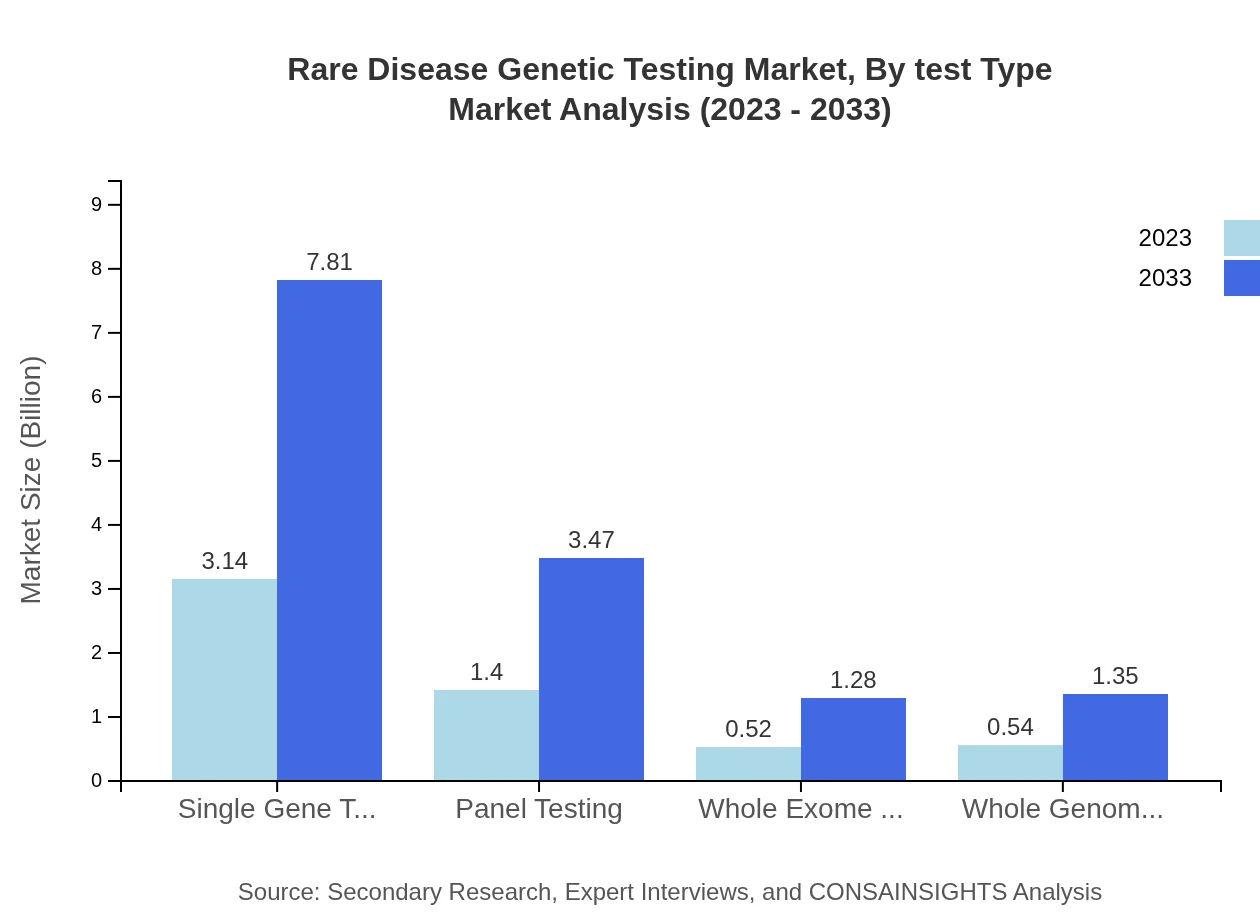
Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Analysis By Test Type
The Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market is significantly driven by test types such as Single Gene Testing, Panel Testing, Whole Exome Sequencing, and Whole Genome Sequencing. The market for Single Gene Testing is projected to grow from $3.14 billion in 2023 to $7.81 billion by 2033, maintaining a share of 56.14%. Panel Testing and Next-Generation Sequencing are also witnessing considerable growth, reflecting their essential role in accurately diagnosing various rare conditions.
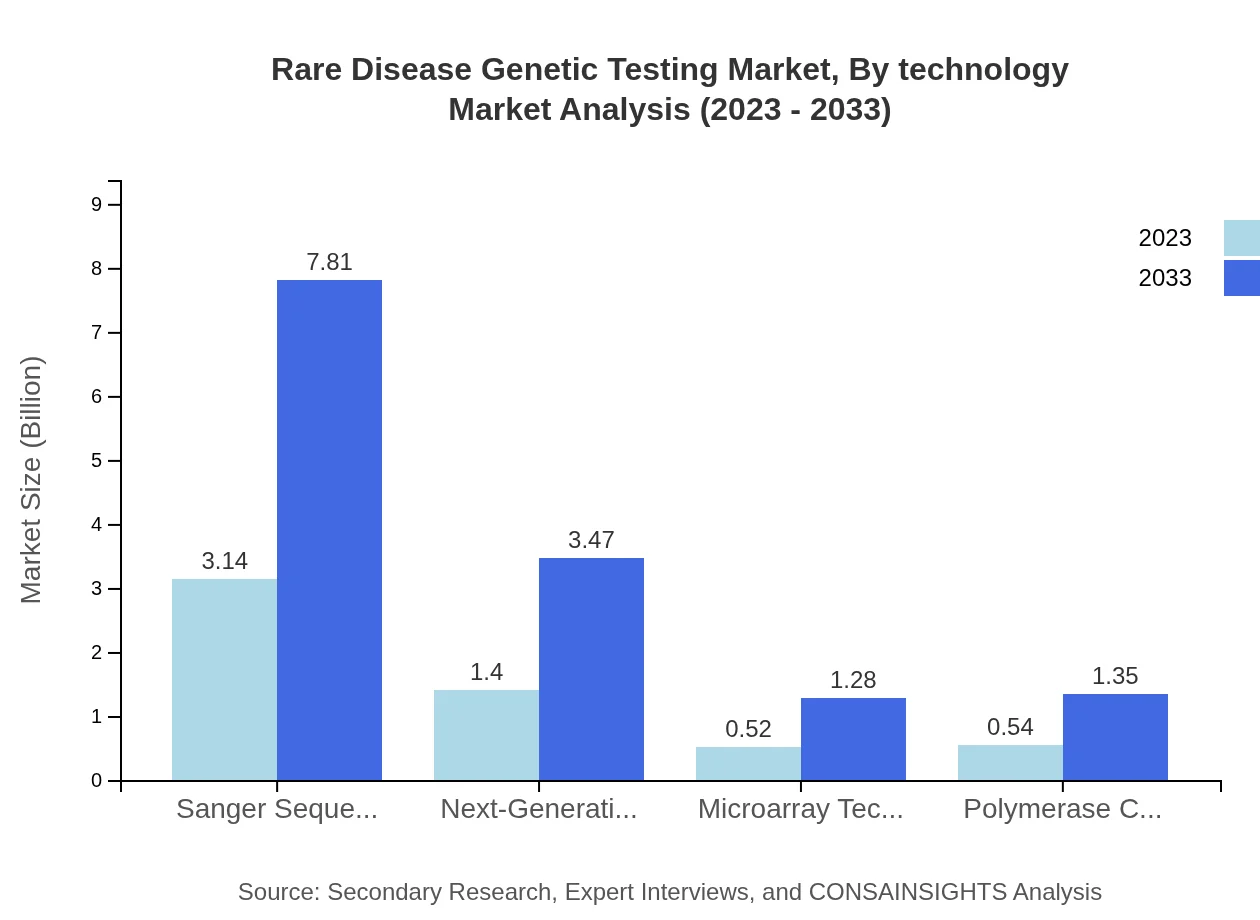
Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Analysis By Technology
The market by technology indicates that Next-Generation Sequencing holds a significant share due to its efficiency and accuracy in genetic analysis. In 2023, it represents $1.40 billion and is expected to reach $3.47 billion by 2033, covering around 24.94% of the testing applications for rare diseases. Technologies such as Sanger Sequencing and Microarray are also integral, with consistent market shares reflecting their established use in genetic testing.
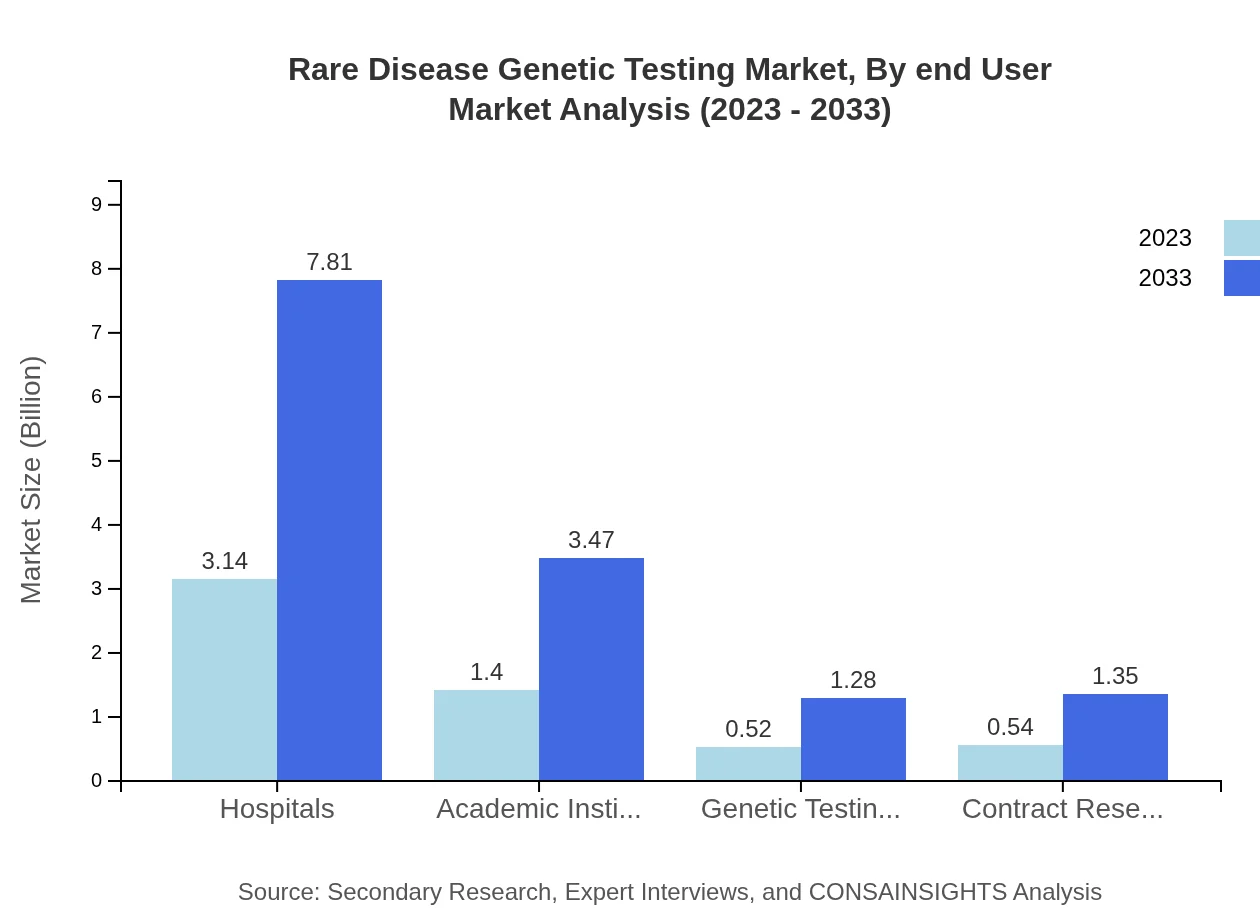
Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Analysis By End User
Hospitals are the primary end-users of genetic tests, capturing 56.14% of the market share in 2023, with a growth trajectory from $3.14 billion to $7.81 billion by 2033. Academic institutions and Laboratories are also significant users, demonstrating a strong demand for genetic testing services in various research and diagnostic settings.
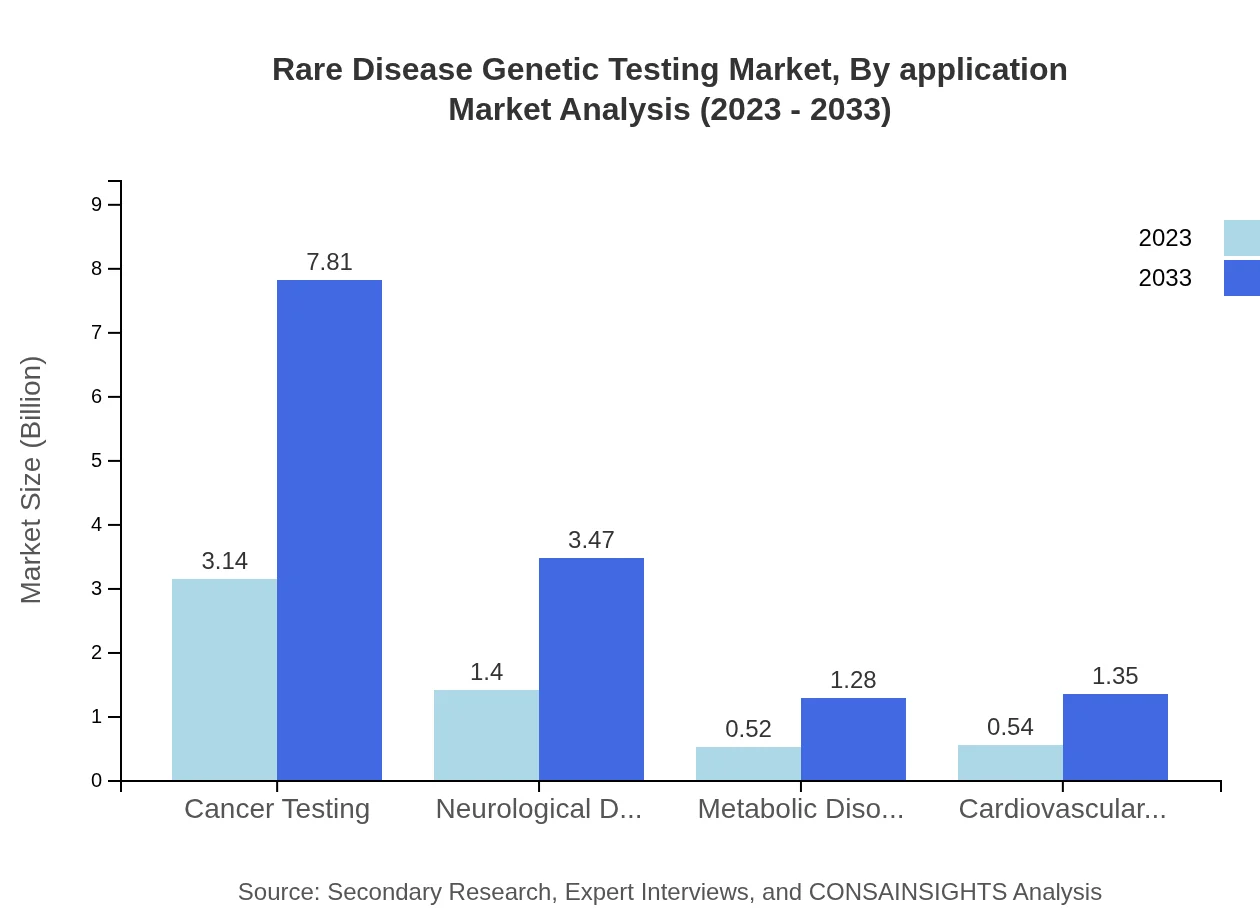
Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Analysis By Application
Applications in Cancer Testing for rare diseases lead the market, reflecting a growth from $3.14 billion in 2023 to $7.81 billion by 2033. Neurological, metabolic, and cardiovascular disorders also form key application sectors, driven by increasing genetic research and diagnostic needs to tackle these complex diseases effectively.
Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Rare Disease Genetic Testing Industry
Illumina:
A leader in sequencing and array-based solutions for genetic testing, Illumina is known for its innovations in next-generation sequencing technologies.Thermo Fisher Scientific:
Thermo Fisher Scientific offers a broad range of genomic technologies and reagents that empower researchers and clinicians to advance genetic testing for rare diseases.Genomatix:
Specializing in bioinformatics, Genomatix provides software tools that aid in the analysis of genomic data, enhancing the accuracy and utility of genetic tests.Roche Diagnostics:
Roche Diagnostics deals with medical devices and biotechnology, offering advanced genetic testing solutions that help in the rapid diagnosis of rare diseases.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of rare disease genetic testing?
The rare disease genetic testing market is valued at $5.6 billion in 2023, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.2%. This indicates substantial growth potential, driven by advancements in technology and increased demand for genetic testing.
What are the key market players or companies in the rare disease genetic testing industry?
Key players in the rare disease genetic testing market include genetic testing labs, hospitals, and academic institutions. Prominent companies often collaborate to enhance their testing capabilities and expand their product offerings, ensuring a comprehensive market presence.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the rare disease genetic testing industry?
Growth in the rare disease genetic testing industry is fueled by technological advancements, increased prevalence of rare diseases, and supportive regulatory frameworks. Personalized medicine trends and heightened public awareness about genetic disorders also play a significant role in market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the rare disease genetic testing market?
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to exhibit significant growth in the rare disease genetic testing market, increasing from $1.02 billion in 2023 to $2.53 billion by 2033. This growth is attributed to rising healthcare expenditure and increased access to testing facilities.
Does Consainsights provide customized market report data for the rare disease genetic testing industry?
Yes, Consainsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the rare disease genetic testing industry. This can include detailed analyses, forecasts, and insights based on varying parameters and criteria customized for individual client requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this rare disease genetic testing market research project?
Deliverables from a rare disease genetic testing market research project typically include comprehensive reports, segmentation analyses, competitive landscape evaluations, market trends, projections, and regional insights, providing stakeholders with the data needed for informed decision-making.
What are the market trends of rare disease genetic testing?
Current trends in the rare disease genetic testing market include rising adoption of next-generation sequencing, growth in demand for panel testing, and shifts towards personalized medicine approaches. The increasing integration of digital health technologies further enhances testing efficiency and accessibility.