Rfid Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: rfid
Rfid Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the RFID market, including market size, trends, regional insights, segmentation, and leading players, with forecasts extending to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $12.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $30.69 Billion |
| Top Companies | Zebra Technologies, Impinj, Inc., Alien Technology, Avery Dennison Corporation |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
RFID Market Overview
Customize Rfid Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Rfid market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Rfid's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Rfid
What is the Market Size & CAGR of the RFID Market in 2023?
RFID Industry Analysis
RFID Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
RFID Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Rfid Market Report:
In Europe, the market is set to grow substantially, from $3.91 billion in 2023 to $10.00 billion by 2033. European countries are increasingly investing in innovative technologies and sustainability, promoting the use of RFID for better resource management and operational efficiency.Asia Pacific Rfid Market Report:
The RFID market in the Asia Pacific region is expected to grow from $2.15 billion in 2023 to approximately $5.51 billion by 2033. Development in this region is driven by increased adoption in retail and logistics sectors, coupled with advancements in RFID technology. Countries like China and Japan are leading contributors to market growth due to their robust manufacturing sectors and technological innovation.North America Rfid Market Report:
North America's RFID market is projected to expand from $4.47 billion in 2023 to $11.42 billion by 2033, leading globally due to high adoption rates in various sectors, particularly healthcare and retail. The region benefits from significant technological advancements and strong investments in automation and supply chain enhancements.South America Rfid Market Report:
In South America, the RFID market is forecasted to increase from $0.23 billion in 2023 to $0.58 billion by 2033. The growth is gradual, reflecting an increase in awareness and adoption of automated tracking systems in retail and logistics, although challenges such as economic instability can hinder more rapid expansion.Middle East & Africa Rfid Market Report:
The RFID market in the Middle East and Africa is estimated to rise from $1.24 billion in 2023 to $3.18 billion by 2033. Although currently a smaller market, growth is driven by efforts to modernize industries and improve supply chain visibility, particularly in logistics and manufacturing.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
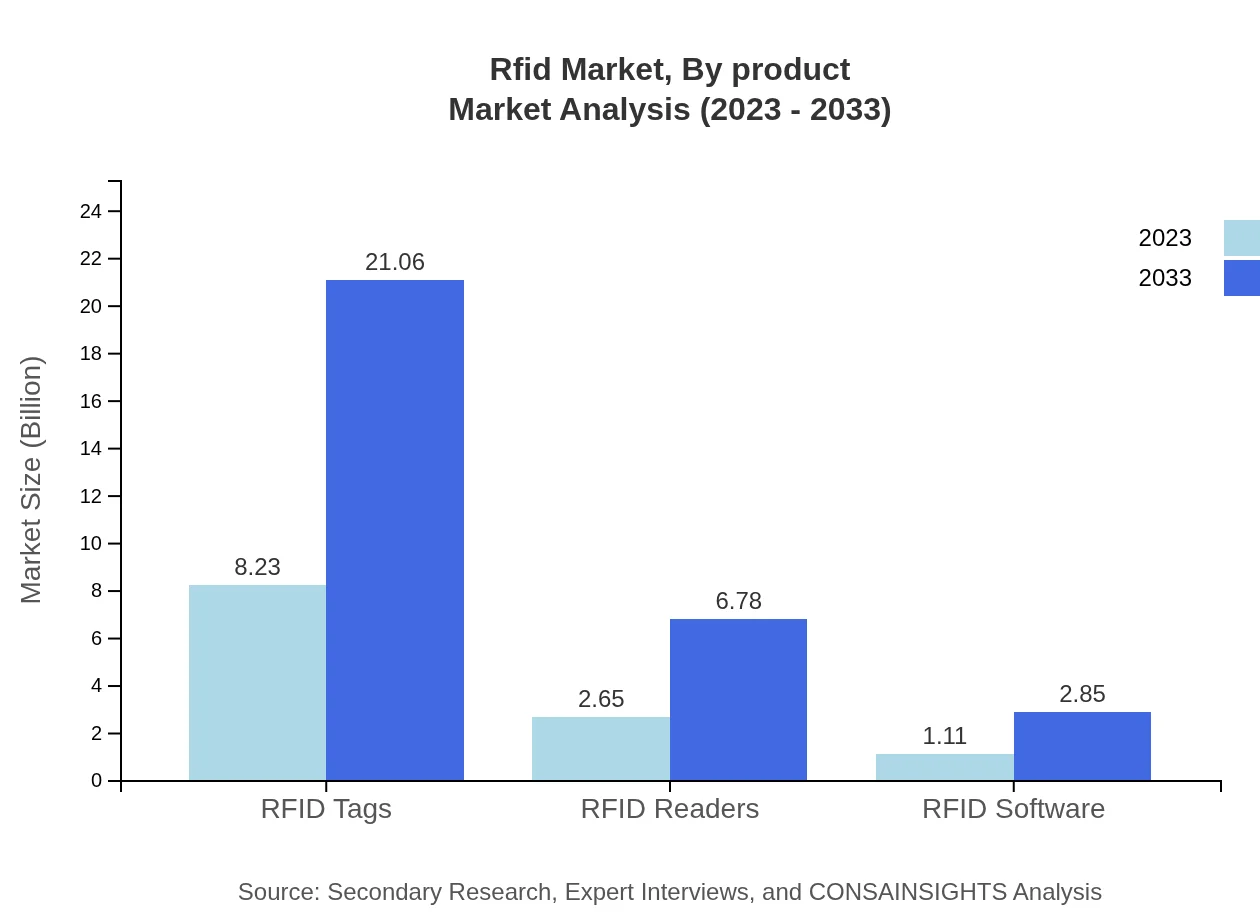
Rfid Market Analysis By Product
RFID Tags: The dominant segment, projected to grow from $8.23 billion in 2023 to $21.06 billion by 2033, representing 68.61% of the market share throughout the period. RFID Readers: Expected to increase from $2.65 billion to $6.78 billion, capturing about 22.1% market share. RFID Software: Anticipated growth from $1.11 billion to $2.85 billion, making up 9.29% of the market.
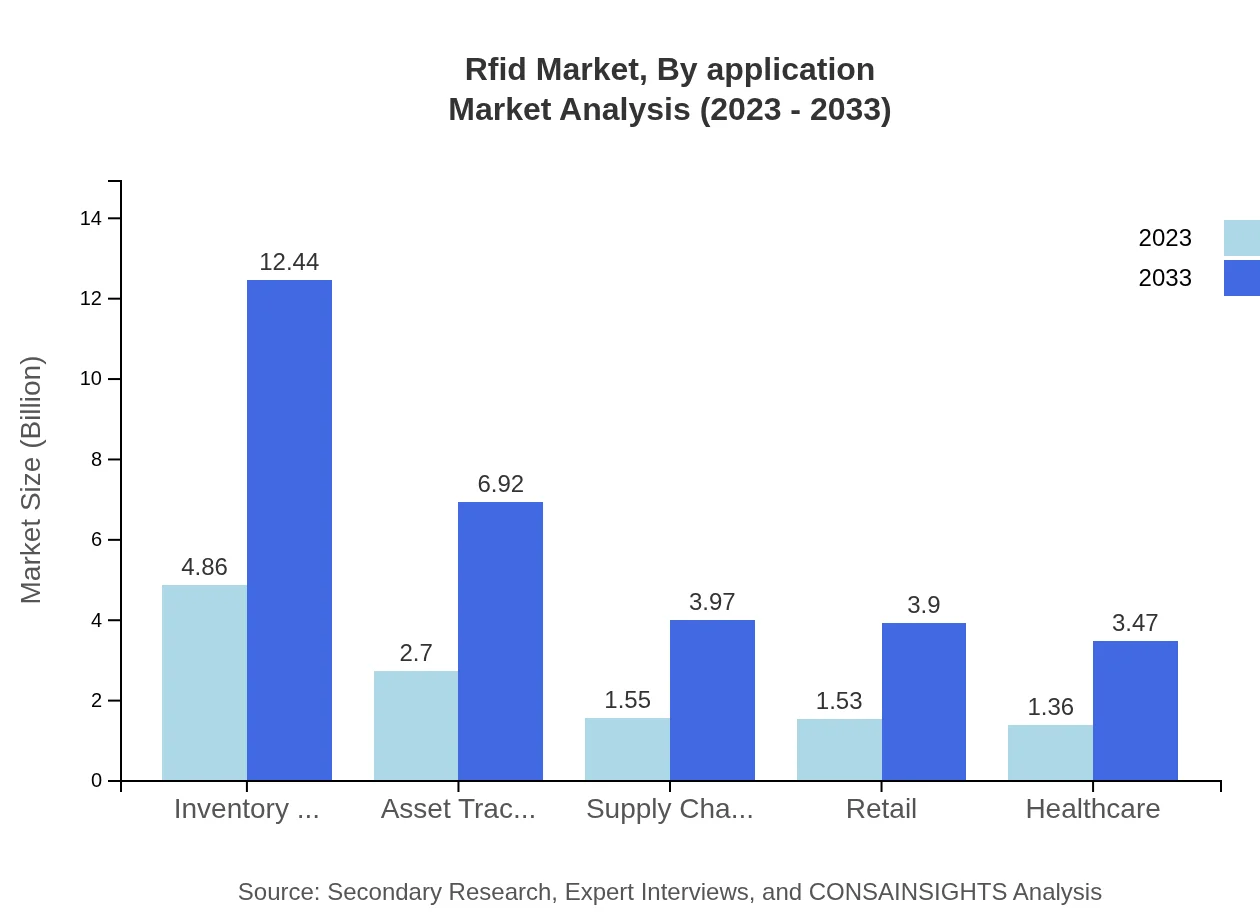
Rfid Market Analysis By Application
Key applications include Retail, Manufacturing, Logistics, Healthcare, and Government. Retail leads, growing from $4.86 billion in 2023 to $12.44 billion by 2033, holding 40.52% market share. Logistics and inventory management are also significant, with similar growth patterns and shares.
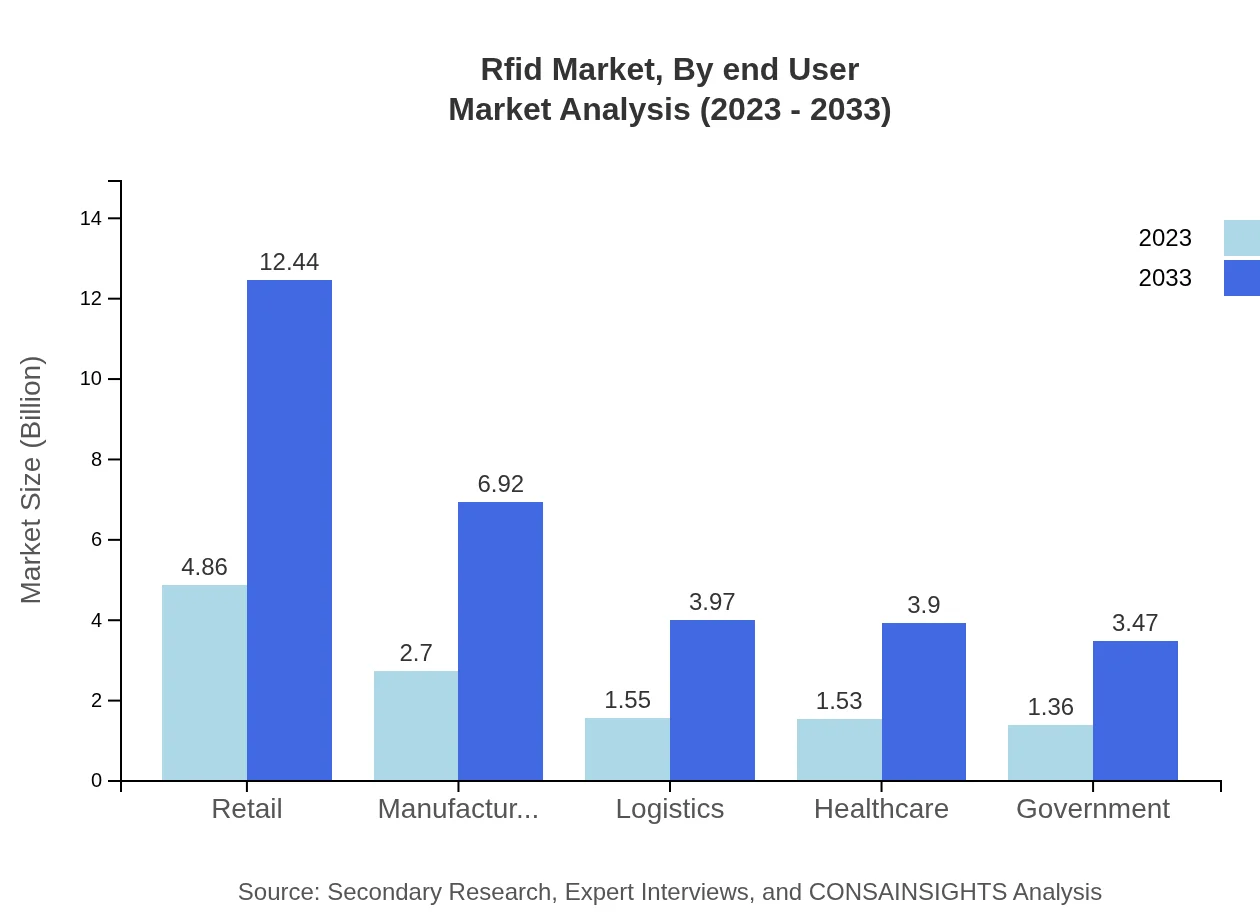
Rfid Market Analysis By End User
Major end-users include Retail, Manufacturing, Logistics, Healthcare, and Government. Retail occupies the largest share, followed closely by Manufacturing and Logistics, reflecting their high demand for tracking and operational efficiency.
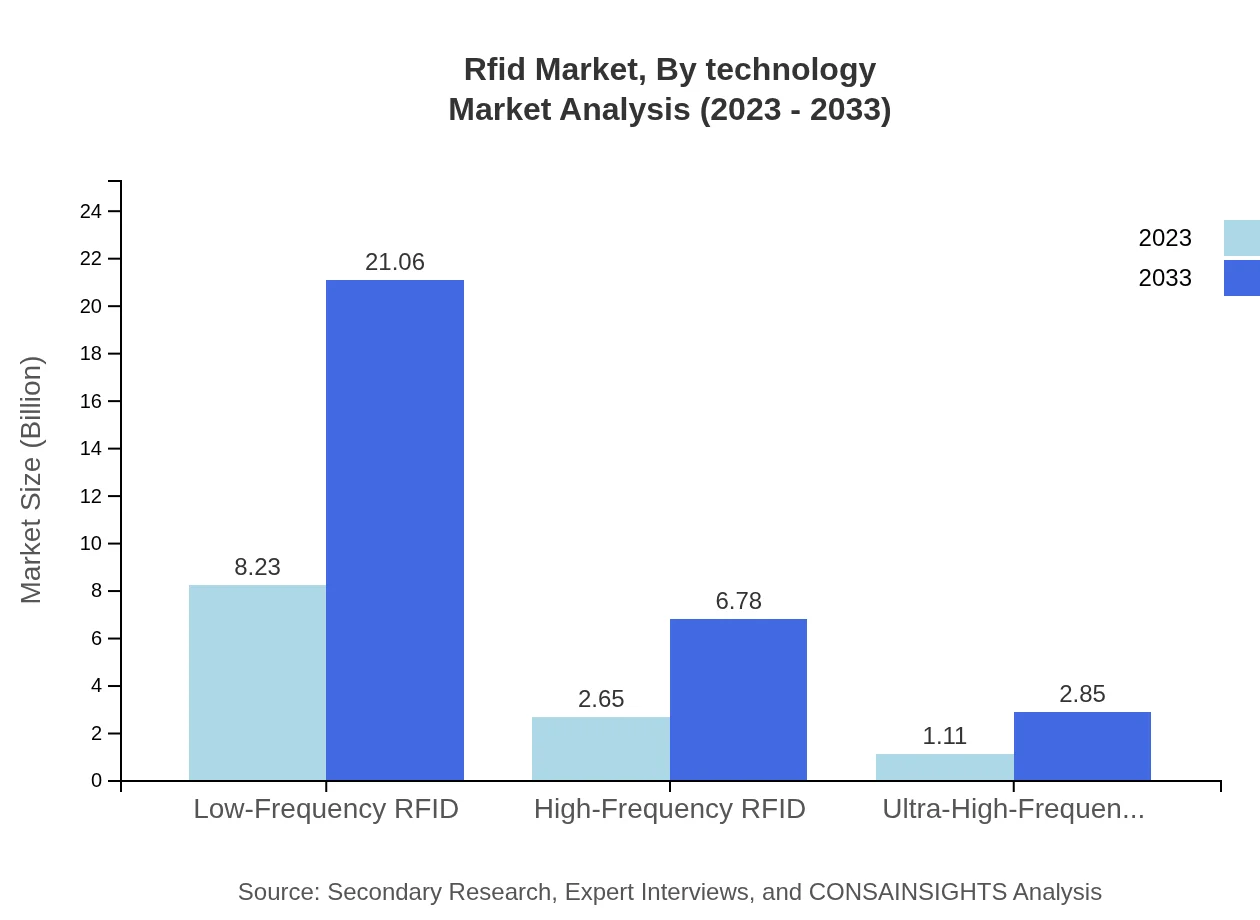
Rfid Market Analysis By Technology
The technology segment highlights Low-Frequency, High-Frequency, and Ultra-High-Frequency RFID systems. Low-Frequency RFID is leading, projected to grow significantly to match robust application demands.
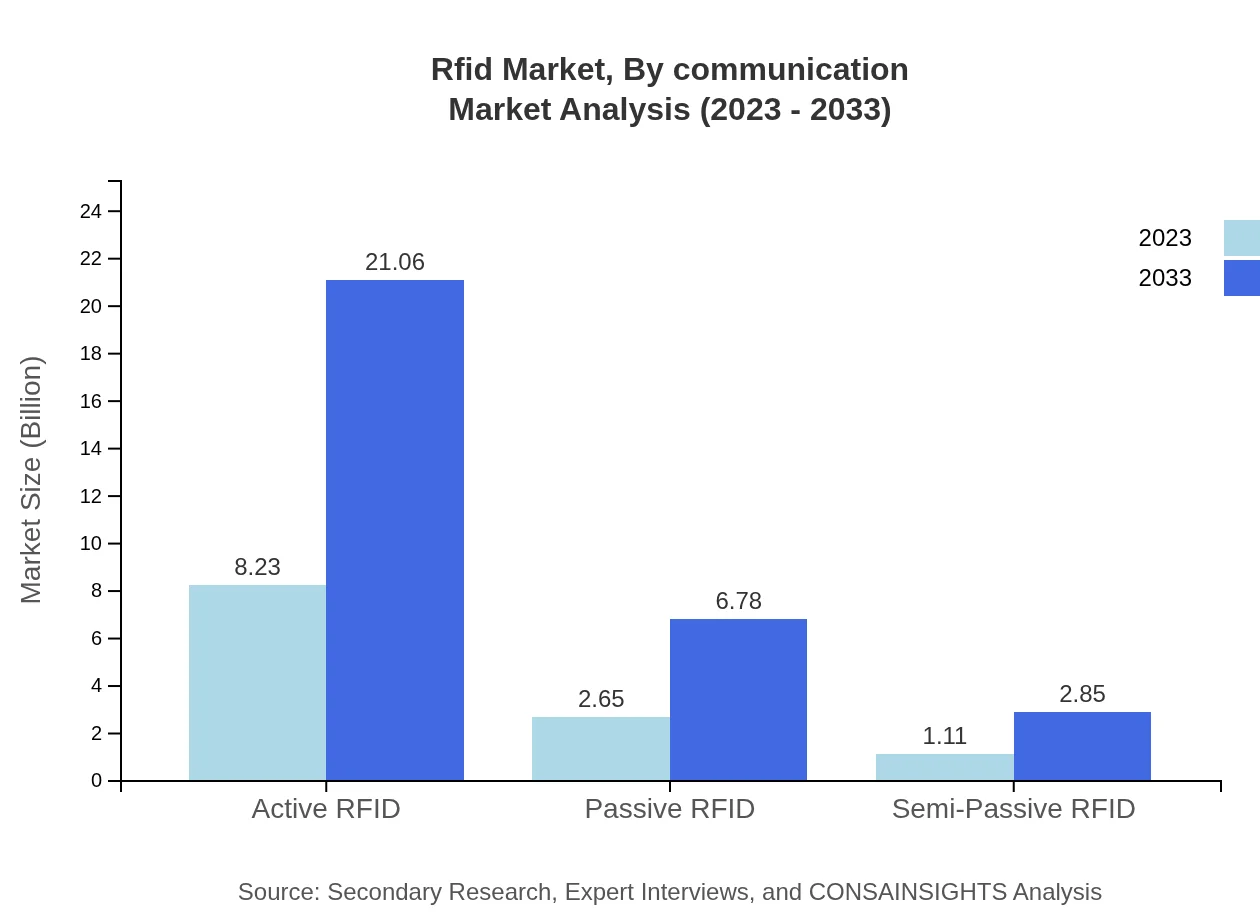
Rfid Market Analysis By Communication
Analysis of communication methods shows strong growth potential, especially with innovations that enhance connectivity and security in automated systems, fitting into the burgeoning automation trends.
RFID Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in RFID Industry
Zebra Technologies:
A leading provider of advanced RFID technology solutions, Zebra Technologies specializes in tracking and visibility solutions, helping businesses enhance automation and improve operational efficiency.Impinj, Inc.:
Impinj focuses on Internet of Things (IoT) solutions, providing RFID technology that connects billions of everyday items, enhancing operational processes across various sectors.Alien Technology:
Known for innovative RFID technology, Alien Technology offers a range of solutions aimed at improving supply chain management and logistics efficiency.Avery Dennison Corporation:
Avery Dennison is a global leader in apparel tagging and RFID solutions, committed to enhancing brand visibility and retail efficiency through innovative materials and technology.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of RFID?
The RFID market is currently valued at approximately $12 Billion and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 9.5% from 2023 to 2033. This growth reflects increasing adoption across various industries, driven by the benefits of real-time data and inventory management.
What are the key market players or companies in the RFID industry?
Several key players dominate the RFID market, including Zebra Technologies, Impinj, Avery Dennison, NXP Semiconductors, and Alien Technology. These companies are known for their innovative RFID technologies and solutions that cater to various sectors.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the RFID industry?
Key drivers for RFID industry growth include enhanced supply chain efficiency, inventory management precision, proliferation of IoT applications, and regulatory mandates in sectors like healthcare. Increased demand for contactless solutions post-pandemic also boosts market growth.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the RFID market?
The fastest-growing region in the RFID market is North America, with a projected growth from $4.47 Billion in 2023 to $11.42 Billion by 2033. Europe and Asia-Pacific also show significant growth potential in the coming years.
Does Consainsights provide customized market report data for the RFID industry?
Yes, Consainsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific client needs in the RFID industry. Clients can request detailed analytics, forecasts, and insights based on desired parameters such as geographic focus, market segments, or applications.
What deliverables can I expect from this RFID market research project?
From this RFID market research project, clients can expect comprehensive reports including market size, growth forecasts, segment analysis, competitive landscape profiles, and strategic insights on emerging trends within the RFID sector.
What are the market trends of RFID?
Current market trends in RFID include the rise of active RFID applications, integration with IoT, advancements in RFID software solutions, and an increasing focus on sustainability. Moreover, sectors like retail and healthcare are rapidly adopting these technologies.