Rna Sequencing Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: rna-sequencing
Rna Sequencing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the RNA sequencing market, detailing market size, trends, segments, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. Key insights into technological advancements, regional performances, and competitive landscapes are also included.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
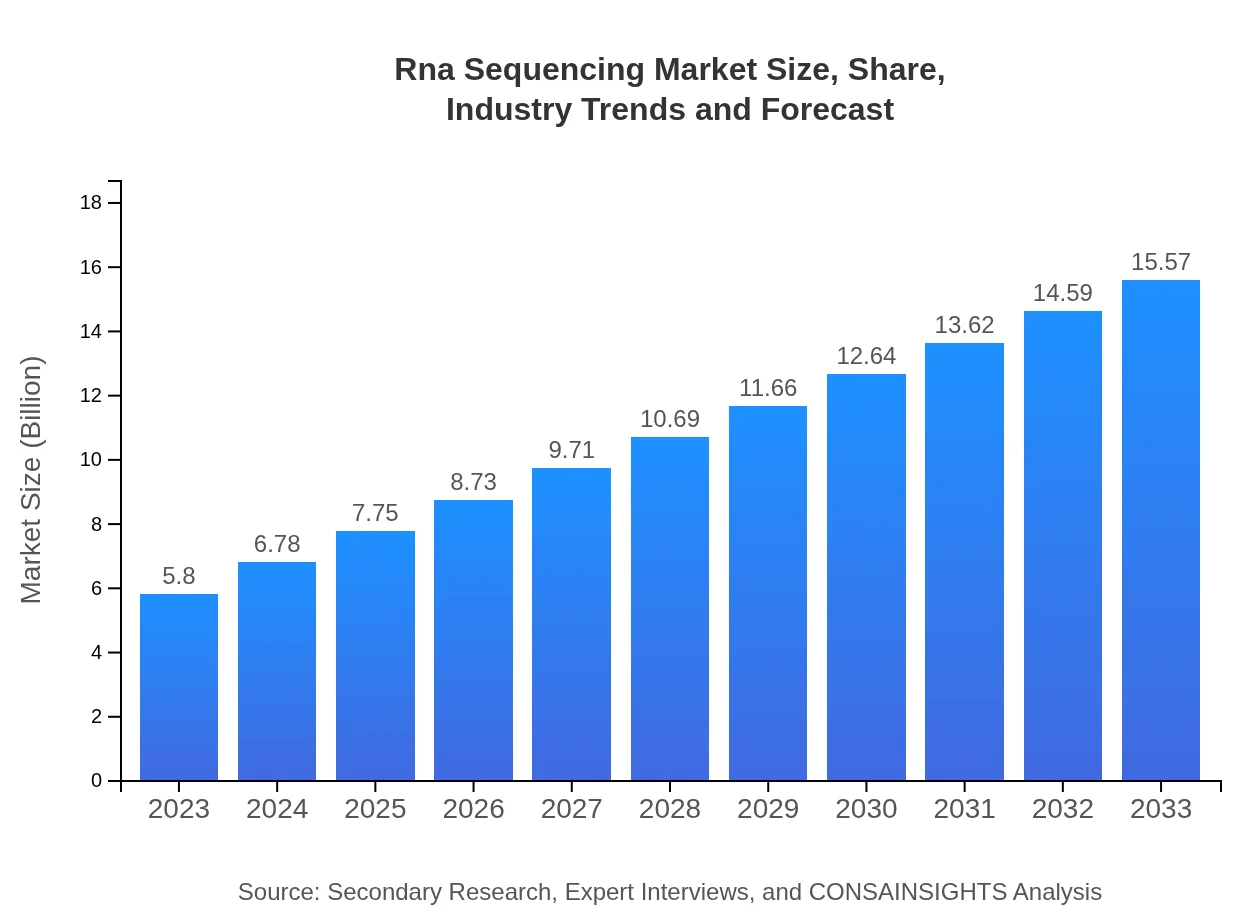
| 2023 Market Size | $5.80 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 10% |
| 2033 Market Size | $15.57 Billion |
| Top Companies | Illumina, Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Roche Sequencing Solutions, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
RNA Sequencing Market Overview
Customize Rna Sequencing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Rna Sequencing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Rna Sequencing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Rna Sequencing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of RNA Sequencing market in 2023?
RNA Sequencing Industry Analysis
RNA Sequencing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
RNA Sequencing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Rna Sequencing Market Report:
The European RNA sequencing market is valued at around $1.54 billion in 2023, expected to rise to $4.13 billion by 2033. Europe is renowned for its emphasis on personalized medicine and ongoing research in genomics. The European Union's initiatives, such as the Horizon Europe program, are instrumental in fostering collaborations across the biotechnology and healthcare sectors, further encouraging market growth.Asia Pacific Rna Sequencing Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the RNA sequencing market is valued at approximately $1.20 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $3.22 billion by 2033, reflecting a robust CAGR. This growth is driven by increasing investments in life sciences research and collaborations among academic institutions. Additionally, the growing prevalence of chronic diseases and the rising focus on precision medicine are propelling the market. Countries such as China, Japan, and India are expected to contribute significantly to the market growth due to their expanding research initiatives and healthcare infrastructure improvements.North America Rna Sequencing Market Report:
North America currently leads the RNA sequencing market, valued at approximately $2.11 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $5.66 billion by 2033. The region's dominance stems from its established healthcare infrastructure, extensive investments in biotech research, and the presence of prominent market players. The United States remains at the forefront due to its advanced technological capabilities and significant healthcare expenditures.South America Rna Sequencing Market Report:
The South American RNA sequencing market is estimated at $0.30 billion in 2023, with expectations to reach $0.81 billion by 2033. The relatively slower growth compared to other regions is attributed to limited funding for research and development. However, an upsurge in genomics-related studies and rising interest in agricultural biotechnology could enhance market dynamics in the coming years.Middle East & Africa Rna Sequencing Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the RNA sequencing market reached approximately $0.65 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to grow to $1.75 billion by 2033. Factors such as increasing healthcare investments and a growing focus on genomic studies contribute to this growth. The region is witnessing a gradual but steady increase in the adoption of RNA sequencing in research settings, particularly in South Africa and the UAE.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Rna Sequencing Market Analysis By Technique
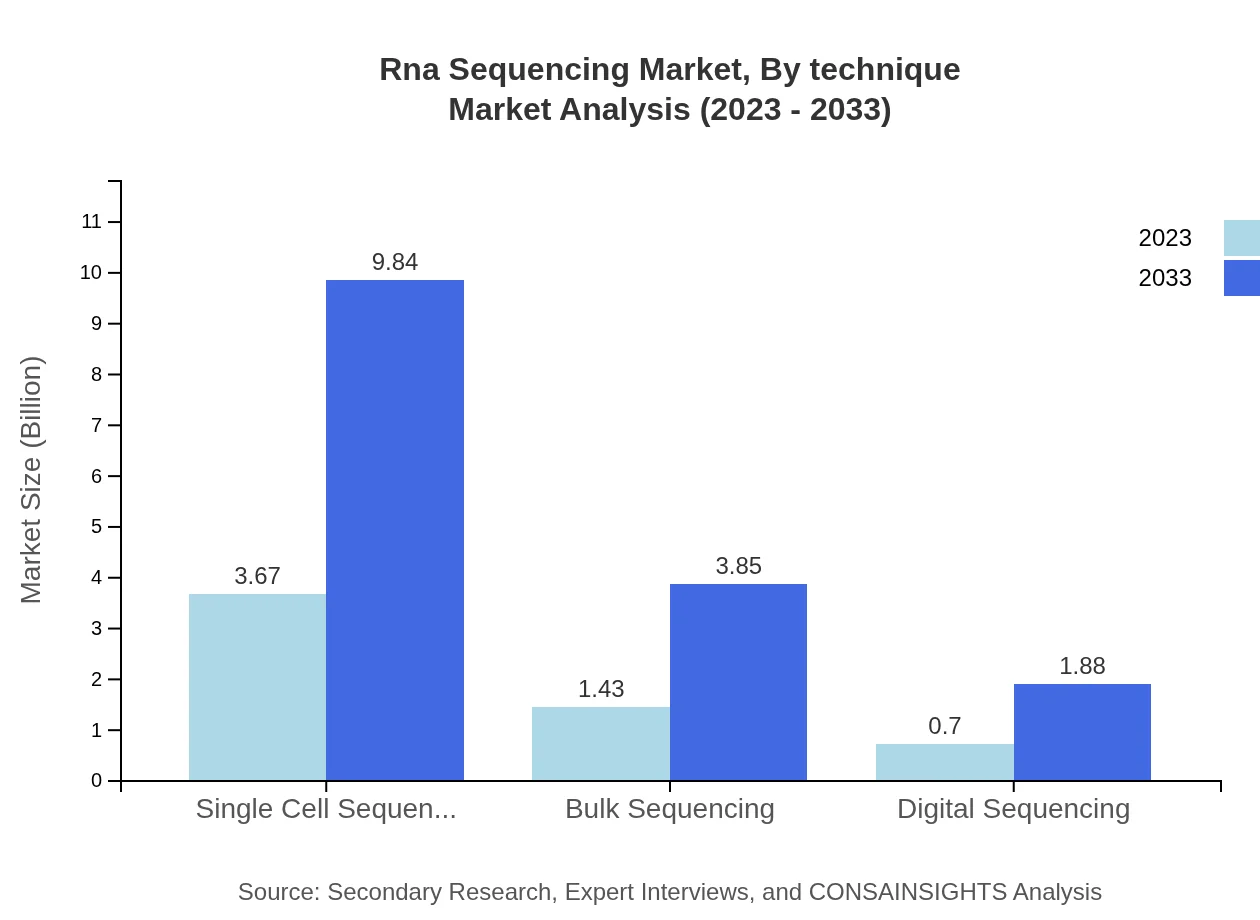
The RNA sequencing market, segmented by technique, is dominated by techniques such as single-cell sequencing, bulk sequencing, and digital sequencing. In 2023, the market for single-cell sequencing is estimated at approximately $3.67 billion, projected to reach $9.84 billion by 2033, accounting for a significant share of around 63.2% in both years. Bulk sequencing follows, currently valued at $1.43 billion and expected to grow to $3.85 billion by 2033, maintaining a market share of about 24.74%. Digital sequencing, valued at $0.70 billion in 2023, is expected to expand to $1.88 billion by 2033, holding about 12.06% of the market share.
Rna Sequencing Market Analysis By Product
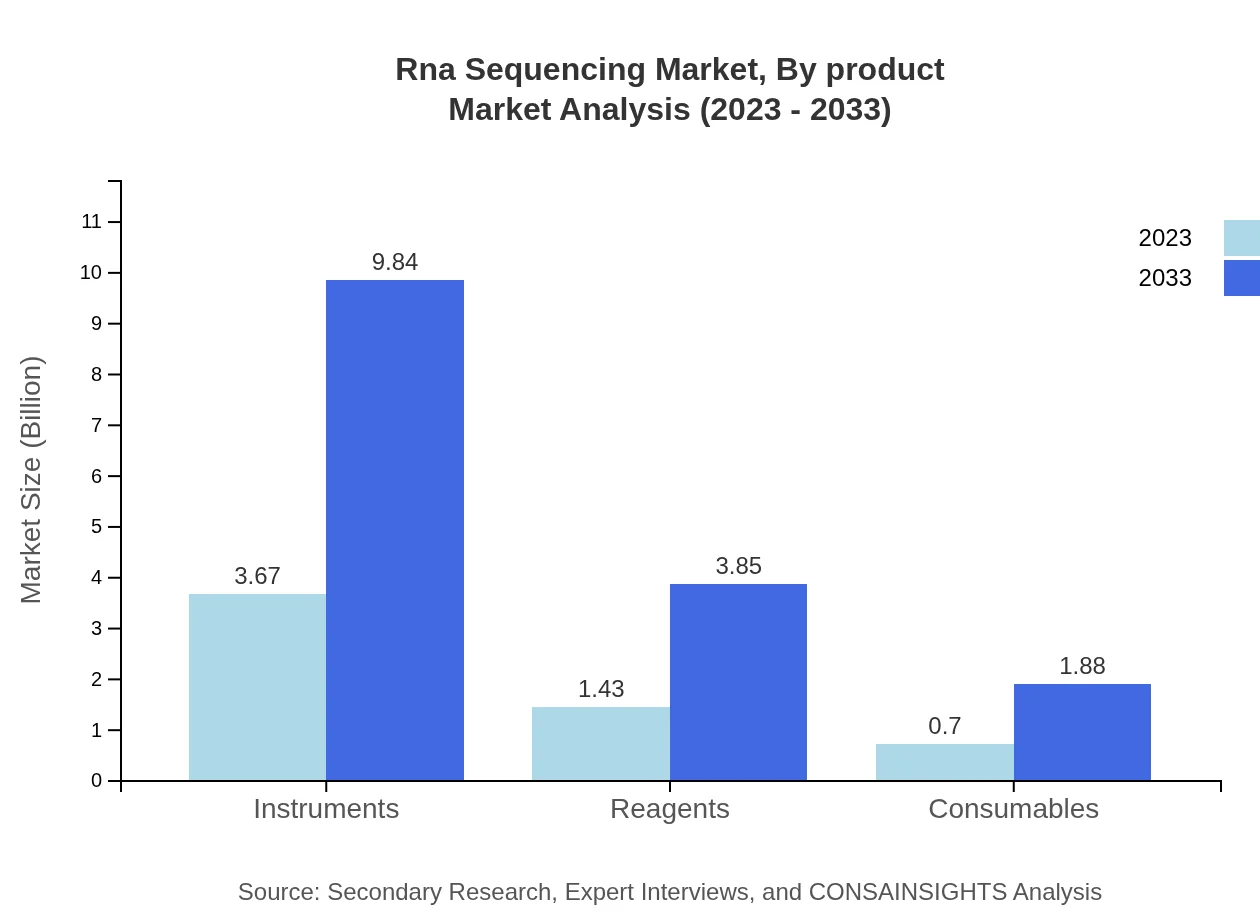
The RNA sequencing market is segmented by product into instruments, reagents, and consumables. Instruments dominate the market with a size of $3.67 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $9.84 billion by 2033, maintaining a share of 63.2%. Reagents are predicted to grow from $1.43 billion in 2023 to $3.85 billion by 2033, representing a significant share of 24.74%. Consumables, while smaller, are showing promising growth, from $0.70 billion in 2023 to $1.88 billion by 2033, holding a share of 12.06%.
Rna Sequencing Market Analysis By Application
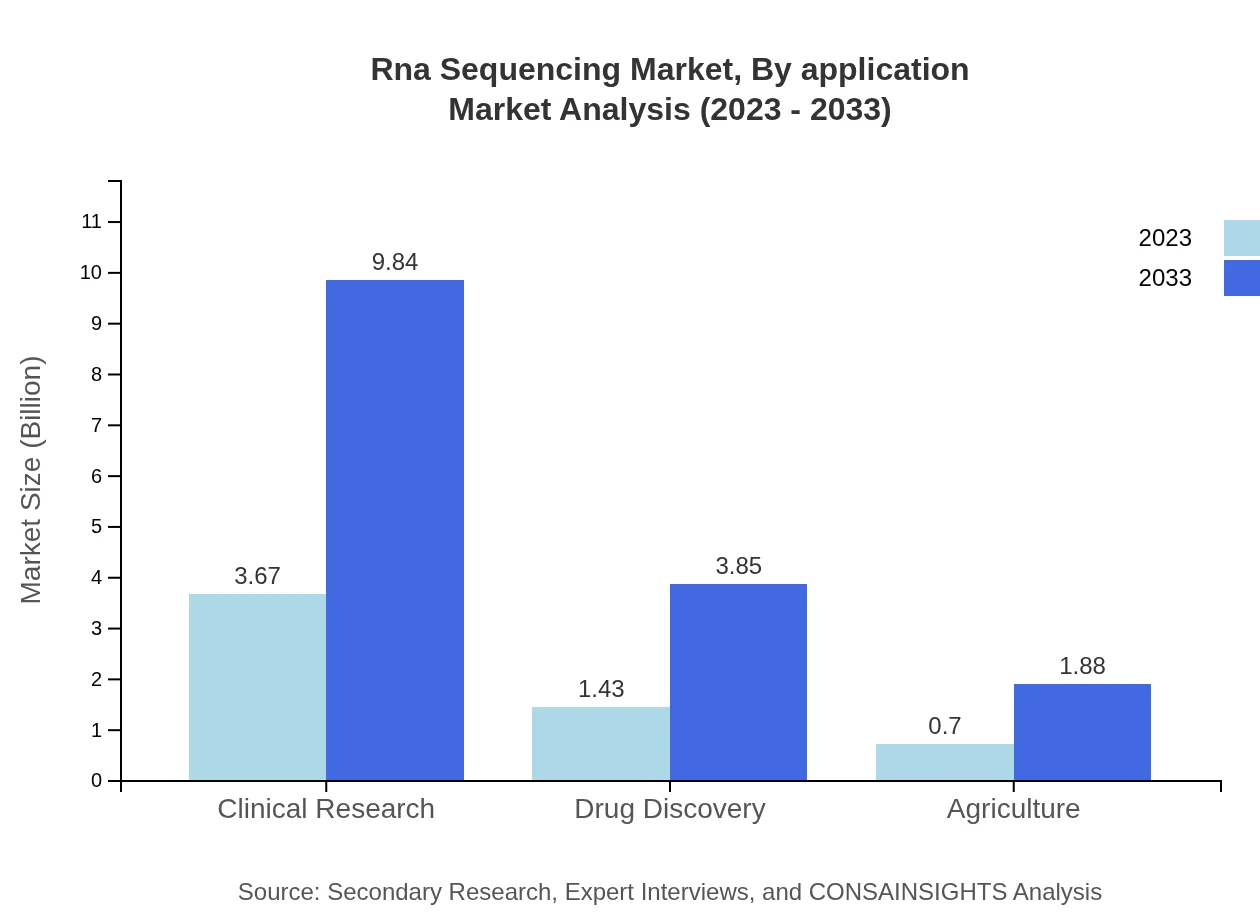
The market segmentation by application highlights significant demand in clinical research, drug discovery, and agriculture. Clinical research dominates the application segment with a size of $3.67 billion in 2023, expected to reach $9.84 billion by 2033, maintaining a market share of 63.2%. Drug discovery values at $1.43 billion currently is anticipated to grow to $3.85 billion by 2033, representing a share of 24.74%. Agriculture-related applications are expected to reach $1.88 billion by the same year, indicating a growing market focus.
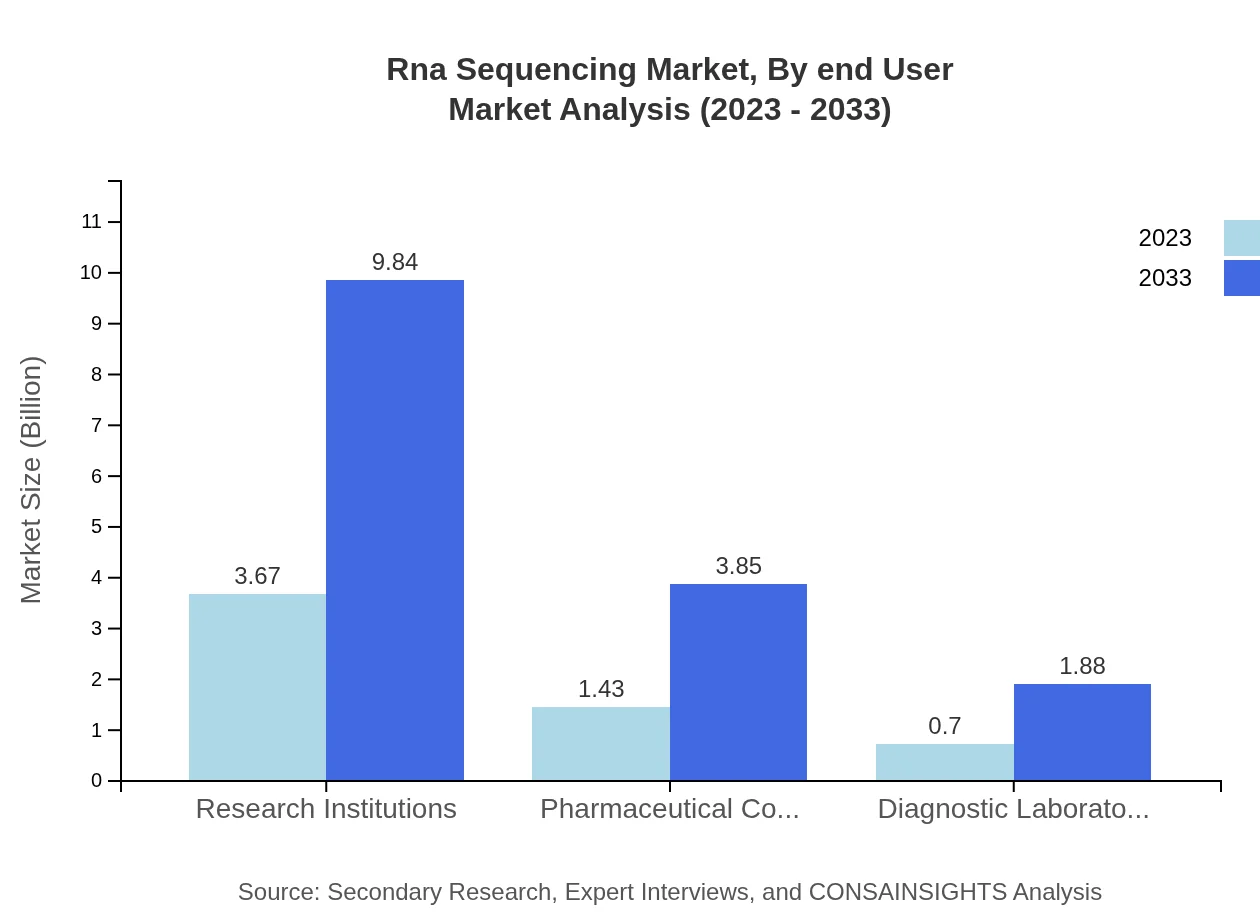
Rna Sequencing Market Analysis By End User
The RNA sequencing market's end-user segmentation reveals substantial contributions from research institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and diagnostic laboratories. Research institutions lead with $3.67 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $9.84 billion by 2033, sustaining a share of 63.2%. Pharmaceutical companies follow with $1.43 billion in 2023, anticipated to rise to $3.85 billion by 2033, capturing a market share of 24.74%. Diagnostic laboratories, while smaller, show consistent growth, projected to expand from $0.70 billion to $1.88 billion over the same period, holding a share of 12.06%.
RNA Sequencing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in RNA Sequencing Industry
Illumina, Inc.:
Illumina is a leading company in the genetic analysis market and is recognized for its advanced sequencing technologies and systems. Their products, particularly the sequencing equipment, play a crucial role in facilitating high-throughput RNA sequencing.Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.:
Thermo Fisher is a major player in the RNA sequencing field, providing comprehensive solutions for research, including reagents, instruments, and technical support, enhancing the efficiency of RNA analysis in various applications.Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.:
Bio-Rad is well-known in the life sciences sector for its innovative tools and services, supporting RNA sequencing and genomics research, particularly through its offerings in molecular biology kits and reagents.Roche Sequencing Solutions, Inc.:
Roche Sequencing Solutions focuses on delivering innovative sequencing technologies that support accurate and efficient RNA sequencing, catering primarily to clinical and research markets.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of RNA sequencing?
The RNA sequencing market is currently valued at approximately $5.8 billion and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10% over the next decade. This growth signals increasing interest and investment in genetic research and diagnostics.
What are the key market players or companies in this RNA sequencing industry?
Key players in the RNA sequencing market include Illumina, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Pacific Biosciences. These companies lead with their innovative sequencing technologies and broad range of products, spanning instruments and reagents.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the RNA sequencing industry?
The growth of the RNA sequencing industry is primarily driven by advancements in genomic technologies, increased funding for genomic projects, and the rising prevalence of genetic disorders, leading to heightened demand for RNA sequencing services.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the RNA sequencing market?
Among various regions, North America is the fastest-growing market for RNA sequencing, projected to expand from $2.11 billion in 2023 to $5.66 billion by 2033, indicating robust investments in genomic research and technology.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the RNA sequencing industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the RNA sequencing industry, enabling clients to access detailed insights and trends relevant to their business context.
What deliverables can I expect from this RNA sequencing market research project?
Clients can expect comprehensive deliverables including detailed market analysis reports, regional market segmentation data, competitive landscape analysis, and forecasts that cover various segments like instruments and reagents.
What are the market trends of RNA sequencing?
Current market trends in RNA sequencing include a shift towards single-cell sequencing approaches, integration of AI for data analysis, and growing applications in clinical diagnostics and personalized medicine, indicating ongoing innovation.