Robotics Industry Coverage Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: robotics-industry-coverage
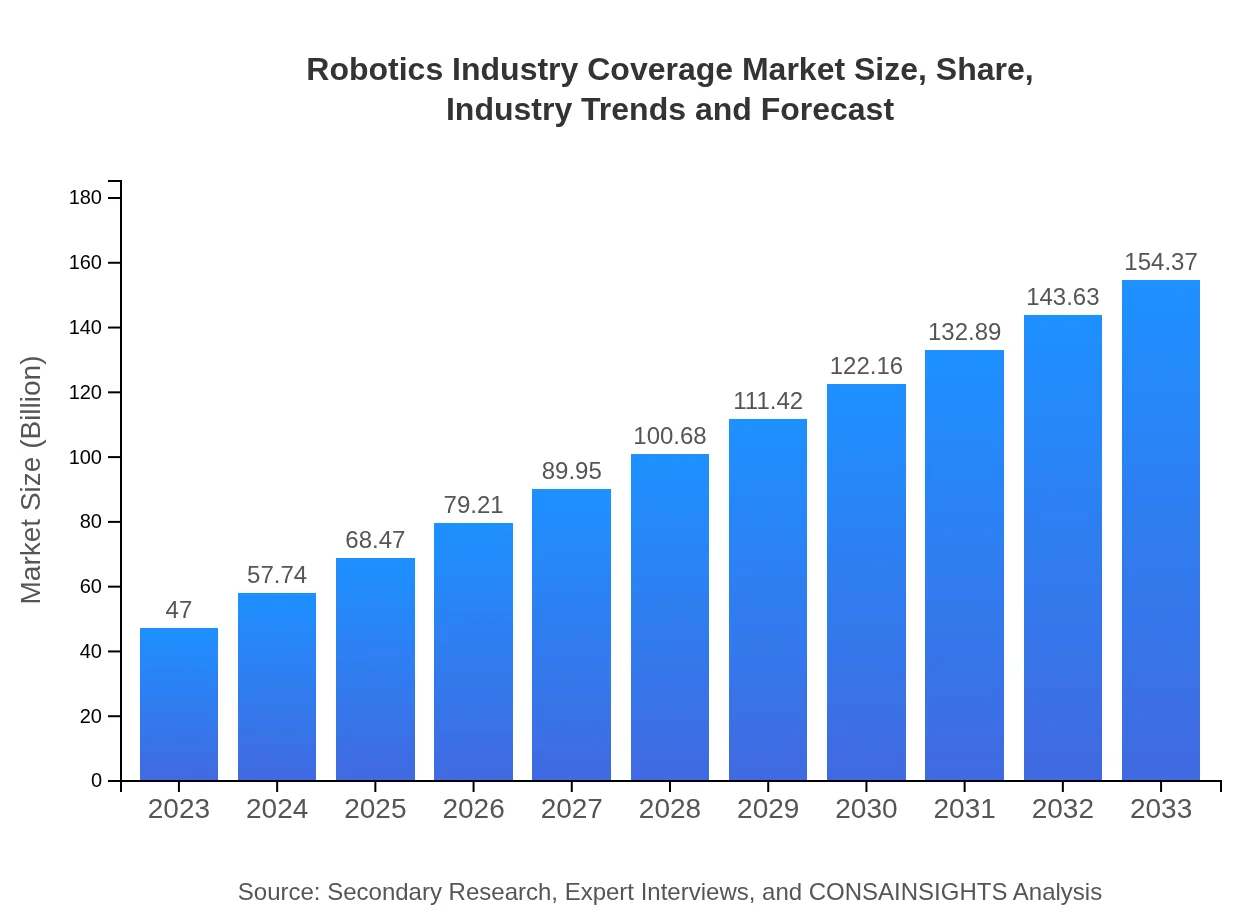
Robotics Industry Coverage Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This market report provides comprehensive insights into the Robotics Industry Coverage from 2023 to 2033, analyzing market trends, size, technology impacts, segment performance, and regional developments. It aims to equip stakeholders with data-driven recommendations for strategic decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $47.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 12.1% |
| 2033 Market Size | $154.37 Billion |
| Top Companies | ABB Ltd., Fanuc Corporation, KUKA AG, Boston Dynamics, iRobot Corporation |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Robotics Industry Coverage Market Overview
Customize Robotics Industry Coverage Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Robotics Industry Coverage market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Robotics Industry Coverage's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Robotics Industry Coverage
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Robotics Industry Coverage market in 2023?
Robotics Industry Coverage Industry Analysis
Robotics Industry Coverage Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Robotics Industry Coverage Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Robotics Industry Coverage Market Report:
The European robotics market stands at $16.47 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to $54.11 billion by 2033. The increase is propelled by stringent compliance regulations, workforce productivity demands, and a strong focus on sustainability in manufacturing practices.Asia Pacific Robotics Industry Coverage Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is experiencing robust growth in the robotics market, valued at approximately $8.87 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $29.14 billion by 2033. Factors such as rapid industrialization, increasing technological adoption, and government initiatives to promote automation significantly drive this expansion.North America Robotics Industry Coverage Market Report:
North America, with a market size of $16.08 billion in 2023, is projected to expand to $52.82 billion by 2033. The U.S. leads the way due to significant investments in robotics in manufacturing and defense, supported by a strong R&D environment that fosters technological advancements.South America Robotics Industry Coverage Market Report:
The South American market for robotics is estimated at $3.83 billion in 2023, with expectations of reaching $12.57 billion by 2033. The region's growth is sparked by investments in automation in various industries, such as mining and agriculture, even though it currently faces infrastructural challenges.Middle East & Africa Robotics Industry Coverage Market Report:
The market in the Middle East and Africa is smaller but growing, with a market value of $1.74 billion in 2023, projected to hit $5.73 billion by 2033. Factors driving growth include investment in tech sectors and a push for modernization and automation in key industries.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
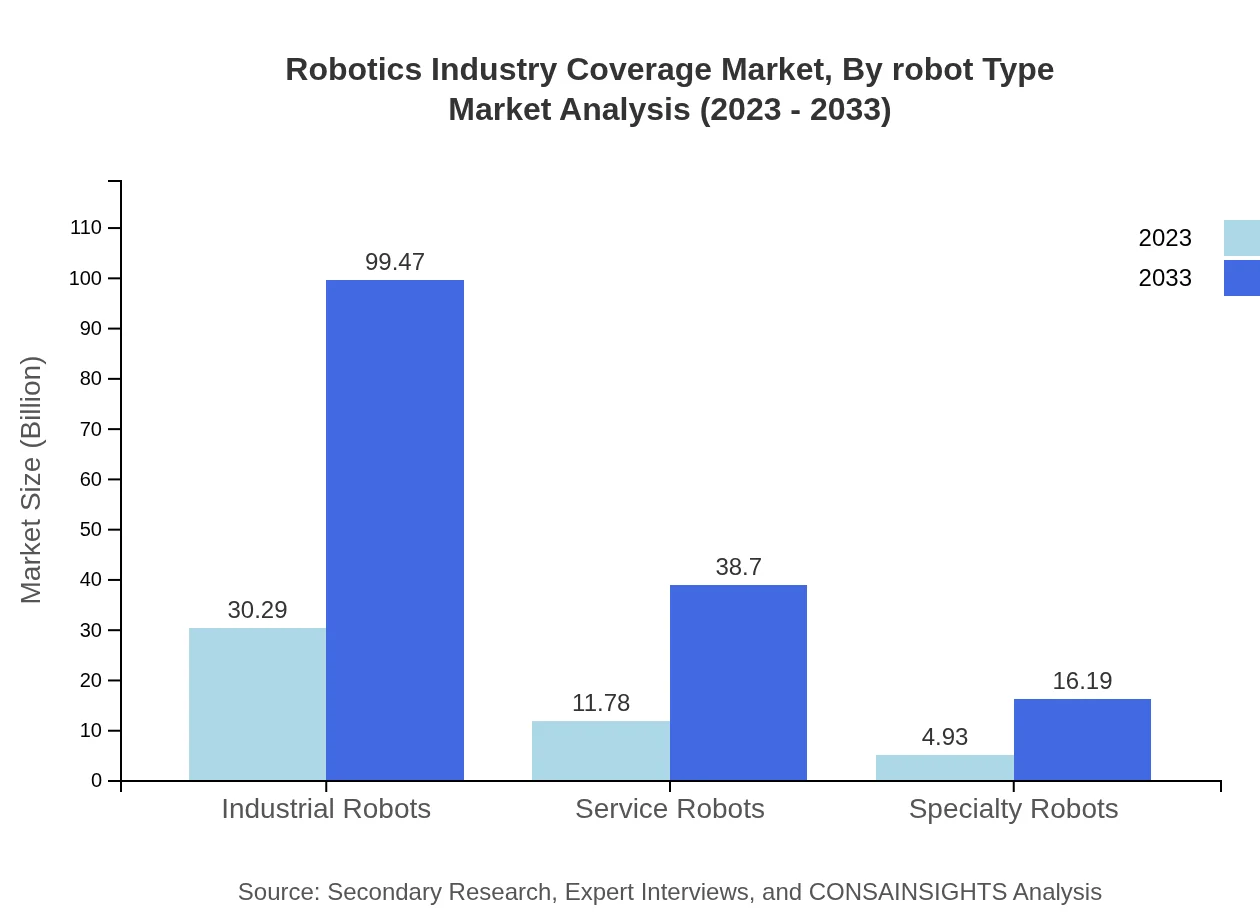
Robotics Industry Coverage Market Analysis By Robot Type
In 2023, industrial robots dominate the market at $30.29 billion, projected to reach $99.47 billion by 2033. Service robots, valued at $11.78 billion, are expected to grow to $38.70 billion, while specialty robots range from $4.93 billion to $16.19 billion. These trends indicate a diversified market with growing acceptance of robots across various sectors.
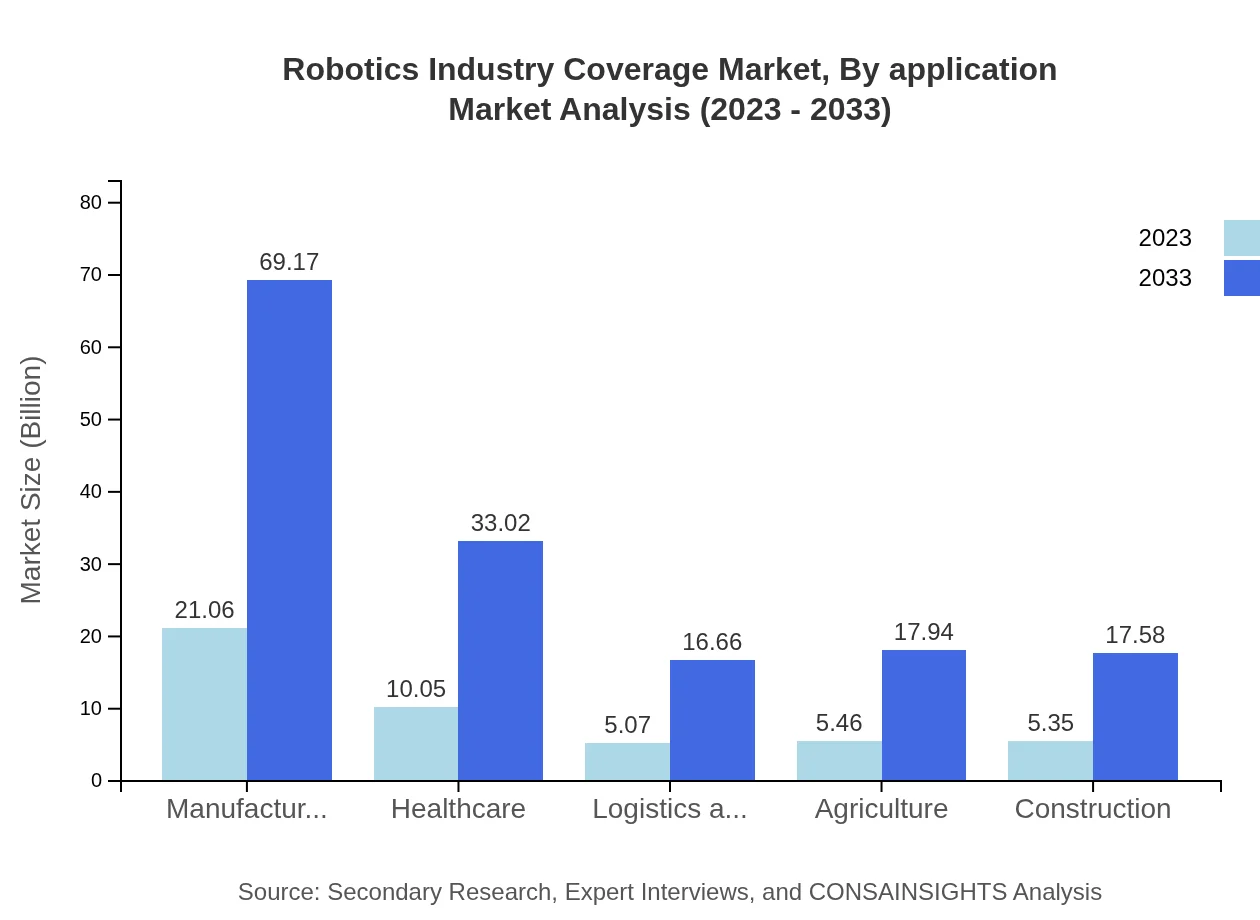
Robotics Industry Coverage Market Analysis By Application
Manufacturing remains the largest application area, expected to rise from $21.06 billion in 2023 to $69.17 billion by 2033, while healthcare's segment moves from $10.05 billion to $33.02 billion. Other significant sectors include retail, defense, logistics, and agriculture, reflecting robotics' versatility and applicability.
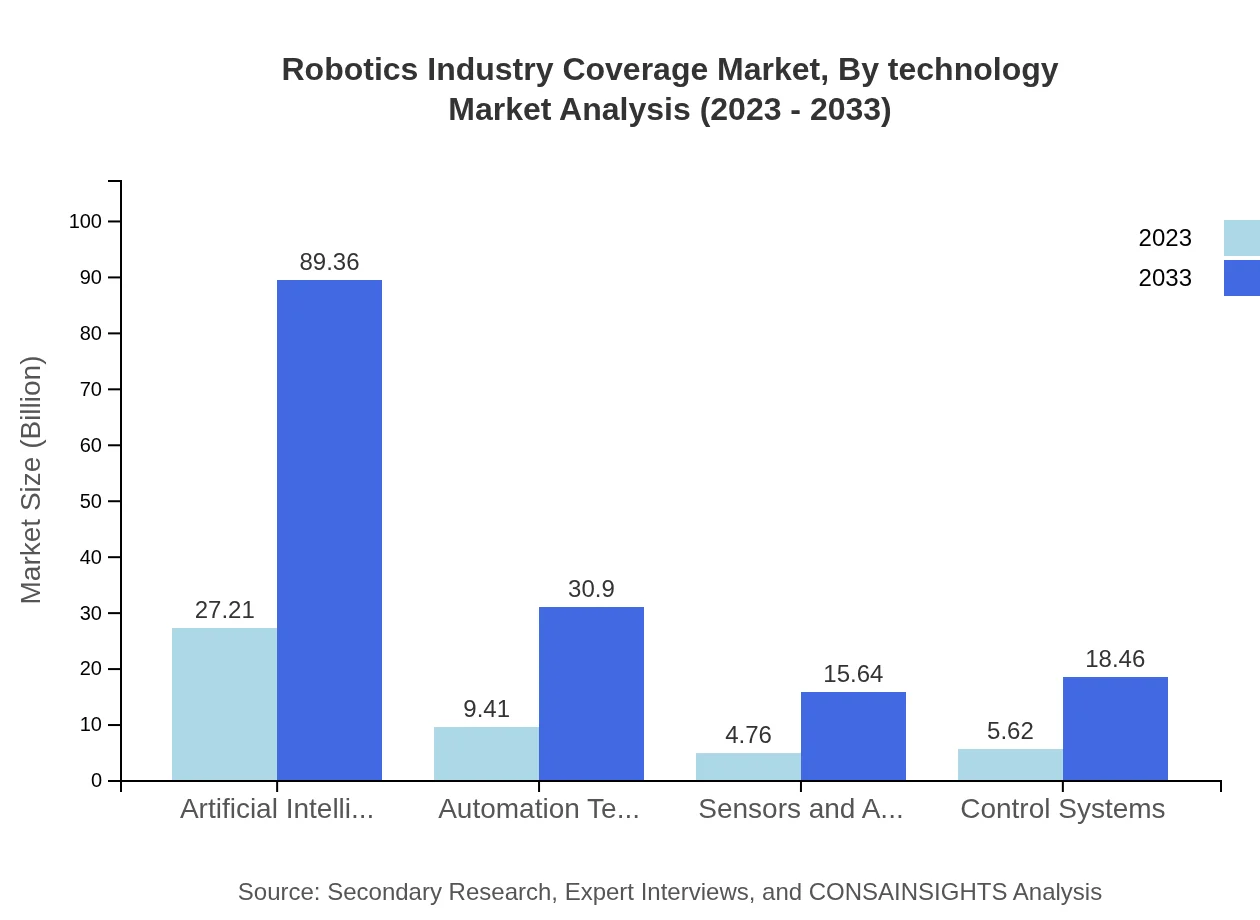
Robotics Industry Coverage Market Analysis By Technology
Artificial intelligence, a leading technology in robotics, shows growth from $27.21 billion in 2023 to $89.36 billion by 2033. Advanced automation technologies and sensors and actuators also reflect increasing market shares and innovation adoption. This signifies that technological advancement is a key driver for expansion in this industry.
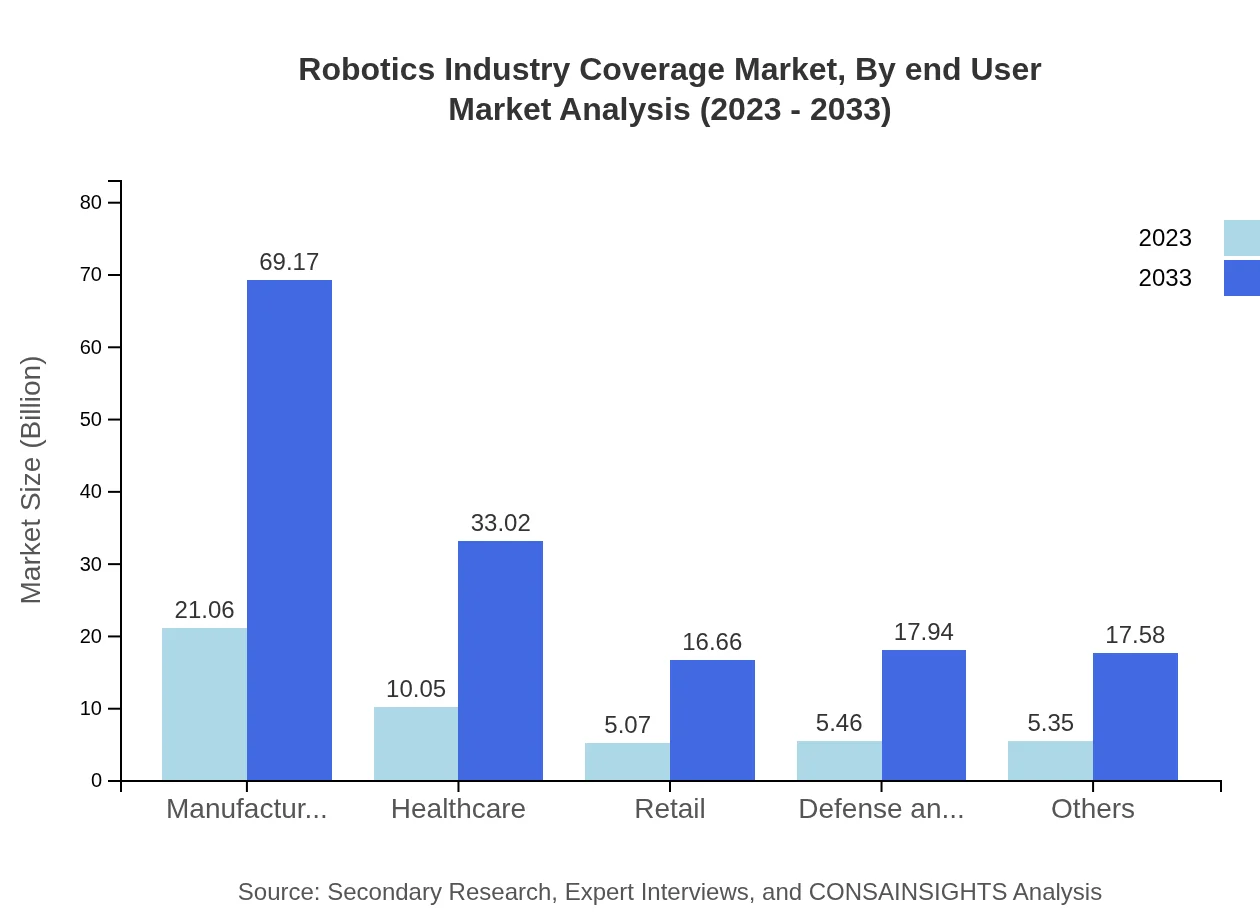
Robotics Industry Coverage Market Analysis By End User
The end-user industry analysis reveals significant growth in manufacturing (projected to remain at 44.81% share) and healthcare (21.39% share), reflecting strong investments in productivity and efficiency. Emerging markets such as logistics and agriculture are also gaining ground, indicating broader acceptance of robotics across various sectors.
Robotics Industry Coverage Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Robotics Industry Coverage Industry
ABB Ltd.:
A leader in industrial robotics, ABB specializes in automation and innovative robotics solutions, driving efficiencies in manufacturing and production processes.Fanuc Corporation:
A major player in automation and robotics, Fanuc manufactures a variety of industrial robots, control systems, and CNC solutions for numerous industries.KUKA AG:
Known for developing innovative automation solutions, KUKA specializes in robotics and system integration for various applications across multiple industries.Boston Dynamics:
Renowned for its cutting-edge robotics solutions, Boston Dynamics focuses heavily on mobile robots, garnering attention in defense and logistics sectors.iRobot Corporation:
A pioneering developer of consumer robots, iRobot specializes in smart home robotics, enhancing consumer daily life through automation technologies.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of robotics Industry Coverage?
The market size of the robotics industry is projected to reach $47 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.1% from 2023 onwards.
What are the key market players or companies in this robotics Industry Coverage industry?
Key players in the robotics industry include companies specializing in automation, AI, manufacturing robots, and healthcare solutions, contributing to innovation and competitive advancements in robotics technology.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the robotics Industry Coverage industry?
Major factors driving growth include increasing automation needs across industries, advancements in AI and machine learning, and a rising demand for efficiency and productivity in manufacturing and healthcare sectors.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the robotics Industry Coverage?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing in the robotics industry, projected to grow from $8.87 billion in 2023 to $29.14 billion by 2033, driven by industrial automation adoption.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the robotics Industry Coverage industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific needs within the robotics industry, enabling businesses to gain insights aligned with their market strategies.
What deliverables can I expect from this robotics Industry Coverage market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis reports, segmented data insights, competitive landscape assessments, and forecasts, all tailored to the robotics industry specifics.
What are the market trends of robotics Industry Coverage?
Current trends include increasing integration of AI in robotics, growth in service robots across various sectors, and an expanding focus on autonomous systems and smart manufacturing solutions.