Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: satellite-based-earth-observation
Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Satellite Based Earth Observation market, including market size, trends, forecasts, and regional insights from 2023 to 2033. It aims to present valuable data that aids stakeholders in making informed decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
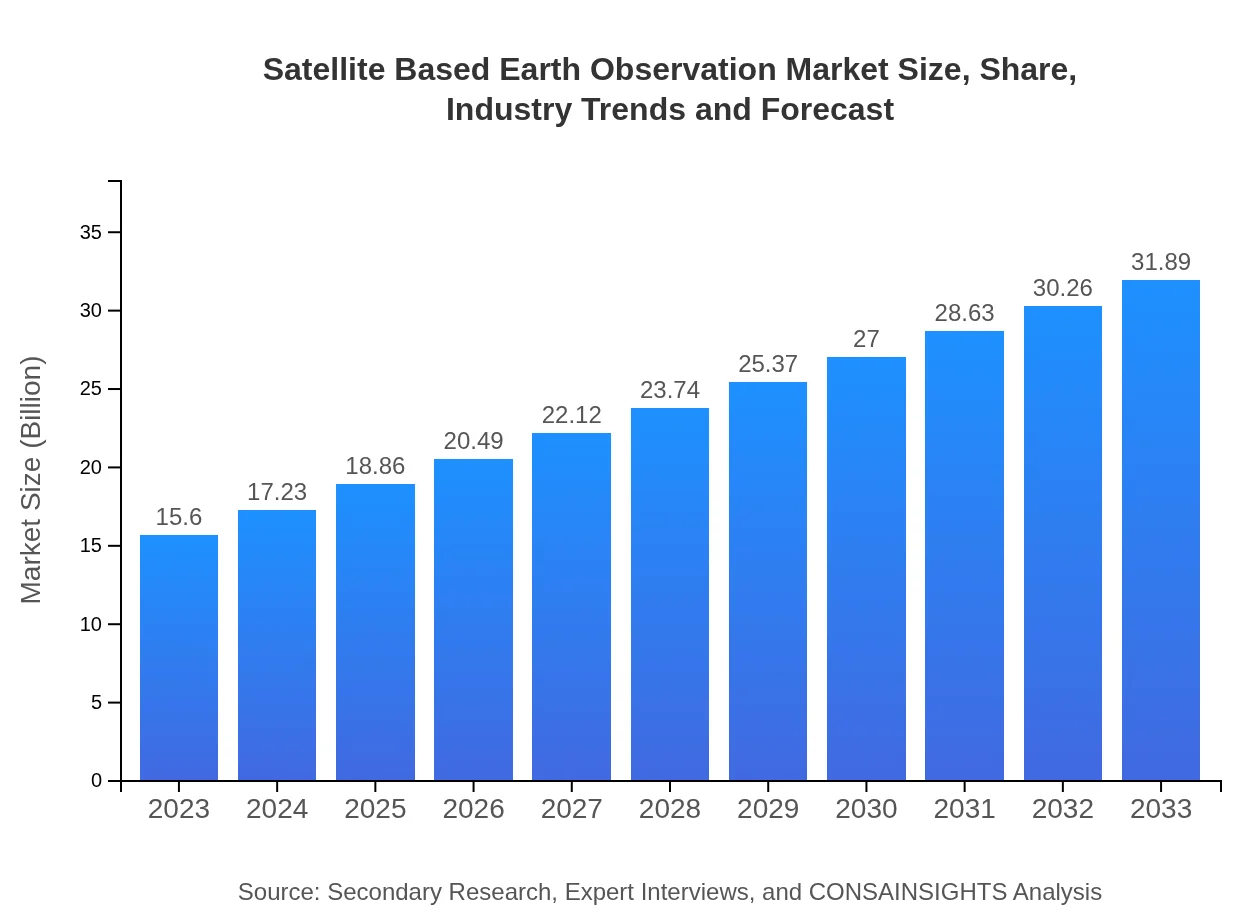
| 2023 Market Size | $15.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $31.89 Billion |
| Top Companies | Maxar Technologies, European Space Agency (ESA), Planet Labs, Airbus Defence and Space |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Overview
Customize Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Satellite Based Earth Observation market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Satellite Based Earth Observation's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Satellite Based Earth Observation
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Satellite Based Earth Observation market in 2023?
Satellite Based Earth Observation Industry Analysis
Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Report:
In Europe, the market is expected to rise from $3.92 billion in 2023 to $8.01 billion by 2033. The focus on sustainable development and precision agriculture coupled with collaborative European Space Agency initiatives drives this growth.Asia Pacific Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Report:
In the Asia-Pacific region, the Satellite Based Earth Observation market is projected to grow from $3.03 billion in 2023 to $6.19 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by increasing investments in satellite technology and the growing demand for environmental monitoring services.North America Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Report:
North America holds a significant share of the SBEO market, expected to increase from $5.62 billion in 2023 to approximately $11.49 billion by 2033. The substantial growth in this region is attributed to high governmental funding and a robust technological landscape.South America Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Report:
The South American market is set to grow from $0.87 billion in 2023 to $1.78 billion by 2033. This growth is driven primarily by advancements in agricultural monitoring and environmental protection efforts against climate change.Middle East & Africa Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's Satellite Based Earth Observation market will grow from $2.16 billion in 2023 to $4.42 billion by 2033, influenced by increased applications in disaster management and environmental monitoring.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Analysis By Application
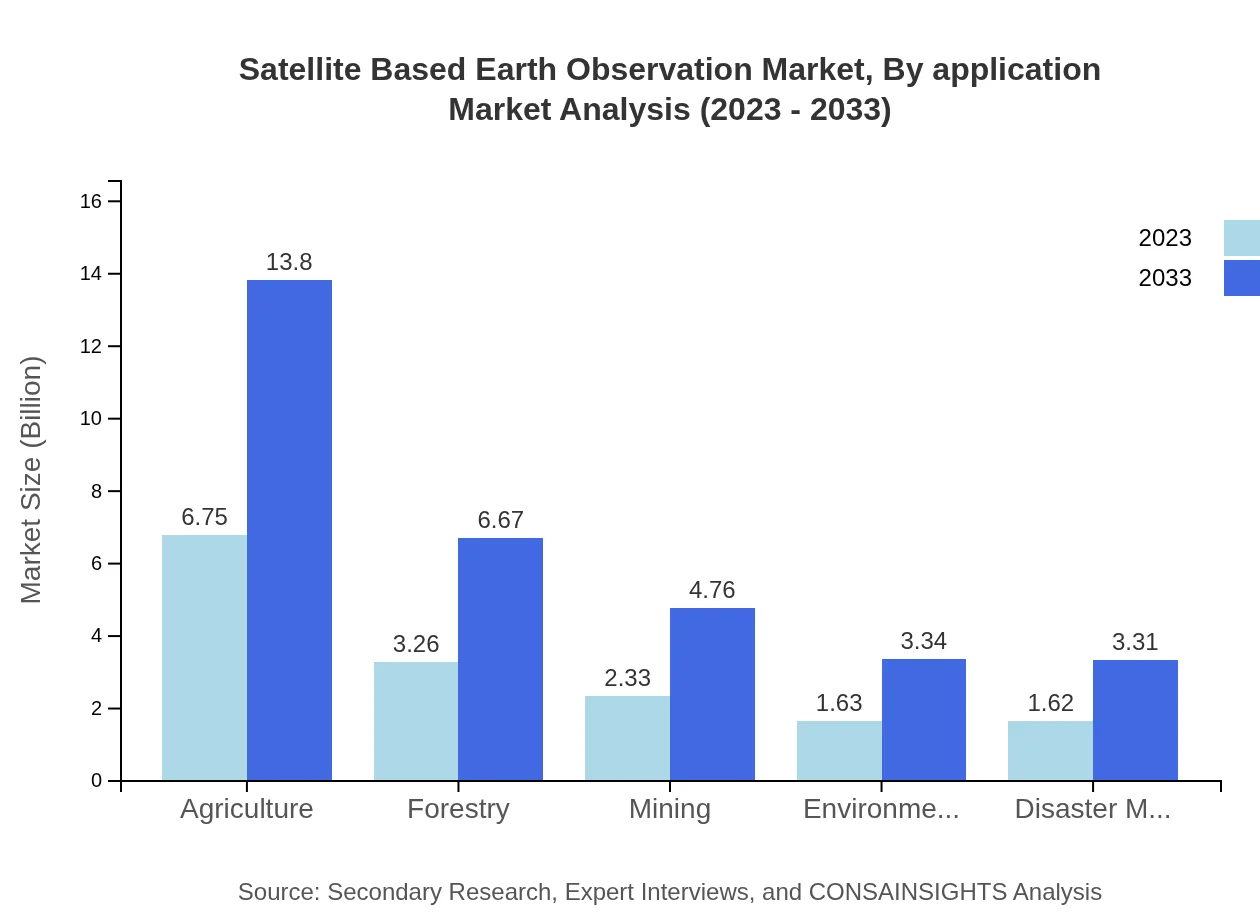
Applications of Satellite Based Earth Observation include agriculture ($6.75 billion currently, growing to $13.80 billion by 2033, contributing 43.29% to market share), forestry, with significant growth anticipated from $3.26 billion to $6.67 billion (20.92% share), and mining, expected to grow from $2.33 billion to $4.76 billion (14.94% share). Environmental monitoring and disaster management also play critical roles in this landscape, each representing 10.46% and 10.39% market shares, respectively.
Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Analysis By Technology
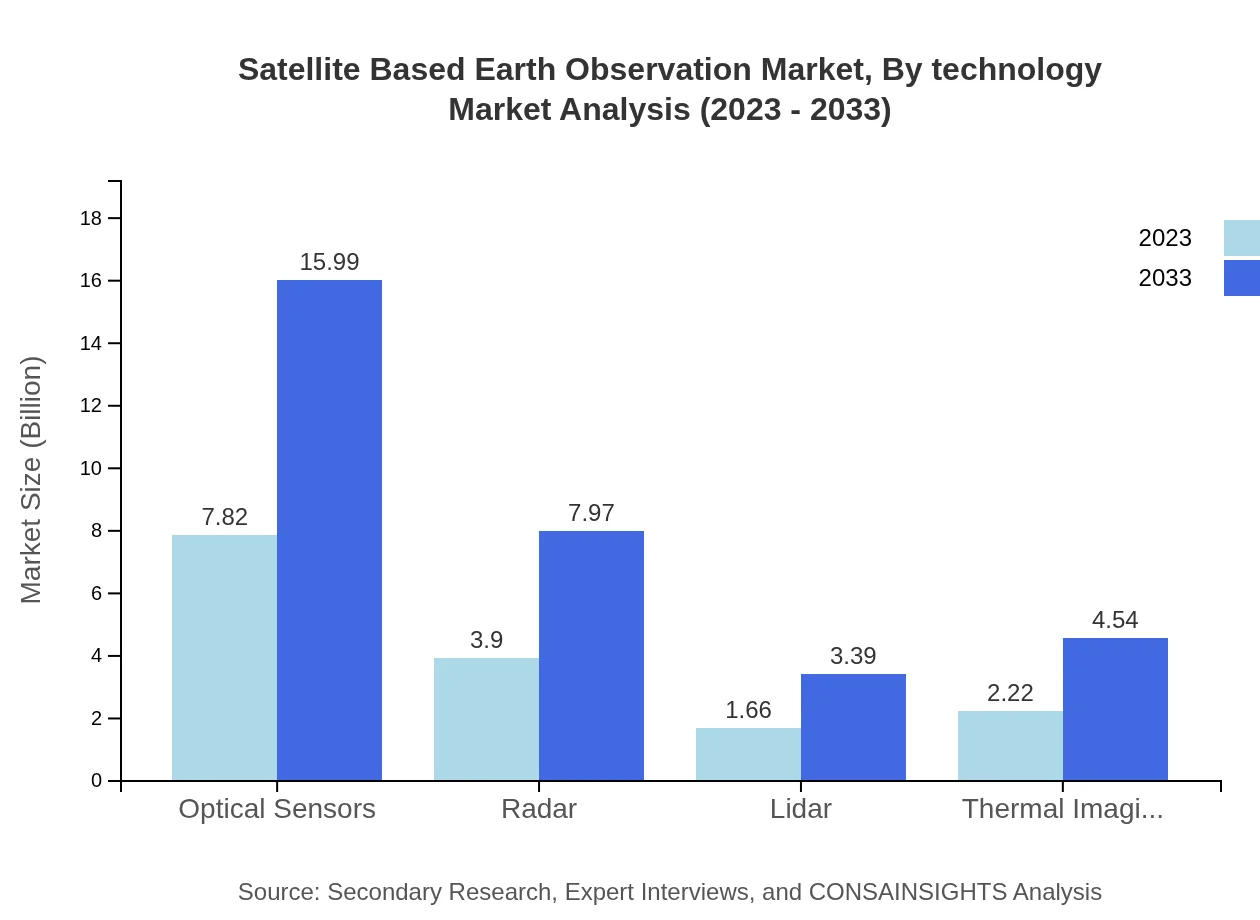
Technological segmentation highlights the dominance of optical sensors, valued at $7.82 billion and projected to reach $15.99 billion, capturing a 50.15% market share. Radar technologies follow, with current revenues of $3.90 billion expected to grow to $7.97 billion (24.99% share). Lidar and thermal imaging technologies also show growth potential, contributing 10.63% and 14.23% market shares, respectively.
Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Analysis By End User
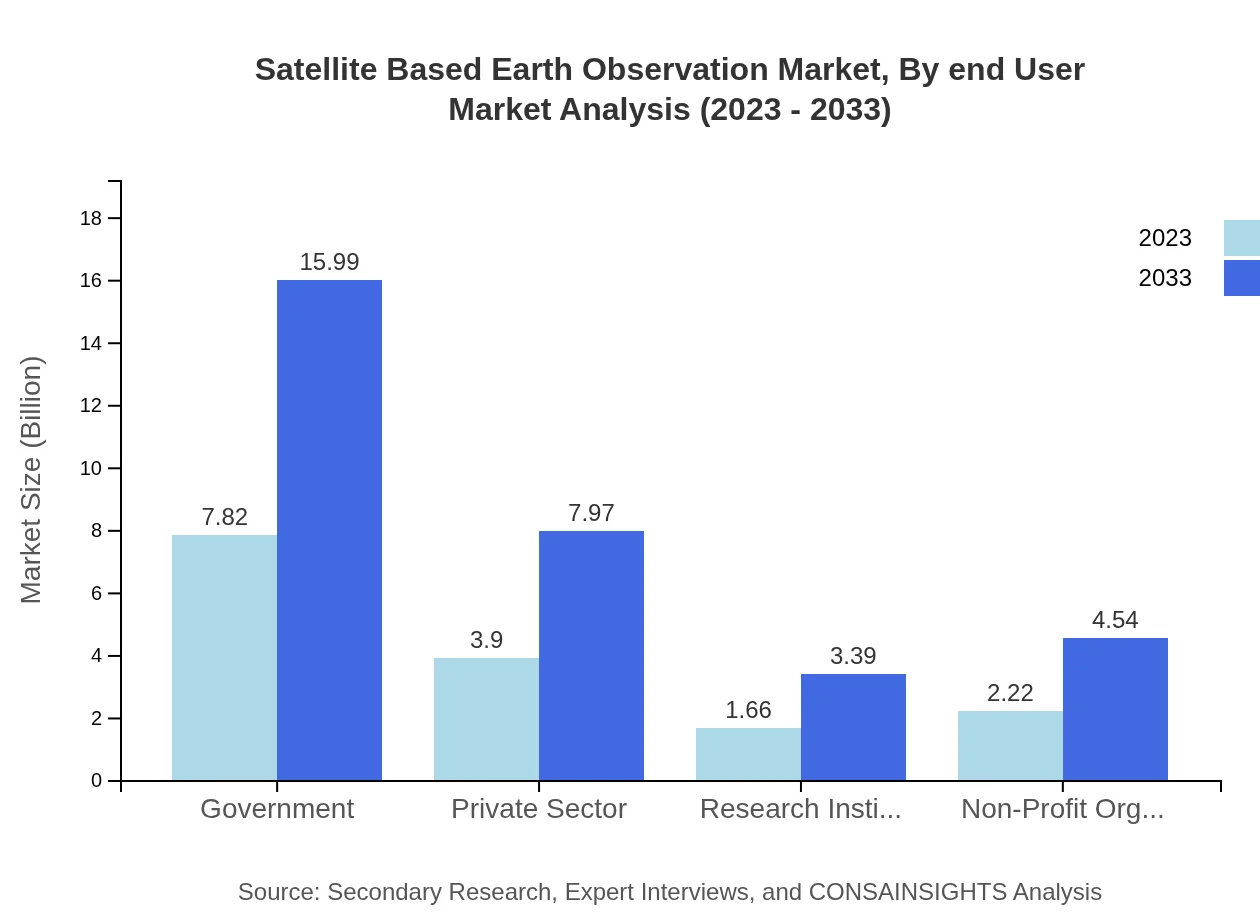
The end-user segmentation indicates that government agencies are the largest consumers, commanding a market size of $7.82 billion, growing to $15.99 billion by 2033 (50.15% share). The private sector, research institutes, and non-profit organizations also play significant roles, contributing to a diversified market that enhances overall industry resilience.
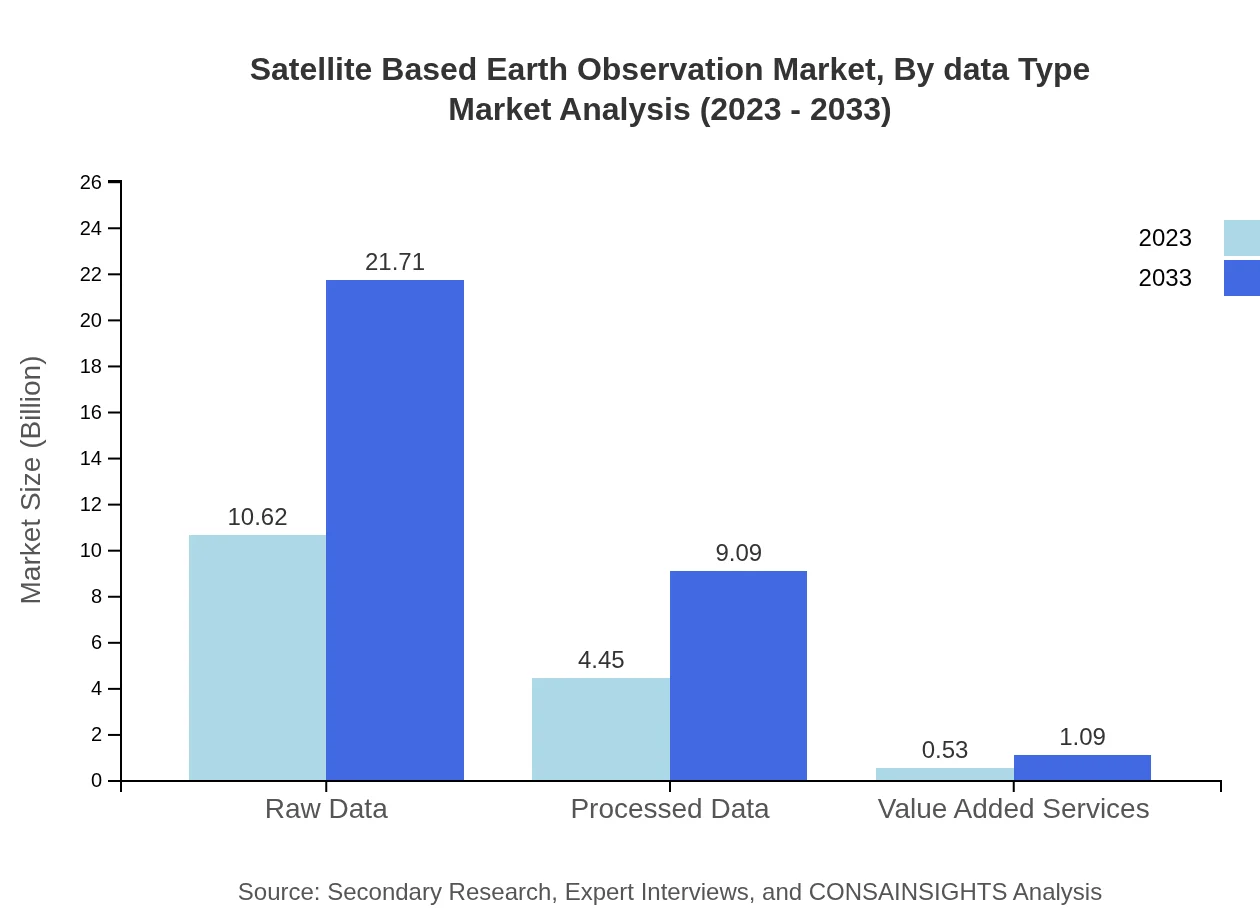
Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Analysis By Data Type
In terms of data types, raw data constitutes the majority segment, currently valued at $10.62 billion and expected to grow to $21.71 billion, capturing 68.08% of the market share. Processed data follows with a significant focus on value-added services, underscoring the industry's shift toward more sophisticated data offerings.
Satellite Based Earth Observation Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Satellite Based Earth Observation Industry
Maxar Technologies:
A leader in satellite imagery and geospatial data products, Maxar is known for its high-resolution imaging capabilities and significant contributions to various industries, including defense and agriculture.European Space Agency (ESA):
An intergovernmental organization dedicated to the exploration of space, ESA also plays a vital role in environmental monitoring and climate change research through its Earth Observation programs.Planet Labs:
Planet is a private Earth imaging company that operates satellites that provide high-frequency imaging and analytics, contributing significantly to agriculture, forestry, and urban planning sectors.Airbus Defence and Space:
Part of Airbus Group, this company specializes in satellite systems and Earth observation analytics, offering extensive data services and products to commercial and governmental customers worldwide.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of satellite Based earth observation?
The global satellite-based earth observation market is valued at approximately $15.6 billion in 2023, with a forecasted compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% through 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the satellite Based earth observation industry?
Key players in the satellite-based earth observation market include major organizations such as Maxar Technologies, Planet Labs, Airbus, and NASA. These companies significantly influence market dynamics through technological innovation and high-quality data provision.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the satellite Based earth observation industry?
Growth in the satellite-based earth observation industry is primarily driven by increased demand for remote sensing data for agriculture, urban planning, environmental monitoring, and disaster management, fueled by advancements in satellite technology and data analytics.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the satellite Based earth observation market?
The Asia-Pacific region is the fastest-growing market for satellite-based earth observation, projected to grow from $3.03 billion in 2023 to $6.19 billion by 2033, highlighting its increasing investments in satellite technology and analytics.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the satellite Based earth observation industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the satellite-based earth observation industry, allowing clients to access detailed insights relevant to their operational focus and strategic goals.
What deliverables can I expect from this satellite Based earth observation market research project?
Deliverables from the satellite-based earth observation market research will typically include comprehensive reports, segmented data analyses, trend analysis, and actionable insights tailored to inform your business strategies and decision-making.
What are the market trends of satellite Based earth observation?
Current trends in the satellite-based earth observation market include increasing adoption of AI for data analysis, a shift towards cloud-based services, and growing partnerships between private firms and government agencies to enhance data accuracy and access.