Satellite Market Report
Published Date: 03 February 2026 | Report Code: satellite
Satellite Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides comprehensive insights into the Satellite market, covering market size, key trends, regional analyses, and forecasts for the period 2023 to 2033. It offers a detailed examination of the segments and major players within the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
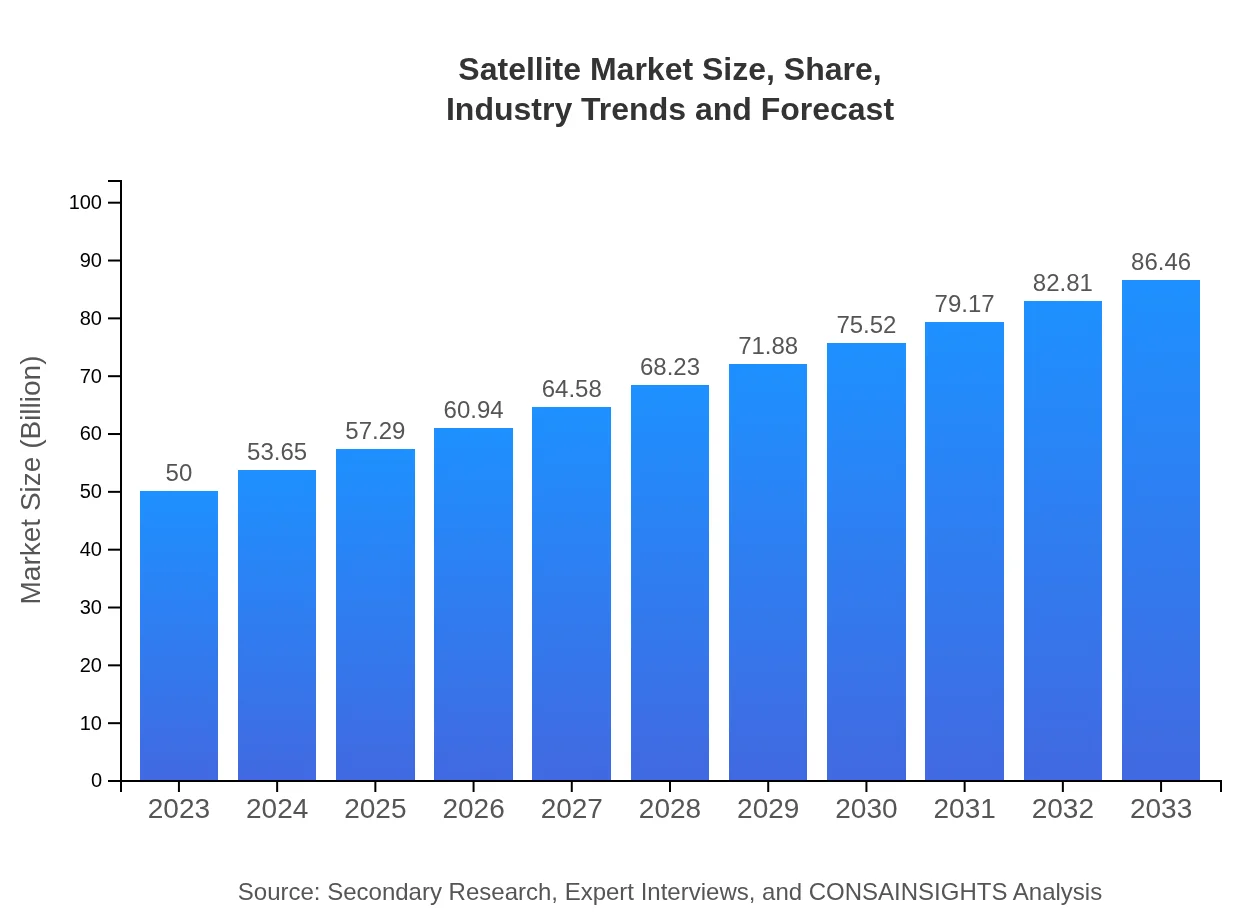
| 2023 Market Size | $50.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $86.46 Billion |
| Top Companies | SpaceX, SES S.A., Intelsat, Eutelsat Communications, Iridium Communications |
| Last Modified Date | 03 February 2026 |
Satellite Market Overview
Customize Satellite Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Satellite market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Satellite's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Satellite
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Satellite market in 2023?
Satellite Industry Analysis
Satellite Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Satellite Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Satellite Market Report:
Europe's Satellite market is anticipated to grow from USD 14.56 billion in 2023 to USD 25.18 billion by 2033. The European Space Agency's investments and strong regulatory frameworks support innovation in satellite technology, while increasing demand for broadband connectivity drives market expansion.Asia Pacific Satellite Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is experiencing significant growth in the Satellite market, with an expected market size of USD 16.44 billion by 2033, up from USD 9.51 billion in 2023. Factors contributing to this increase include rising demand for satellite services in telecommunications and navigation, alongside government initiatives in space exploration.North America Satellite Market Report:
North America remains a leading region in the Satellite market, expected to reach USD 27.82 billion by 2033, a substantial rise from USD 16.09 billion in 2023. The region's robust space exploration efforts and the presence of several key market players, along with advances in satellite technology, significantly contribute to its dominance.South America Satellite Market Report:
In South America, the Satellite market is projected to grow from USD 4.96 billion in 2023 to USD 8.57 billion by 2033. Economic development and a push to enhance telecommunications infrastructure are major drivers for market growth, with countries investing in satellite systems for broader connectivity.Middle East & Africa Satellite Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the Satellite market is expected to increase from USD 4.88 billion in 2023 to USD 8.45 billion by 2033. Investments in telecommunications and space technology, combined with geopolitical factors and defense spending, are key growth contributors.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
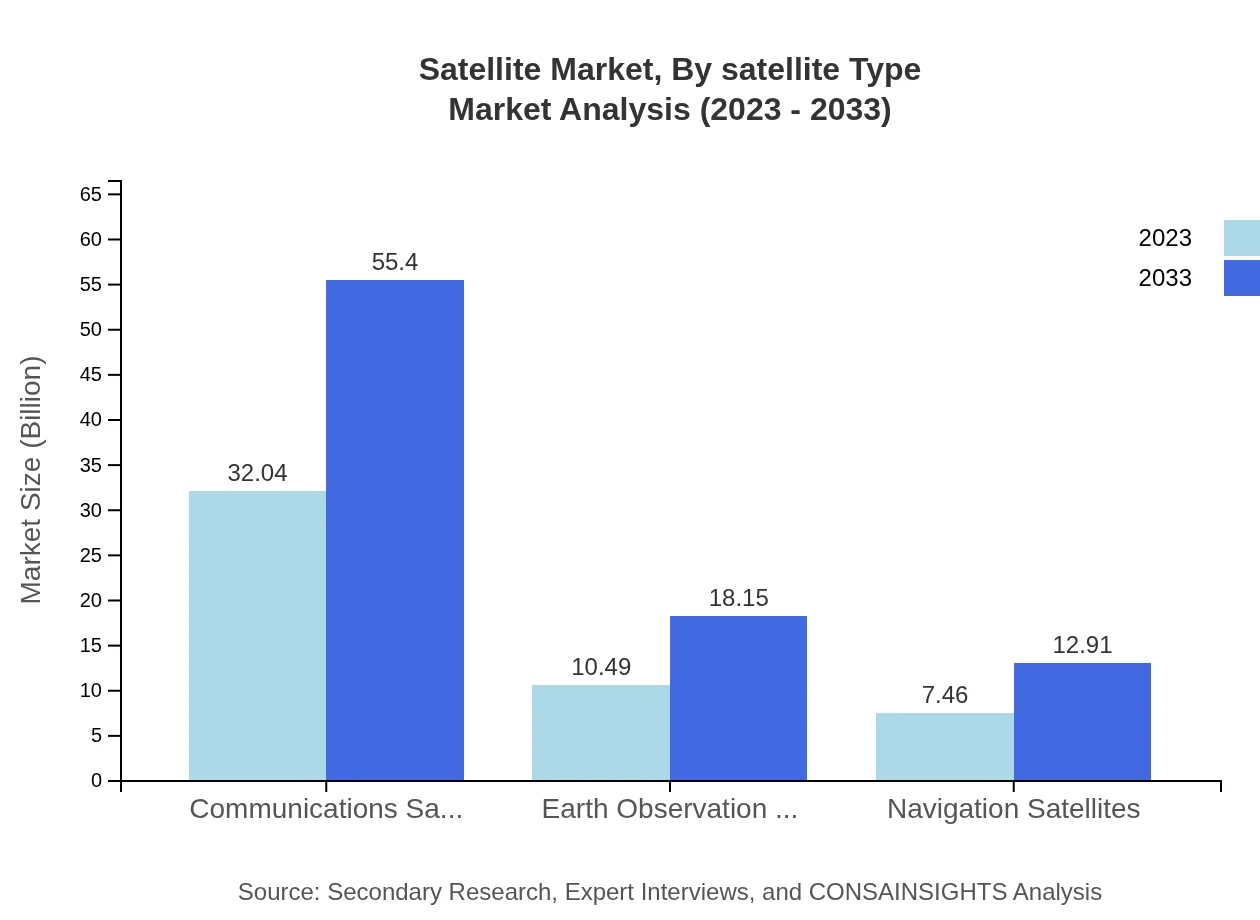
Satellite Market Analysis By Satellite Type
In terms of satellite type, the Communications Satellites segment dominates with a market size expected to reach USD 55.40 billion by 2033, growing from USD 32.04 billion in 2023. Earth Observation Satellites and Navigation Satellites also present significant growth, driven by applications in agriculture, environmental monitoring, and global positioning.
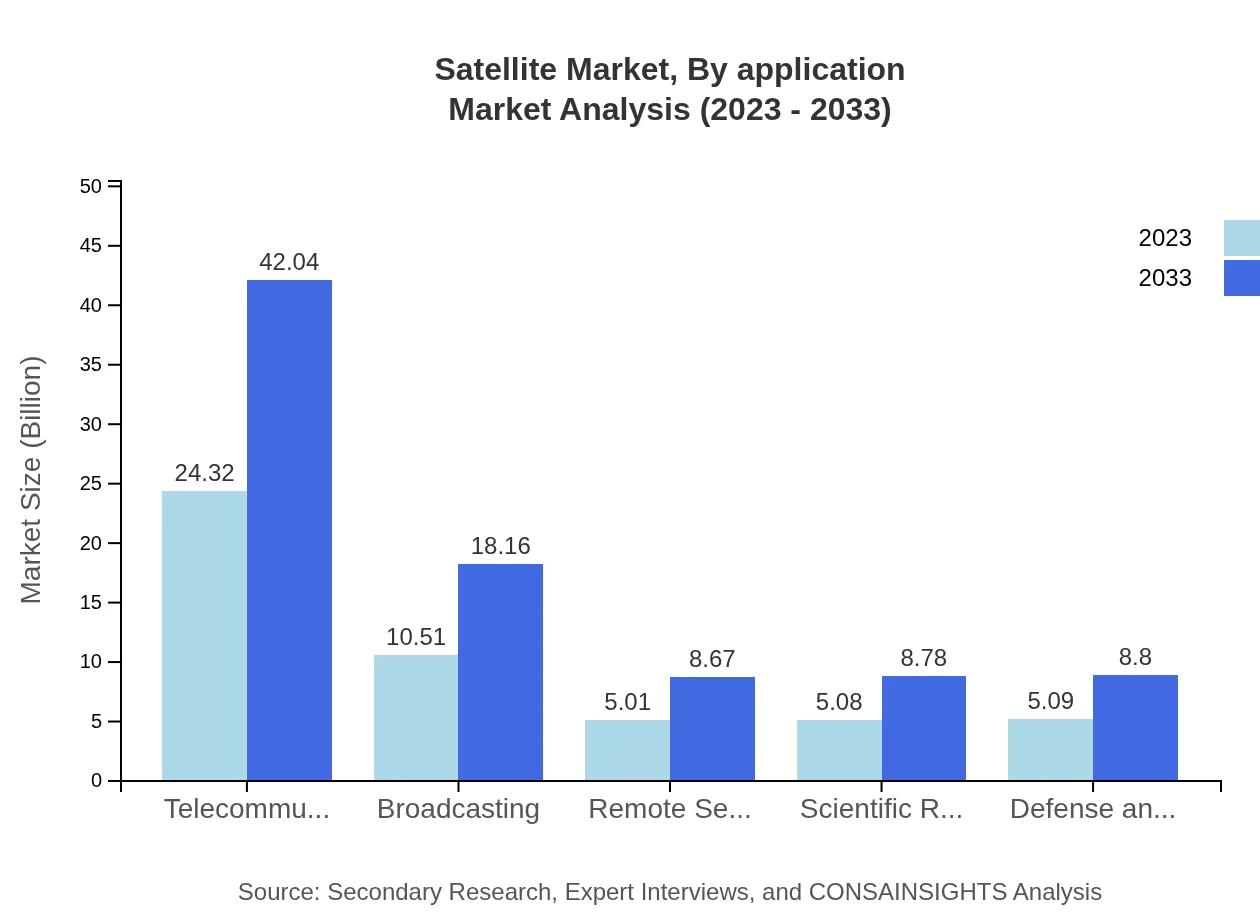
Satellite Market Analysis By Application
The Telecommunications application segment is the largest, projected to see a rise in market size from USD 24.32 billion in 2023 to USD 42.04 billion in 2033. This segment benefits from increasing data traffic demands and mobile communication needs, followed by Broadcasting, Remote Sensing, and Scientific Research segments exhibiting steady growth.
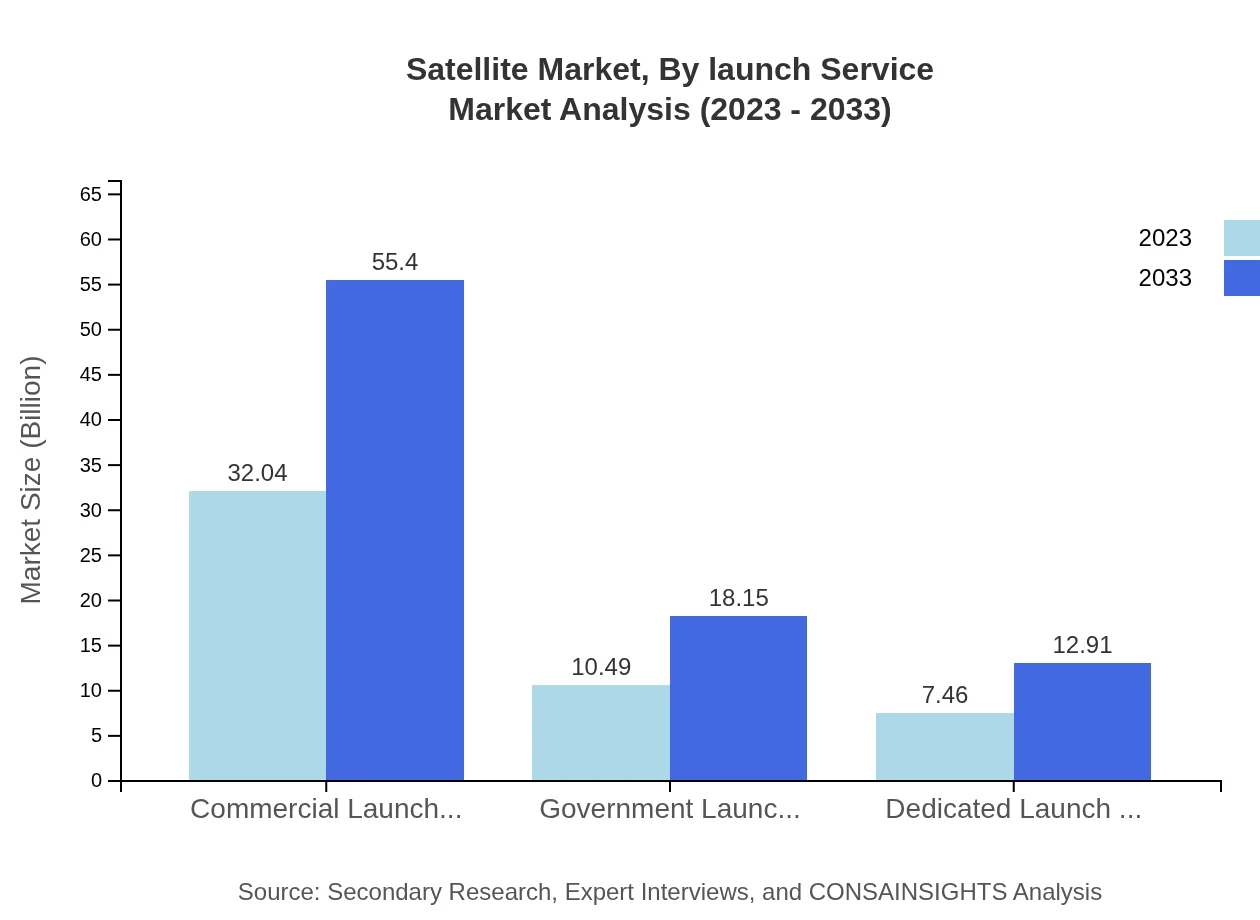
Satellite Market Analysis By Launch Service
The Commercial Launch Services segment is anticipated to expand from USD 32.04 billion in 2023 to USD 55.40 billion by 2033, reflecting the growing number of satellites being sent to orbit. Government and dedicated launch services also remain essential as they cater to specific missions for various governmental and private entities.
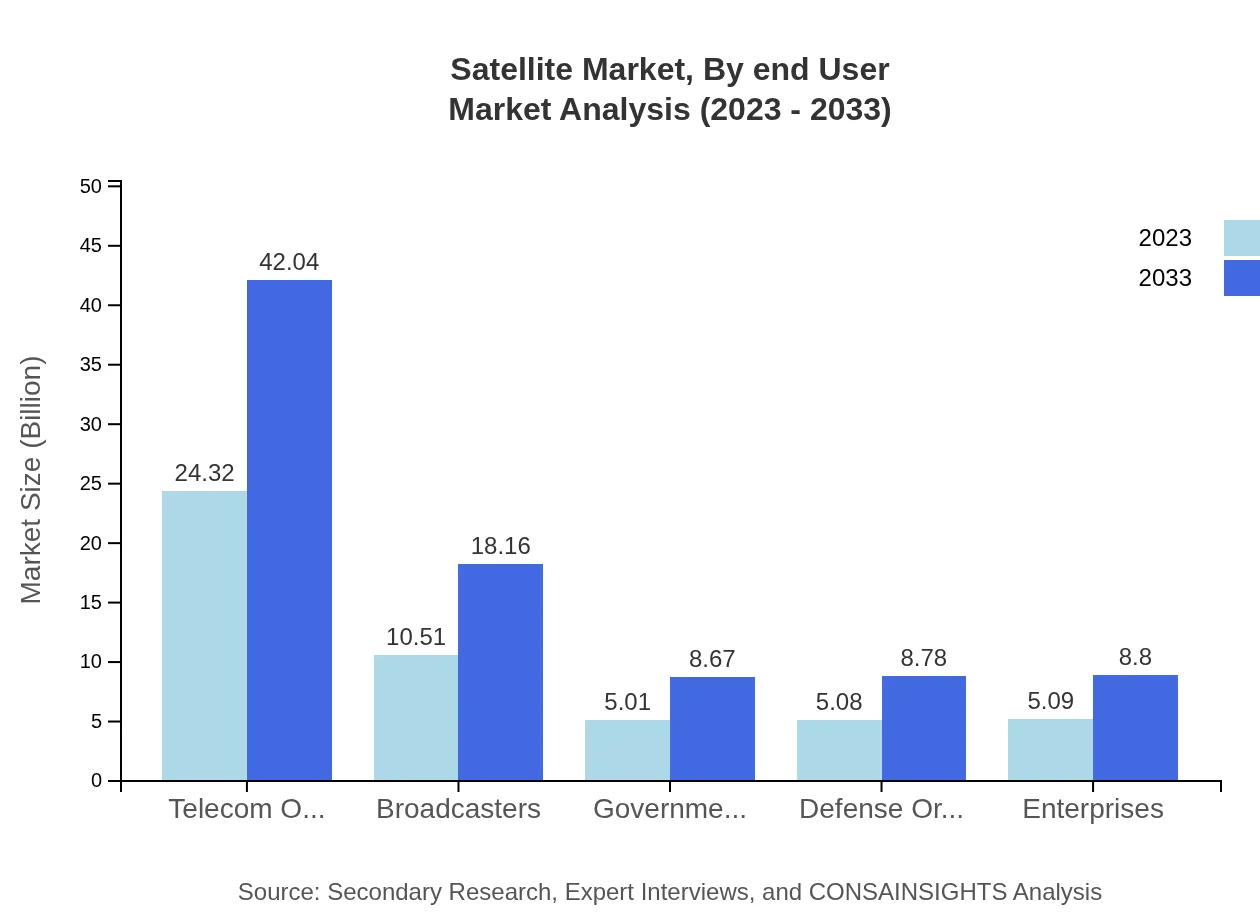
Satellite Market Analysis By End User
Telecommunications is the primary end-user segment, expected to account for a market share of 48.63% in 2023, with notable growth anticipated as the demand for broadband access extends to remote regions. Other significant end-users include government agencies, defense organizations, enterprises, and broadcasters.
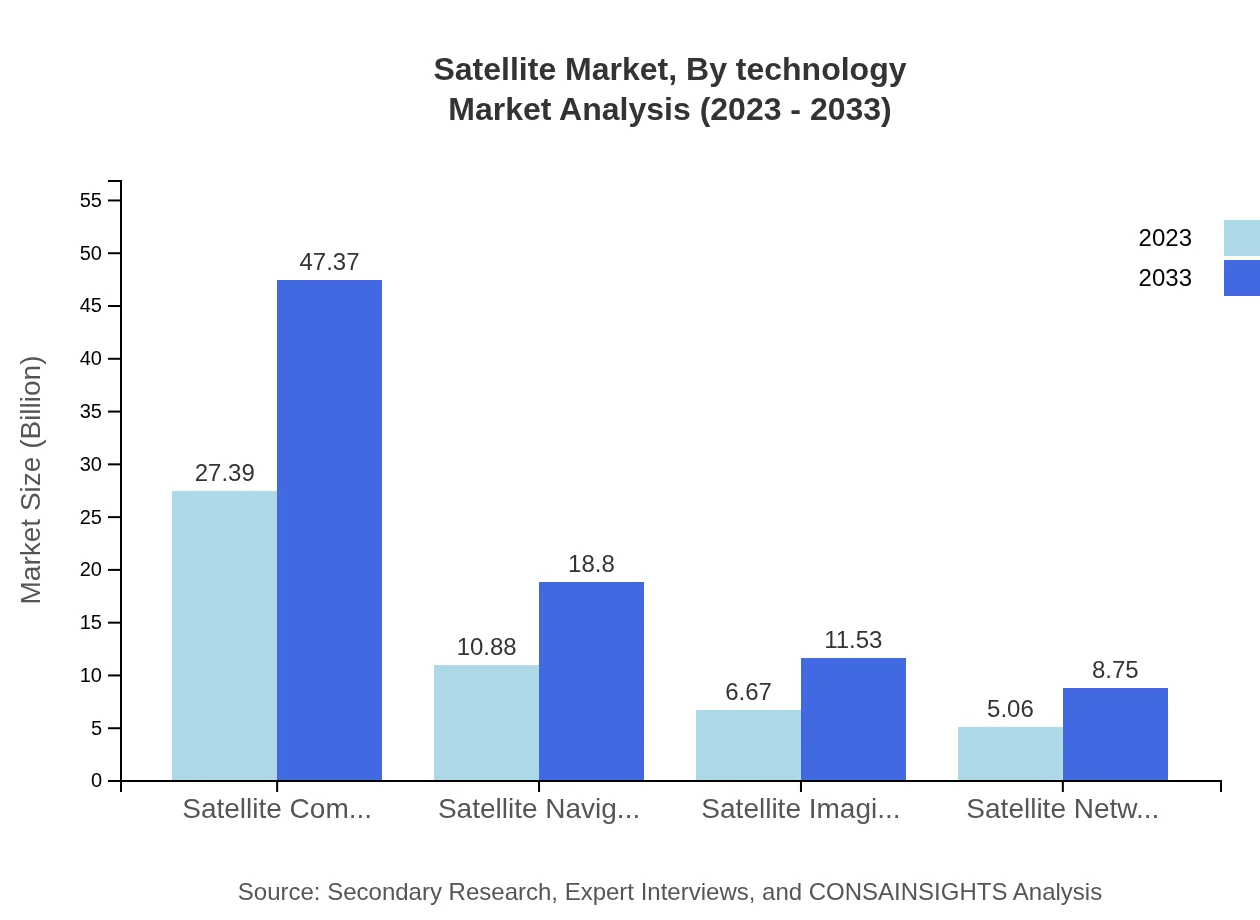
Satellite Market Analysis By Technology
Mobile satellite communications technology is witnessing substantial advancements, projected to grow from USD 27.39 billion in 2023 to USD 47.37 billion by 2033. Innovations in satellite networking and imaging technologies are among the key developments impacting the market, enhancing data transmission and analytics capabilities.
Satellite Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Satellite Industry
SpaceX:
SpaceX leads in satellite launch services with its Falcon 9 and Starship rockets, actively deploying a constellation of satellites for its Starlink broadband project.SES S.A.:
SES S.A. is a prominent satellite operator providing satellite communication services across global markets, excelling in telecommunications and broadcasting.Intelsat:
A pioneer in satellite communications, Intelsat provides critical satellite services for media, cloud, and data networking, supporting global connectivity.Eutelsat Communications:
Eutelsat is a key player in the satellite industry, offering diverse communication solutions and fostering innovation in satellite services.Iridium Communications:
Iridium specializes in satellite communications, delivering voice and data services across remote locations via its unique LEO satellite constellation.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of satellite?
The global satellite market is projected to grow from a size of $50 billion in 2023 to an estimated $84 billion by 2033, achieving a CAGR of 5.5% during this period.
What are the key market players or companies in this satellite industry?
Key market players in the satellite industry include leading companies such as SpaceX, Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Intelsat, which dominate satellite manufacturing, launch services, and communications.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the satellite industry?
The satellite industry growth is driven by increased demand for satellite communications, advancements in technology, growing space exploration initiatives, and rising applications in sectors like agriculture, healthcare, and defense.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the satellite market?
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the satellite market, expected to grow from $9.51 billion in 2023 to $16.44 billion by 2033, indicating substantial investment and growth opportunities.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the satellite industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs and objectives within the satellite industry, enabling businesses to gain deeper insights.
What deliverables can I expect from this satellite market research project?
Deliverables from the satellite market research project include a comprehensive report detailing market size, growth projections, competitive analysis, segmentation, and regional insights.
What are the market trends of satellite?
Current market trends indicate a shift towards enhanced satellite communications technologies, utilization of small satellites, and increased collaborations between government entities and private companies.