Sea Freight Forwarding Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: sea-freight-forwarding
Sea Freight Forwarding Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This market report provides comprehensive insights into the Sea Freight Forwarding industry, covering market size, growth rates, trends, segmentation, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It aims to equip stakeholders with key information for strategic decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
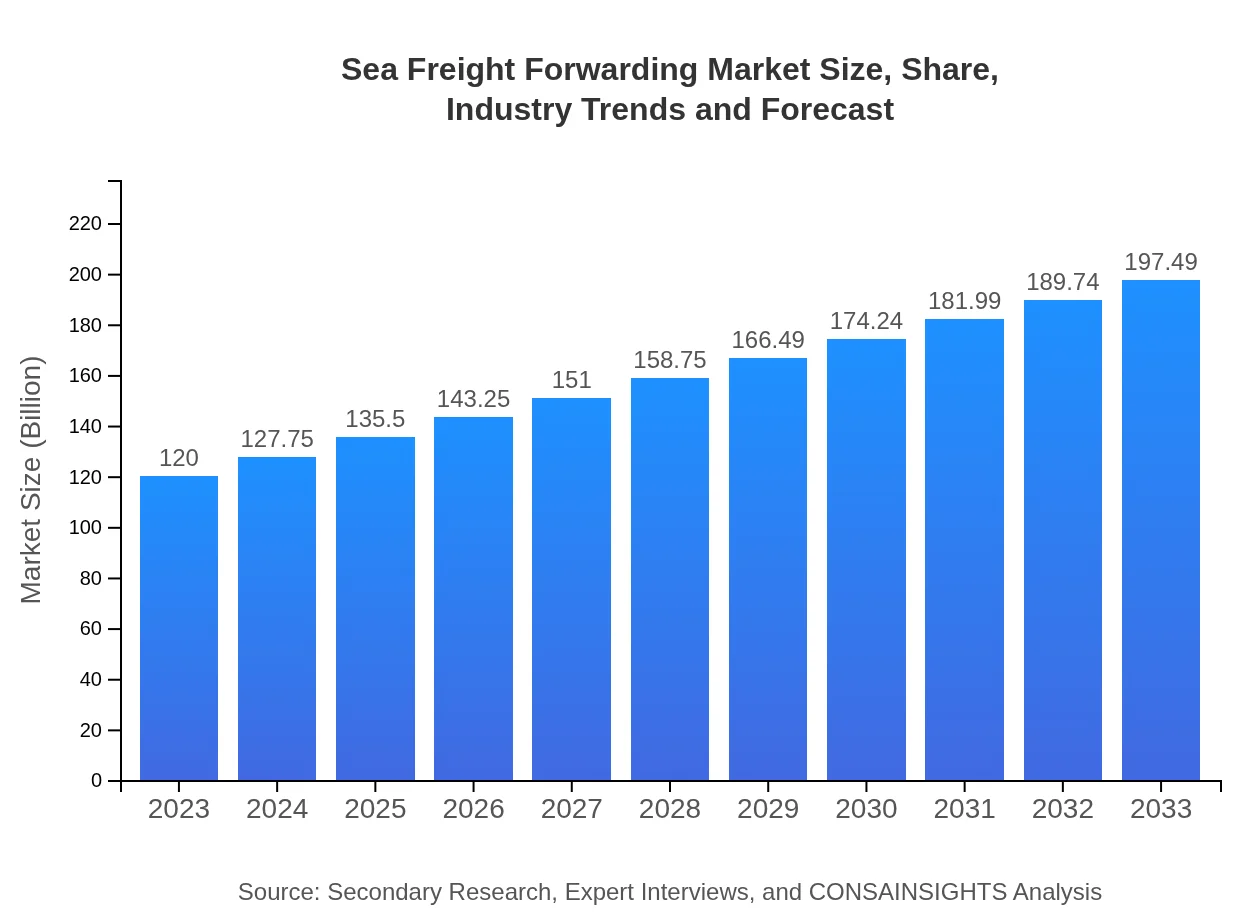
| 2023 Market Size | $120.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $197.49 Billion |
| Top Companies | DHL Global Forwarding, Kuehne + Nagel, DB Schenker, Nippon Express |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Sea Freight Forwarding Market Overview
Customize Sea Freight Forwarding Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Sea Freight Forwarding market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Sea Freight Forwarding's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Sea Freight Forwarding
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Sea Freight Forwarding market in 2023?
Sea Freight Forwarding Industry Analysis
Sea Freight Forwarding Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Sea Freight Forwarding Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Sea Freight Forwarding Market Report:
Europe is the largest market for sea freight forwarding, valued at $43.90 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $72.24 billion by 2033. The region's diverse economy and strong trade relationships contribute to its substantial market size, with a steady increase in demand for forwarding services.Asia Pacific Sea Freight Forwarding Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is projected to witness robust growth, with a market size estimated at $19.63 billion in 2023, expanding to $32.31 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by the increasing demand for imports and exports, particularly in countries like China and India, which are major hubs for manufacturing and trade.North America Sea Freight Forwarding Market Report:
The North American market stands at $38.81 billion in 2023 and is estimated to reach $63.87 billion by 2033. This region benefits from a well-established logistics framework and a high volume of imported goods, particularly in the retail and e-commerce sectors.South America Sea Freight Forwarding Market Report:
South America has a smaller market size of $3.18 billion in 2023, growing to $5.23 billion by 2033. The region's growth is driven by the expansion of trade agreements and infrastructure improvements, enhancing its connectivity with global markets.Middle East & Africa Sea Freight Forwarding Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is valued at $14.48 billion in 2023, growing to $23.84 billion by 2033. This growth reflects the region's emerging markets and increasing investment in infrastructure, which enhances its role as a logistics hub.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
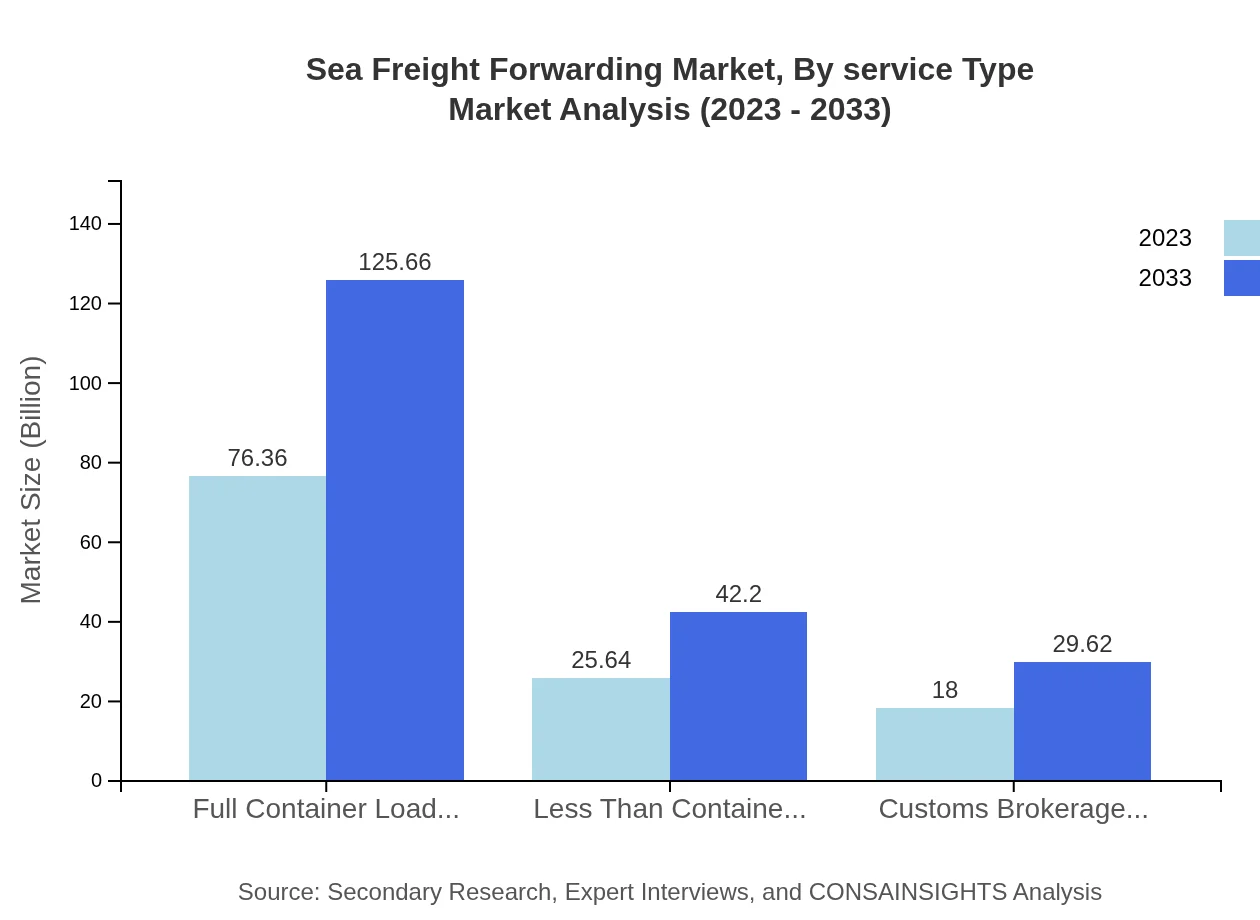
Sea Freight Forwarding Market Analysis By Service Type
Key service types in the sea freight forwarding market include Full Container Load (FCL), recognized for its efficiency in transporting large shipments, and Less Than Container Load (LCL), catering to smaller, mixed shipments. Innovations in tracking technology and automation tools are improving the logistics process, enhancing efficiency across both FCL and LCL services.
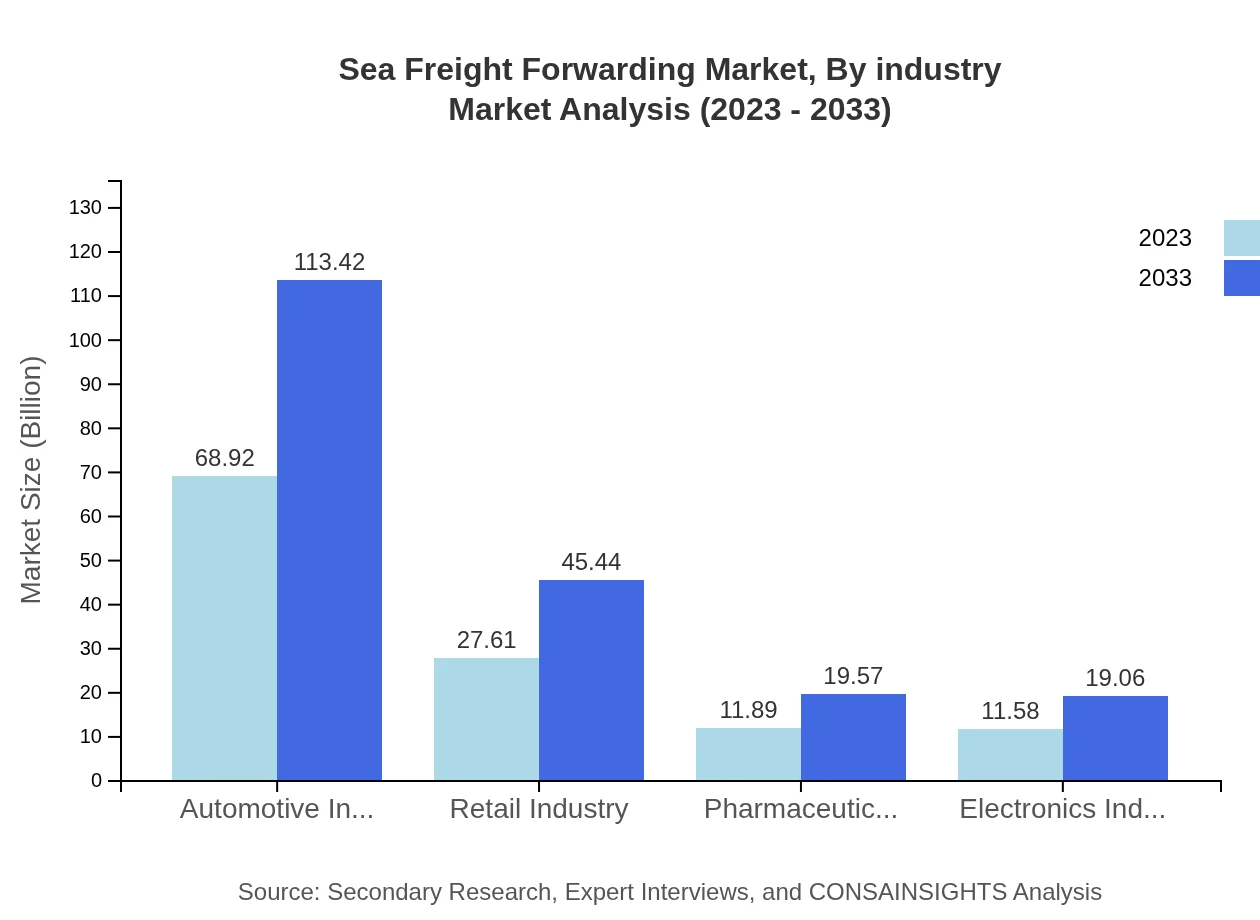
Sea Freight Forwarding Market Analysis By Industry
The automotive industry remains a significant segment, with a market size of $68.92 billion in 2023 projected to reach $113.42 billion by 2033. The retail industry follows, expected to grow from $27.61 billion in 2023 to $45.44 billion by 2033. Meanwhile, the pharmaceuticals and electronics sectors also represent critical areas of activity, each driving demand for reliable freight forwarding services.
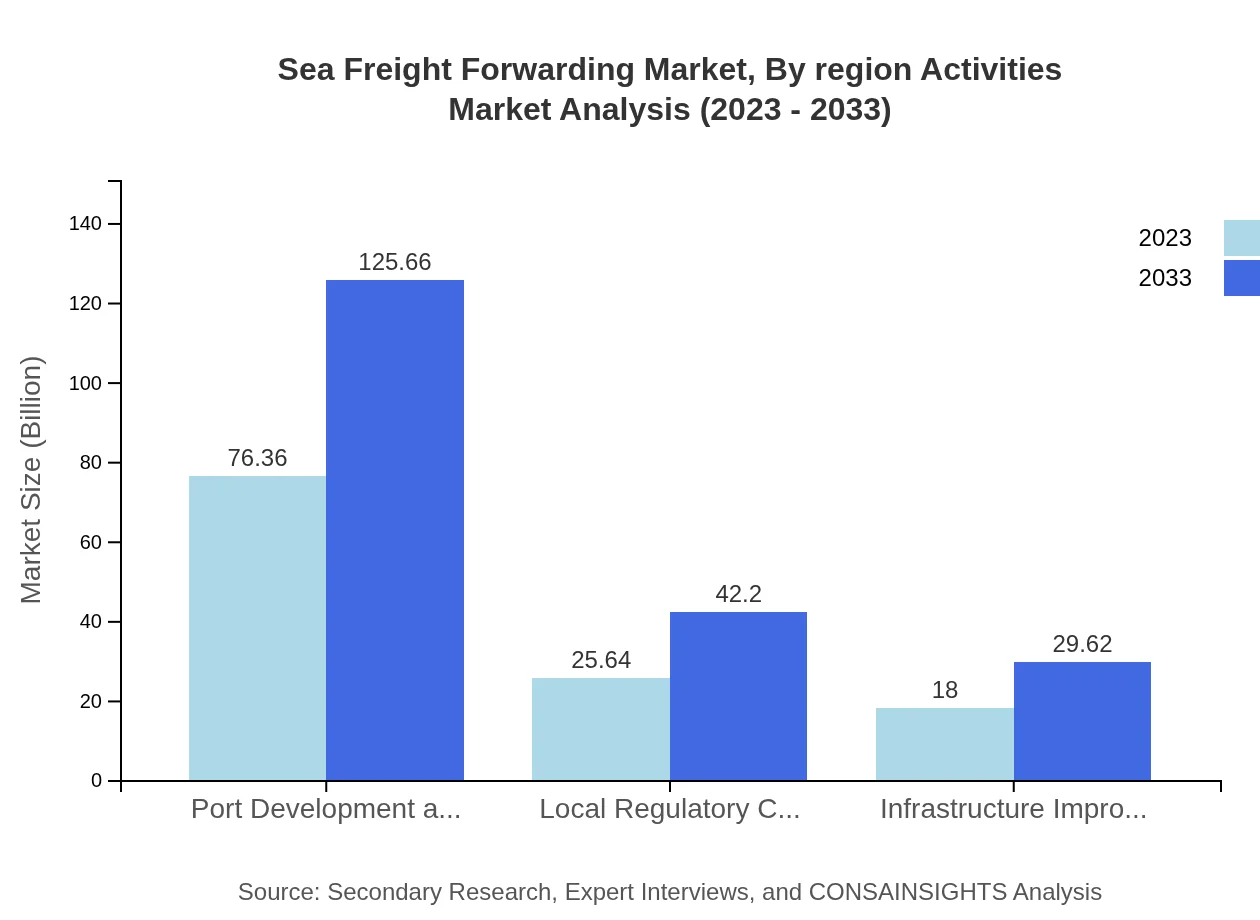
Sea Freight Forwarding Market Analysis By Region Activities
Regional activity patterns highlight a heightened demand for services in Asia-Pacific and North America due to large trade volumes. Companies in these regions are increasingly focused on optimizing their logistics operations to meet the growing expectations of fast delivery times and reliability.
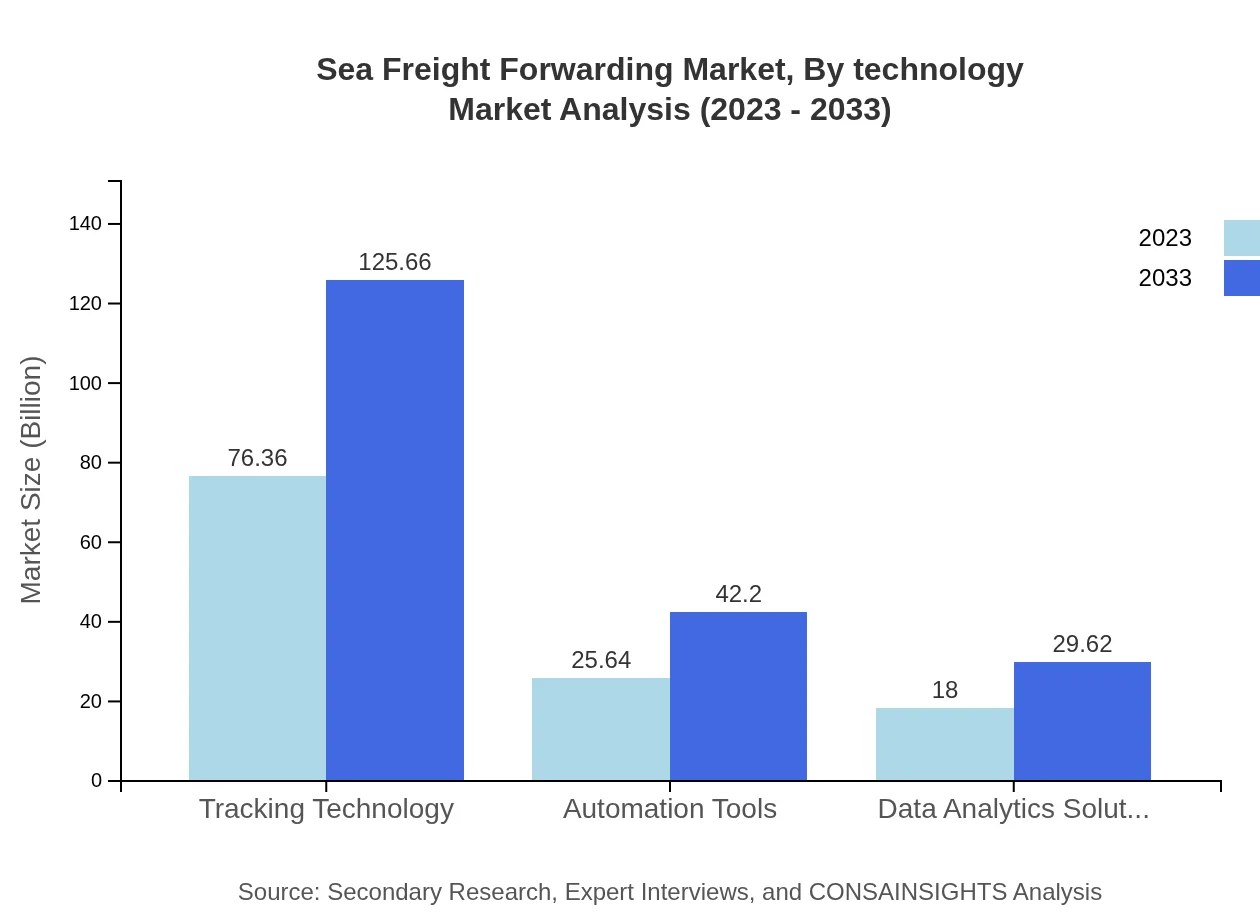
Sea Freight Forwarding Market Analysis By Technology
Adoption of advanced technologies such as data analytics solutions, which are poised to grow from $18.00 billion in 2023 to $29.62 billion by 2033, is transforming the sea freight forwarding landscape. Additionally, automation and tracking technologies are enhancing operational efficiency, leading to better service delivery and customer satisfaction.
Sea Freight Forwarding Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Sea Freight Forwarding Industry
DHL Global Forwarding:
A leading player in the logistics domain, DHL offers comprehensive sea freight services globally, with a strong emphasis on sustainability and digital innovation.Kuehne + Nagel:
With a vast network, Kuehne + Nagel specializes in integrated logistics solutions, including sea freight forwarding, catering to various industries.DB Schenker:
DB Schenker provides a wide range of supply chain solutions, with significant capabilities in sea freight services, emphasizing technology-driven processes.Nippon Express:
A prominent Japanese logistics company, Nippon Express offers comprehensive ocean freight solutions, focusing on customer-specific logistics management.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of sea Freight Forwarding?
The sea freight forwarding market is valued at approximately $120 billion in 2023. It is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5% over the next decade, reaching significant expansion by 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the sea Freight Forwarding industry?
Key players in the sea freight forwarding market include multinational logistics companies, specialized freight forwarders, and shipping conglomerates. Their diverse service offerings drive competition and innovation in the industry.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the sea Freight Forwarding industry?
Growth in the sea freight forwarding industry is driven by rising global trade, advancements in logistics technology, and increasing demand for efficient shipping solutions. Environmental regulations and port infrastructure improvements also play pivotal roles.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the sea Freight Forwarding?
The fastest-growing region in the sea freight forwarding market is Europe, expected to expand from $43.90 billion in 2023 to $72.24 billion by 2033, reflecting significant investment and demand growth in logistics.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the sea Freight Forwarding industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the sea freight forwarding industry, providing relevant and actionable insights to support strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this sea Freight Forwarding market research project?
From the sea freight forwarding market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports including market trends, segmentation analysis, regional insights, and forecasts, along with expert recommendations and strategic implications.
What are the market trends of sea Freight Forwarding?
Key trends in the sea freight forwarding sector include digital transformation, automation of shipping processes, increasing use of data analytics, and a growing focus on sustainability and green logistics initiatives.