Seed Cotton Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: seed-cotton
Seed Cotton Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This market report on Seed Cotton provides comprehensive insights into market conditions, size, trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It explores various market segments, regional analyses, and the overall growth trajectory of the seed cotton industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
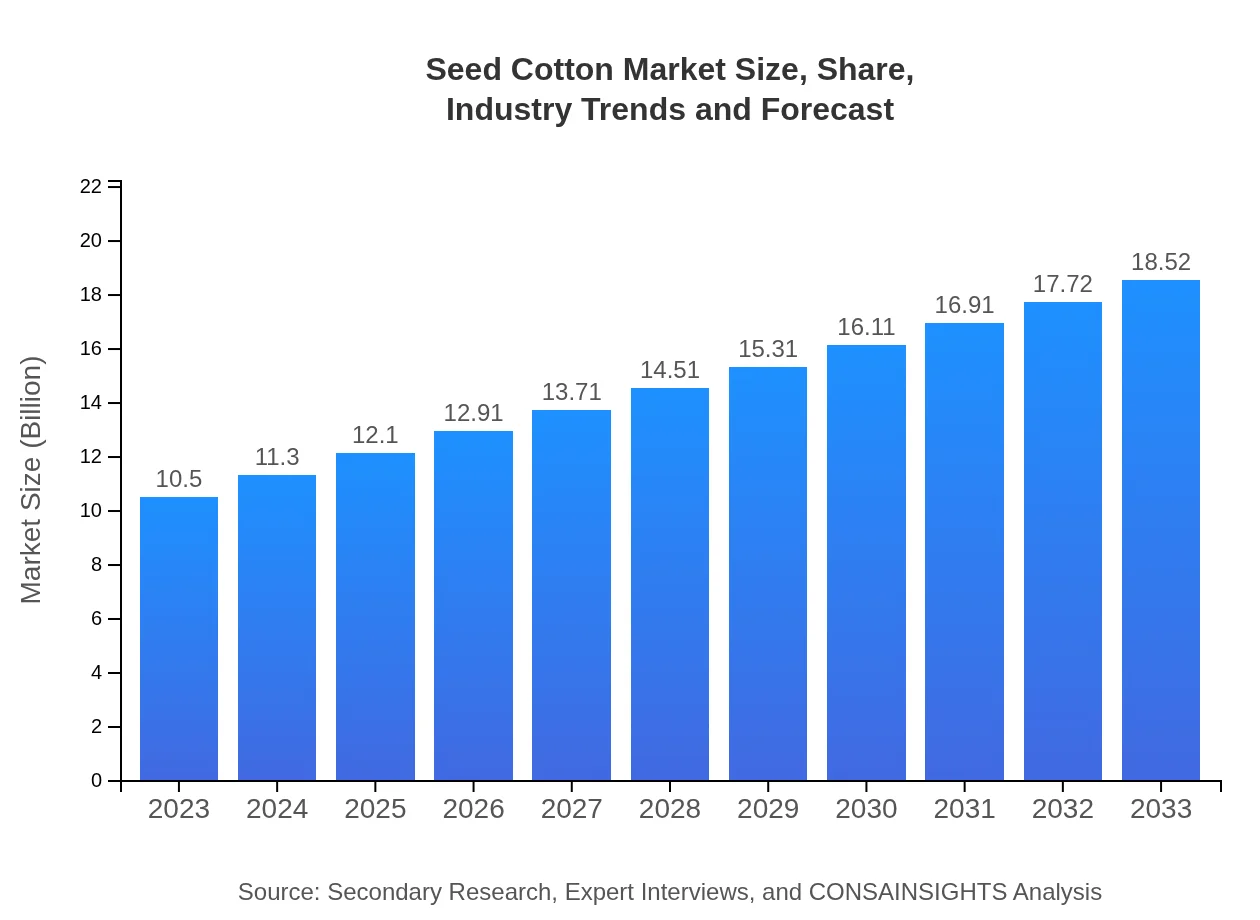
| 2023 Market Size | $10.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5.7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $18.52 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cargill, Inc., BASF SE, Olam International, American Vanguard Corporation, Benson Hill, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Seed Cotton Market Overview
Customize Seed Cotton Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Seed Cotton market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Seed Cotton's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Seed Cotton
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Seed Cotton market in 2023?
Seed Cotton Industry Analysis
Seed Cotton Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Seed Cotton Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Seed Cotton Market Report:
Europe’s Seed Cotton market was valued at $3.37 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $5.94 billion by 2033. Factors such as sustainability trends and rising demand for organic cotton contribute to growth, as European consumers increasingly prefer environmentally friendly products.Asia Pacific Seed Cotton Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Seed Cotton market is poised for substantial growth. The market was valued at approximately $1.69 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around $2.99 billion by 2033. Major producing countries like India and China are driving production with advances in cultivation techniques and increased acreage. Additionally, consumer demand for cotton products continues to rise.North America Seed Cotton Market Report:
North America boasts a robust Seed Cotton market, valued at $3.88 billion in 2023, projected to increase to $6.85 billion by 2033. The region benefits from established cotton production capabilities, technological advancements, and strong industry players focusing on organic cultivation.South America Seed Cotton Market Report:
The South American Seed Cotton market, valued at $0.12 billion in 2023, is expected to grow modestly to $0.22 billion by 2033. The growth is primarily attributed to improving agricultural practices and increasing exports. However, competition from synthetic fibers remains a challenge.Middle East & Africa Seed Cotton Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the Seed Cotton market is growing gradually, with a valuation of $1.43 billion in 2023 and projected growth to $2.52 billion by 2033. The region is focusing on improving irrigation and crop management practices to boost cotton production.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
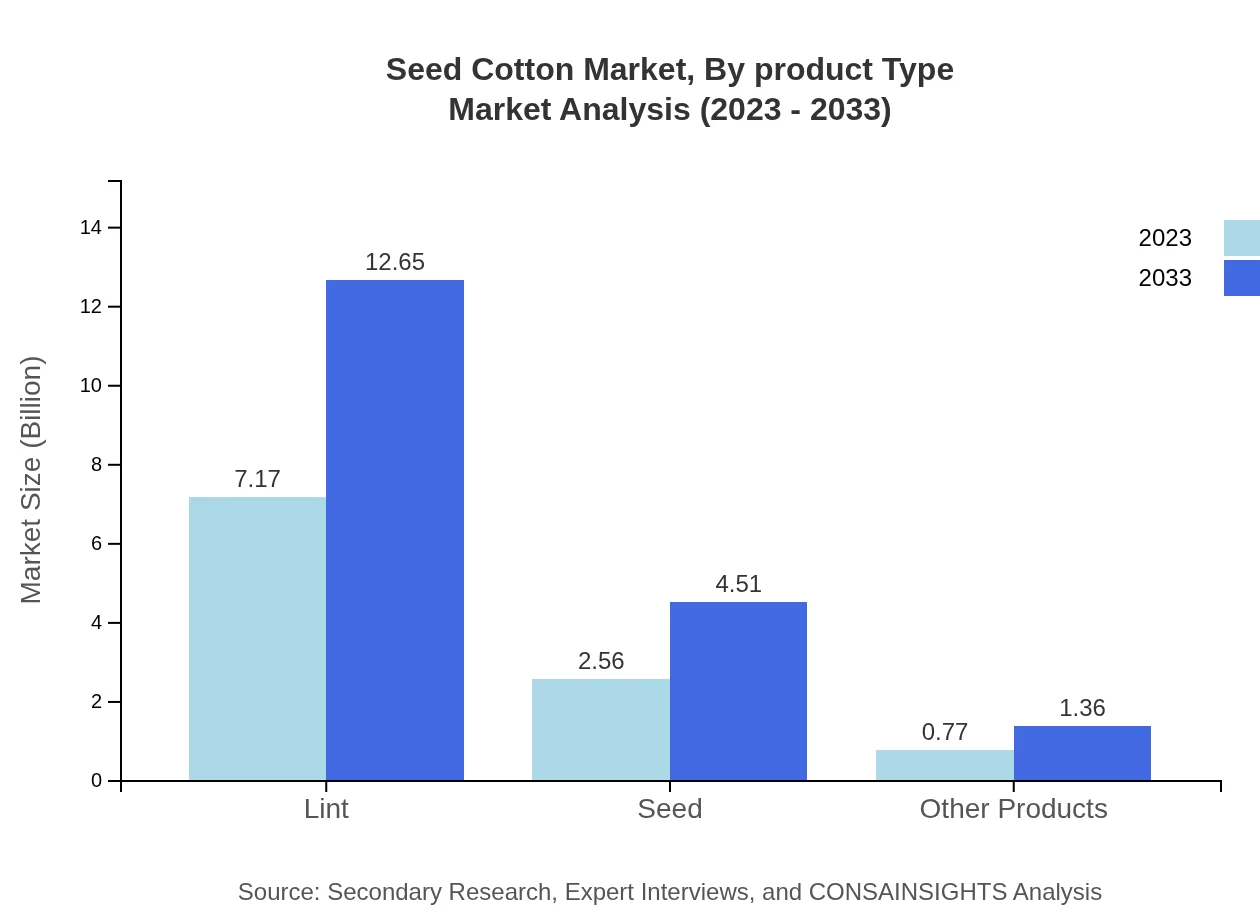
Seed Cotton Market Analysis By Product Type
The Seed Cotton market by product type includes cotton lint, seeds, oil, and other derivatives. Cotton lint accounts for a substantial share, valued at $7.17 billion in 2023 and projected to reach $12.65 billion by 2033. The importance of lint in textile production drives this category, while cotton seeds and oil also show significant growth due to their diverse applications.
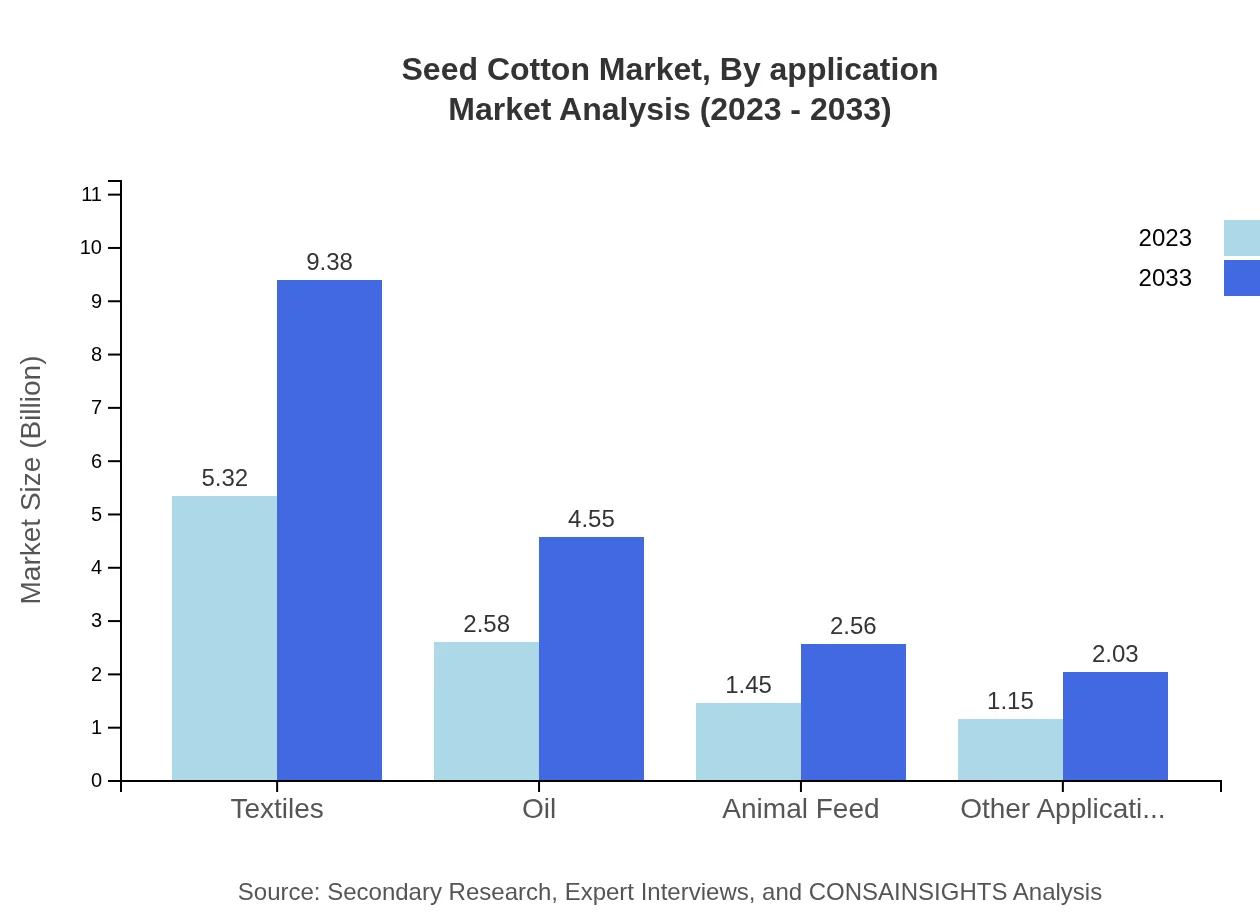
Seed Cotton Market Analysis By Application
The Seed Cotton market across applications consists primarily of textiles, animal feed, oil, and other uses. The textile segment leads with a market size of $5.32 billion in 2023, expected to reach $9.38 billion by 2033, driven by the global fashion industry's demand for cotton fabrics.
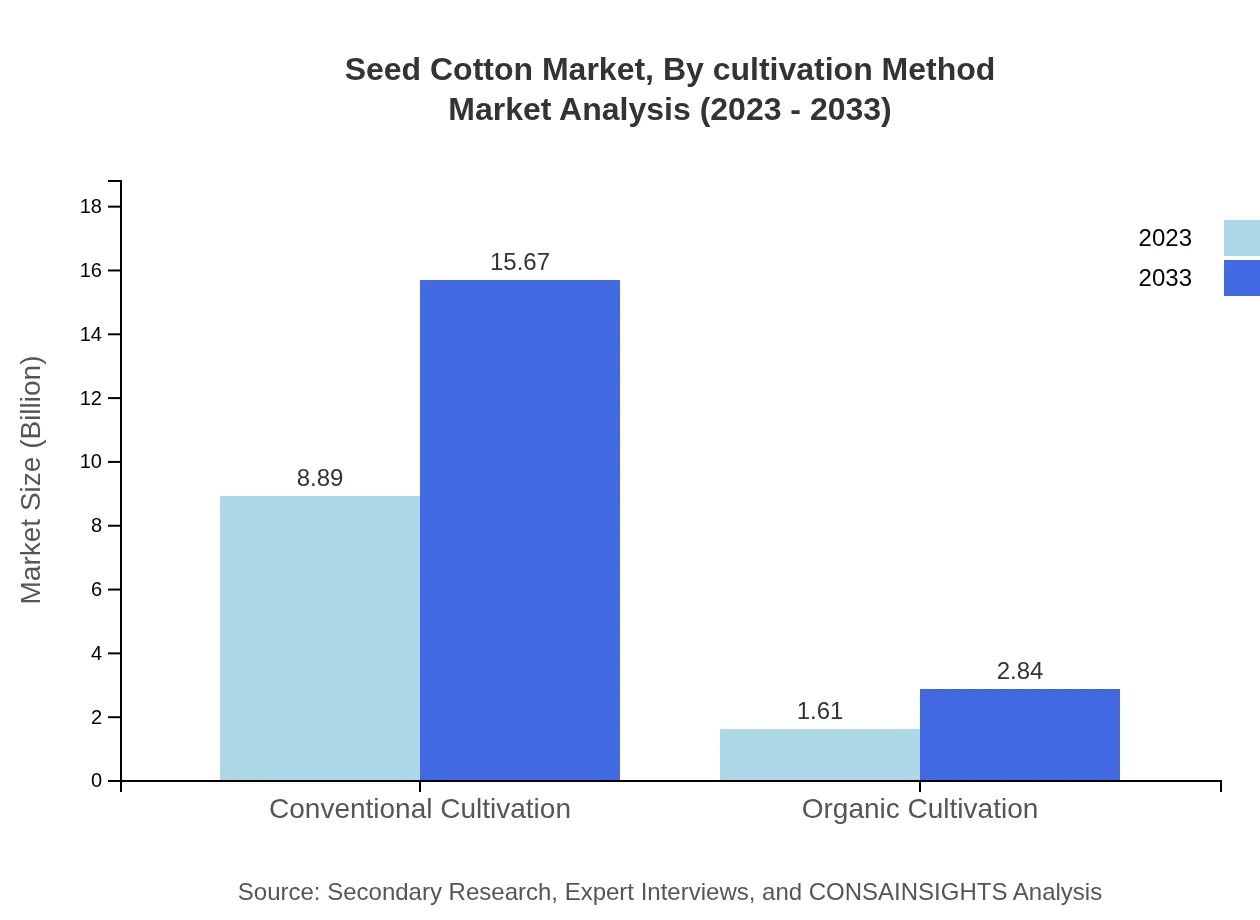
Seed Cotton Market Analysis By Cultivation Method
The market is divided into conventional and organic cultivation methods. Conventional cultivation remains dominant, valued at $8.89 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $15.67 billion by 2033. Organic cultivation, although smaller, is experiencing growth due to the rising demand for sustainable farming practices.
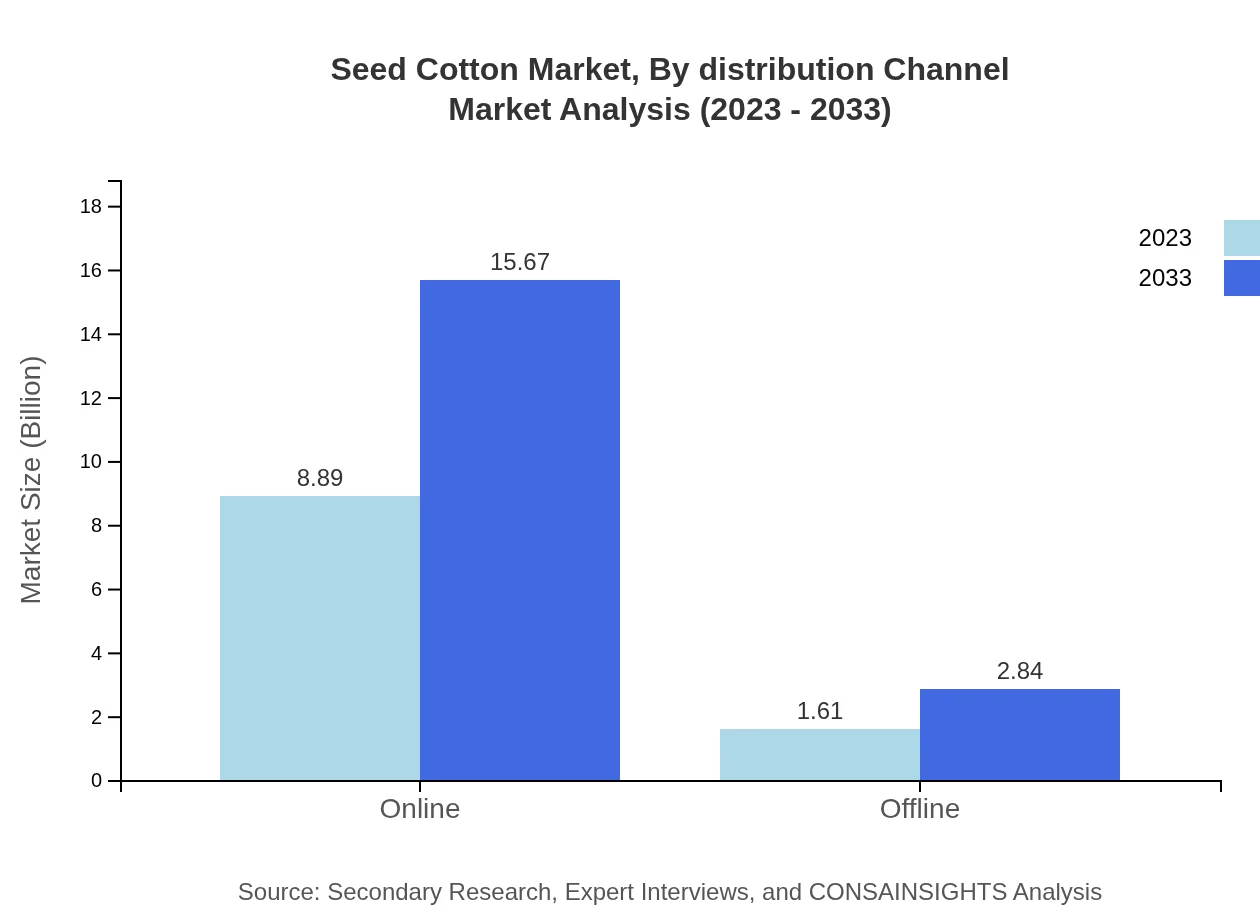
Seed Cotton Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The Seed Cotton market is segmented by distribution channels into online and offline sales. Online channels are emerging as a significant sales method due to convenience, accounting for $8.89 billion in 2023. Meanwhile, offline channels remain important for traditional retail and farmer distribution efforts.
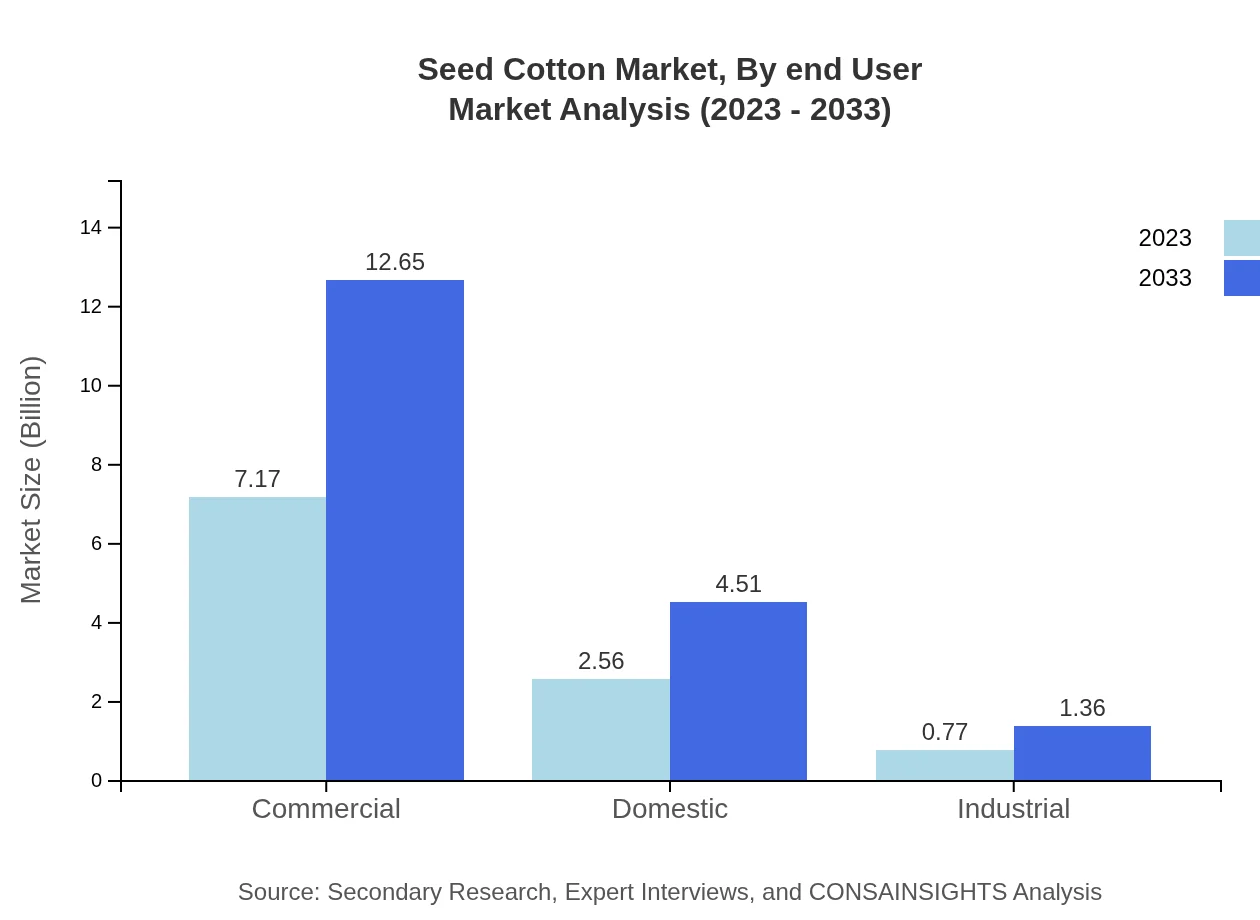
Seed Cotton Market Analysis By End User
The end-user segmentation includes textile manufacturers, food producers, and animal feed producers. Textile manufacturers use a substantial portion of seed cotton, which aligns with the projected growth in the textile segment. The continuous development in cotton processing technologies and higher standards for quality are expected to boost this segment further.
Seed Cotton Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Seed Cotton Industry
Cargill, Inc.:
A prominent agricultural corporation that provides the agricultural, food, and industrial markets with high-quality seed and other agricultural products.BASF SE:
A leading chemical company involved in the agricultural sector, BASF is known for its innovative seed products and sustainable agriculture initiatives.Olam International:
A global food and agri-business company that plays a significant role in the seed cotton market, promoting sustainable farming and supply chain solutions.American Vanguard Corporation:
Involved in developing innovative agricultural products, including seed coatings and solutions for seed production.Benson Hill, Inc.:
A technology-driven food company focused on sustainable agricultural practices and cotton seed innovation.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of seed Cotton?
The global seed-cotton market is projected to reach a size of 10.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.7% from 2023. This growth reflects increasing demand in various sectors and a robust market presence.
What are the key market players or companies in the seed Cotton industry?
Key players in the seed-cotton market include major agricultural firms focused on cottonseed production and distribution. Collaborations, innovation in biotechnology, and sustainable farming practices drive competitive dynamics within the industry.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the seed Cotton industry?
Growth in the seed-cotton industry is primarily driven by rising demand for cotton products in textiles, increasing agricultural productivity, and innovations in cotton seed technology, which enhance yield and sustainability.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the seed Cotton market?
The fastest-growing region in the seed-cotton market is Europe, with its market expected to increase from 3.37 billion in 2023 to 5.94 billion by 2033, reflecting innovative agricultural practices and increasing cotton demand.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the seed Cotton industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to client specifications in the seed-cotton industry, addressing unique business needs, trends, and opportunities for strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this seed Cotton market research project?
Deliverables from the seed-cotton market research project include detailed market analysis, segment insights, competitive landscape assessment, and forecasts that guide strategic planning and investment decisions.
What are the market trends of seed Cotton?
Current trends in the seed-cotton market include a shift towards organic cultivation, technological advancements in seed production, and the growth of e-commerce channels for distribution, shaping the future landscape.