Seed Processing Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: seed-processing
Seed Processing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report analyzes the Seed Processing market from 2023 to 2033, providing insights on market trends, size, growth forecasts, and technological advancements in the industry. It also highlights key segments and leading players shaping this dynamic market.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
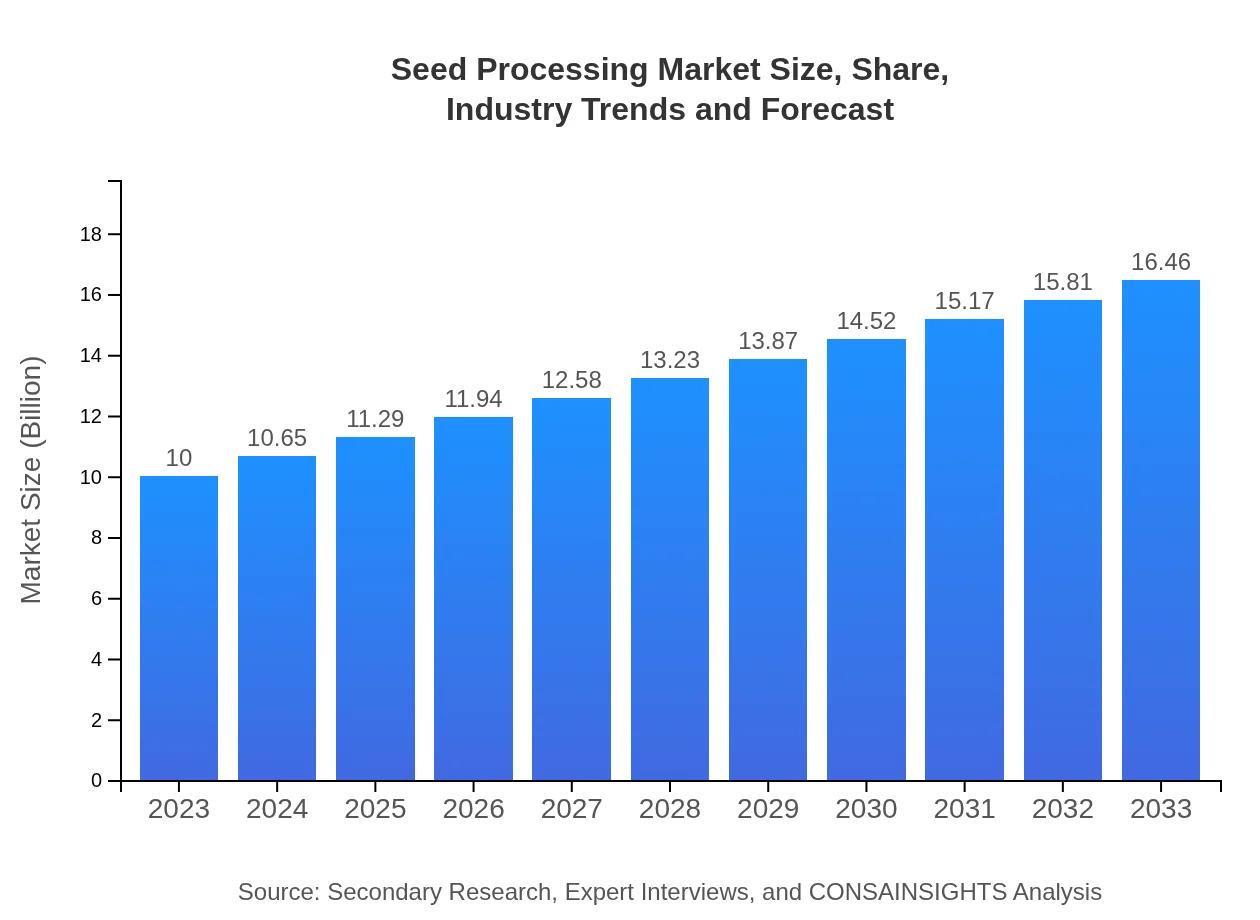
| 2023 Market Size | $10.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $16.46 Billion |
| Top Companies | BASF, DuPont, Syngenta |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Seed Processing Market Overview
Customize Seed Processing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Seed Processing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Seed Processing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Seed Processing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Seed Processing market in 2023?
Seed Processing Industry Analysis
Seed Processing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Seed Processing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Seed Processing Market Report:
Europe is expected to see a growth from $3.29 billion in 2023 to $5.41 billion by 2033, with strong regulatory frameworks pushing for quality standards in seed production. Sustainability concerns also drive innovation in seed processing across the region.Asia Pacific Seed Processing Market Report:
The Seed Processing market in the Asia-Pacific region shows promising growth, projecting a market size of $1.95 billion in 2023 to $3.20 billion by 2033, reflecting a strong focus on agricultural advancements and investments. Countries like China and India are leading this growth due to escalating food production needs and the adoption of innovative seed technologies.North America Seed Processing Market Report:
North America, with a 2023 market size of $3.25 billion projected to grow to $5.34 billion by 2033, is leading in seed processing technology innovations. The presence of major seed companies and a well-developed agricultural infrastructure bolster this expanding market.South America Seed Processing Market Report:
In South America, the market is anticipated to expand from $0.67 billion in 2023 to $1.10 billion by 2033. Brazil and Argentina are pivotal in driving this growth, stimulated by increasing agricultural exports and modernization of farming practices.Middle East & Africa Seed Processing Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is growing from a valuation of $0.86 billion in 2023 to $1.41 billion by 2033. Efforts to enhance food security and agricultural practices amidst climate challenges are key drivers of this growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
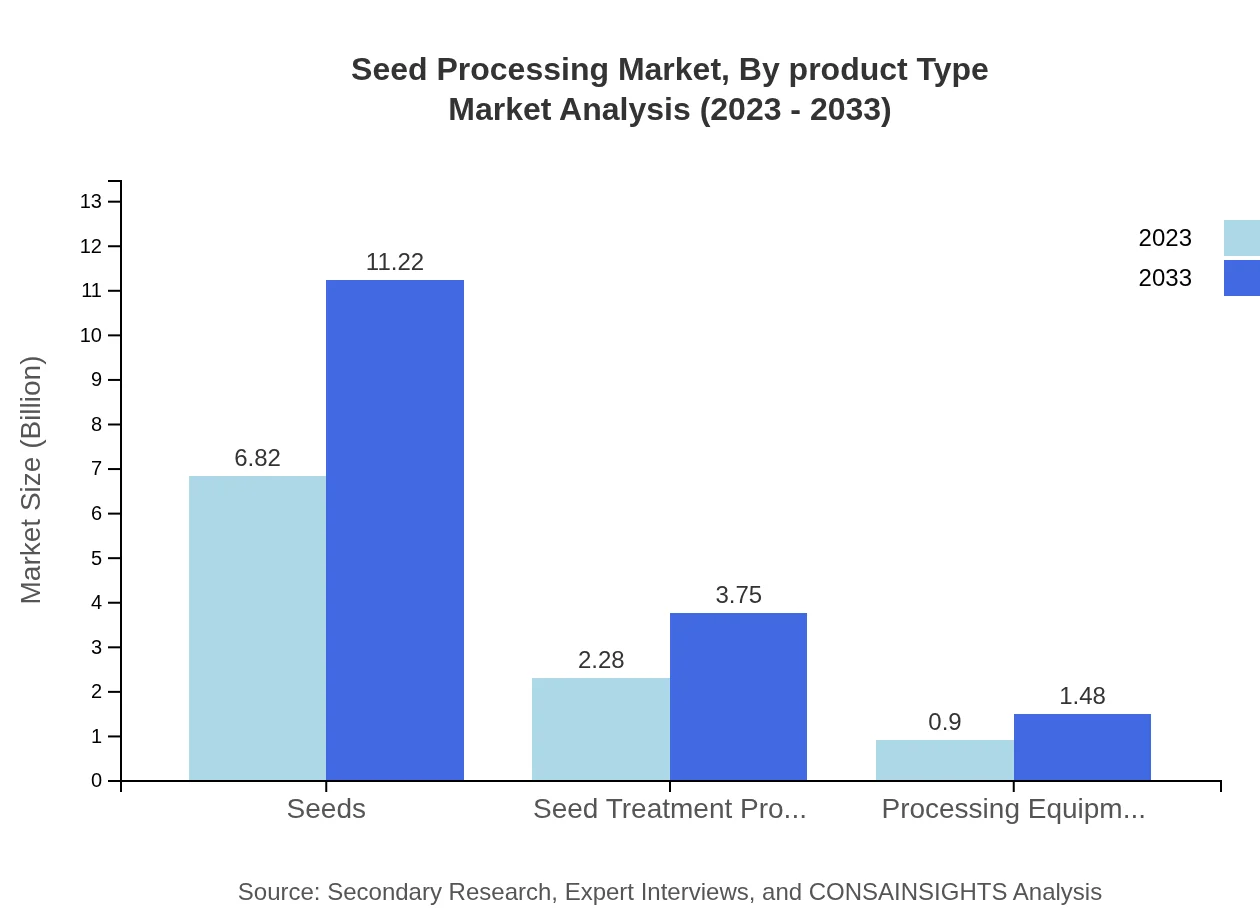
Seed Processing Market Analysis By Product Type
The Seed Processing market by product type includes crucial segments such as mechanical processing, heat treatment, and chemical processing. Mechanical processing, leading the market with a projected size of $6.82 billion in 2023, is expected to reach $11.22 billion by 2033, while heat treatment is anticipated to grow from $2.28 billion to $3.75 billion over the same period.
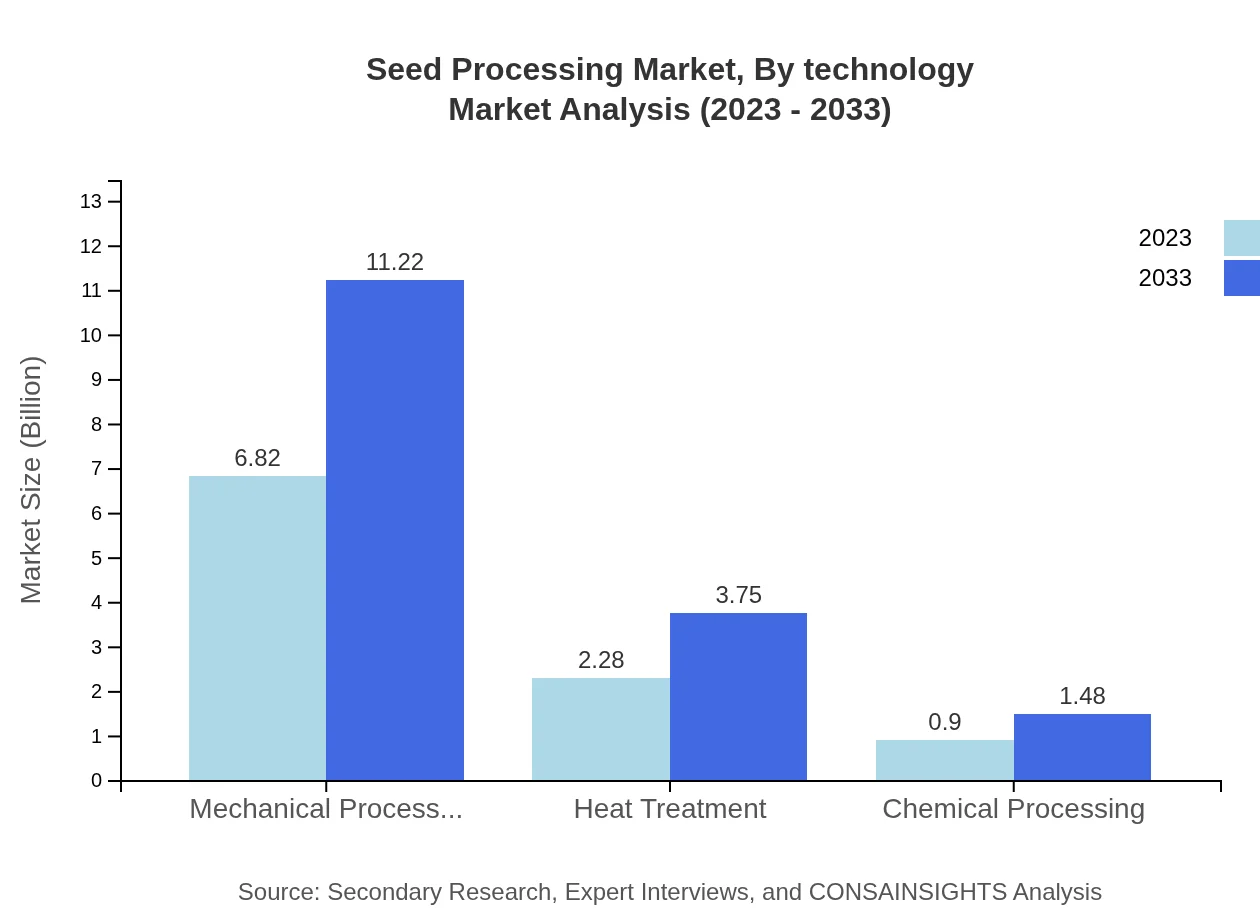
Seed Processing Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements significantly impact the Seed Processing market. Innovations in automation and digitalization are redefining operational efficiencies and effectiveness. Mechanized seed processing techniques dominate, complemented by heat treatment and chemical processing methodologies, thereby enhancing seed quality and yield.
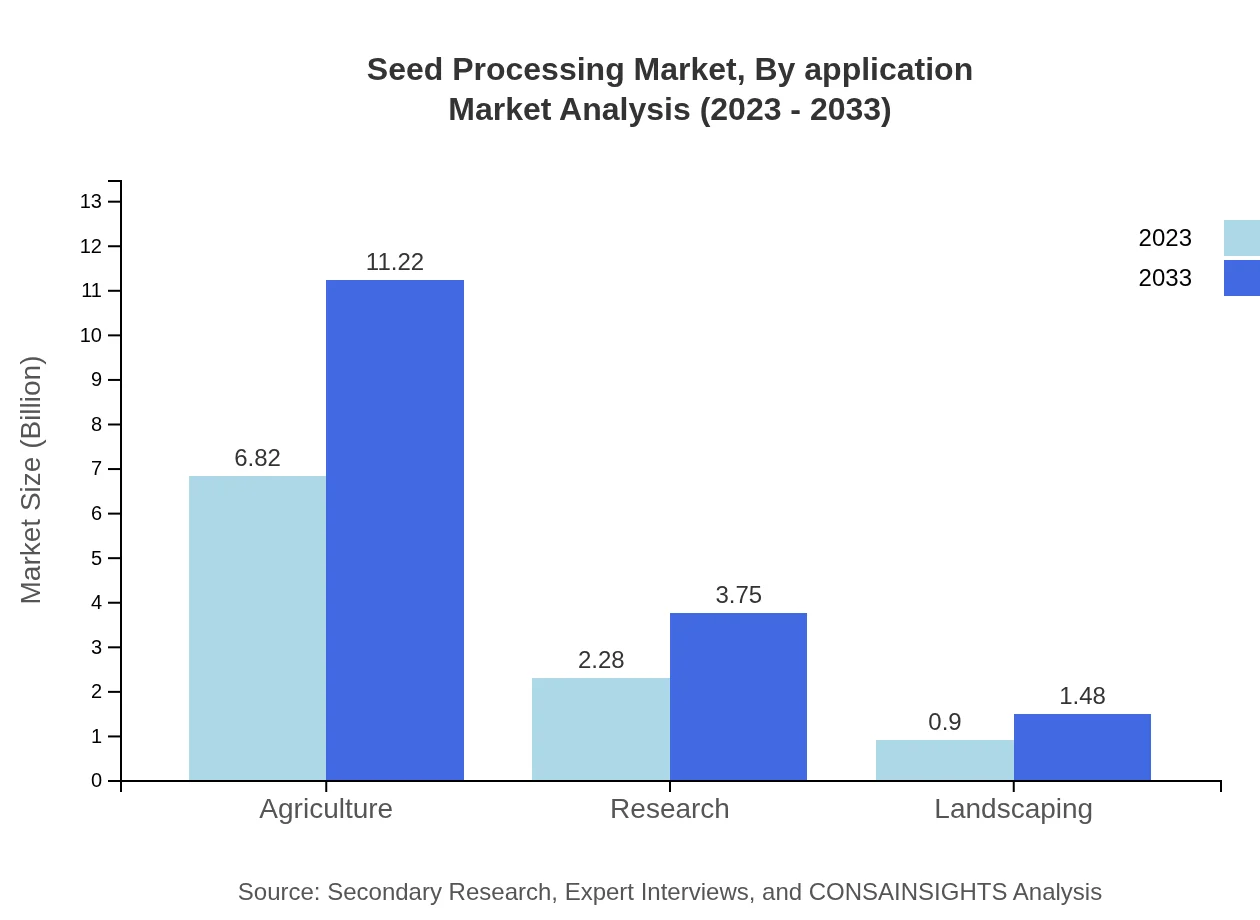
Seed Processing Market Analysis By Application
Applications of seed processing span various sectors, including agriculture, research, and landscaping. The agriculture segment is notable, showcasing a robust market presence, projected to extend from $6.82 billion in 2023 to $11.22 billion by 2033, reflecting the critical role of processed seeds in agricultural productivity.
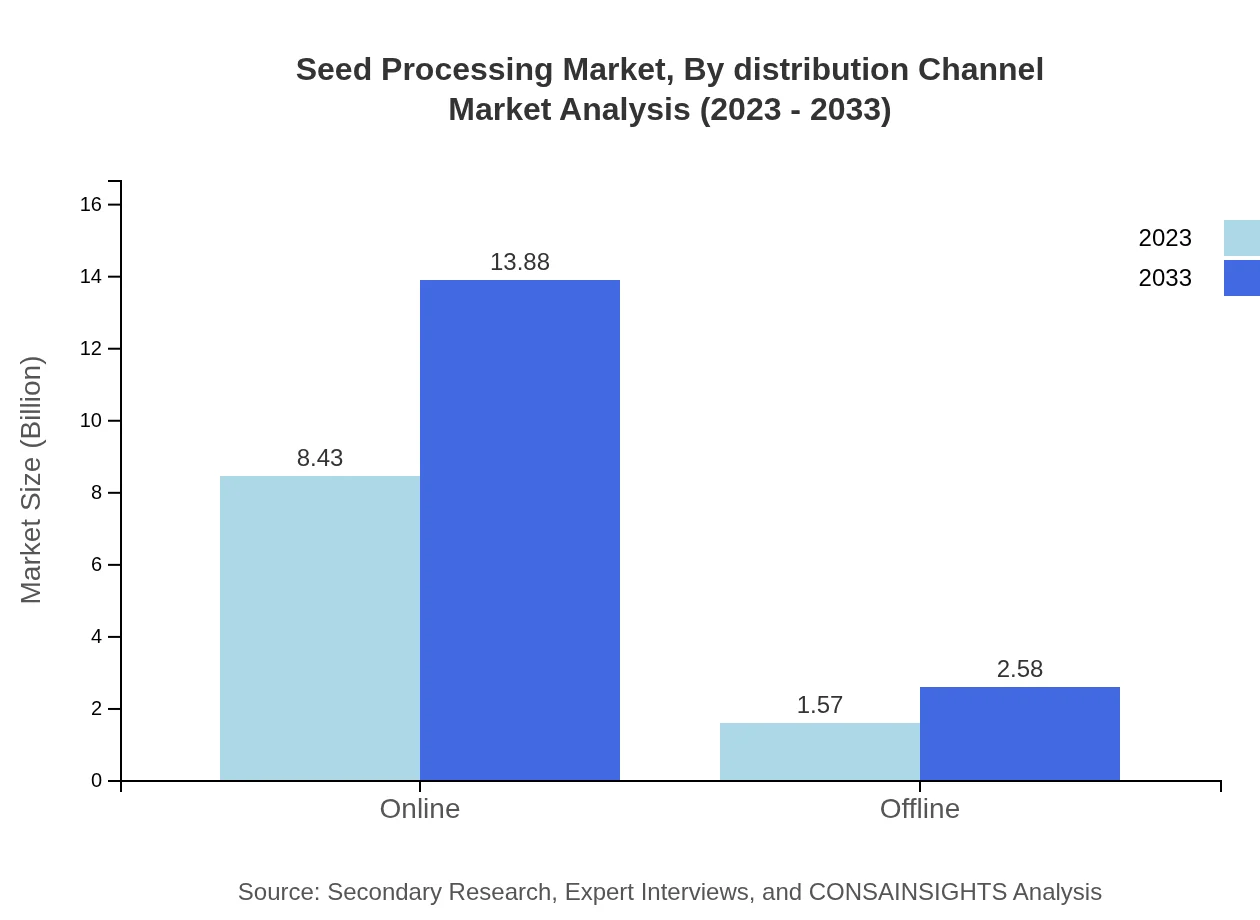
Seed Processing Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The distribution channels segment includes online and offline strategies. Online sales are expected to dominate with a market share over 84% in 2023, growing its footprint to approximately $13.88 billion by 2033, while offline channels continue to maintain a supportive role in regional distribution networks.
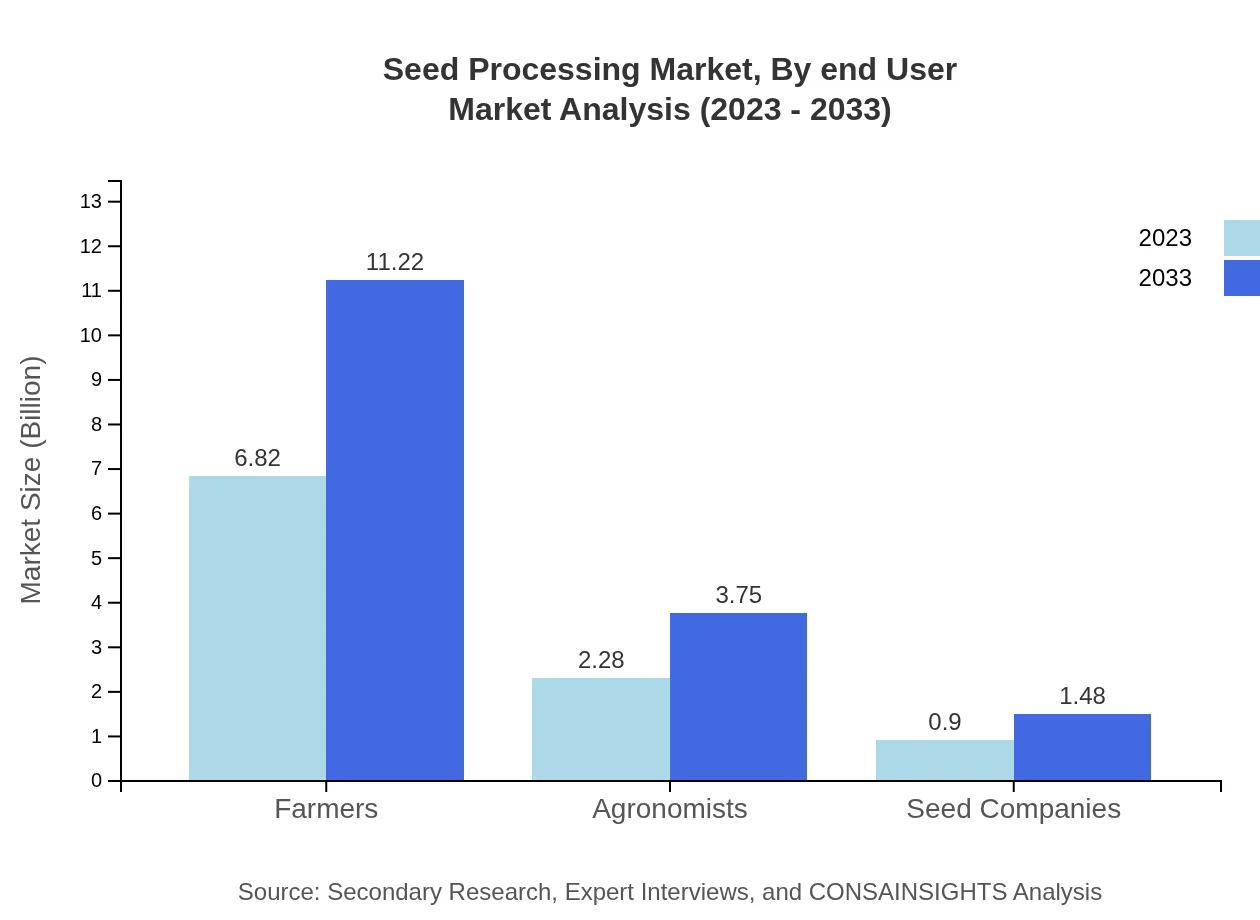
Seed Processing Market Analysis By End User
Key end-users in the Seed Processing market include farmers, agronomists, and seed companies. Farmers account for a significant share, showcasing a steady growth from $6.82 billion in 2023 to $11.22 billion by 2033, underpinning the critical nature of seed processing in farming operations.
Seed Processing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Seed Processing Industry
BASF:
BASF is a leading global player in agricultural solutions, focusing on chemical and biotechnology-based seed treatments, advanced seed processing technologies, and sustainable agriculture practices.DuPont:
DuPont is renowned for its innovative seed processing solutions, specializing in crop genetics and advanced technologies that enhance seed performance and optimize agricultural yields.Syngenta:
Syngenta stands as a key contributor to the seed processing industry, offering a diverse portfolio of high-quality seeds and cutting-edge technologies designed for various agricultural needs.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of seed processing?
The global seed processing market is valued at approximately $10 billion in 2023, with an expected growth to around $16.2 billion by 2033, reflecting a CAGR of 5%. This growth highlights the rising importance of seed processing in agriculture.
What are the key market players or companies in the seed processing industry?
Key players in the seed processing market include Syngenta AG, Bayer Crop Science, BASF SE, DowDuPont, and Limagrain. These companies dominate through innovation in seed technology and processing techniques, crucial for enhancing crop yield and quality.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the seed processing industry?
The growth in the seed processing industry is driven by increasing agricultural productivity demands, technological advancements in seed treatment, rising investments in research and development, and growing awareness of improved seed quality among farmers.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the seed processing market?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing in the seed processing market, expected to grow from $1.95 billion in 2023 to $3.20 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by rising population and agricultural demands.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the seed processing industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the seed processing industry, catering to specific client needs. This includes tailored insights and analyses to help stakeholders make informed decisions.
What deliverables can I expect from this seed processing market research project?
From the seed processing market research project, expect detailed reports including market size, growth forecasts, competitive landscape, regional analysis, segment breakdowns, and actionable insights to inform strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of seed processing?
Current trends in the seed processing market involve increasing adoption of mechanization, advanced seed treatments, growth in organic seed market, and emphasis on sustainability, all driven by consumer demand for higher quality and environmentally friendly products.