Seed Testing Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: seed-testing
Seed Testing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the seed testing market, exploring market dynamics, segmentation, and regional insights, along with forecasts up to 2033. It aims to deliver crucial insights into market trends, key players, and future growth opportunities in the seed testing industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
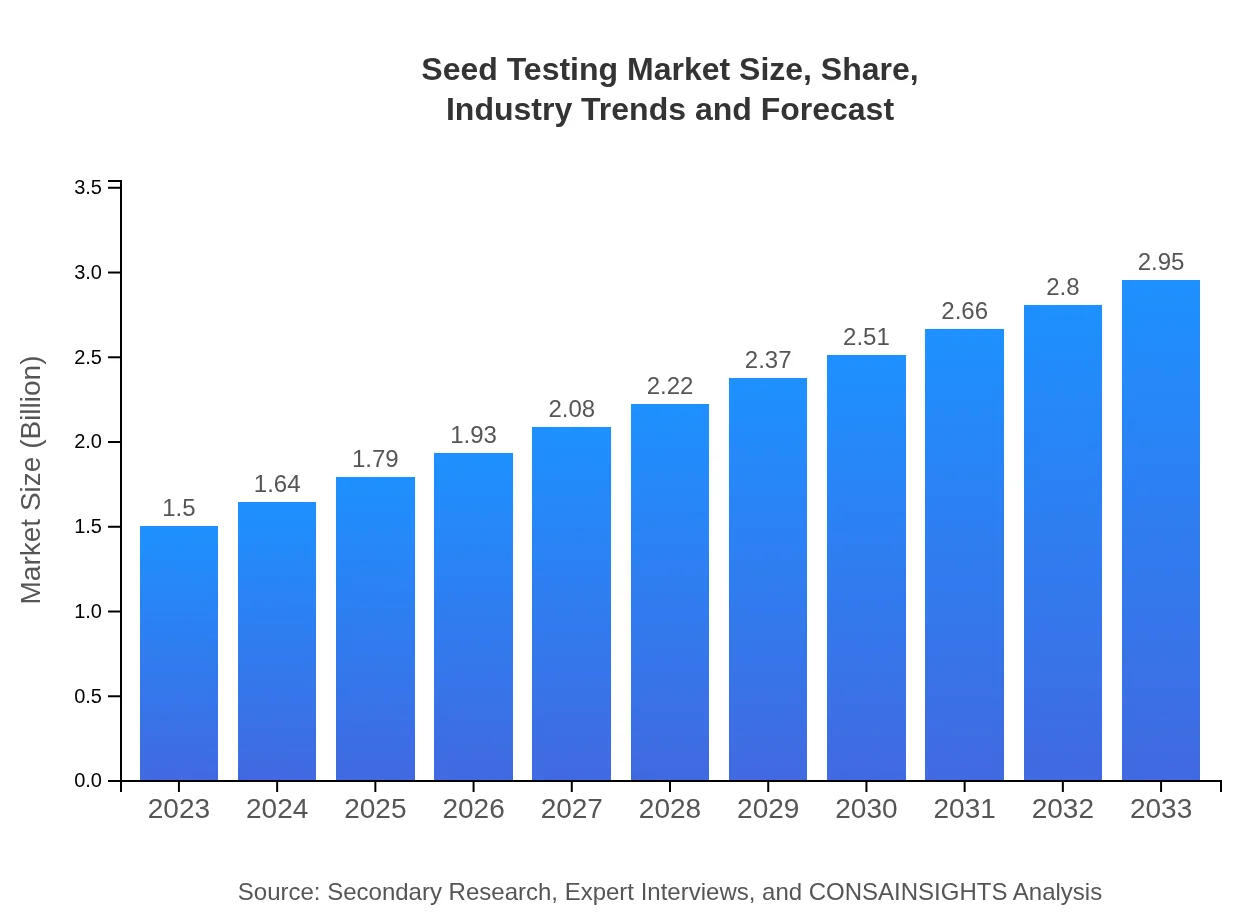
| 2023 Market Size | $1.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $2.95 Billion |
| Top Companies | SGS SA, Bureau Veritas, Eurofins Scientific, Intertek Group plc, DSM Nutritional Products |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Seed Testing Market Overview
Customize Seed Testing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Seed Testing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Seed Testing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Seed Testing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Seed Testing market in 2023?
Seed Testing Industry Analysis
Seed Testing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Seed Testing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Seed Testing Market Report:
Europe's seed testing market was valued at approximately $0.40 billion in 2023, projected to double to $0.79 billion by 2033. The increase in quality seed production and the focus on sustainable practices among European farmers drive this market.Asia Pacific Seed Testing Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is a significant player in the seed testing market, with a market size of approximately $0.30 billion in 2023 and expected to grow to $0.58 billion by 2033. The growth is driven by demand for hybrid seeds and various governmental initiatives to improve agricultural output in countries like India and China.North America Seed Testing Market Report:
North America holds a substantial share of the market with a size of around $0.53 billion in 2023, forecasted to grow to $1.05 billion by 2033. This growth is attributed to advanced agricultural practices, higher adoption rates of genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and stricter regulatory standards.South America Seed Testing Market Report:
In South America, the seed testing market size was about $0.11 billion in 2023, projected to reach $0.21 billion by 2033. The region is seeing rising investments in agricultural productivity, further promoting the demand for effective seed testing.Middle East & Africa Seed Testing Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region anticipate growth from $0.16 billion in 2023 to $0.31 billion by 2033. Urbanization and an increase in agriculture-based economies are fuelling the demand for seed testing services.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
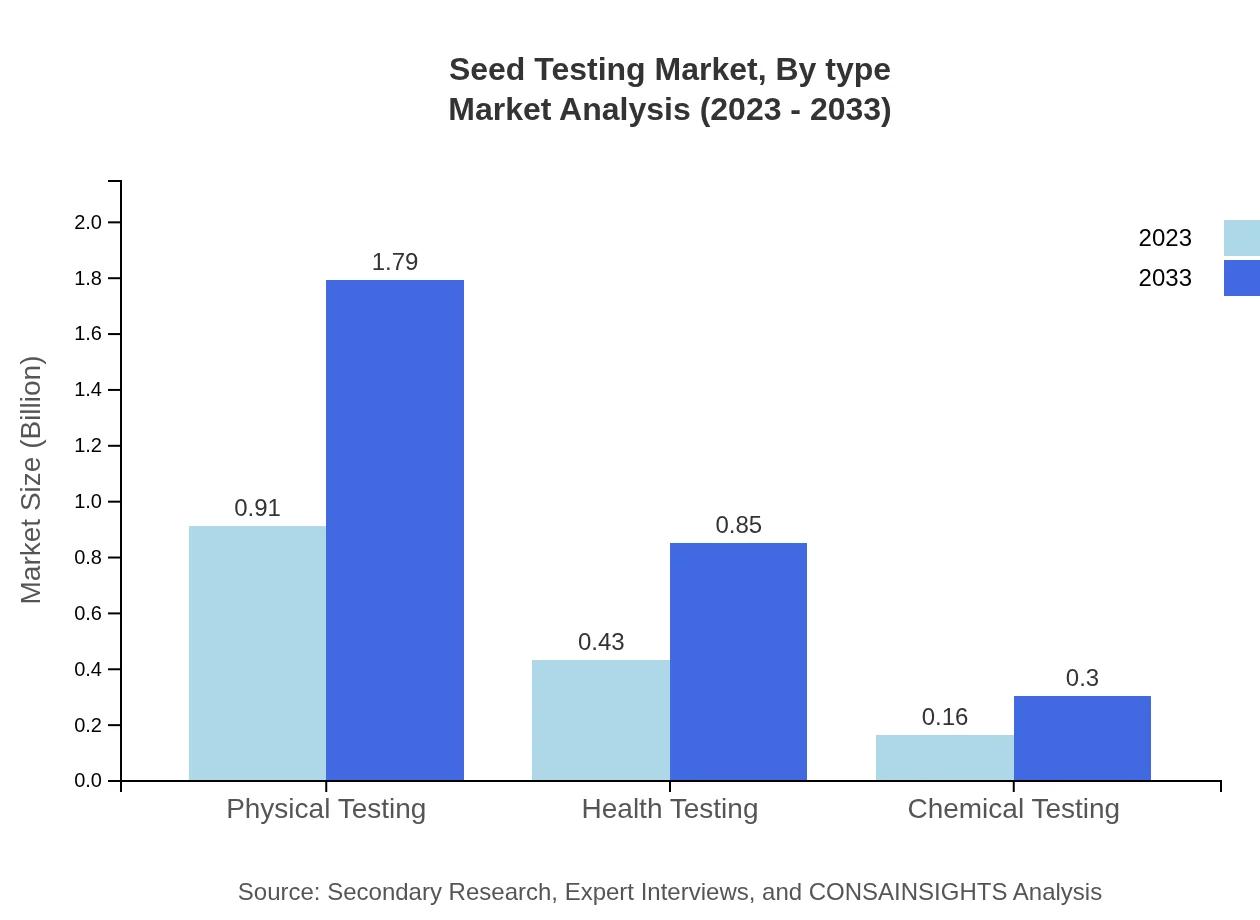
Seed Testing Market Analysis By Type
Physical Testing is the dominant segment with a market size of $0.91 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $1.79 billion by 2033, accounting for 60.84% of the total market share. Health Testing, valued at $0.43 billion in 2023, will grow to $0.85 billion by 2033, holding 28.82% market share. Chemical Testing represents a smaller portion at $0.16 billion in 2023, reaching $0.30 billion by 2033. Laboratory Testing remains significant at $1.23 billion in 2023, growing to $2.41 billion by 2033, capturing 81.76% of the market share.
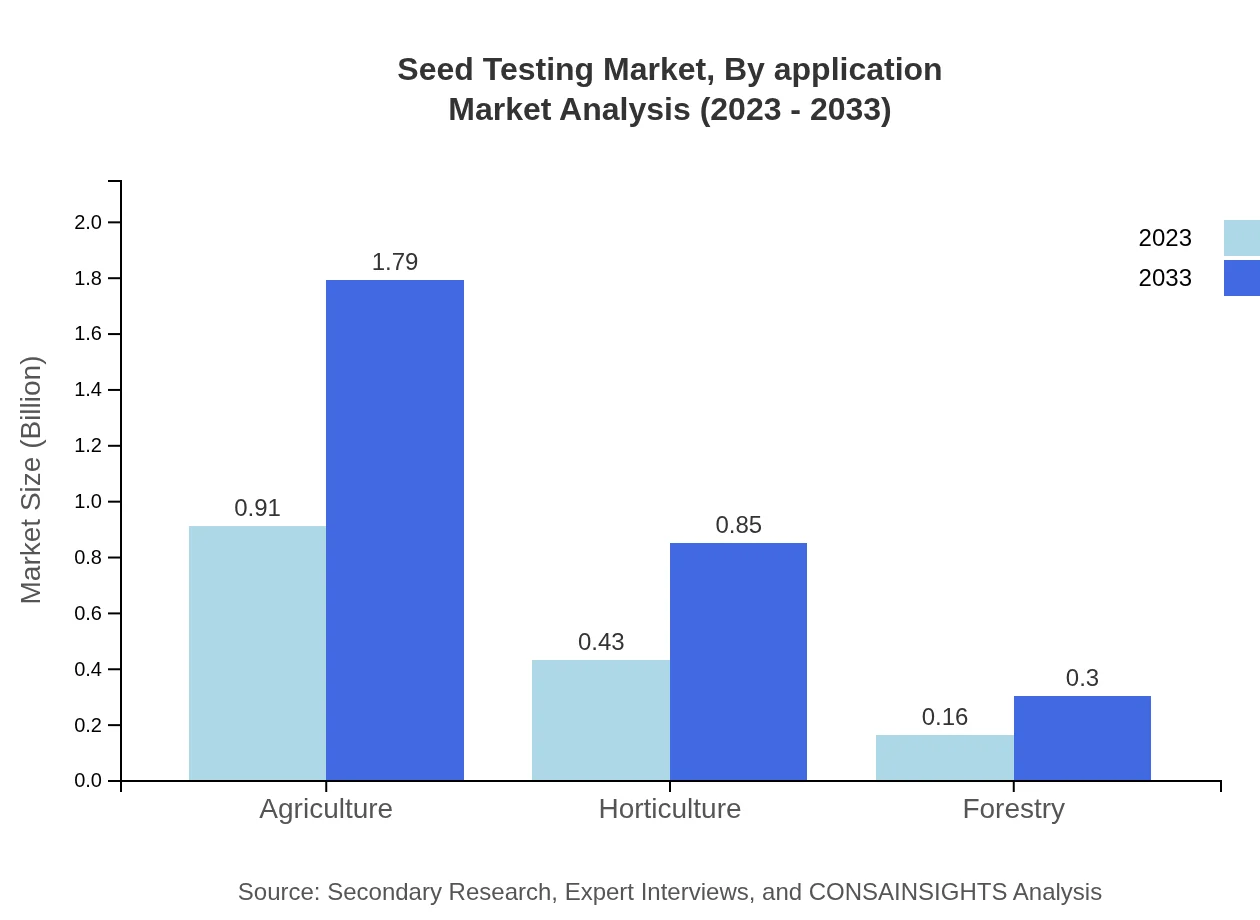
Seed Testing Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, Agriculture is the largest segment with a market size of $0.91 billion in 2023, expected to increase to $1.79 billion by 2033, reflecting a 60.84% share. Horticulture testing stands at $0.43 billion in 2023 with a projected growth to $0.85 billion in 2033, comprising 28.82%. Forestry testing accounts for $0.16 billion in 2023, growing to $0.30 billion by 2033.
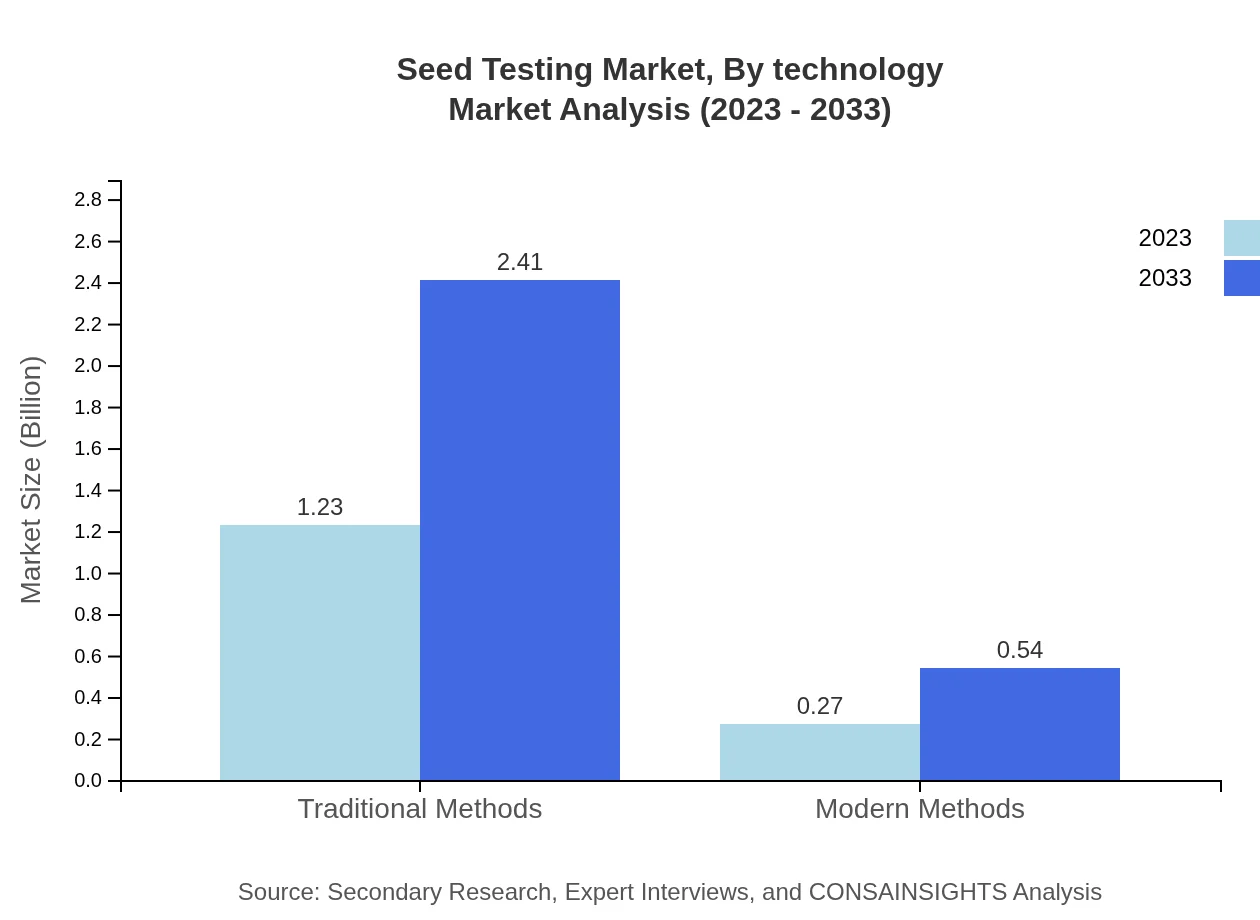
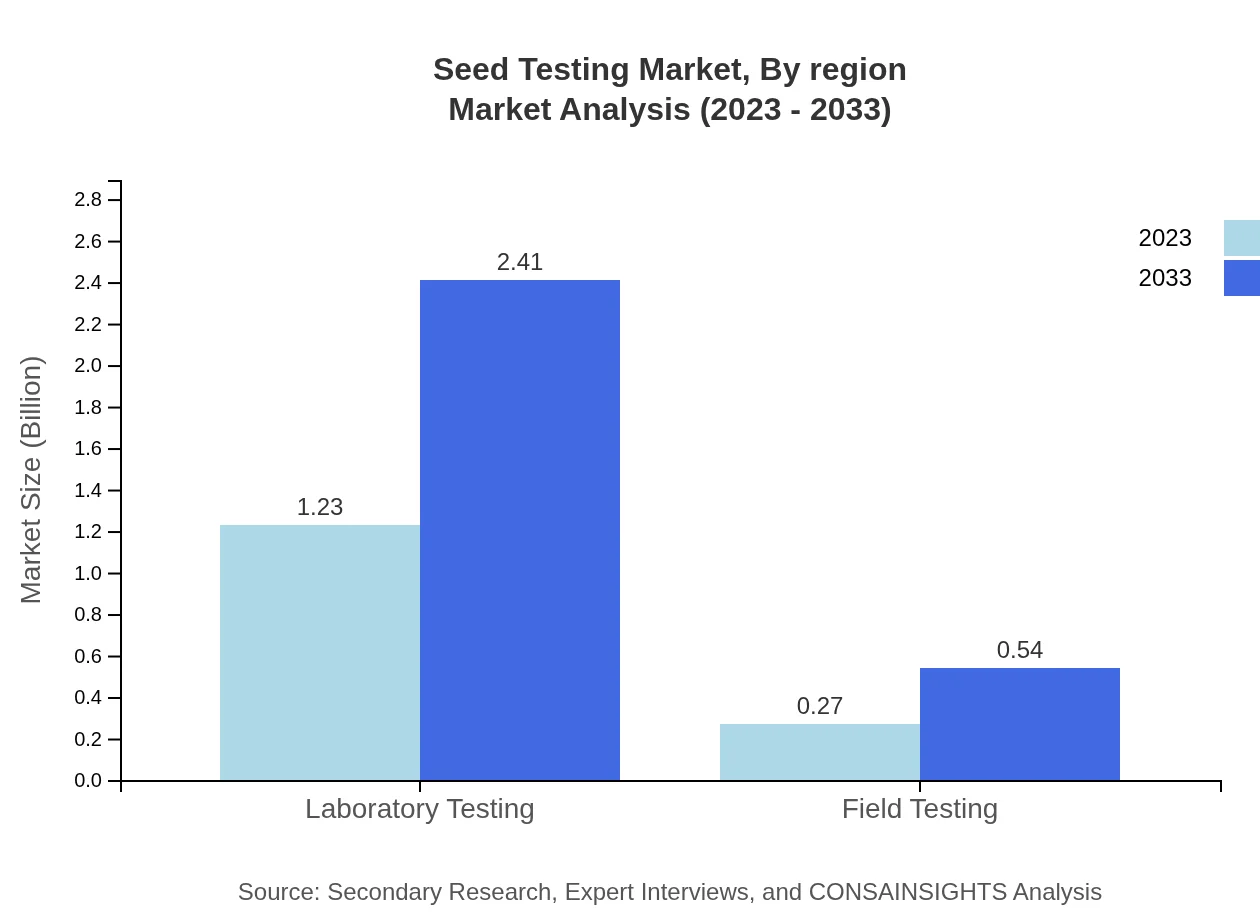
Seed Testing Market Analysis By Technology
Traditional Methods in seed testing dominate the market with a size of $1.23 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to $2.41 billion by 2033, accounting for 81.76% market share. Conversely, Modern Methods yield a size of $0.27 billion in 2023, growing to $0.54 billion by 2033, capturing an 18.24% share.
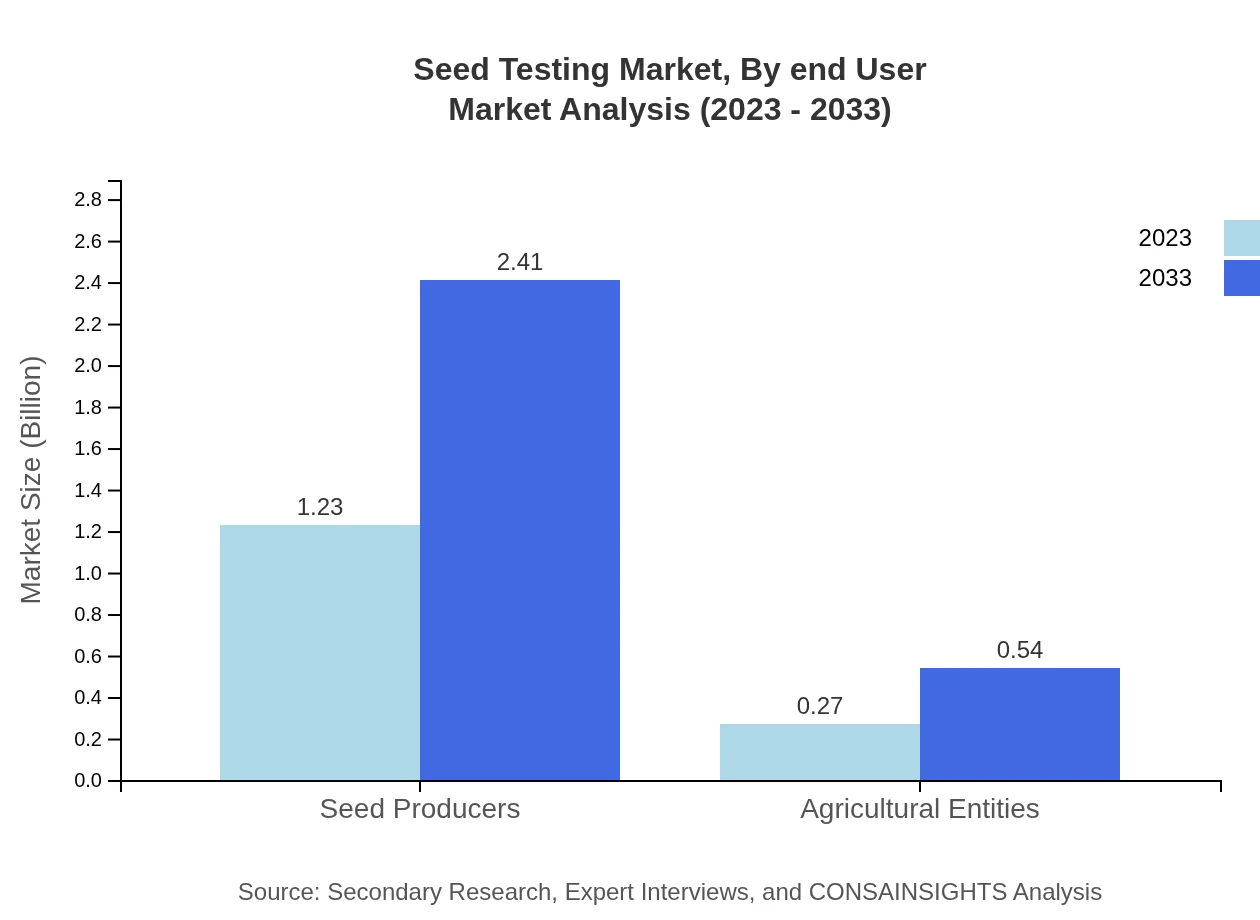
Seed Testing Market Analysis By End User
Seed Producers constitute the largest end-user segment in seed testing, valued at $1.23 billion in 2023, projected to reach $2.41 billion by 2033, representing 81.76%. Agricultural entities are valued at $0.27 billion in 2023, with a growth forecast to $0.54 billion by 2033, representing an 18.24% share.
Seed Testing Market Analysis By Region
The market is segmented regionally, highlighting that North America and Europe are leaders in terms of revenue generation in seed testing services, while the Asia-Pacific region shows the fastest growth potential due to its agricultural demands. Emerging markets in the Middle East and Africa also present opportunities due to their developing agricultural sectors.
Seed Testing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Seed Testing Industry
SGS SA:
A world leader in inspection, verification, testing, and certification, SGS offers a wide range of seed testing services ensuring the quality and germination of seeds.Bureau Veritas:
An international leader in testing, inspection, and certification, Bureau Veritas provides seed testing services that comply with international standards.Eurofins Scientific:
Eurofins provides a comprehensive range of seed testing services globally, focusing on genetic and trait analysis for improved seed quality.Intertek Group plc:
With expertise in quality assurance and quality control, Intertek offers seed testing services that help businesses to meet the regulatory standards.DSM Nutritional Products:
DSM offers seed testing services focusing on improving nutritional aspects of seeds and ensuring they meet customer demands.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of seed Testing?
The global seed-testing market is valued at approximately 1.5 billion USD in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2033, indicating robust growth in this essential agricultural sector.
What are the key market players or companies in this seed Testing industry?
Key players in the seed-testing industry include large agricultural corporations and specialized laboratories. Companies focus on ensuring seed quality and meeting industry standards, driving competition and innovation within the sector.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the seed Testing industry?
Growth drivers include increased demand for genetically modified seeds, stringent food safety regulations, and a rising emphasis on agricultural productivity, which all necessitate reliable seed-testing practices.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the seed Testing?
The North American seed-testing market is the fastest-growing region, with its market size expected to increase from 0.53 billion USD in 2023 to 1.05 billion USD by 2033, reflecting significant investment in agricultural technologies.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the seed Testing industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to client needs in the seed-testing industry, ensuring access to specific insights relevant to unique business goals and market dynamics.
What deliverables can I expect from this seed Testing market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis reports, segmented data, trend forecasts, regional insights, and competitive landscape evaluations, all designed to inform strategic decision-making for clients.
What are the market trends of seed testing?
Key trends include a shift towards laboratory-tested seeds, rising adoption of digital technologies for testing, and greater regulatory scrutiny, which collectively enhance seed quality and agricultural efficiency.