Seeds Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: seeds
Seeds Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Seeds market from 2023 to 2033, covering market size, growth trends, and segmentation insights across different regions and product types.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
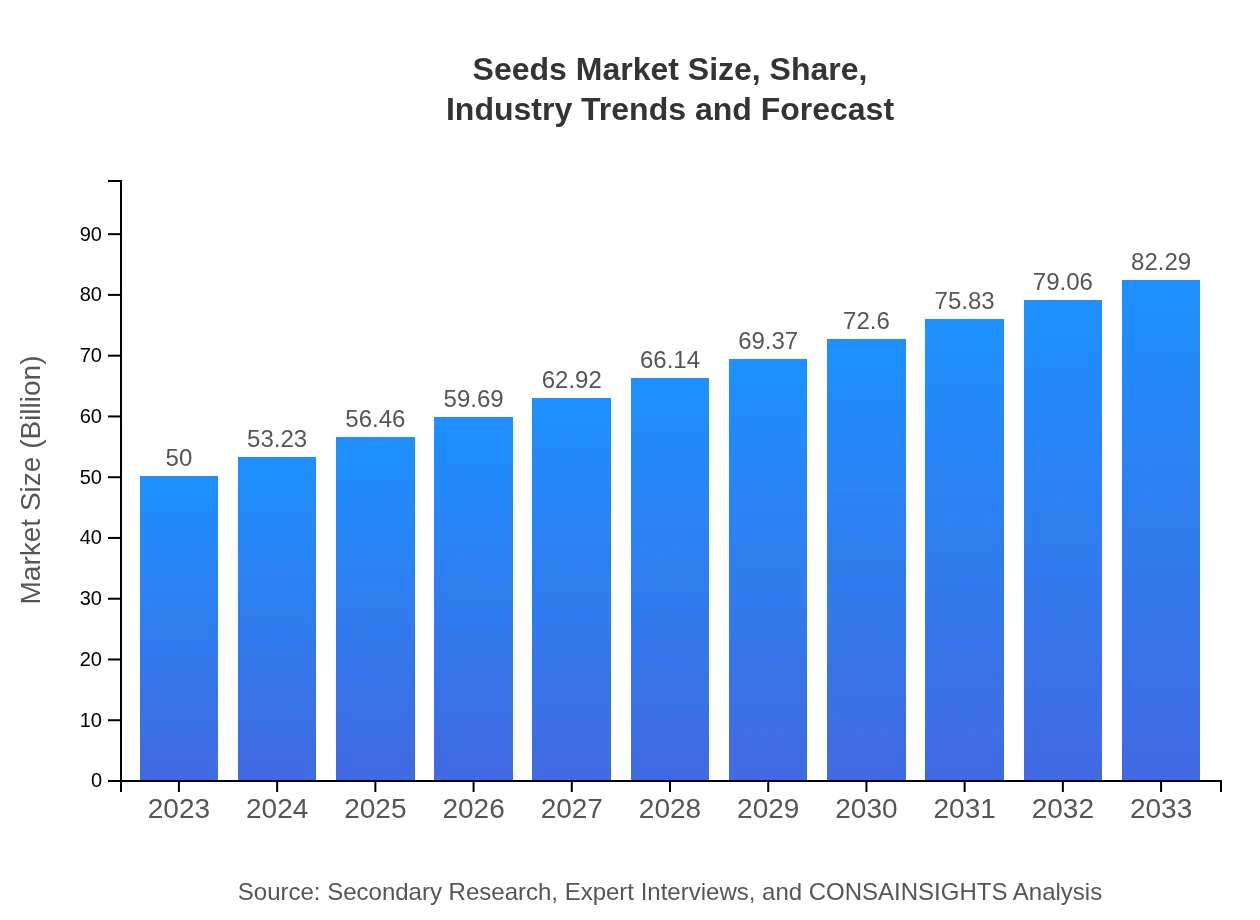
| 2023 Market Size | $50.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $82.29 Billion |
| Top Companies | Bayer AG, Syngenta, Corteva Agriscience, DowDuPont, Limagrain |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Seeds Market Overview
Customize Seeds Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Seeds market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Seeds's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Seeds
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Seeds market in 2023?
Seeds Industry Analysis
Seeds Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Seeds Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Seeds Market Report:
The European market, valued at $12.87 billion in 2023, is anticipated to grow to $21.17 billion by 2033. Europe’s stringent regulations surrounding GMOs and a rising preference for organic seeds are driving growth, reinforcing sustainable agricultural practices.Asia Pacific Seeds Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is projected to witness substantial growth, with the market size estimated at $9.79 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $16.11 billion by 2033. Countries like India and China are significant contributors due to their vast agricultural land and increasing adoption of advanced seed technologies.North America Seeds Market Report:
North America represented a remarkable market size of $16.68 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $27.46 billion by 2033. The dominance of genetically modified and organic seeds is notable here, aided by significant investment in agricultural research and development.South America Seeds Market Report:
In South America, the market was valued at $4.98 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $8.20 billion by 2033. The region’s agriculture is heavily reliant on seed varieties suited for its unique climate, along with increasing exports of agricultural products driving market demand.Middle East & Africa Seeds Market Report:
The market in the Middle East and Africa is estimated at $5.68 billion in 2023, and is expected to grow to $9.35 billion by 2033. Factors such as rising population, food insecurity, and investment in agricultural initiatives play a pivotal role in this growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
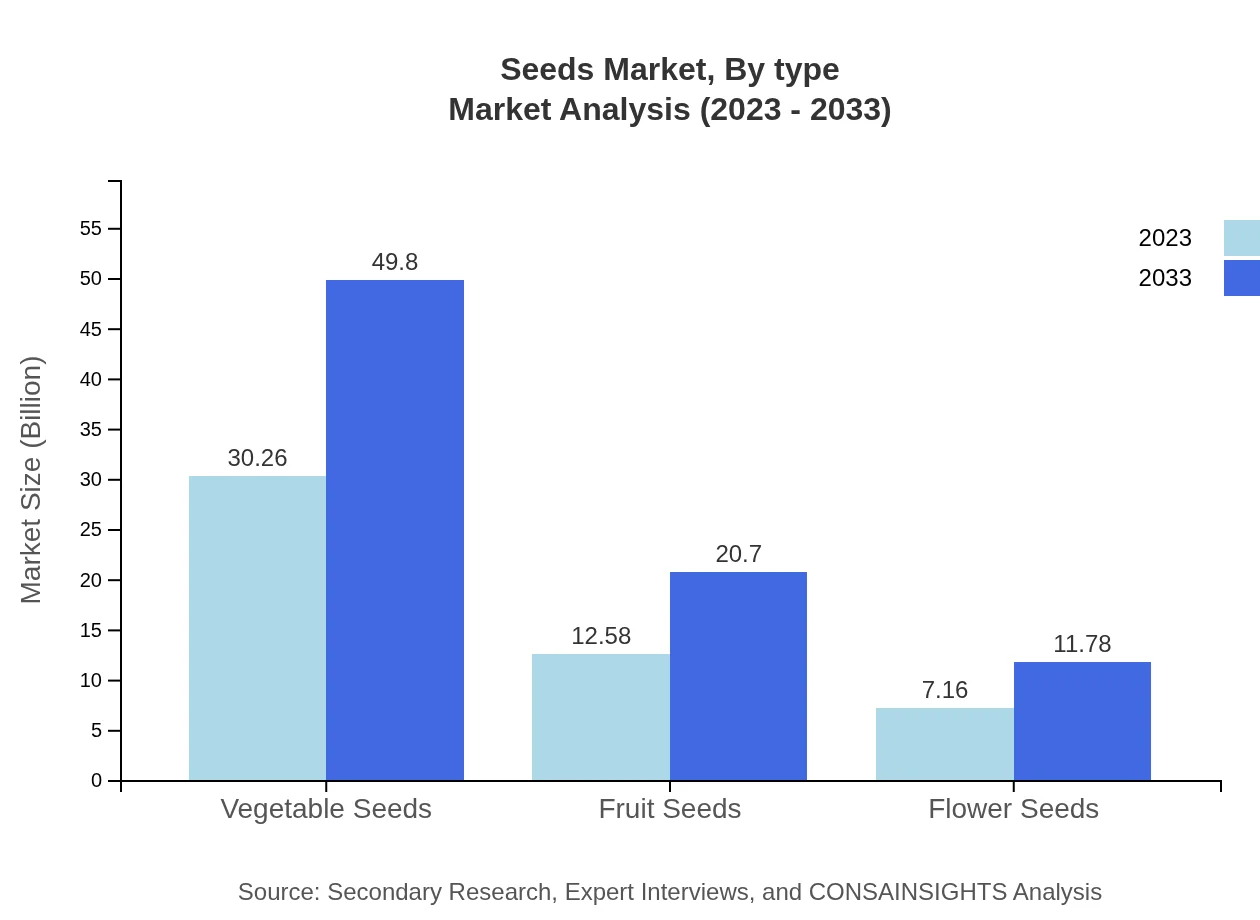
Seeds Market Analysis By Type
The market analysis by type reveals that vegetable seeds are set to grow from $30.26 billion in 2023 to $49.80 billion in 2033, capturing a significant market share of 60.52%. Fruit seeds and flower seeds are also expanding, with values expected to increase from $12.58 billion to $20.70 billion, and from $7.16 billion to $11.78 billion, respectively. Commercial seeds dominate overall share due to high usage in large agricultural operations, while organic seeds are gaining traction, reflecting a shift towards healthier and environmentally-friendly options.
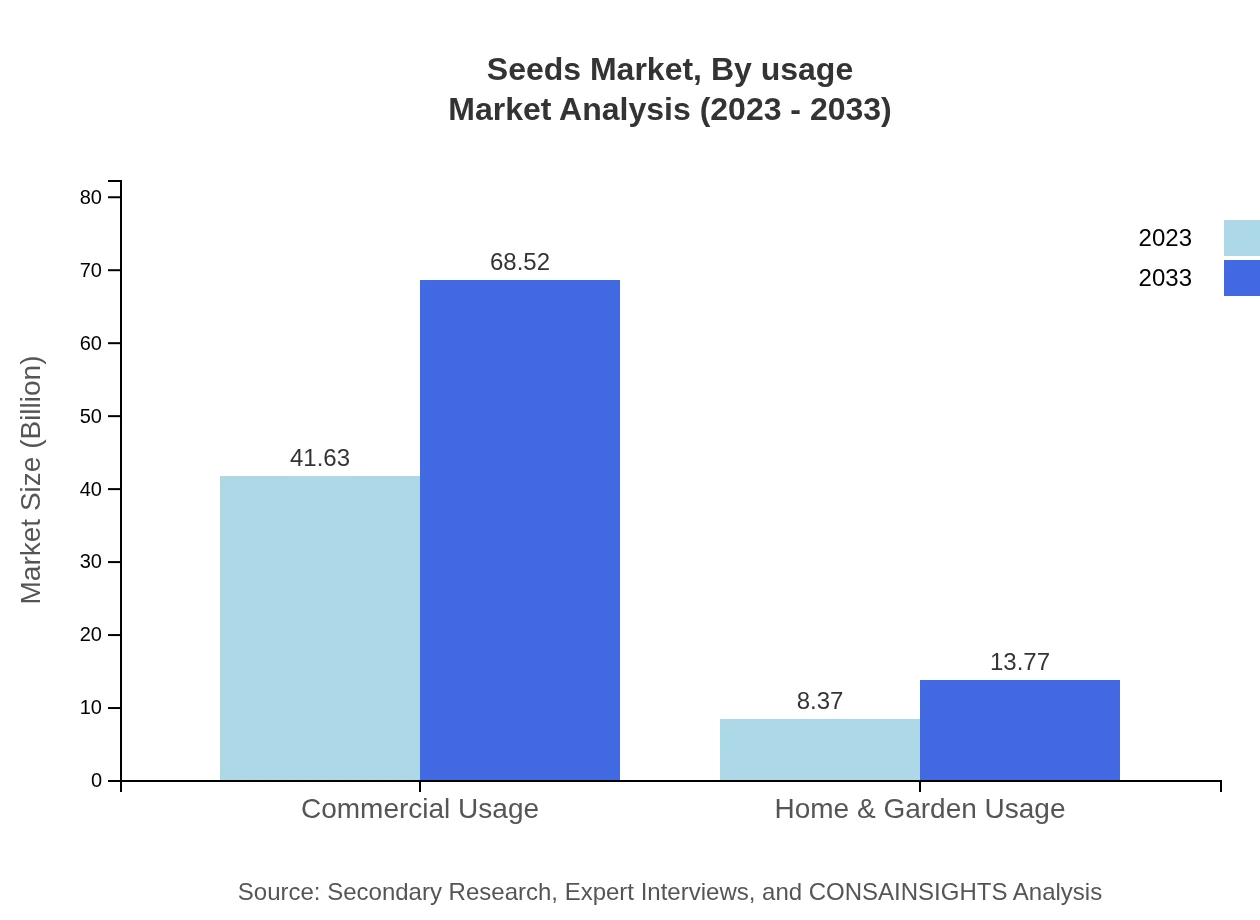
Seeds Market Analysis By Usage
Commercial usage is the largest segment, poised to grow from $41.63 billion in 2023 to $68.52 billion by 2033, accounting for 83.27% of the market share. Home & garden usage is also vital, forecasting an increase from $8.37 billion to $13.77 billion, representing a growing segment among urban gardening enthusiasts.
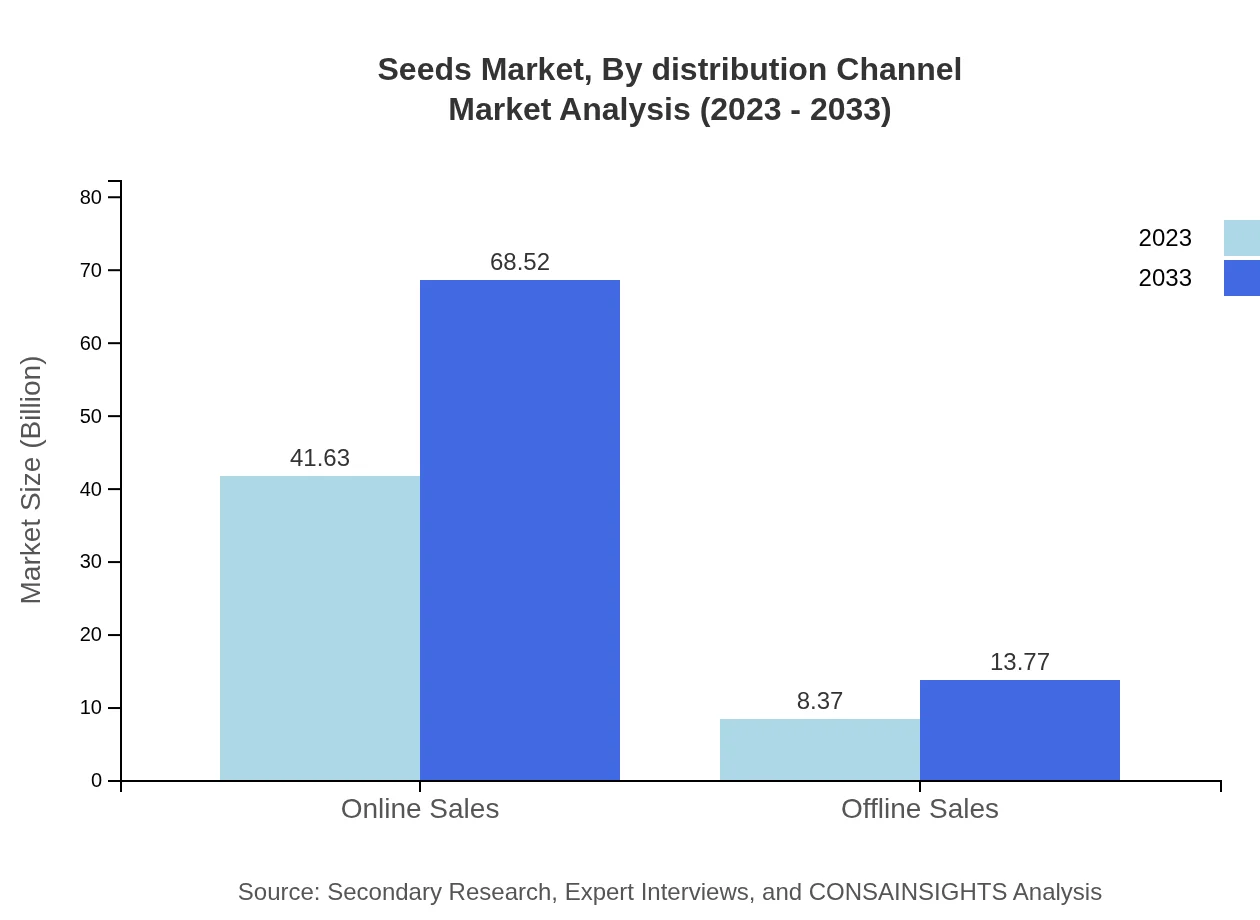
Seeds Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Online sales are revolutionizing the Seeds market, with projections escalating from $41.63 billion in 2023 to $68.52 billion by 2033, maintaining an 83.27% share. Offline sales, while smaller, are incrementally growing from $8.37 billion to $13.77 billion, appealing to traditional consumers.
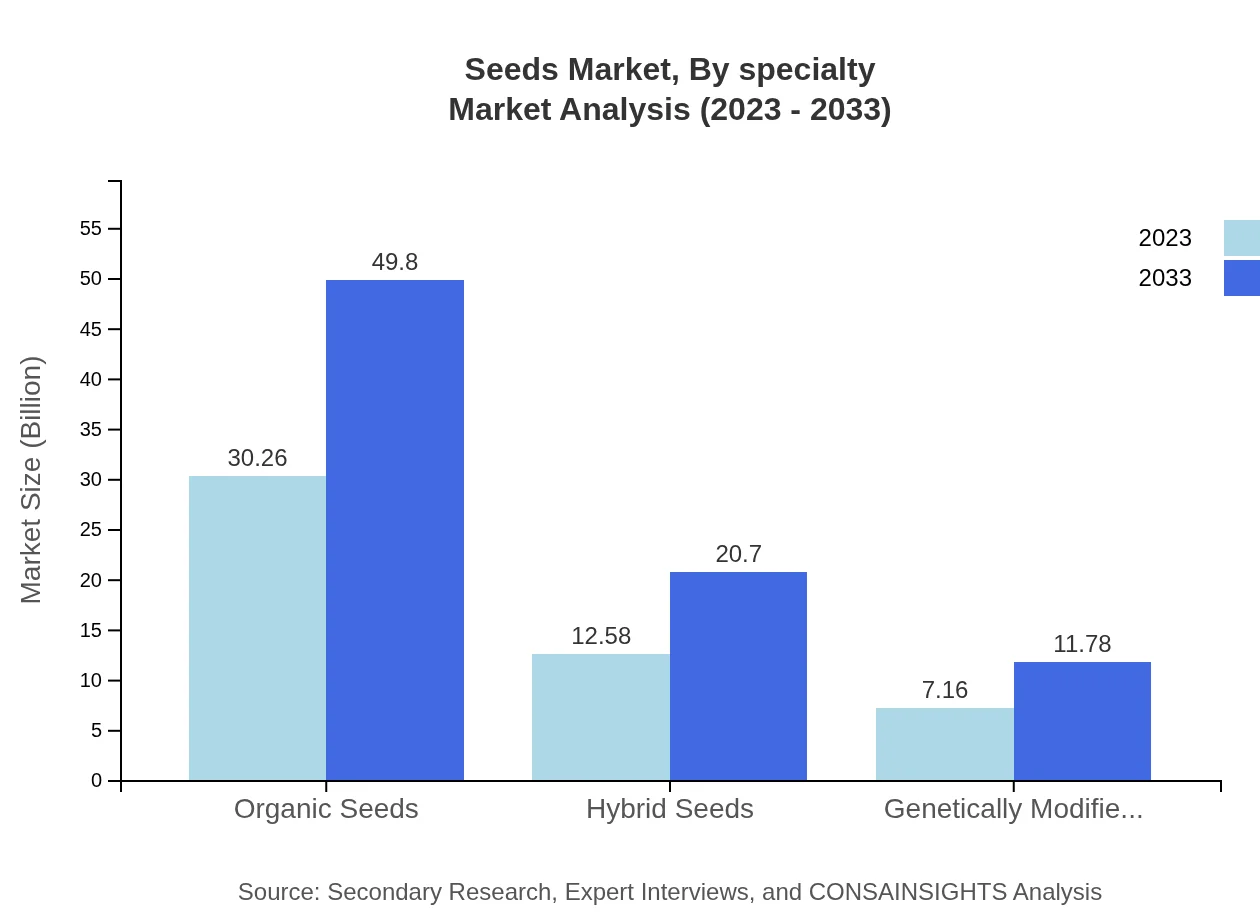
Seeds Market Analysis By Specialty
Specialty seeds, such as organic and hybrid seeds, are seeing notable growth. Organic seeds stand at $30.26 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $49.80 billion by 2033, reflecting strong consumer demand for sustainable and health-conscious options.
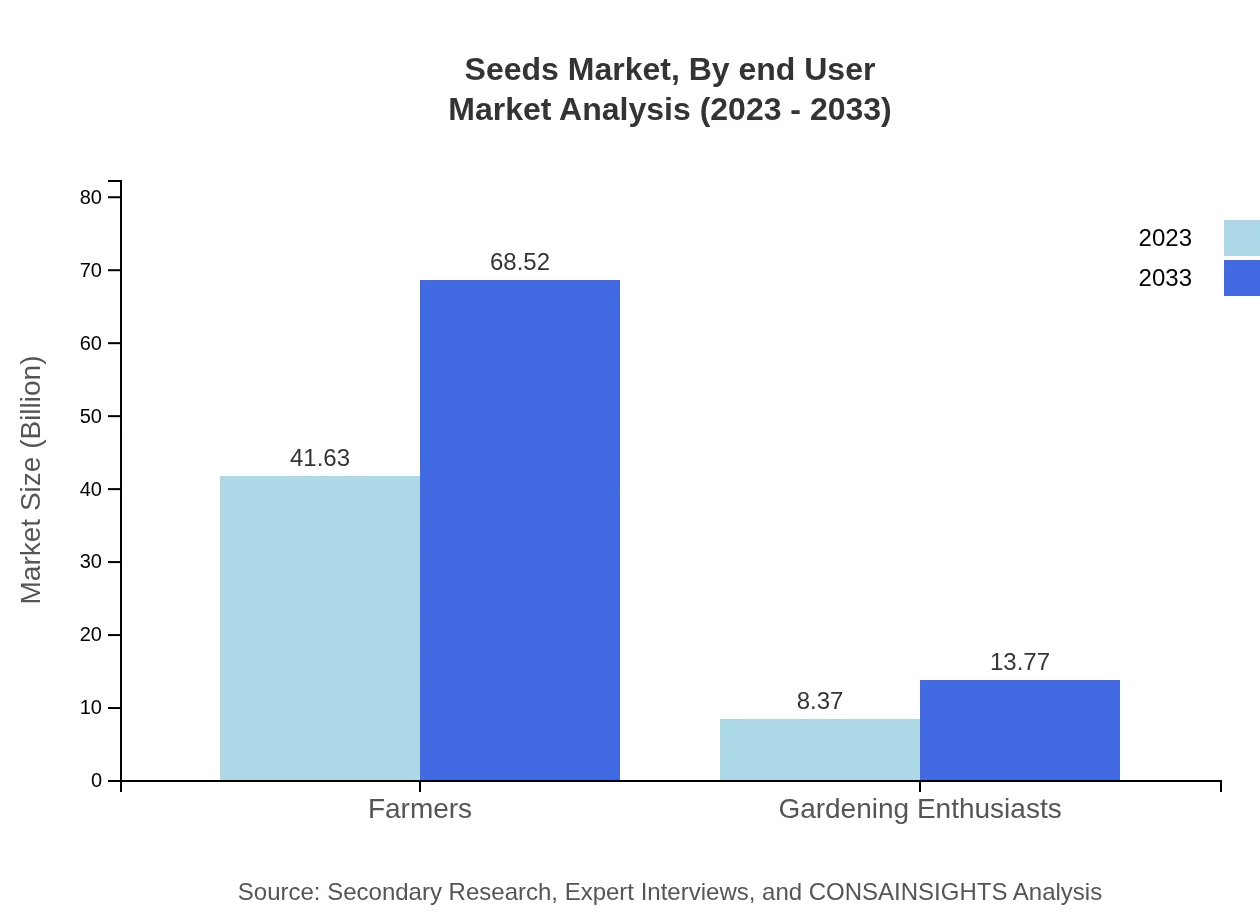
Seeds Market Analysis By End User
Farmers and gardening enthusiasts are the primary end-users of seeds. Farmers are expected to continue driving demand from $41.63 billion in 2023 to $68.52 billion by 2033, while gardening enthusiasts represent a smaller but significant segment, growing from $8.37 billion to $13.77 billion.
Seeds Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Seeds Industry
Bayer AG:
A global leader in agriculture that offers a wide range of seeds from crops to vegetables and is heavily involved in research and development for optimizing seed genetics.Syngenta:
A well-known player in the seeds market, particularly recognized for its innovative approach to developing hybrid seeds that maximize yield and climate resilience.Corteva Agriscience:
This company focuses on seeds and crop protection, leading the charge in sustainable agriculture through diverse seed offerings for various crops.DowDuPont:
With its significant investments in seed technology, DowDuPont is a crucial contributor to advancements in genetically modified and high-yield seeds.Limagrain:
A French cooperative that specializes in a variety of seeds, with emphasis on vegetable seeds, adapting to global demands for agriculture.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of seeds?
The seeds market is currently valued at approximately $50 billion USD, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5% through 2033. This growth is expected to facilitate significant increases in both segment and regional markets.
What are the key market players or companies in the seeds industry?
The seeds industry features prominent players including Bayer CropScience, Corteva Agriscience, and Syngenta. These leaders significantly influence innovation, distribution networks, and market strategies, driving competitive growth.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the seeds industry?
Key growth factors in the seeds industry include rising food demand, technological advancements in seed technology, increased focus on sustainable agricultural practices, and regional investments in agricultural infrastructure.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the seeds market?
The North America region is anticipated to become the fastest-growing market for seeds, expanding from $16.68 billion in 2023 to $27.46 billion by 2033, reflecting strong agricultural investments and adoption of innovative practices.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the seeds industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights specializes in providing tailored market report data for the seeds industry, enabling clients to access specific insights that cater to their unique business needs, strategies, and operational objectives.
What deliverables can I expect from this seeds market research project?
Deliverables from the seeds market research project include detailed reports on market size, growth projections, trend analyses, competitive landscape insights, and strategic recommendations tailored to your business objectives.
What are the market trends of seeds?
Current trends in the seeds market encompass an increase in organic and hybrid seed adoption, growth in online sales channels, and a significant shift towards innovative genetically modified seeds that cater to evolving agricultural needs.