Seismometers Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: seismometers
Seismometers Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Seismometers market, covering trends, segmentation, and future projections from 2023 to 2033. It aims to offer valuable insights into market size, regional dynamics, technological advancements, and the key players shaping the industry's landscape.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
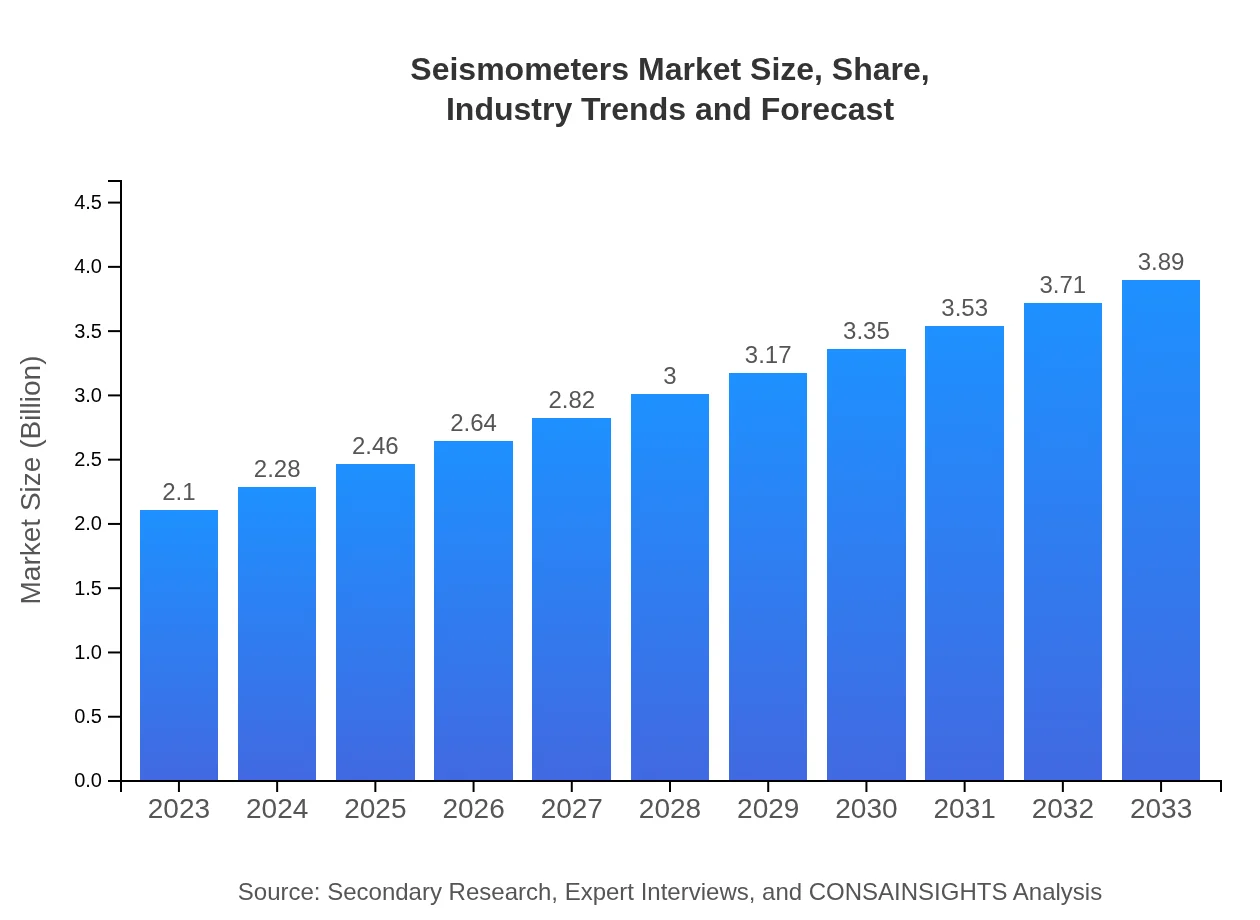
| 2023 Market Size | $2.10 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $3.89 Billion |
| Top Companies | Kinemetrics Inc., RST Instruments Ltd., ZLS, LLC |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Seismometers Market Overview
Customize Seismometers Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Seismometers market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Seismometers's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Seismometers
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Seismometers market in 2023?
Seismometers Industry Analysis
Seismometers Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Seismometers Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Seismometers Market Report:
Europe's market stands at $0.64 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $1.19 billion by 2033, propelled by stringent regulations and investments in earthquake-resistant infrastructure.Asia Pacific Seismometers Market Report:
The Asia Pacific is projected to value approximately $0.34 billion in 2023, growing to $0.63 billion by 2033. Rapid urbanization, increased investment in infrastructure, and heightened earthquake risks in countries like Japan and Indonesia drive market growth.North America Seismometers Market Report:
The North American market is the largest, with a valuation of $0.81 billion in 2023, expected to rise to $1.51 billion by 2033. Advances in technology and strong government focus on disaster preparedness are key growth drivers.South America Seismometers Market Report:
In South America, the market size is expected to increase from $0.04 billion in 2023 to $0.08 billion by 2033. The market remains relatively small but is gaining traction due to rising awareness of earthquake risks.Middle East & Africa Seismometers Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region is anticipated to grow from $0.26 billion in 2023 to $0.48 billion by 2033 as governments enhance disaster management programs and technical capabilities.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
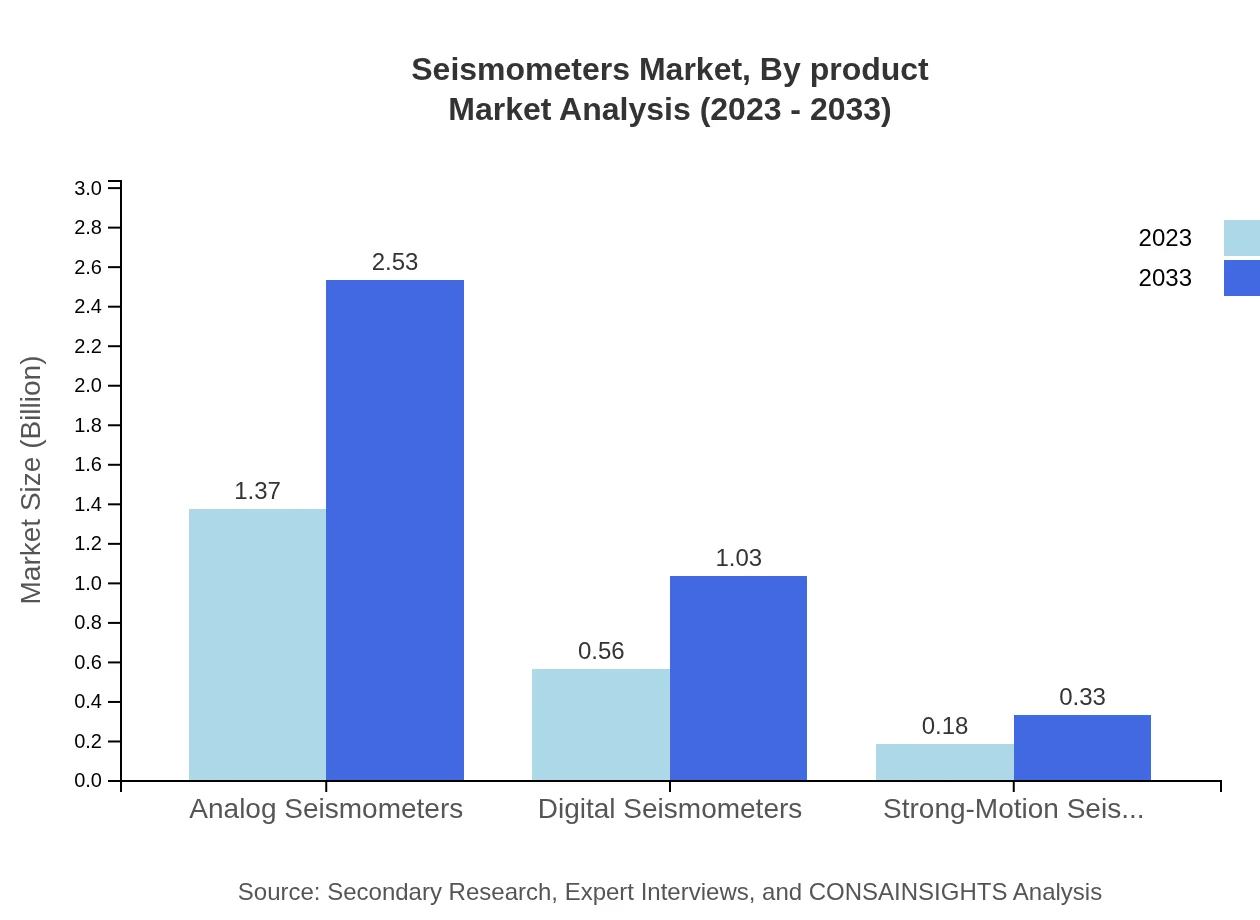
Seismometers Market Analysis By Product
The Seismometers market is dominated by Analog Seismometers, valued at $1.37 billion in 2023, forecasted to reach $2.53 billion by 2033. Digital Seismometers currently hold a market size of $0.56 billion, expected to grow to $1.03 billion. Strong-Motion Seismometers represent a niche segment, growing from $0.18 billion to $0.33 billion over the same period.
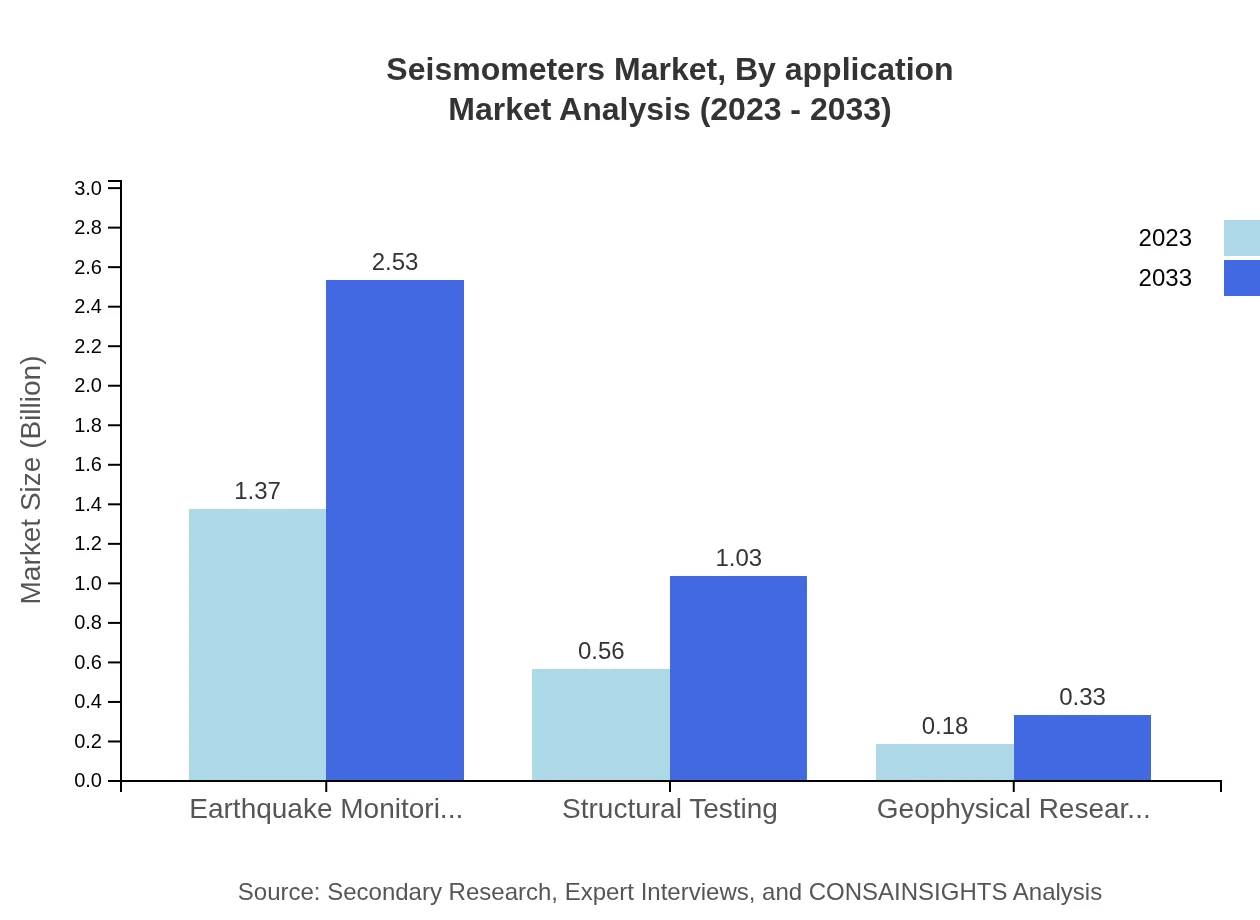
Seismometers Market Analysis By Application
Earthquake monitoring is a crucial application segment, valued at $1.37 billion in 2023, expected to see growth to $2.53 billion. Structural testing and geophysical research showcase significant growth potential, indicating a diversified need in various sectors.
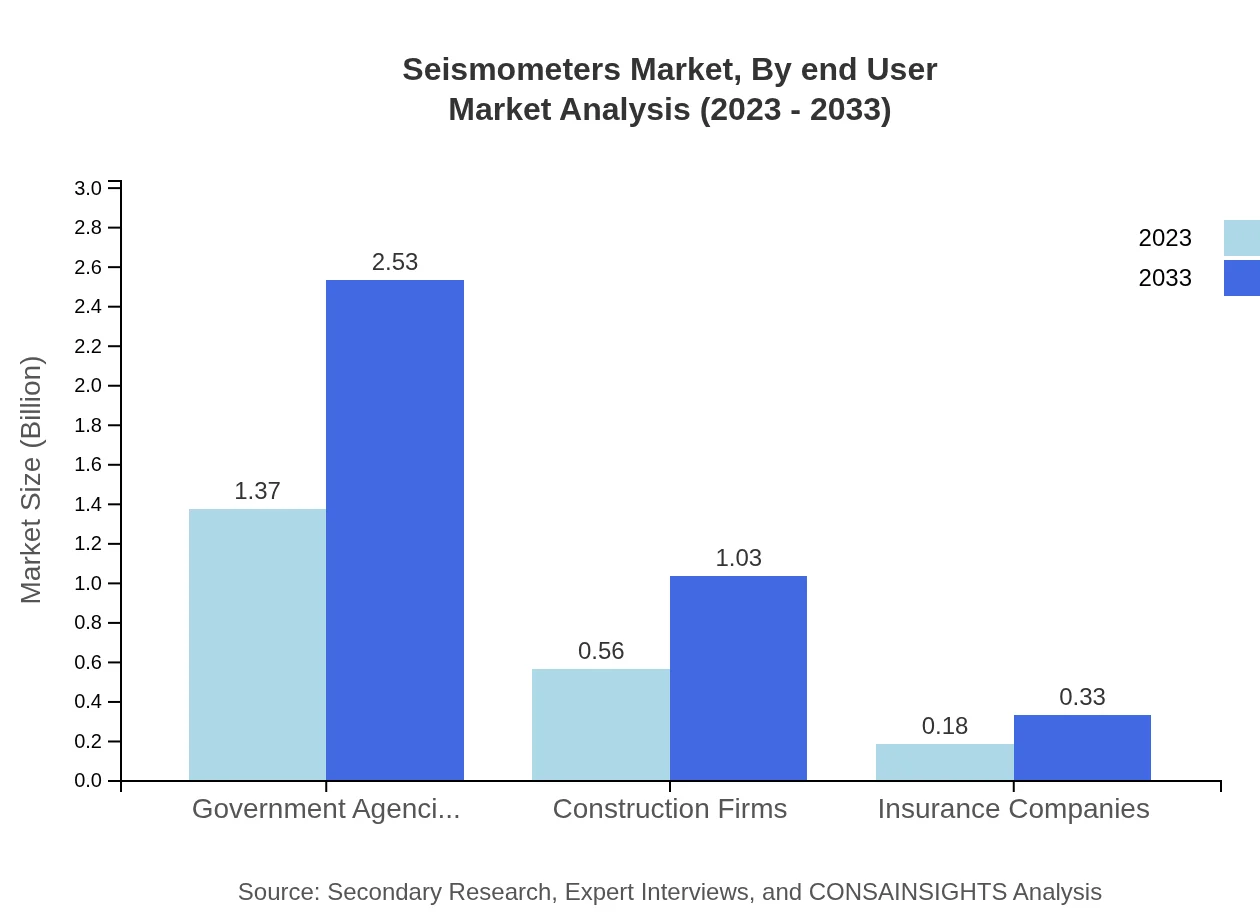
Seismometers Market Analysis By End User
Government agencies dominate the Seismometers market as end-users with a share of 65.03% in 2023. Construction firms and insurance companies are significant for market growth, reflecting the breadth of application across sectors driven by safety concerns.
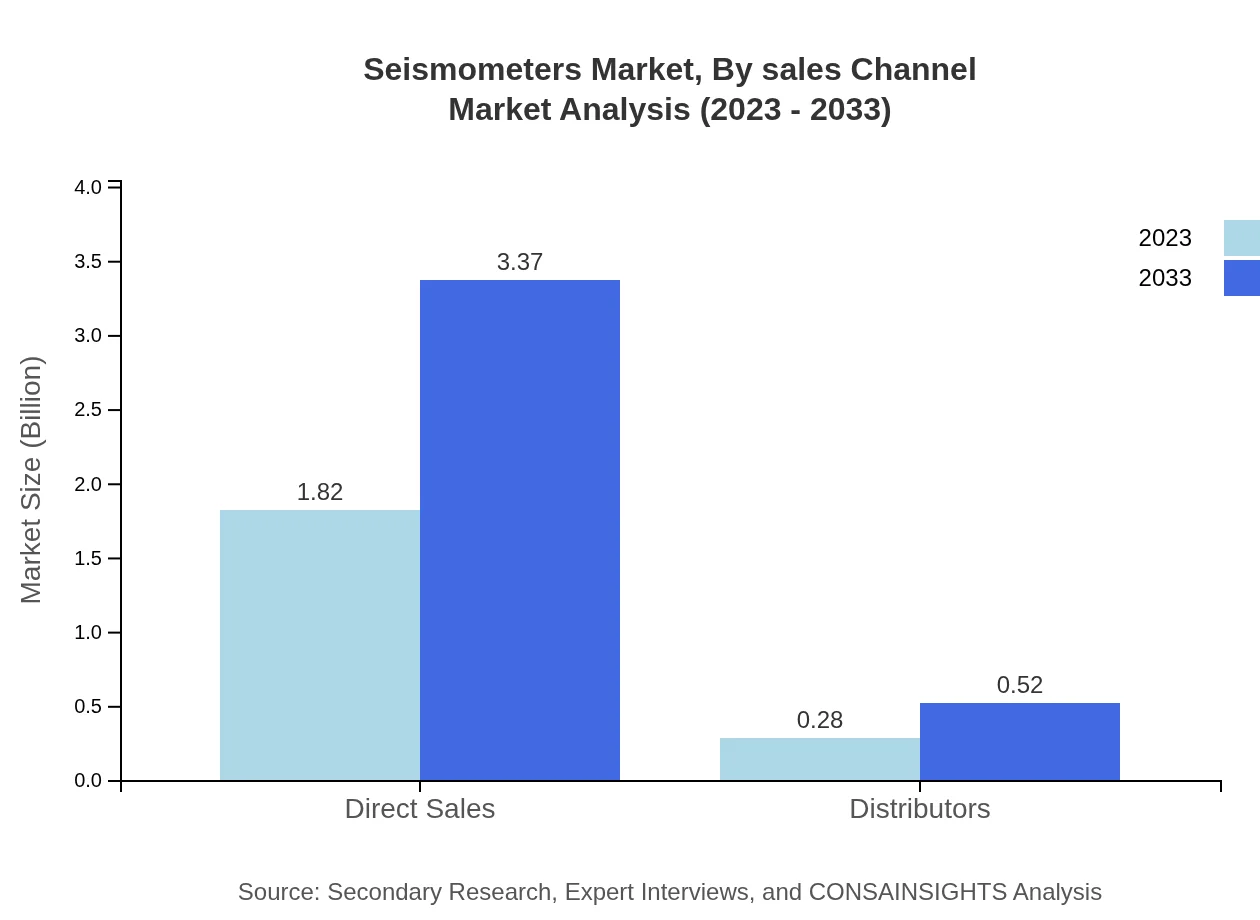
Seismometers Market Analysis By Sales Channel
Direct sales channels are expected to command a major share, accounting for 86.69% of the market size in 2023. Distributors play a smaller role, emphasizing the direct relationship between manufacturers and customers.
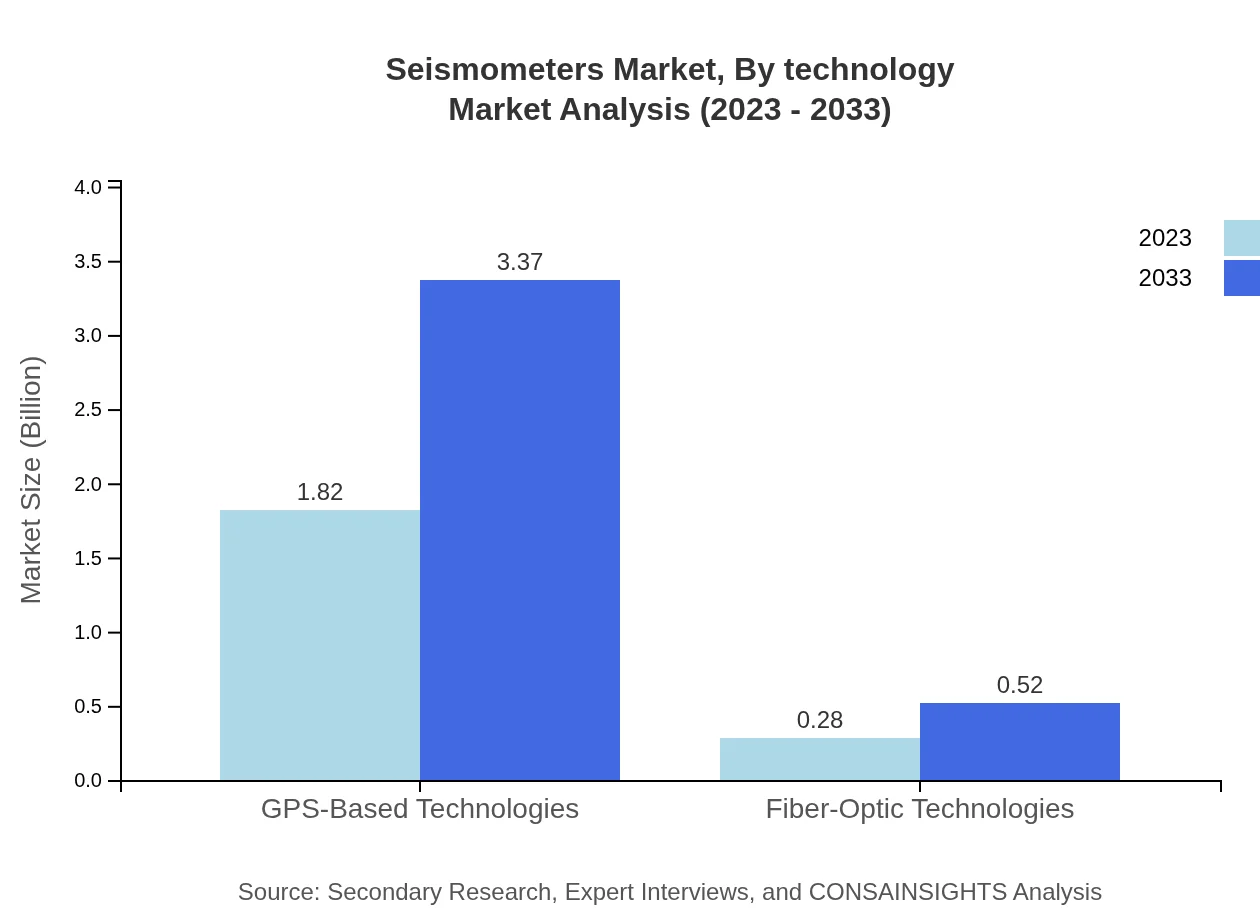
Seismometers Market Analysis By Technology
GPS-Based Technologies lead the market with an 86.69% share, valued at $1.82 billion in 2023. Fiber-Optic Technologies also plays a vital role, yet more development is required to meet upcoming demands.
Seismometers Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Seismometers Industry
Kinemetrics Inc.:
A leader in seismic instrumentation and monitoring systems, Kinemetrics offers innovative solutions for earthquake monitoring and has significantly contributed to enhancing seismic safety.RST Instruments Ltd.:
Profoundly engaged in the sensors industry, RST provides a wide range of seismographs and motion sensors, thereby supporting infrastructure and safety projects globally.ZLS, LLC:
Specializing in advanced seismic and environmental monitoring, ZLS designs and manufactures state-of-the-art seismometers with a focus on data accuracy and functionality.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of seismometers?
The seismometers market is valued at $2.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.2% through 2033, indicating significant growth opportunities and evolving industry dynamics.
What are the key market players or companies in the seismometers industry?
Key market players in the seismometers industry include major companies that specialize in geophysical instruments and monitoring technologies, focusing on providing advanced solutions for earthquake detection and structural assessment.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the seismometers industry?
Growth drivers for the seismometers industry include increasing demand for earthquake monitoring systems, advancements in technology, and rising investments in infrastructure development, which necessitate improved seismic analysis.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the seismometers market?
The fastest-growing region for seismometers is North America, with market growth from $0.81 billion in 2023 to $1.51 billion by 2033. This growth reflects the region's investment in advanced seismic monitoring technologies.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the seismometers industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific client needs within the seismometers industry, ensuring relevant insights that cater to particular research requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this seismometers market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables including detailed market analysis, growth forecasts, competitive landscape insights, and segmented data covering various applications and geographic regions.
What are the market trends of seismometers?
Key market trends for seismometers include the rise of digital technologies, increasing integration of GPS and fiber-optic technologies, and a focus on sustainable monitoring solutions in response to growing environmental concerns.