Self Organizing Network Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: self-organizing-network
Self Organizing Network Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides in-depth analysis and forecasts for the Self Organizing Network market spanning from 2023 to 2033. Key insights include market size, growth dynamics, segment analysis, and regional performance, supporting stakeholders with valuable data for strategic decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
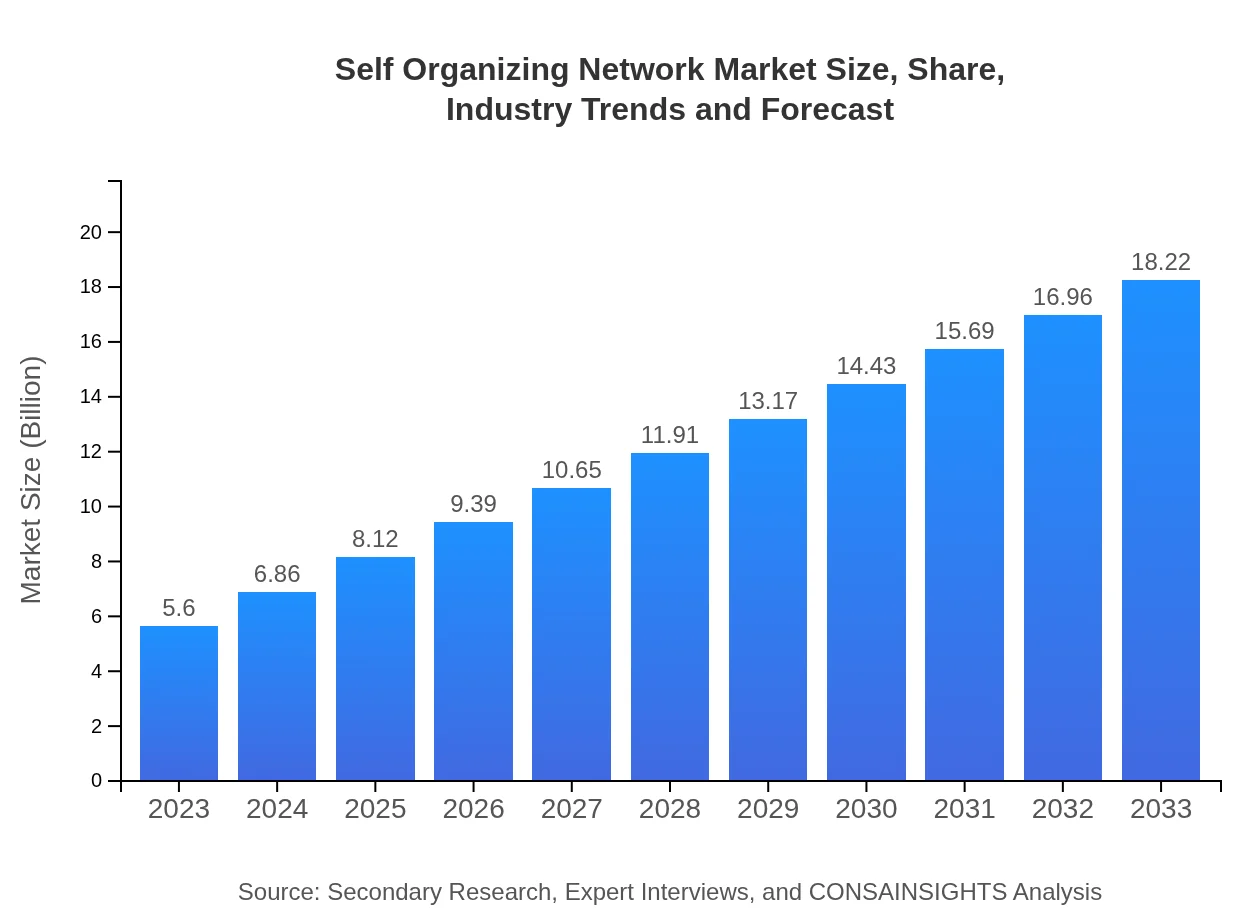
| 2023 Market Size | $5.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 12% |
| 2033 Market Size | $18.22 Billion |
| Top Companies | Ericsson , Nokia , Huawei , ZTE |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Self Organizing Network Market Overview
Customize Self Organizing Network Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Self Organizing Network market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Self Organizing Network's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Self Organizing Network
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Self Organizing Network market in 2023?
Self Organizing Network Industry Analysis
Self Organizing Network Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Self Organizing Network Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Self Organizing Network Market Report:
In Europe, the market will grow significantly from USD 1.74 million in 2023 to USD 5.67 million by 2033. EU policies promoting digital transformation and improved network performance are expected to boost SON technology adoption. Countries such as Germany and the UK are at the forefront.Asia Pacific Self Organizing Network Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Self Organizing Network market is projected to grow from USD 1.06 million in 2023 to USD 3.45 million by 2033. Increasing mobile data traffic and the push towards 5G rollouts significantly contribute to this growth. Countries like China and India are leading in adoption, driven by the need for enhanced mobile services.North America Self Organizing Network Market Report:
The North America market is estimated to escalate from USD 2.03 million in 2023 to USD 6.59 million by 2033. The presence of major telecom players and continuous investments in enhancing network capabilities are primary growth drivers. The region is anticipated to adopt SON solutions at an accelerated pace, especially with the ongoing 5G deployments.South America Self Organizing Network Market Report:
For South America, the market is expected to grow from USD 0.17 million in 2023 to USD 0.56 million by 2033. The limited yet expanding telecom infrastructure coupled with rising demand for improved network management is driving SON adoption in this region. Government initiatives to improve connectivity further support this growth.Middle East & Africa Self Organizing Network Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is projected to increase from USD 0.60 million in 2023 to USD 1.95 million by 2033, with growth driven by ongoing infrastructure improvements and the need for energy-efficient solutions. Recent investments in 5G technology are promoting the adoption of SON in the region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
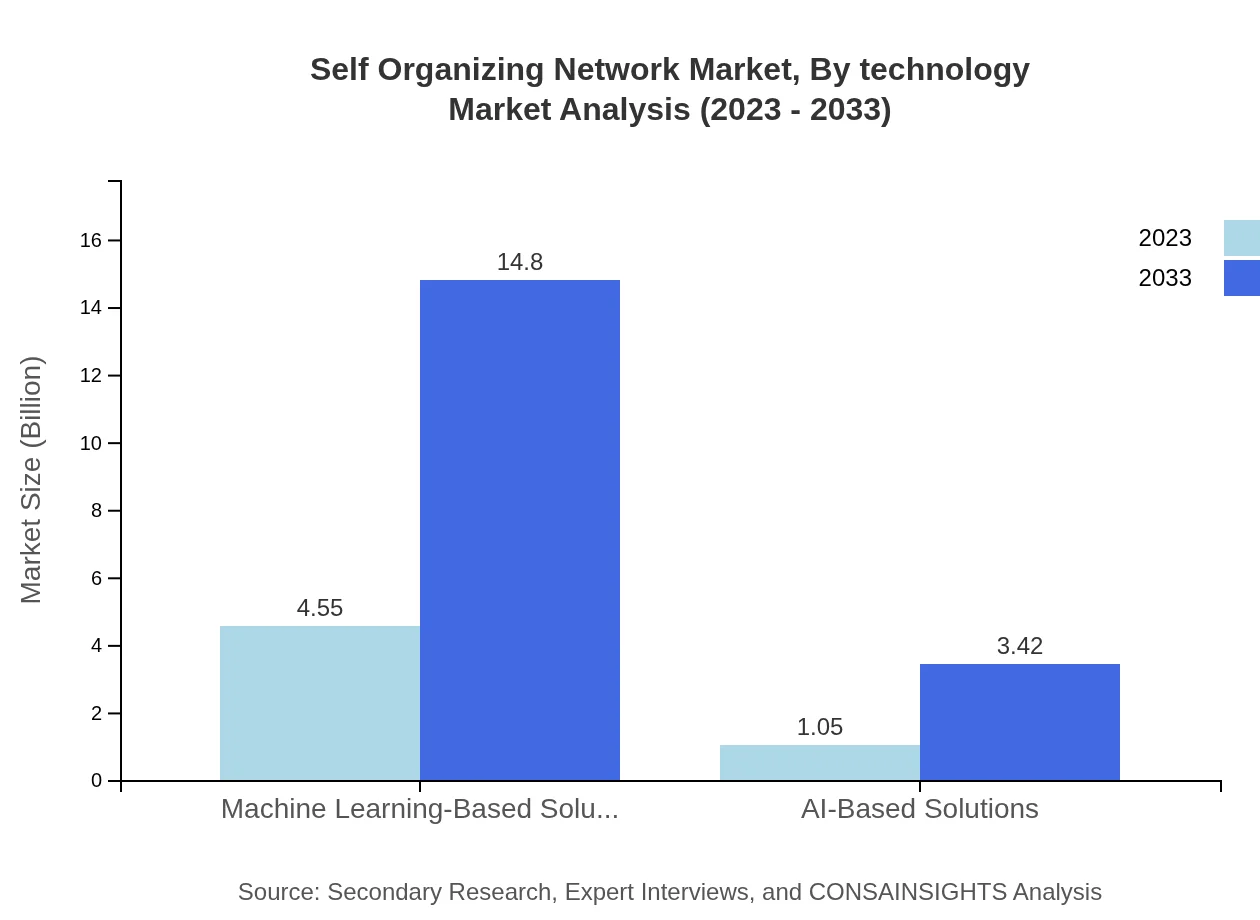
Self Organizing Network Market Analysis By Technology
The Self Organizing Network market by technology comprises segments such as Machine Learning-Based Solutions and AI-Based Solutions. In 2023, Machine Learning solutions are expected to dominate the market with USD 4.55 million, growing to USD 14.80 million by 2033, holding an 81.25% share. AI-Based solutions are also gaining traction, expected to grow from USD 1.05 million to USD 3.42 million during the same period, constituting an 18.75% market share.
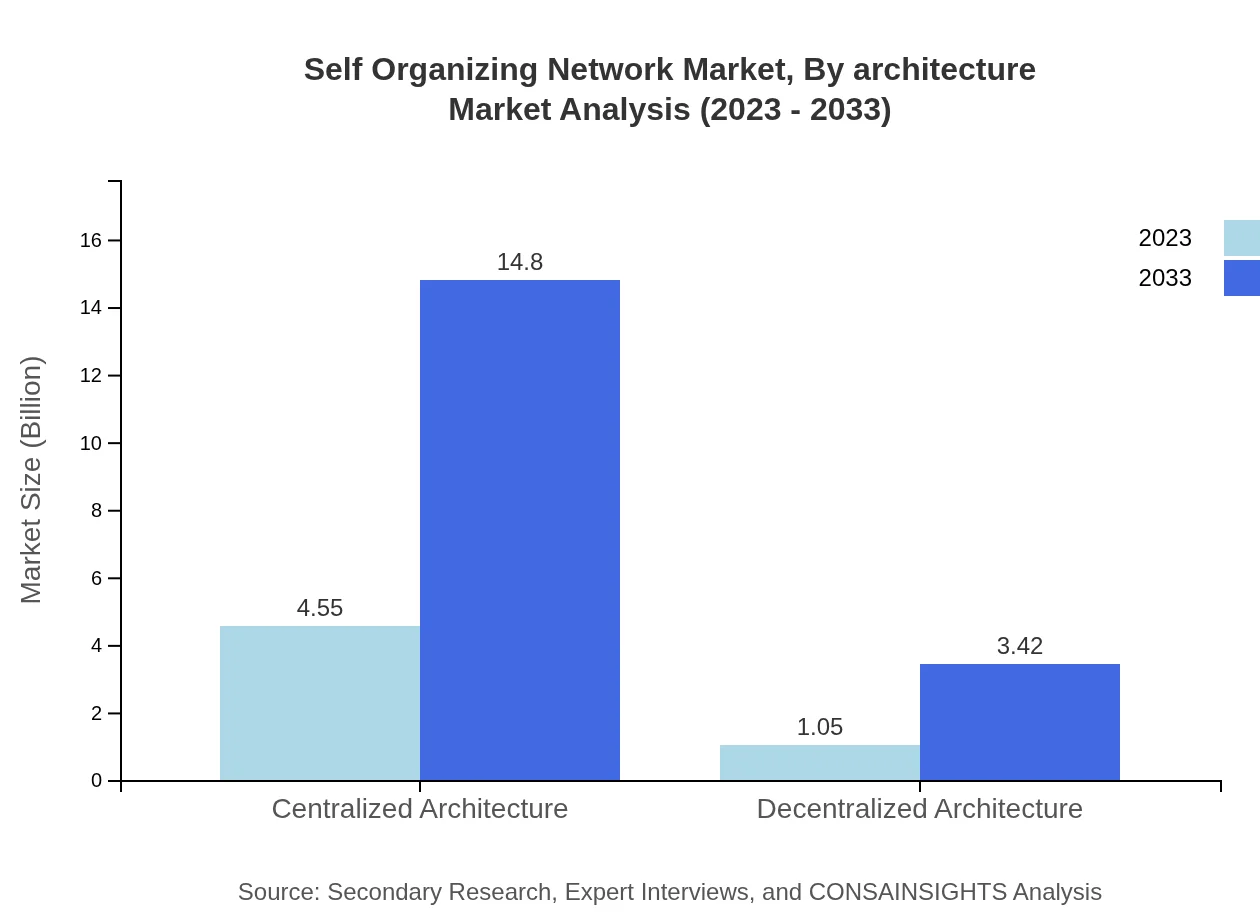
Self Organizing Network Market Analysis By Architecture
In terms of architecture, the market is divided into Centralized and Decentralized architectures. Centralized architectures predominate, reaching USD 4.55 million in 2023 and expected to grow to USD 14.80 million by 2033, maintaining an 81.25% share. Decentralized architectures will see growth from USD 1.05 million to USD 3.42 million, achieving an 18.75% market share.
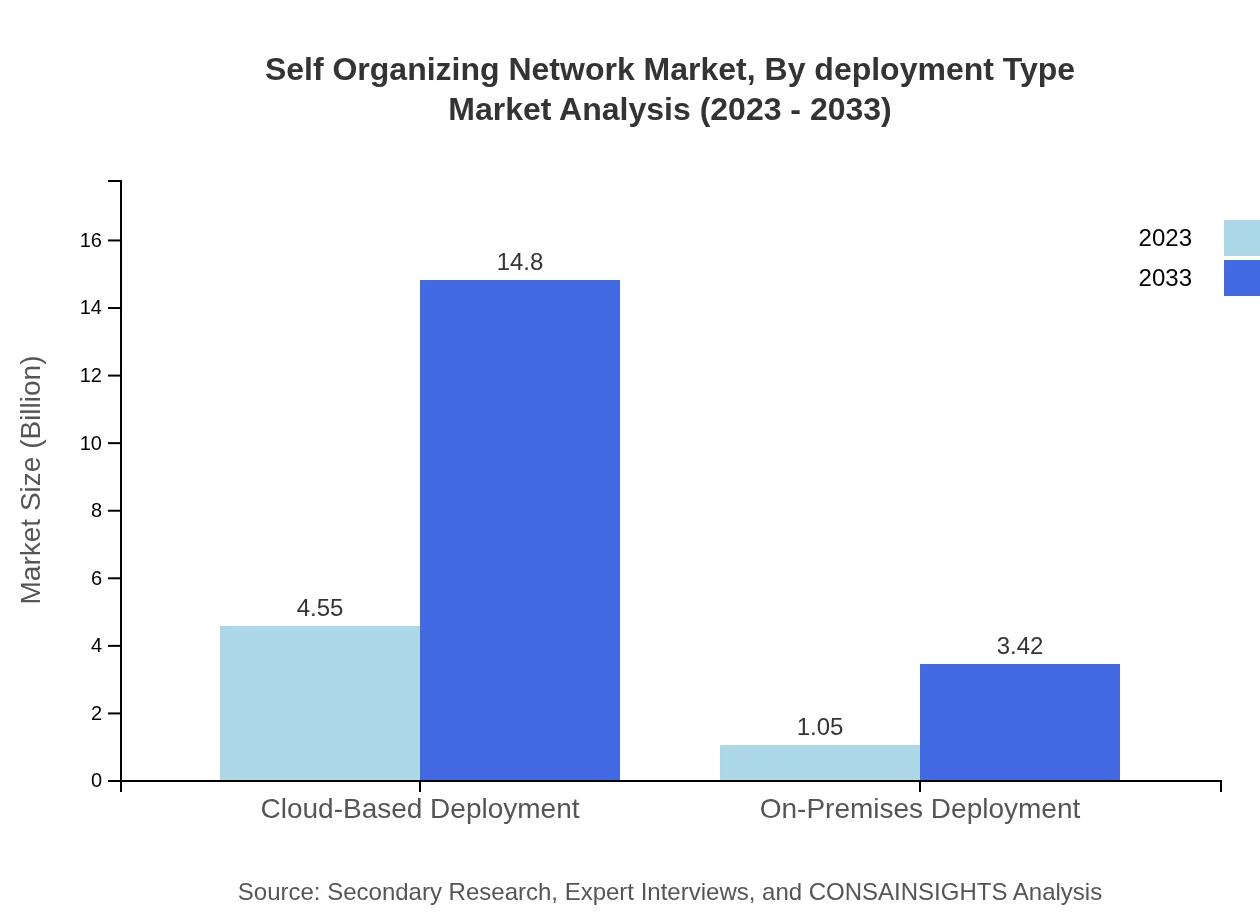
Self Organizing Network Market Analysis By Deployment Type
The Self Organizing Network market by deployment type includes Cloud-Based and On-Premises models. Cloud-Based Deployment is realizing significant growth, forecasted from USD 4.55 million in 2023 to USD 14.80 million by 2033, securing 81.25% market share. Conversely, On-Premises Deployment is also increasing but at a smaller scale, with estimates moving from USD 1.05 million to USD 3.42 million, representing an 18.75% share.
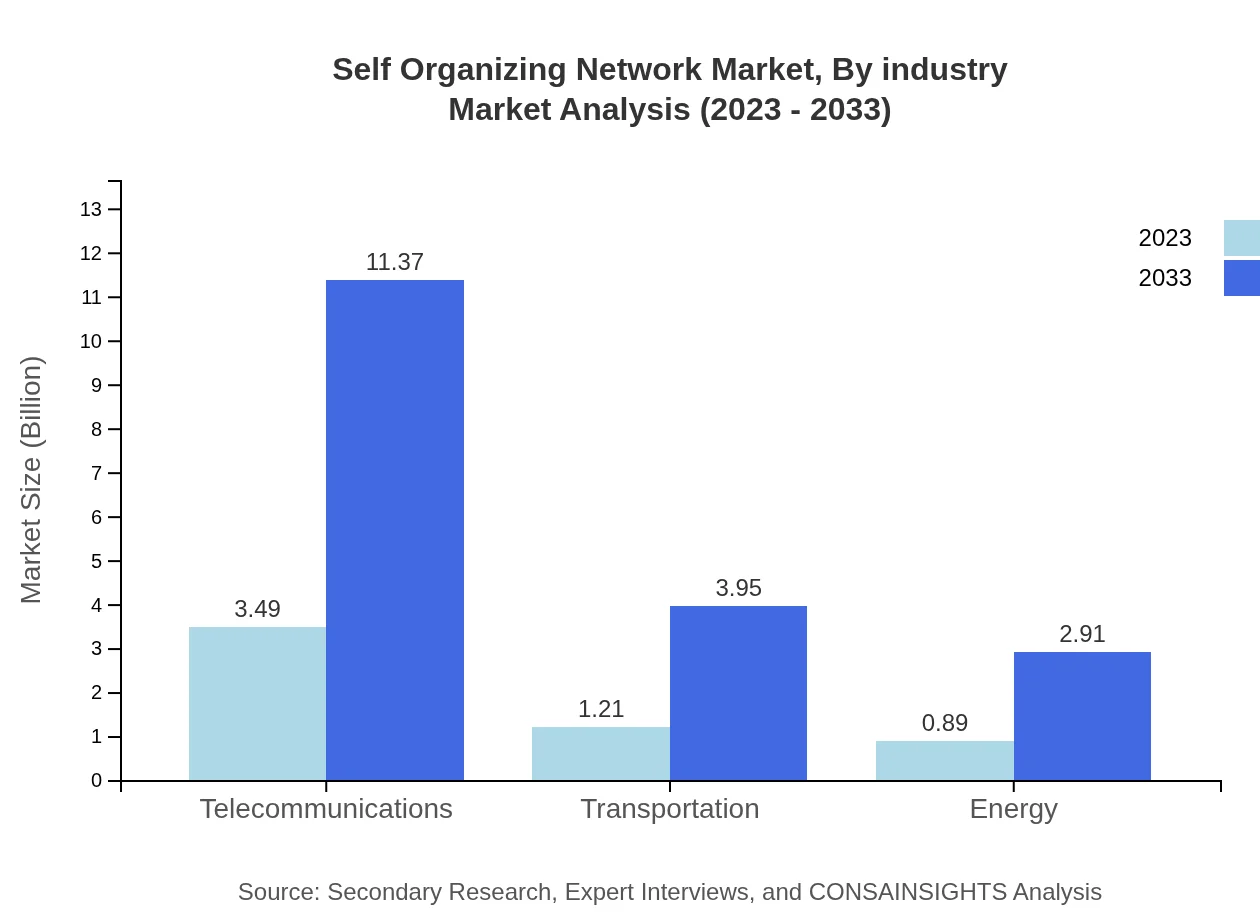
Self Organizing Network Market Analysis By Industry
The industries driving the SON market include Telecommunications, Transportation, and Energy sectors. Telecommunications dominate with a market size of USD 3.49 million in 2023, expected to reach USD 11.37 million by 2033, accounting for 62.39%. The Transportation sector will grow from USD 1.21 million to USD 3.95 million with a 21.66% market share. Meanwhile, the Energy sector's growth is anticipated from USD 0.89 million to USD 2.91 million, capturing a 15.95% market share.
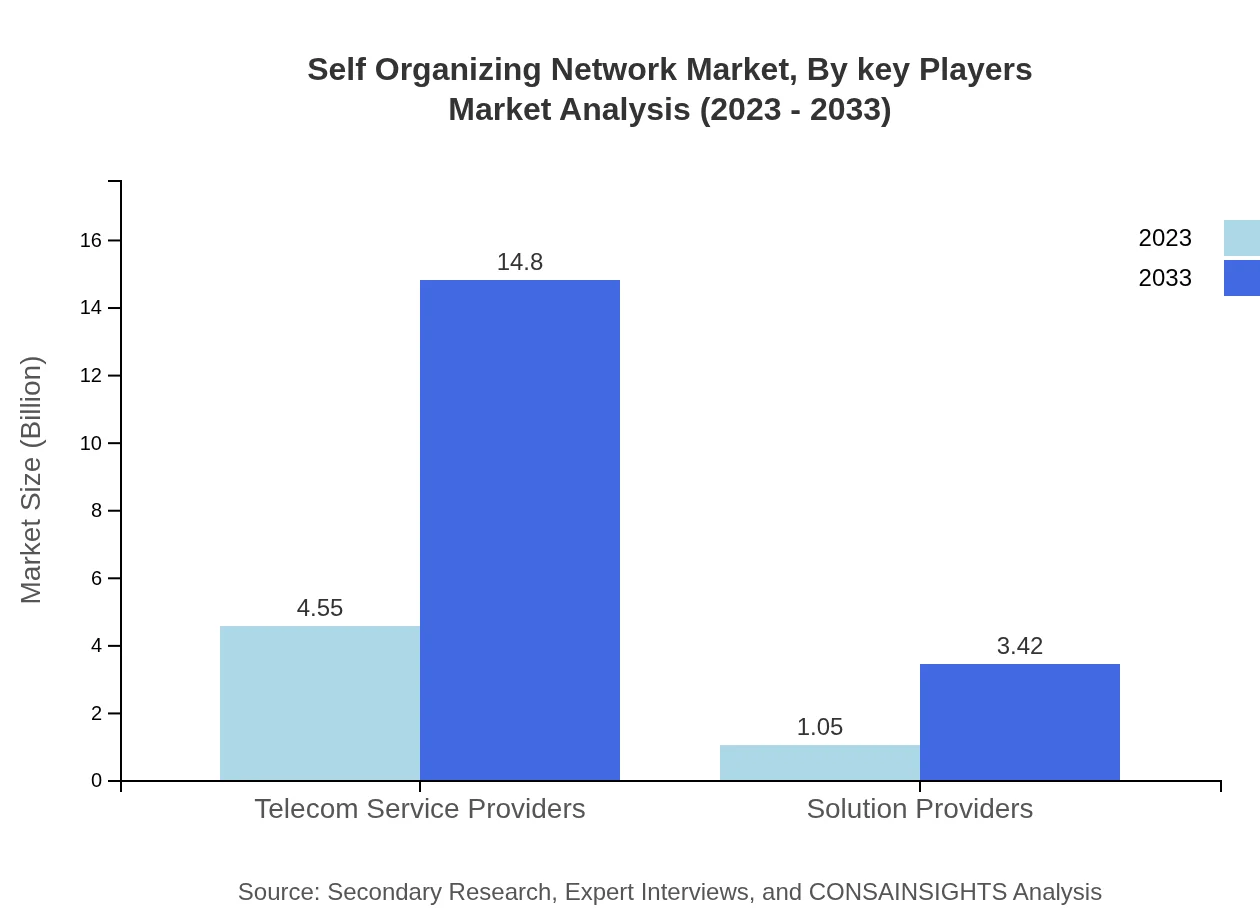
Self Organizing Network Market Analysis By Key Players
Key players in the Self Organizing Network industry include notable technology providers and telecom operators that lead in innovations and implementation advancements. Companies such as Ericsson, Nokia, and Huawei play critical roles in shaping the landscape by delivering robust SON solutions tailored for 5G and beyond.
Self Organizing Network Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Self Organizing Network Industry
Ericsson :
Ericsson leads in providing comprehensive SON solutions that optimize network performance across various spectrums.Nokia :
Nokia offers innovative SON technologies aimed at enhancing the 5G experience with adaptive network management tools.Huawei :
Huawei continually invests in SON technologies, contributing significantly to automating network management on a global scale.ZTE:
ZTE is known for its development of adaptive SON frameworks which facilitate seamless integration in existing network infrastructures.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of self Organizing Network?
The global self-organizing network market is projected to reach $5.6 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 12%. This growth signals increased investment and adoption in autonomous network solutions across industries.
What are the key market players or companies in this self Organizing Network industry?
Key players in the self-organizing network market include major telecommunications firms, solution providers focusing on AI and machine learning, and companies that enhance network efficiency through automated systems.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the self Organizing network industry?
Growth is driven by the increasing demand for automation in network management, rising network complexity, and the need for efficient resource utilization amidst expanding mobile and data traffic.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the self Organizing network?
The fastest-growing region is Europe, projected to grow from $1.74 billion in 2023 to $5.67 billion by 2033, alongside North America, expanding from $2.03 billion to $6.59 billion.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the self Organizing network industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific needs in the self-organizing network industry, addressing unique queries and requirements of clients.
What deliverables can I expect from this self Organizing network market research project?
Deliverables include market analysis reports, regional insights, competitive landscape evaluations, and detailed segment breakdowns to support strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of self Organizing network?
Current market trends include a surge in AI and machine learning integration, a focus on cloud solutions, and a shift towards decentralized architectures to bolster operational efficiency.