Serverless Computing Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: serverless-computing
Serverless Computing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Serverless Computing market, offering insights into market size, trends, segmentation, and forecasts for the years 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
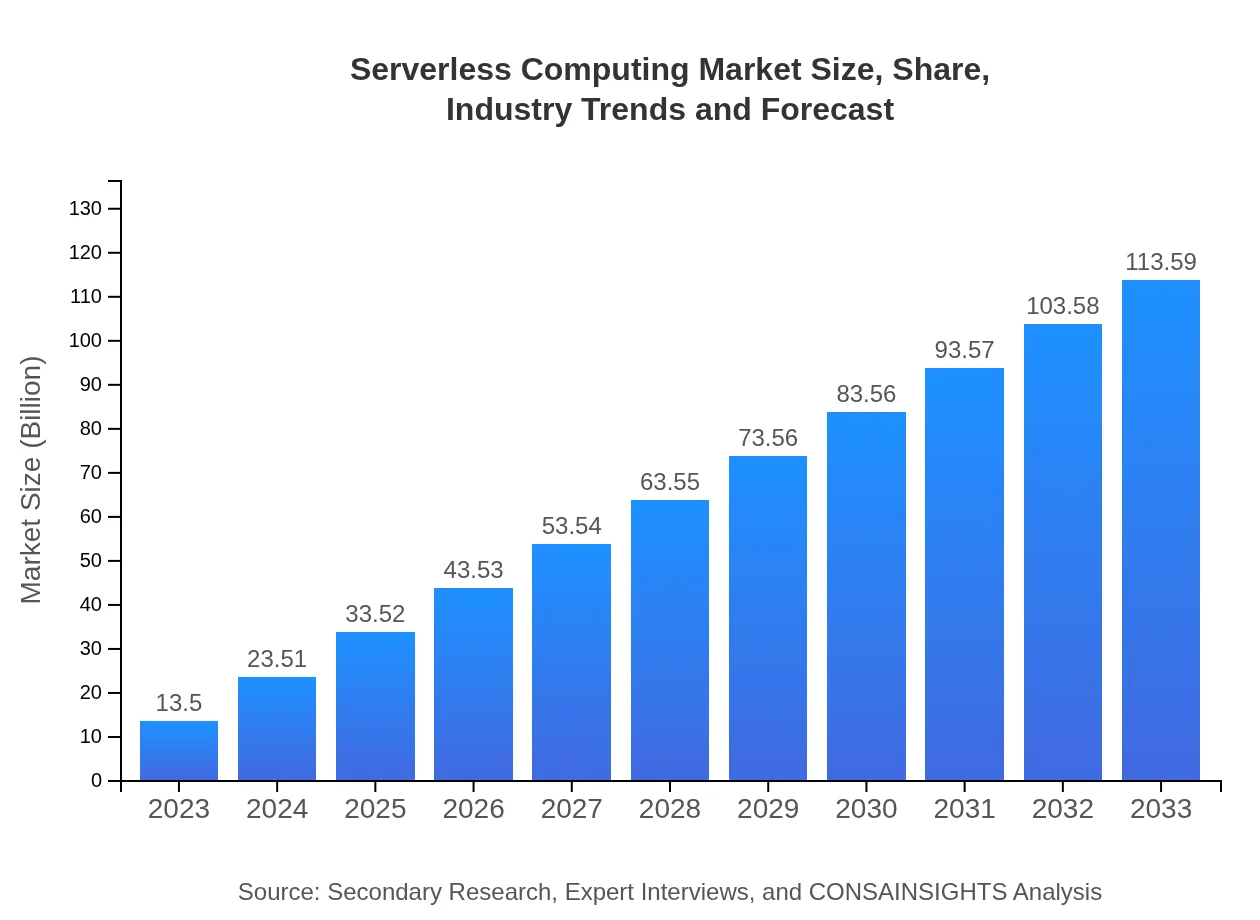
| 2023 Market Size | $13.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 22.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $113.59 Billion |
| Top Companies | Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud Functions |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Serverless Computing Market Overview
Customize Serverless Computing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Serverless Computing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Serverless Computing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Serverless Computing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Serverless Computing market in 2023?
Serverless Computing Industry Analysis
Serverless Computing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Serverless Computing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Serverless Computing Market Report:
In Europe, the market size is $3.50 billion in 2023, growing to $29.44 billion by 2033. The region is witnessing rapid digitalization, and companies in sectors like finance and healthcare are increasingly adopting serverless solutions.Asia Pacific Serverless Computing Market Report:
In 2023, the Serverless Computing market in Asia Pacific is valued at $2.75 billion and is expected to reach $23.15 billion by 2033. The region's growth is propelled by the increasing adoption of cloud technologies and government initiatives promoting the digital economy.North America Serverless Computing Market Report:
North America leads the Serverless Computing market, valued at $4.73 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $39.81 billion by 2033. The significant presence of major cloud service providers and increased investments in cloud infrastructure are key contributing factors.South America Serverless Computing Market Report:
The South American market for Serverless Computing is valued at $0.66 billion in 2023 and forecasted to grow to $5.58 billion by 2033. Rising digital transformation, especially in Brazil and Argentina, drives growth in this region.Middle East & Africa Serverless Computing Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa Serverless Computing market, valued at $1.85 billion in 2023, is expected to reach $15.61 billion by 2033. The growth is spurred by accelerated tech adoption and investment in cloud infrastructure across the region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Serverless Computing Market Analysis By Deployment Model
The deployment model segment of the Serverless Computing market is dominated by public cloud solutions, which are forecasted to significantly outpace private and hybrid models. This trend reflects organizations' preference for flexibility and scalability, with public cloud accounting for $8.35 billion in 2023 and growing to $70.29 billion by 2033.
Serverless Computing Market Analysis By Application
Web applications and mobile applications are key drivers within the application segment. For instance, web applications generated $8.35 billion in revenue in 2023, expected to reach $70.29 billion by 2033, showcasing the paradigm shift towards scalable and efficient application frameworks.
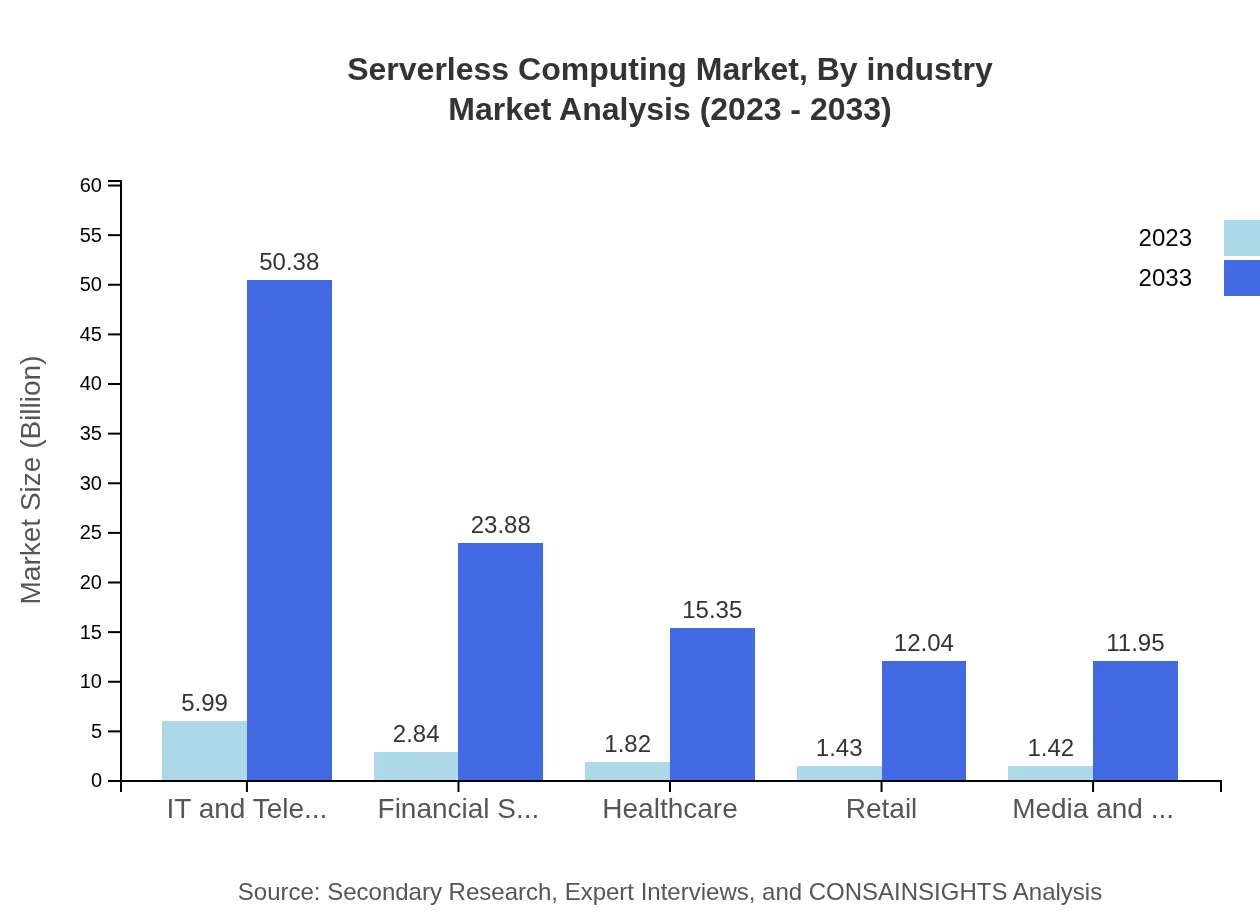
Serverless Computing Market Analysis By Industry
The IT and telecom industry holds the largest share of the Serverless Computing market, valued at $5.99 billion in 2023 and projected to reach $50.38 billion by 2033. Other significant industries include Financial Services and Healthcare, capitalizing on the flexibility serverless architectures provide.
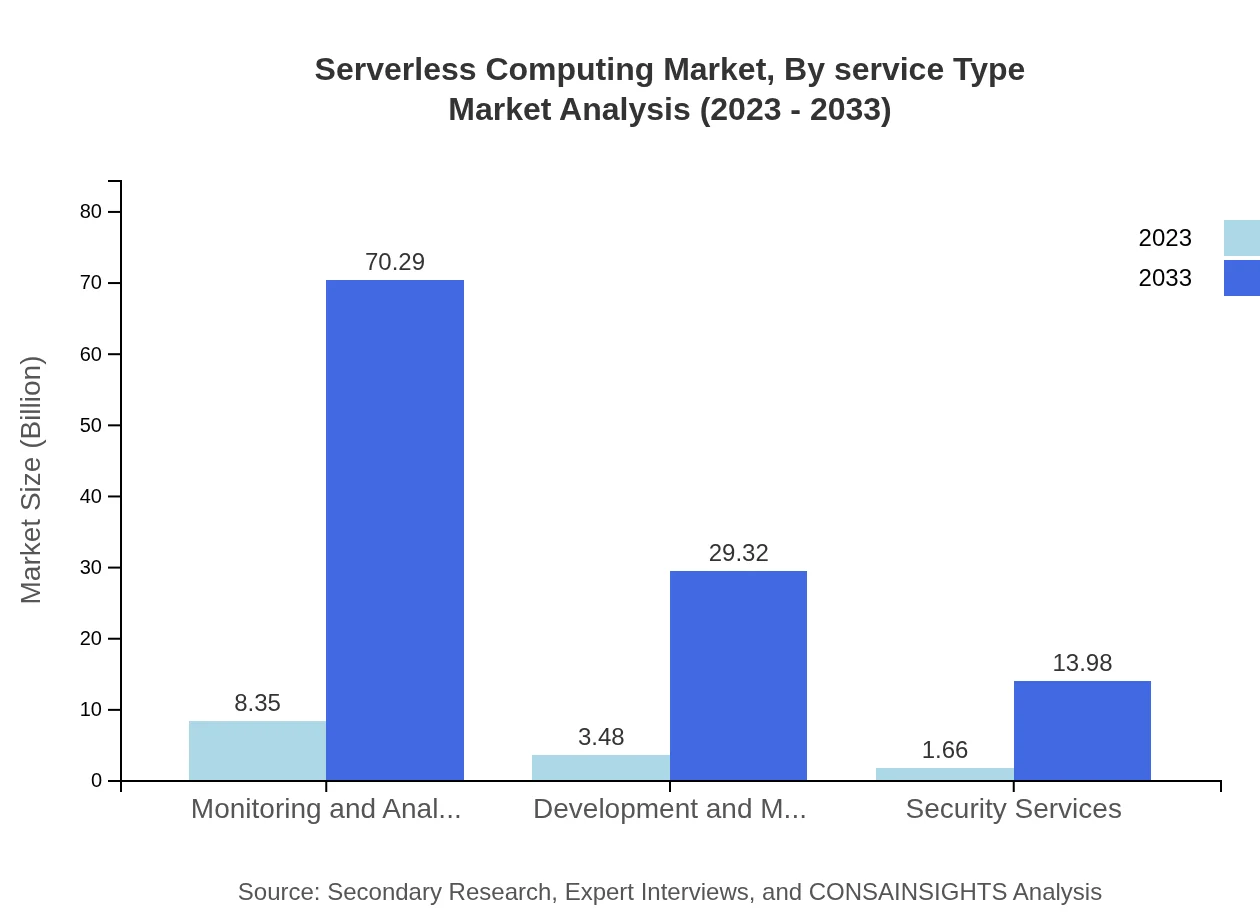
Serverless Computing Market Analysis By Service Type
Function as a Service (FaaS) leads the service type segment, contributing $11.99 billion in 2023 with an anticipated growth to $100.88 billion by 2033. This dominance argues for a prevailing demand for serverless solutions that allow developers to execute code in response to events without provisioning servers.
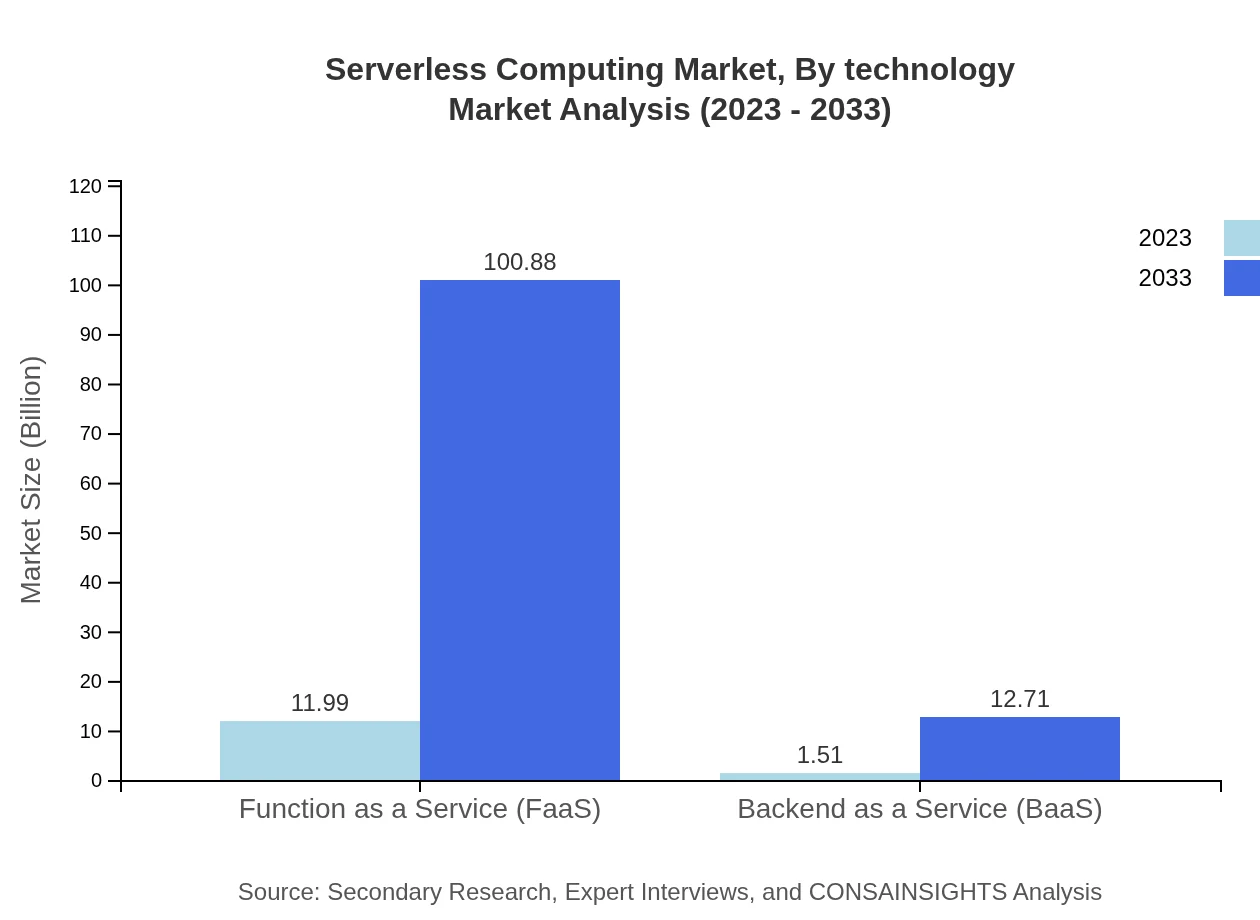
Serverless Computing Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements including containerization and microservices are pivotal in the Serverless Computing landscape. This market fueled by innovation was valued at $4.73 billion in 2023, with considerable forecasts highlighting emerging technologies enhancing deployment efficiency and integration.
Serverless Computing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Serverless Computing Industry
Amazon Web Services (AWS):
AWS is a pioneer in providing serverless computing frameworks, offering AWS Lambda which enables developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers.Microsoft Azure:
Azure Functions allows a serverless computing experience with Microsoft Azure, focusing on event-driven architectures, and is increasingly favored by enterprises seeking hybrid solutions.Google Cloud:
Google Cloud offers Firebase Cloud Functions and Cloud Run, both contributing significantly to the serverless ecosystem, driving adoption through seamless integration with existing application frameworks.IBM Cloud Functions:
IBM's serverless offering harnesses the power of Apache OpenWhisk to enhance application responsiveness, positioning itself effectively in the enterprise market.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of serverless Computing?
The serverless computing market, valued at $13.5 billion in 2023, is projected to grow significantly, achieving a CAGR of 22.3%. This expansion highlights increasing adoption across various sectors driven by demands for efficiency and scalability.
What are the key market players or companies in the serverless Computing industry?
Key players in the serverless computing market include Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, IBM Cloud, and Oracle. These companies are leading innovation through technological advancements and robust service offerings in serverless architecture.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the serverless computing industry?
Primary factors driving the growth in serverless computing include the rising demand for cost-effective computing solutions, increased scalability and agility, and the growing adoption of microservices architecture. Businesses are also focusing on optimizing operational efficiency.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the serverless computing market?
North America is identified as the fastest-growing region, with a market size predicted to reach $39.81 billion by 2033. Key growth factors include technological advancements, high cloud adoption rates, and significant investment in IT infrastructure.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the serverless computing industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored specifically for the serverless computing industry. Clients can receive detailed insights that cater to their strategic needs and market objectives, enhancing their decision-making processes.
What deliverables can I expect from this serverless computing market research project?
Expected deliverables from the serverless computing market research project include comprehensive market analysis reports, trend forecasts, competitive landscape evaluations, and actionable insights. These resources will assist in informed strategic planning and investment.
What are the market trends of serverless computing?
Current trends in serverless computing include the increased adoption of Function as a Service (FaaS), heightened focus on event-driven applications, and greater investment in hybrid cloud models. Companies are increasingly prioritizing security and compliance measures as well.