Shrimp Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: shrimp
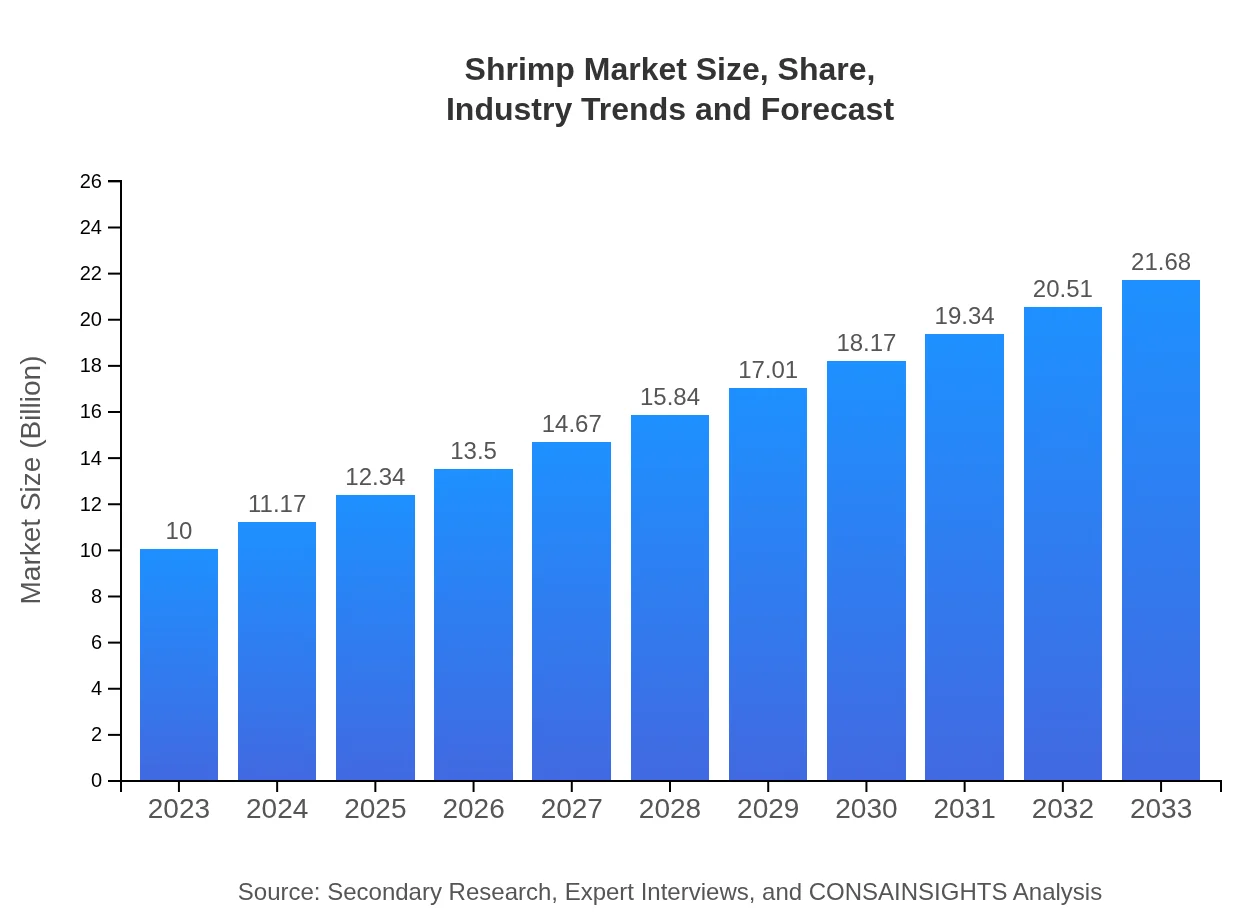
Shrimp Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an extensive analysis of the shrimp market, covering market size, trends, segmentation, and future forecasts from 2023 to 2033. Insights into regional dynamics and industry leaders are presented to inform strategic decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $10.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $21.68 Billion |
| Top Companies | Maruha Nichiro Corporation, Thai Union Group PCL, Seasource, Dongwon Industries |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Shrimp Market Overview
Customize Shrimp Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Shrimp market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Shrimp's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Shrimp
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Shrimp market in 2023?
Shrimp Industry Analysis
Shrimp Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Shrimp Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Shrimp Market Report:
Europe presents a mature market for shrimp, driven by a diverse consumer base and increasing imports from exporting countries. The market size is forecasted to rise from $2.95 billion in 2023 to $6.39 billion by 2033. Health trends favoring seafood consumption and innovative culinary applications are likely to enhance market growth in this region.Asia Pacific Shrimp Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region dominates the global shrimp market, holding nearly 50% of the market share. Major shrimp-producing countries like China, India, and Thailand contribute significantly to the region's output. The high demand for shrimp within the region, coupled with advances in aquaculture techniques, are driving robust market growth. By 2033, the market size in Asia Pacific is projected to reach $3.70 billion, up from $1.71 billion in 2023.North America Shrimp Market Report:
In North America, the shrimp market is characterized by high consumption rates, particularly in the United States. The region's market size is anticipated to surge from $3.86 billion in 2023 to $8.37 billion by 2033, spurred by a growing trend toward seafood consumption and enhanced distribution networks, making shrimp easily accessible to consumers.South America Shrimp Market Report:
South America is an emerging player in the shrimp market, with significant production in countries such as Ecuador and Brazil. The region is focusing on expanding its shrimp farming capabilities and exploring export opportunities. By 2033, the market size in South America is expected to grow to $0.73 billion from $0.34 billion in 2023, reflecting increasing demand and improved farming practices.Middle East & Africa Shrimp Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa represent a smaller, yet promising market for shrimp, supported by growing middle-class populations and increasing exposure to international cuisines. The market is expected to grow from $1.15 billion in 2023 to $2.49 billion by 2033 as demand rises and local production improves with technology and investment.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
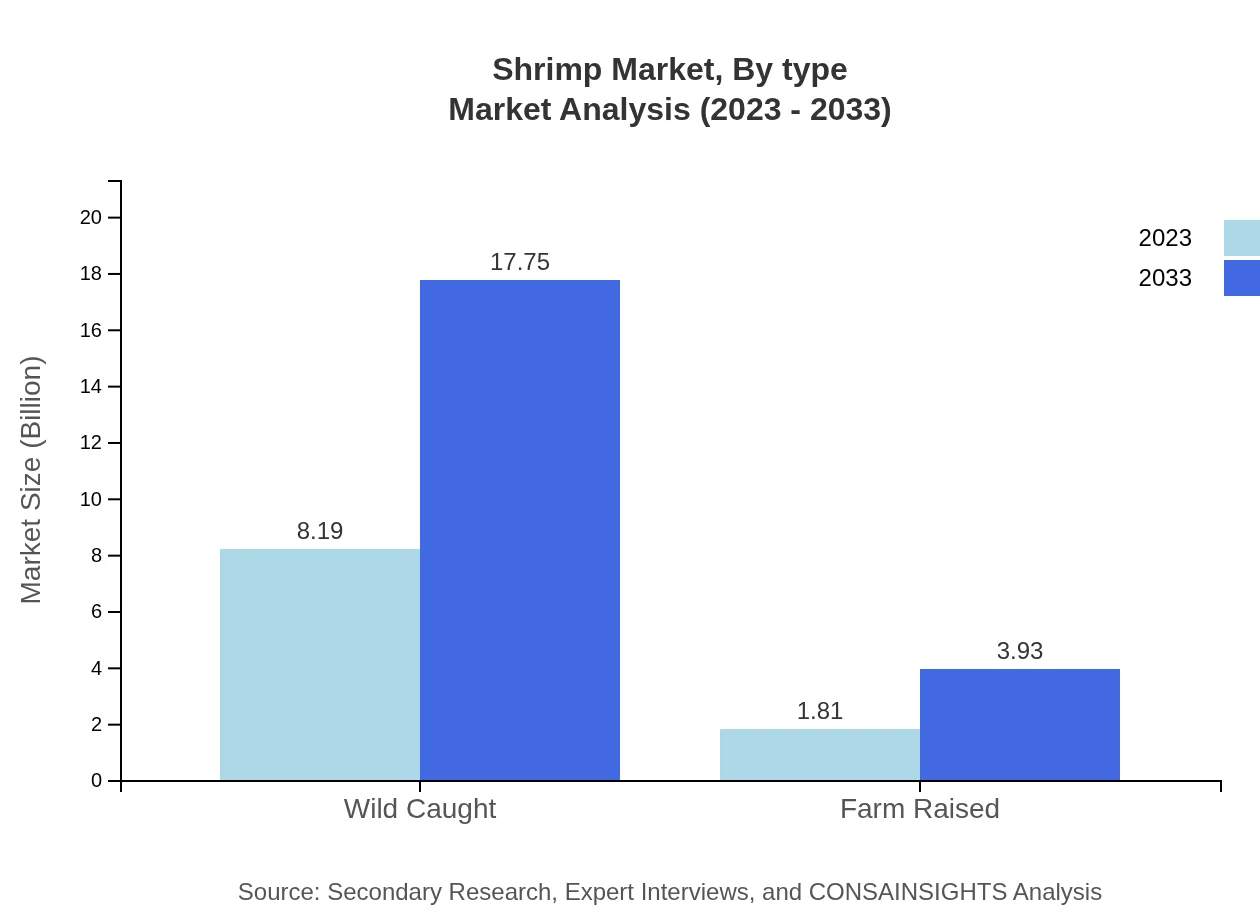
Shrimp Market Analysis By Type
In the shrimp market, wild caught shrimp outperforms farm-raised types, with a market size growing from $8.19 billion in 2023 to $17.75 billion by 2033, maintaining an 81.86% market share. However, farm-raised shrimp is beginning to close this gap, increasing from $1.81 billion in 2023 to $3.93 billion in 2033, with an 18.14% share emphasizing sustainable and controlled production.
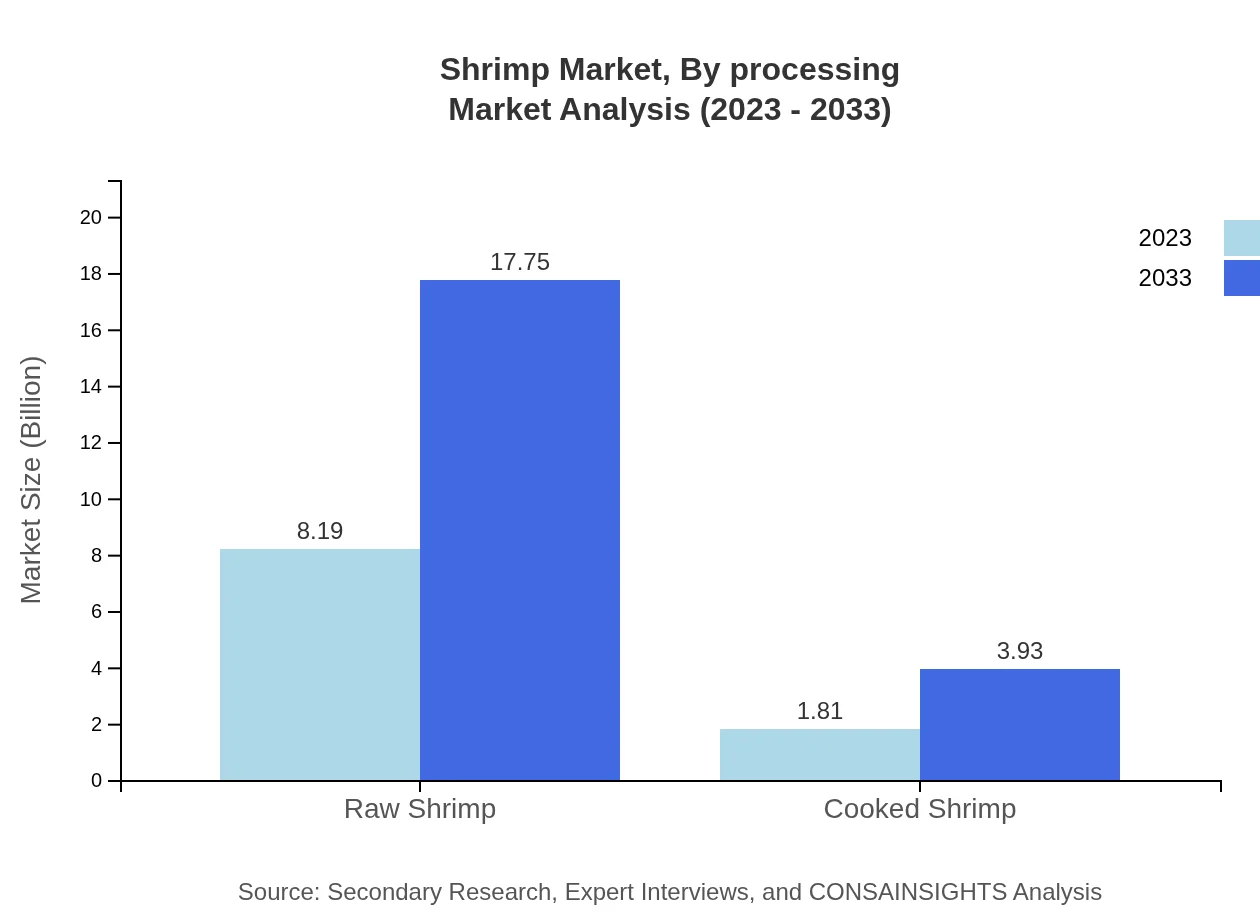
Shrimp Market Analysis By Processing
Raw shrimp continues to dominate the market, with a value soaring from $8.19 billion in 2023 to $17.75 billion by 2033, sharing 81.86% of the processing market. Cooked shrimp, while less dominant, is gaining traction, expanding from $1.81 billion to $3.93 billion over the same period, constituting 18.14% of the processing market.
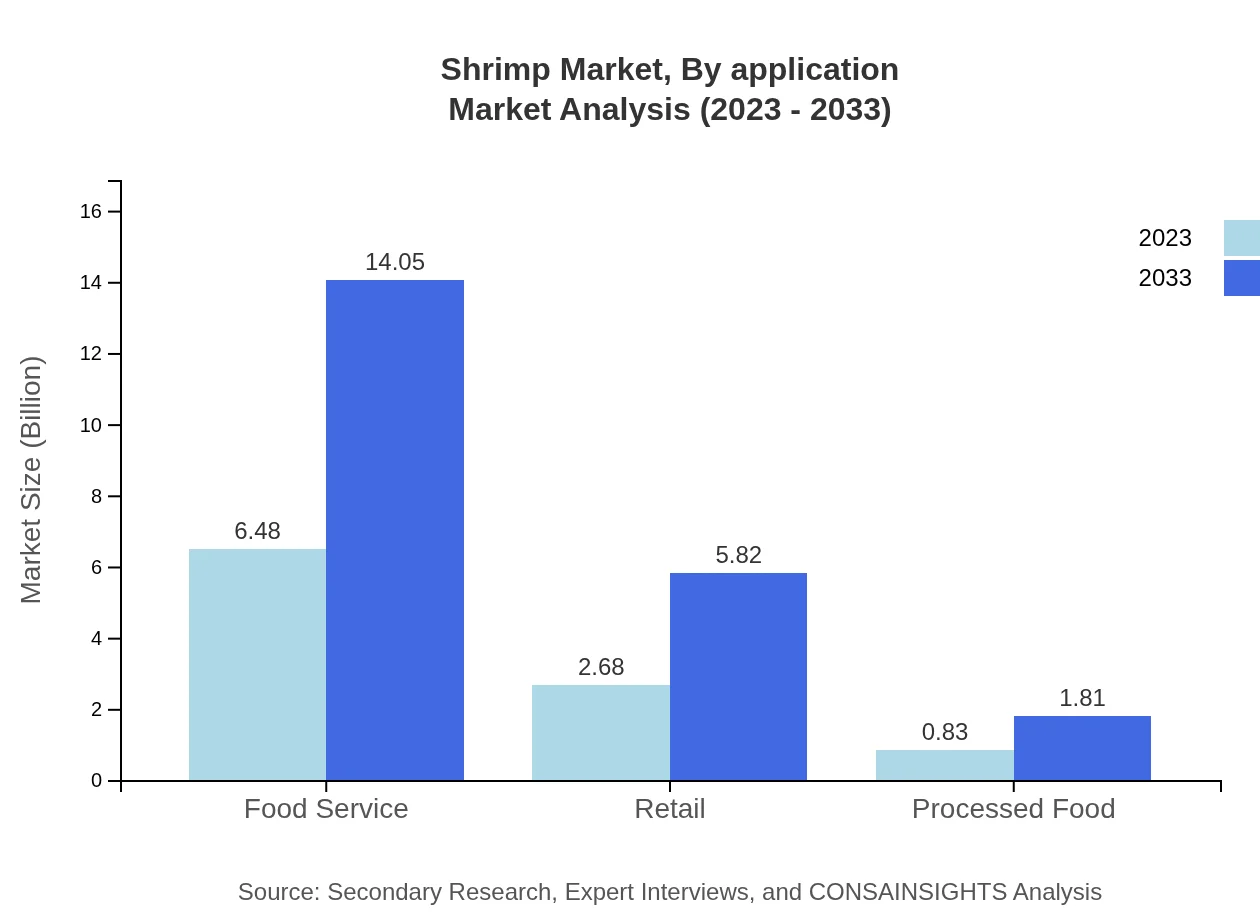
Shrimp Market Analysis By Application
The food service application leads the shrimp market, growing from $6.48 billion in 2023 to $14.05 billion by 2033, capturing 64.82% of the share. The retail segment is also significant, increasing from $2.68 billion to $5.82 billion, while processed food remains smaller, with a projection from $0.83 billion to $1.81 billion, showing steady growth in consumer demand for ready-to-eat shrimp products.
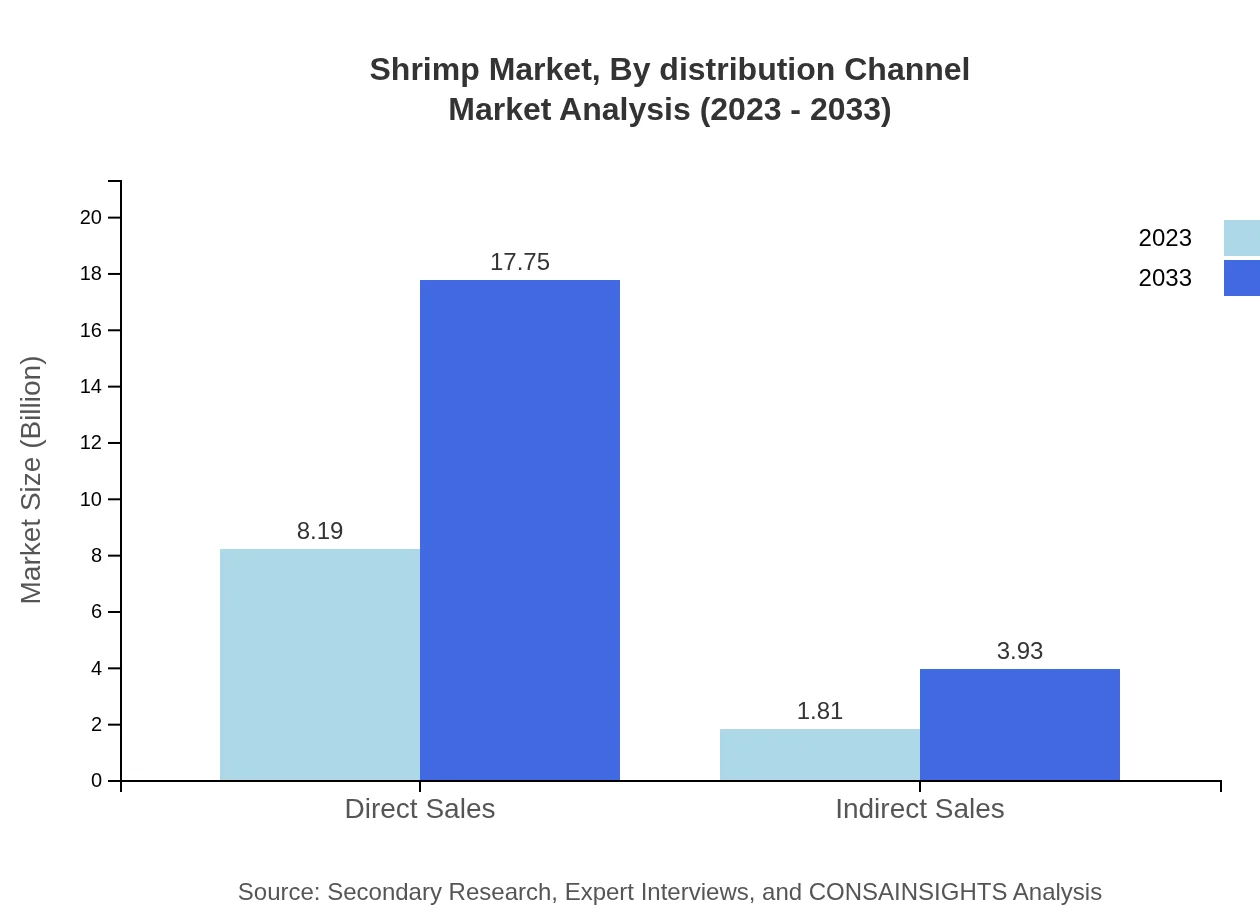
Shrimp Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Direct sales are the preferred channel for shrimp distribution, projected to rise from $8.19 billion in 2023 to $17.75 billion in 2033 with an 81.86% market share. Conversely, indirect sales are growing steadily from $1.81 billion to $3.93 billion, representing 18.14% of the market. This trend reflects the growing importance of e-commerce and retail partnerships.
Shrimp Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Shrimp Industry
Maruha Nichiro Corporation:
A leading global player in seafood, Maruha Nichiro specializes in frozen shrimp and contributes extensively to sustainable aquaculture practices.Thai Union Group PCL:
Known for its well-established shrimp brands, Thai Union is a frontrunner in seafood innovation and responsible sourcing, catering to expanding markets worldwide.Seasource:
A prominent shrimp producer focusing on sustainable farm-raised shrimp, Seasource also engages in global exports and market development.Dongwon Industries:
Dongwon is a key seafood company in South Korea, heavily involved in shrimp production and processing, committed to quality and sustainability.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of shrimp?
The global shrimp market size is currently valued at approximately $10 billion, with an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8%. This significant growth reflects increasing consumer demand and expansion in both wild caught and farm raised shrimp segments.
What are the key market players or companies in this shrimp industry?
Key players in the shrimp industry include major seafood producers and processors, as well as distributors. Notable companies contribute significantly to market size and innovation, ensuring product availability and meeting consumer demands for quality and sustainability.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the shrimp industry?
The shrimp industry's growth is driven by rising seafood consumption, health consciousness, and the popularity of shrimp-based dishes globally. Additionally, advancements in aquaculture and sustainable farming practices are enhancing production efficiency and market availability.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the shrimp market?
Among various regions, North America is the fastest-growing market for shrimp, projected to rise from $3.86 billion in 2023 to $8.37 billion by 2033. Other regions like Europe and Asia Pacific are also demonstrating notable growth in shrimp consumption.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the shrimp industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the shrimp industry. This includes detailed market analysis, trends, and insights that cater to businesses requiring targeted information for strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this shrimp market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables from this project, including detailed market reports, segment analysis, regional insights, and trend forecasting. Additionally, customized data can provide specific insights tailored to your needs, aiding in informed decision-making.
What are the market trends of shrimp?
Market trends for shrimp indicate a shift towards sustainable sourcing and increasing demand for convenience products. The rise in processed shrimp sales is notable, alongside innovations in packaging and product development that cater to health-conscious consumers.