Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: sicklecell-anemia-therapeutics
Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Sicklecell Anemia therapeutics market, focusing on current trends, segment performance, regional insights, and growth forecasts from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
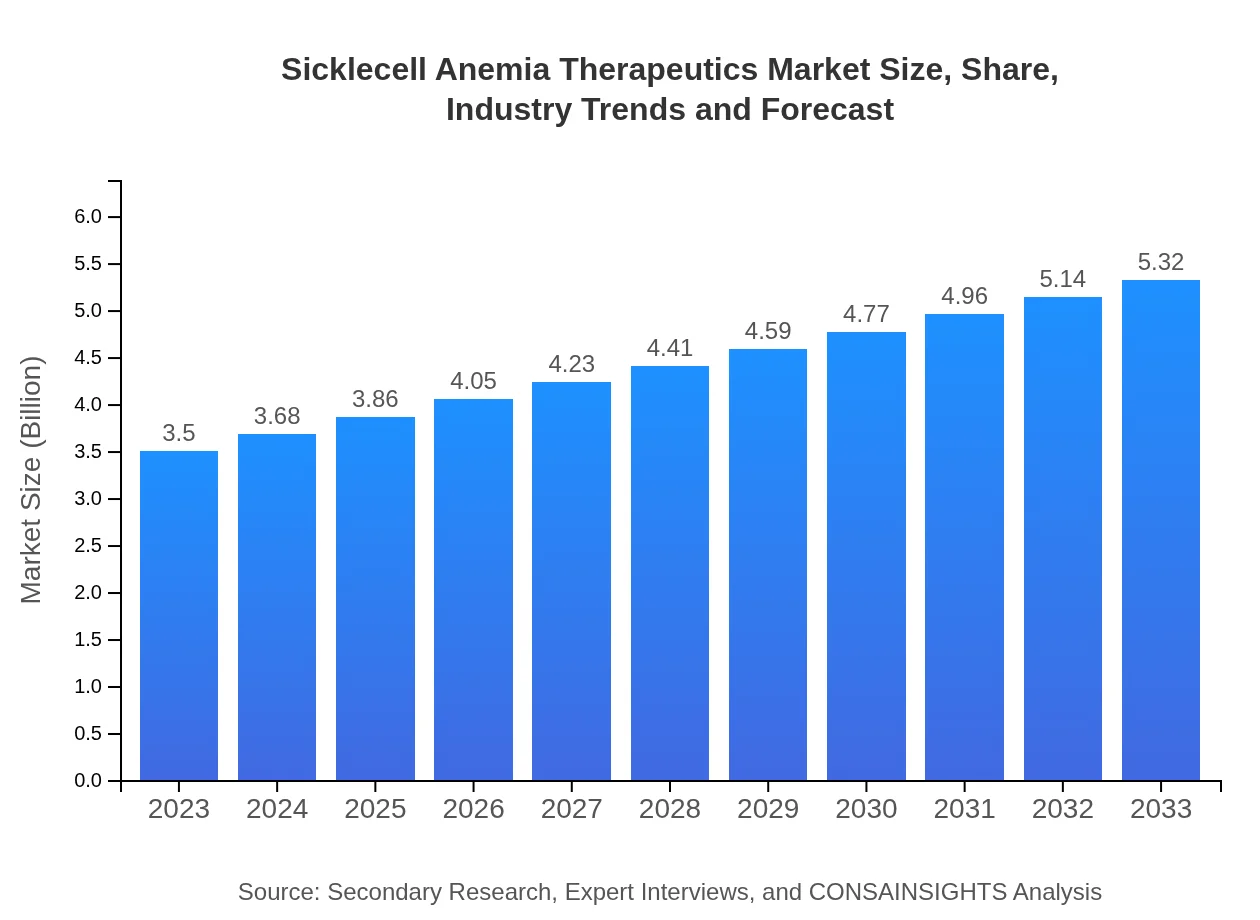
| 2023 Market Size | $3.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $5.32 Billion |
| Top Companies | Novartis, Bluebird Bio, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Overview
Customize Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics market in 2023?
Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Industry Analysis
Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Report:
The European market for Sicklecell Anemia therapeutics is expected to witness growth from $0.85 billion in 2023 to $1.29 billion by 2033. Increased patient awareness and supportive healthcare policies will drive demand for innovative treatment options across the region.Asia Pacific Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Report:
The Asia-Pacific market for Sicklecell Anemia therapeutics is anticipated to grow from $0.74 billion in 2023 to $1.12 billion by 2033, driven by increasing healthcare expenditures, a growing patient population, and advancements in treatment options. Regulatory support for new therapies further boosts market growth.North America Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Report:
North America will continue to dominate the Sicklecell Anemia therapeutics market, growing from $1.20 billion in 2023 to $1.82 billion by 2033. This growth can be attributed to high healthcare spending, advanced research facilities, and the strong presence of leading market players developing innovative therapies.South America Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Report:
In South America, the Sicklecell Anemia therapeutics market is projected to expand from $0.28 billion in 2023 to $0.42 billion by 2033. The growth is primarily focused on improving healthcare access and awareness about Sicklecell Anemia, alongside government initiatives to enhance patient care.Middle East & Africa Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market for Sicklecell Anemia therapeutics is projected to grow from $0.44 billion in 2023 to $0.67 billion by 2033. Efforts to improve healthcare infrastructure and better disease management strategies are essential in shaping the market trajectory.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Analysis By Therapy Type
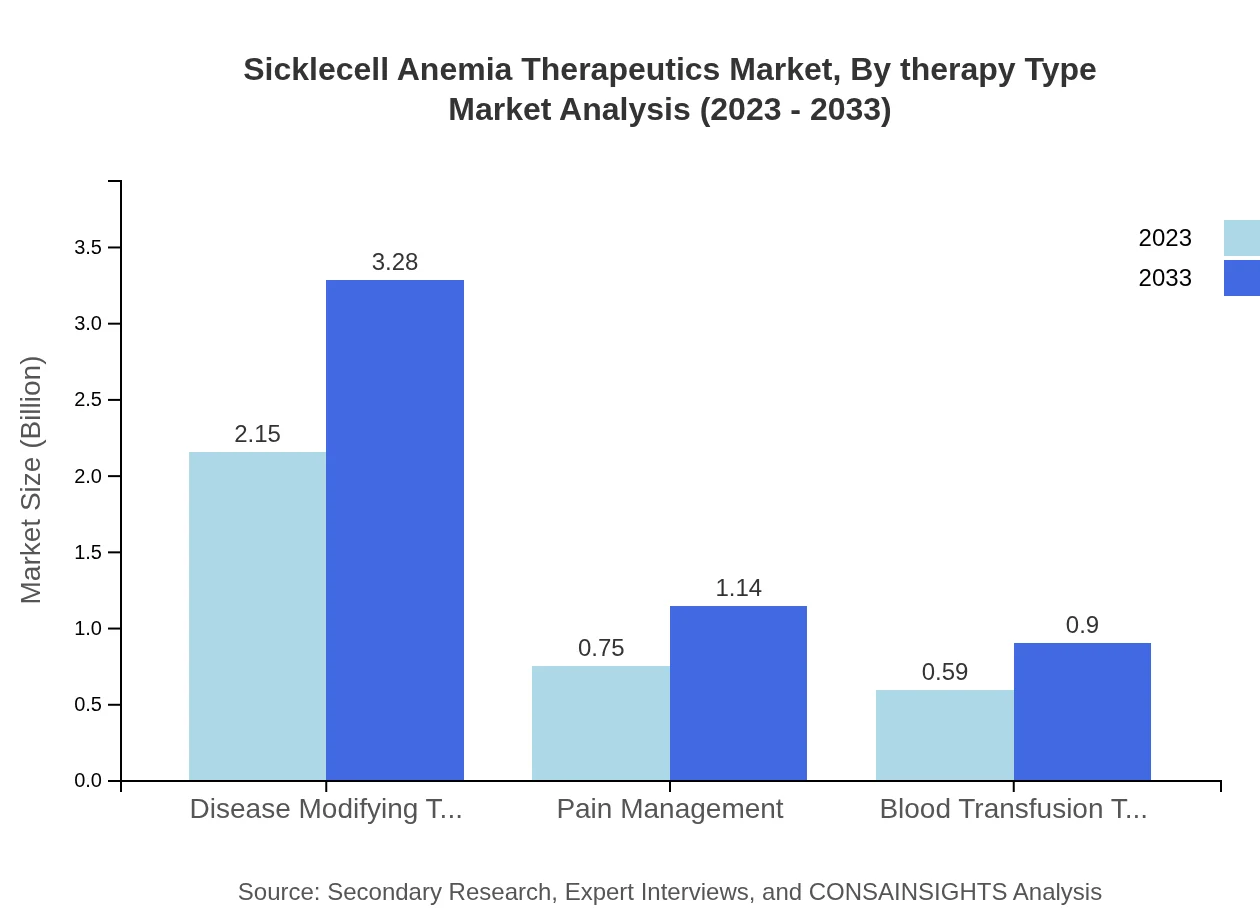
In 2023, the Disease Modifying Therapies segment dominates the market with a size of $2.15 billion and is expected to reach $3.28 billion by 2033, holding a 61.56% market share. Pain Management therapies account for $0.75 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $1.14 billion by 2033, while Blood Transfusion Therapies are valued at $0.59 billion, with an expected increase to $0.90 billion by 2033.
Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Analysis By Route Of Administration
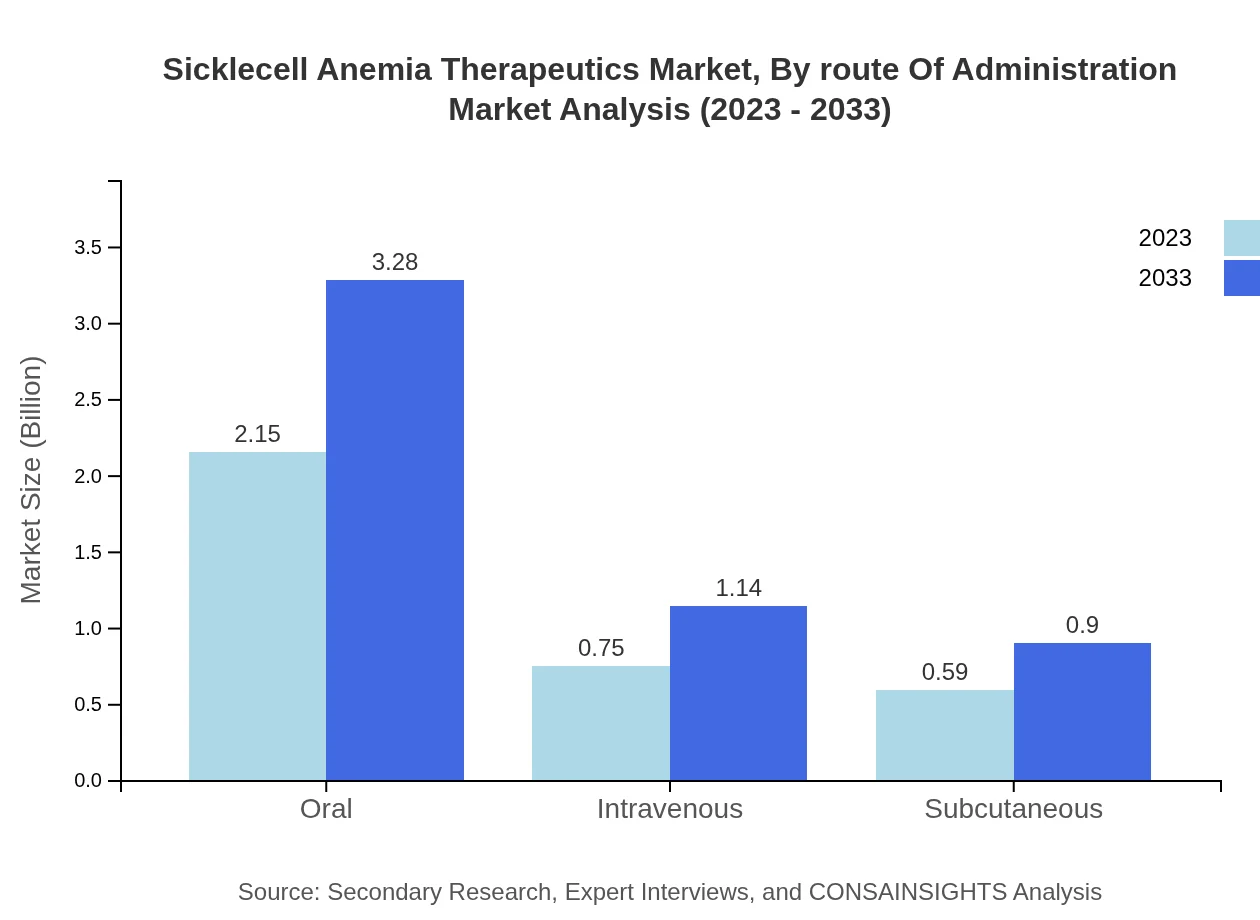
Oral administration remains the leading route, with a market size of $2.15 billion in 2023 and projected to reach $3.28 billion by 2033, constituting a significant share of 61.56%. Intravenous therapies are valued at $0.75 billion, expected to grow to $1.14 billion, while Subcutaneous therapies will move from $0.59 billion in 2023 to $0.90 billion by 2033.
Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Analysis By Patient Age Group
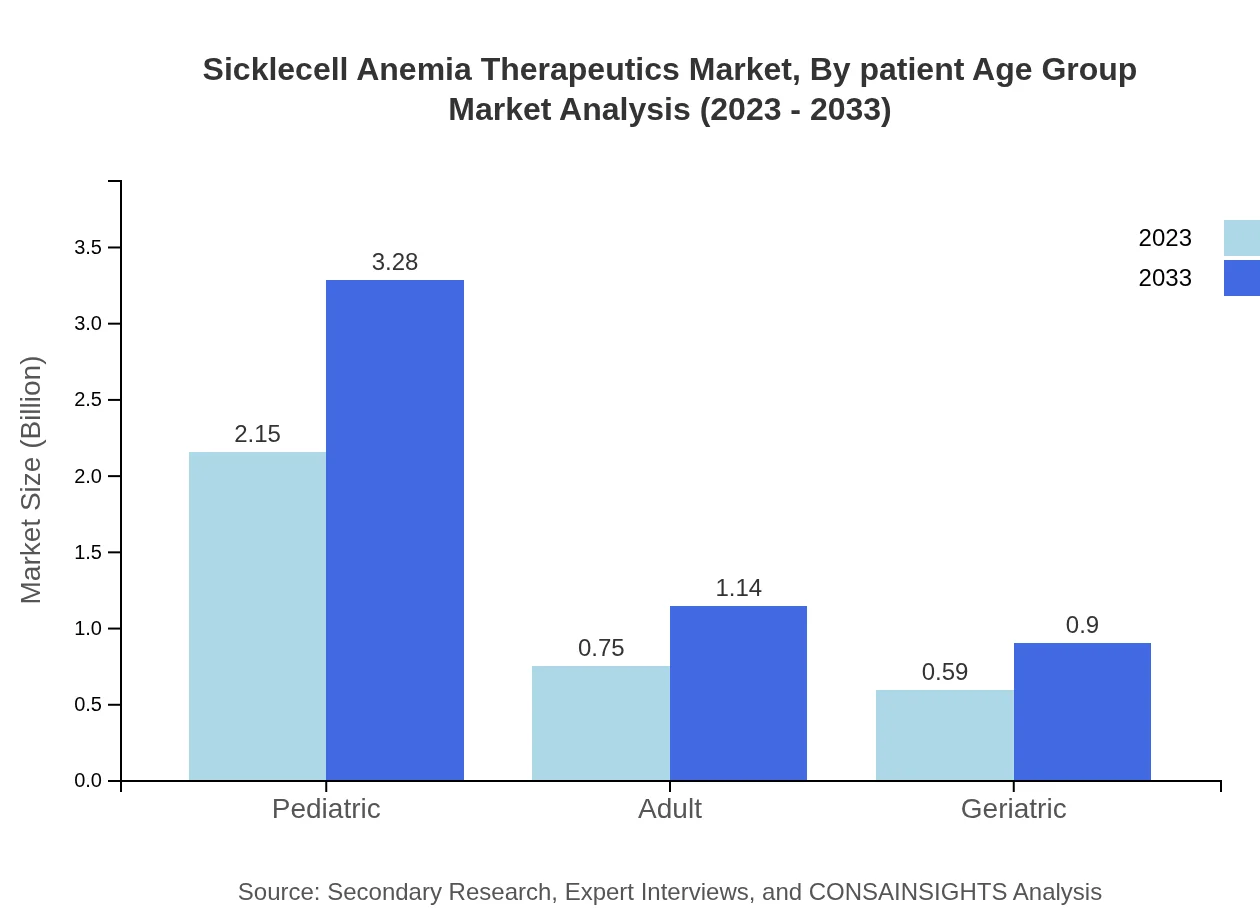
The Pediatric segment represents a significant portion of the market at $2.15 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to $3.28 billion by 2033. The Adult segment is projected to grow from $0.75 billion to $1.14 billion, while the Geriatric segment is expected to grow from $0.59 billion to $0.90 billion over the same period.
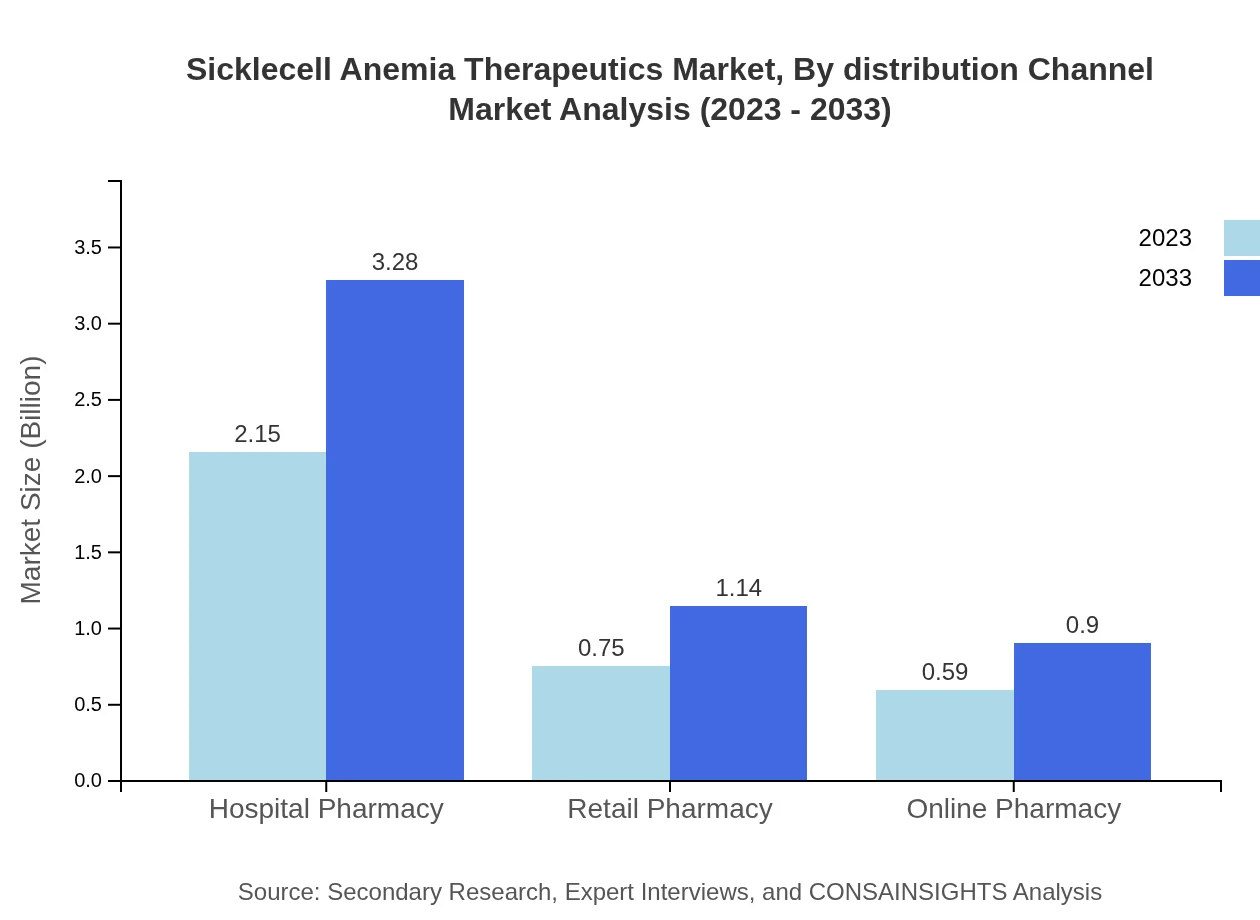
Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Hospital Pharmacy remains a dominant distribution channel, with a market size of $2.15 billion in 2023, predicted to climb to $3.28 billion by 2033. Retail Pharmacies and Online Pharmacies are also critical, with expected growth from $0.75 billion to $1.14 billion and $0.59 billion to $0.90 billion respectively.
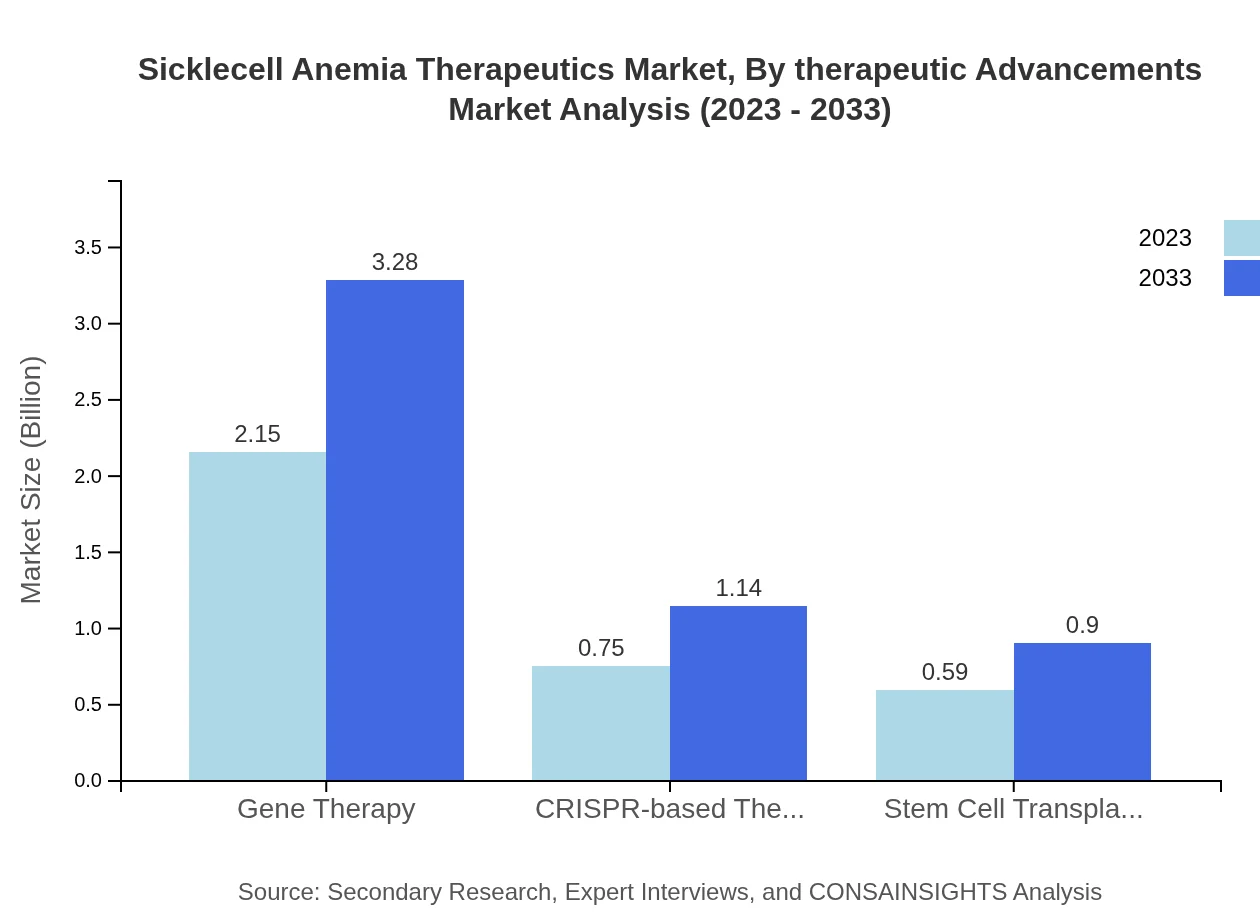
Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Analysis By Therapeutic Advancements
Advancements in Gene Therapy are reshaping the therapeutic landscape, with the market expected to grow from $2.15 billion in 2023 to $3.28 billion by 2033, due to increasing research focusing on innovative gene-editing technologies. CRISPR-based therapies and Stem Cell Transplantation are also expected to see growth, contributing significantly to the evolution of sector treatments.
Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics Industry
Novartis:
A leading player in the pharmaceuticals sector, Novartis is known for its innovative therapies in Sickle Cell disease management, including the development of hydroxyurea for treatment.Bluebird Bio:
A biotechnology company focused on developing gene therapies for genetic disorders, Bluebird Bio is renowned for its progress in curative therapies for Sickle Cell Anemia.Bristol Myers Squibb:
This global biopharmaceutical company has established itself through its diverse portfolio that includes impactful treatments for Sickle Cell Anemia through innovative research and clinical trials.Pfizer :
Pfizer contributes significantly to the industry with its range of therapies designed for Sickle Cell, utilizing modern science to create effective treatment solutions.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics?
The global market size for sickle cell anemia therapeutics is estimated to reach approximately $3.5 billion by 2023, growing at a CAGR of 4.2%. This growth reflects the increasing demand for effective treatments and advancements in medical technology.
What are the key market players or companies in this sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics industry?
Key players in the sickle cell anemia therapeutics market include major pharmaceutical companies that invest heavily in research and development. Notable companies include Novartis, Pfizer, and Bluebird Bio, focusing on innovative treatments and therapies.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics industry?
Driving factors include increased awareness of sickle cell disease, advancements in gene therapy, and enhanced treatment options. Innovations in drug development, along with growing healthcare accessibility, also contribute significantly to market growth.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics?
The North America region shows the fastest growth in the sickle cell anemia therapeutics market, expected to expand from $1.20 billion in 2023 to $1.82 billion by 2033, driven by advanced healthcare systems and increasing research initiatives.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the sickle cell anemia therapeutics industry, ensuring relevant insights to support strategic business decisions.
What deliverables can I expect from this sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics market research project?
Deliverables typically include detailed market analysis reports, insights on competitive landscape, growth forecasts, regional data, and trend analyses, which facilitate informed decision-making and strategic planning.
What are the market trends of sicklecell Anemia Therapeutics?
Current trends include the rise of gene therapies, increased adoption of CRISPR-based therapies, and growth in pediatric treatment segments. Innovations in pain management and enhanced drug delivery methods are also prominent.