Simulation Software Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: simulation-software
Simulation Software Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report delves into the Simulation Software market, covering detailed insights, current trends, market forecasts for 2023-2033, and significant industry dynamics. It provides comprehensive analyses of market size, growth, regional breakdowns, and key players shaping this evolving landscape.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
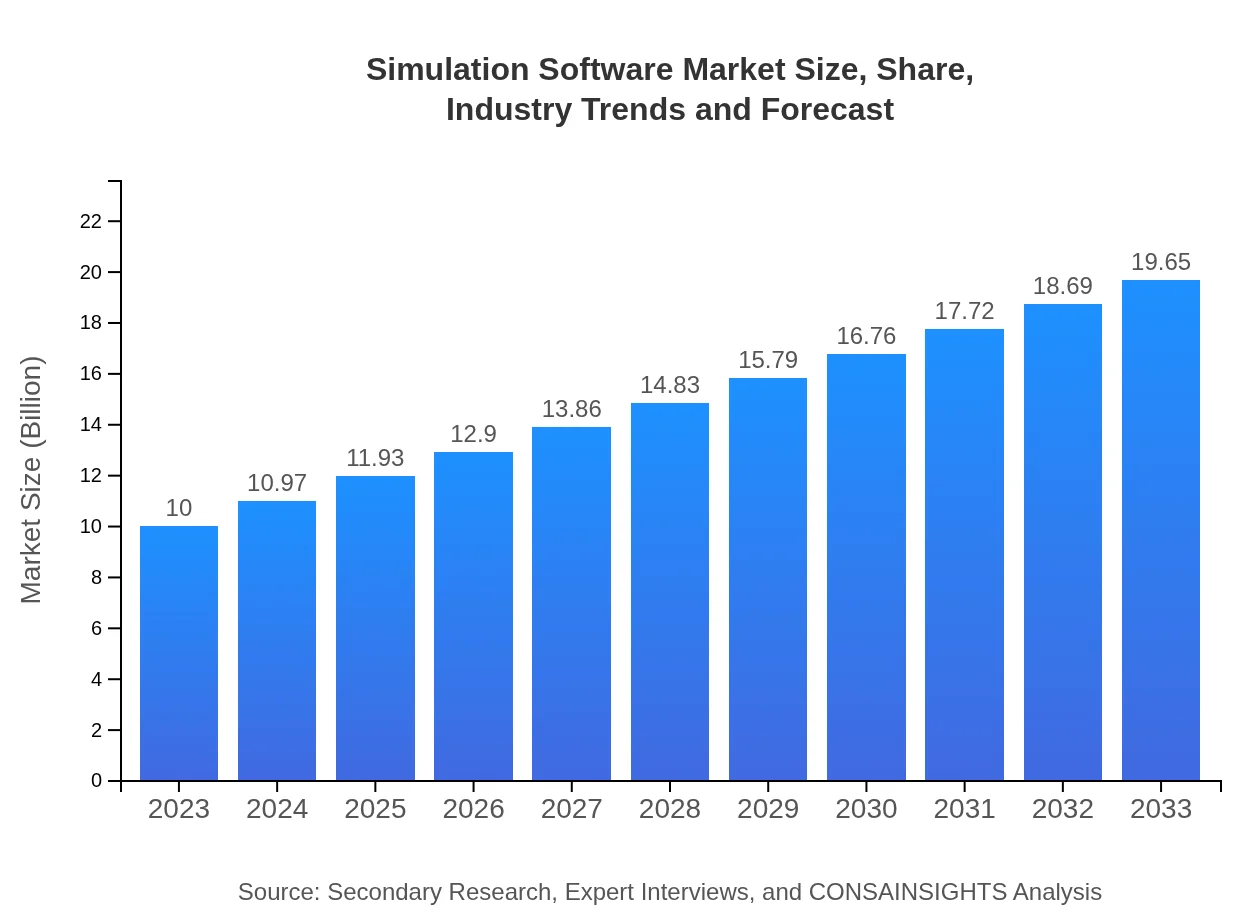
| 2023 Market Size | $10.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $19.65 Billion |
| Top Companies | ANSYS, Inc., Siemens Digital Industries Software, Dassault Systèmes |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Simulation Software Market Overview
Customize Simulation Software Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Simulation Software market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Simulation Software's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Simulation Software
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Simulation Software market in 2023?
Simulation Software Industry Analysis
Simulation Software Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Simulation Software Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Simulation Software Market Report:
The European Simulation Software market amounted to $3.28 billion in 2023 and is looking at a sizable increase to $6.45 billion by 2033. Countries such as Germany and the UK are at the forefront, driven by strong engineering and manufacturing capabilities, coupled with stringent regulatory requirements that necessitate advanced simulations.Asia Pacific Simulation Software Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Simulation Software market was valued at $1.90 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $3.73 billion by 2033. The rapid industrialization and growing demand for design and testing processes in countries like China and India are major drivers for this growth. Enhanced governmental support for manufacturing and technology adoption is further fueling the market.North America Simulation Software Market Report:
North America, with a market size of $3.32 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $6.53 billion by 2033, is the largest market for simulation software. It benefits from high R&D investments, the presence of leading companies, and advancements in technologies like cloud computing and AI, which facilitate simulation processes.South America Simulation Software Market Report:
The South American market for simulation software was approximately $0.71 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $1.40 billion by 2033. Increasing investments in infrastructure projects and a rising focus on optimizing resources in construction and automotive industries are key factors contributing to this growth.Middle East & Africa Simulation Software Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market size was $0.79 billion in 2023, forecasted to reach $1.55 billion by 2033. The region is witnessing a surge in demand due to investments in infrastructure, oil, and gas sectors where simulation software is critical for project planning and execution.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
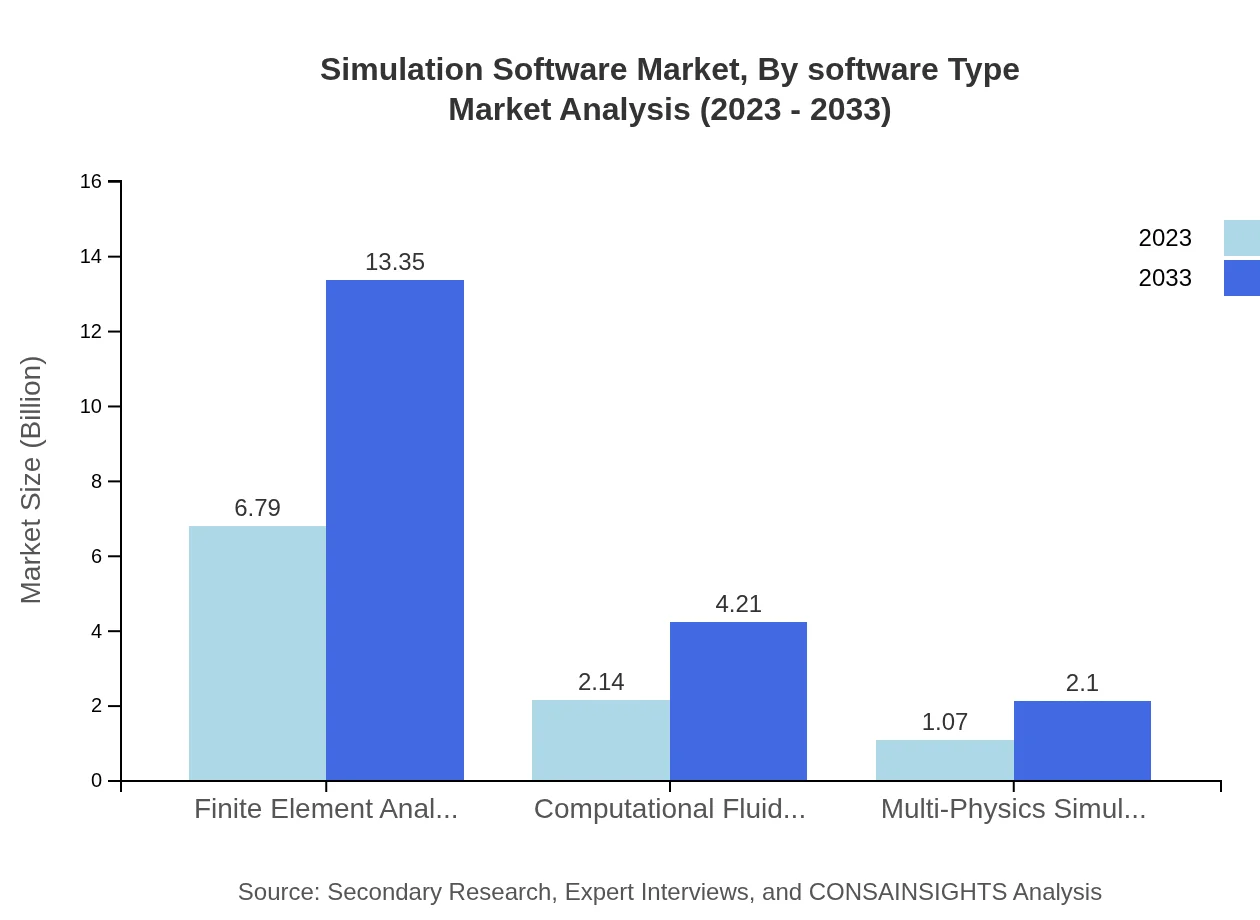
Simulation Software Market Analysis By Software Type
In 2023, the market for finite element analysis (FEA) software is $6.79 billion, representing 67.91% of the total market share. This segment is expected to grow significantly, reaching $13.35 billion by 2033. In parallel, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software holds a market size of $2.14 billion in 2023, appealing particularly to industries such as aerospace and automotive.
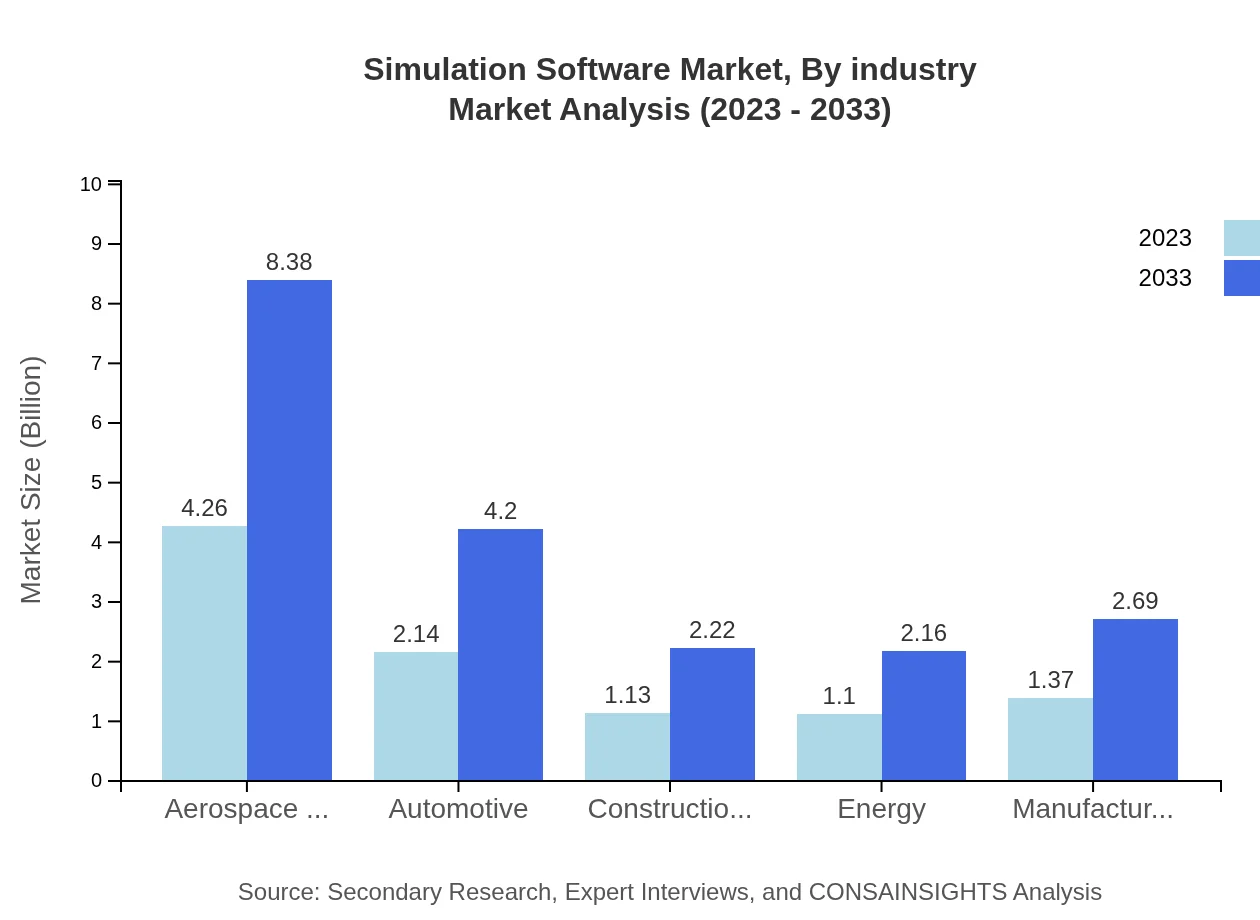
Simulation Software Market Analysis By Industry
Aerospace and Defense leads the industry segmentation with a market size of $4.26 billion in 2023 and a 42.65% share, projected to rise to $8.38 billion by 2033. The automotive sector follows closely with a size of $2.14 billion, expected to grow steadily due to increased simulation needs in vehicle design and testing.
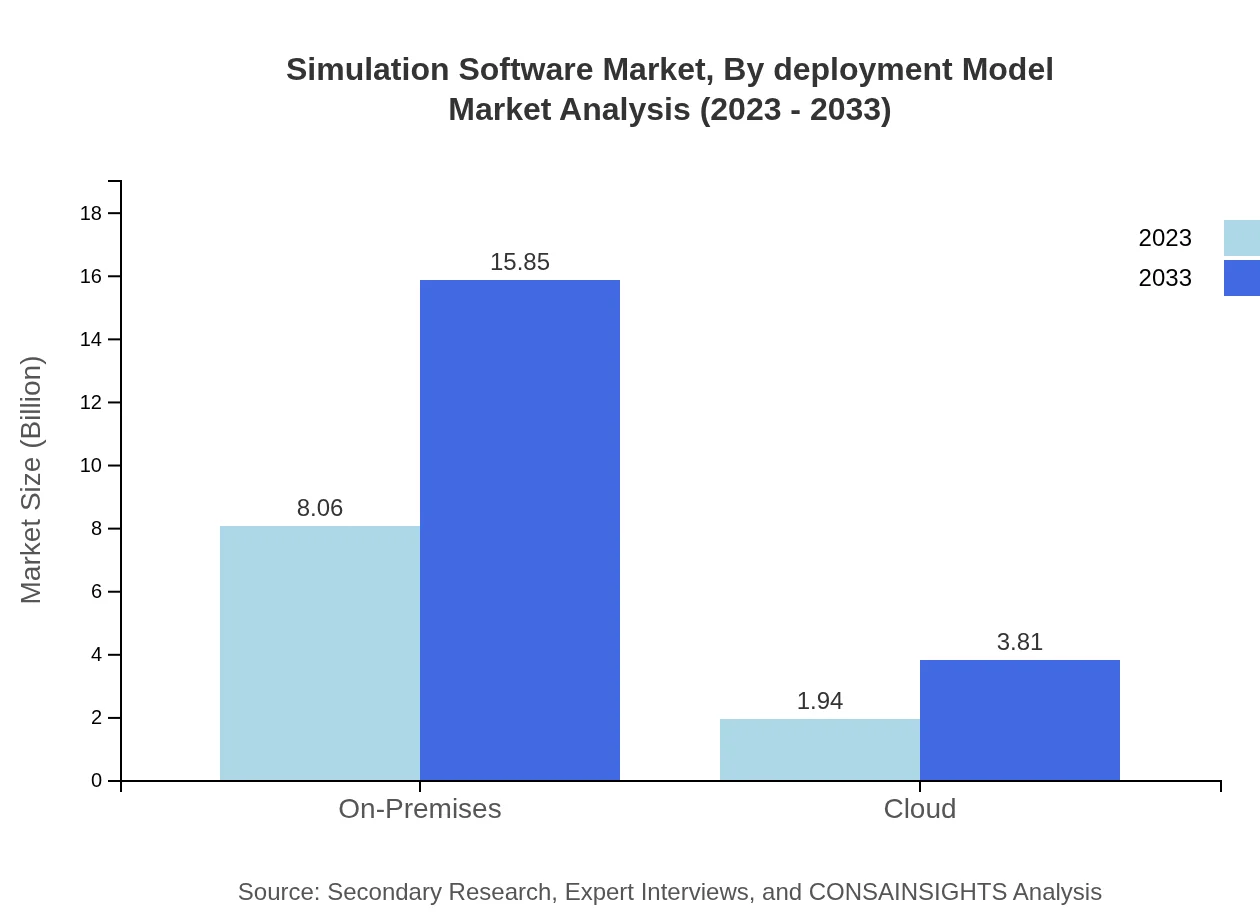
Simulation Software Market Analysis By Deployment Model
The On-Premises deployment model commands a significant share with a market size of $8.06 billion in 2023, representing 80.63% of the market. By 2033, this is expected to reach $15.85 billion. The Cloud deployment model is also gaining traction, expected to expand from $1.94 billion to $3.81 billion over the same period.
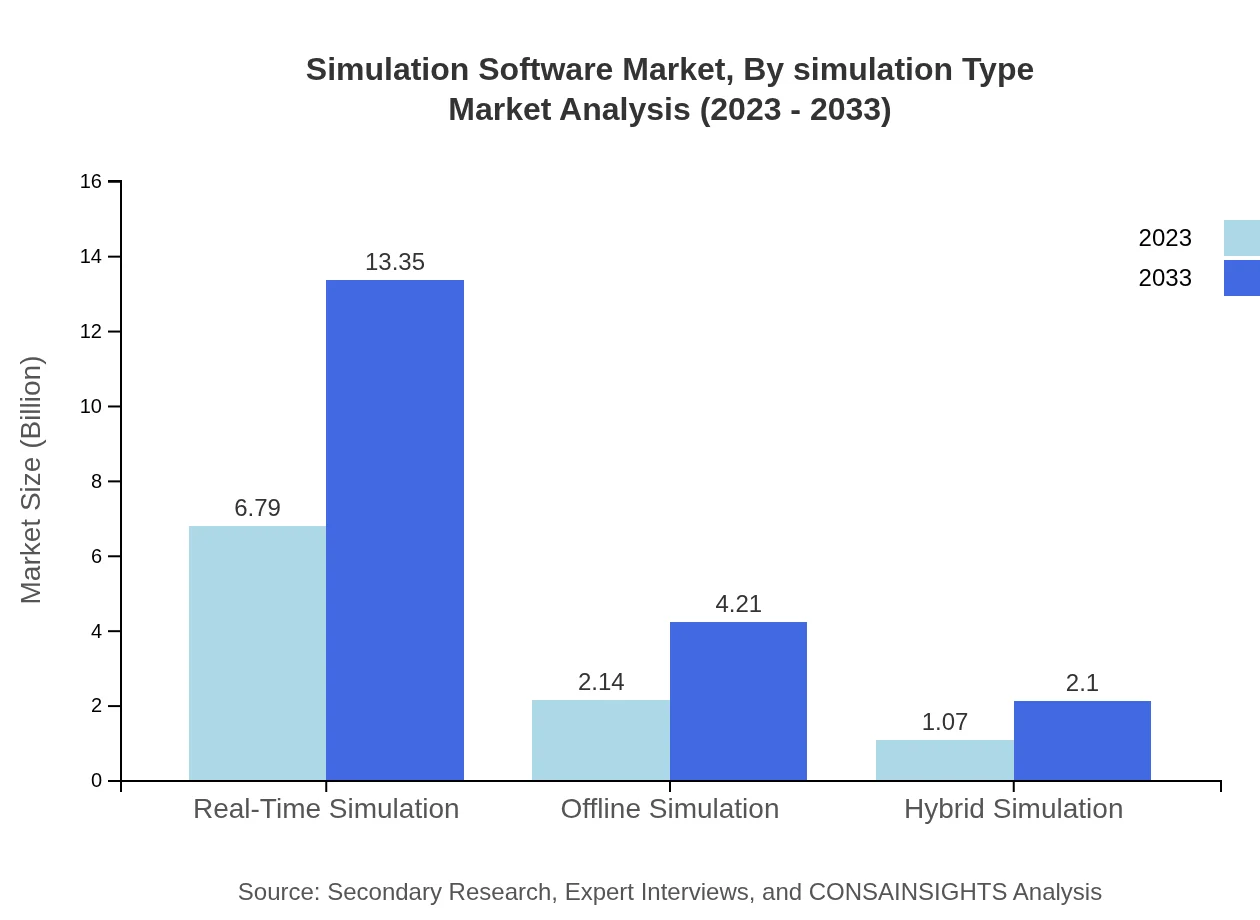
Simulation Software Market Analysis By Simulation Type
Real-Time Simulation accounts for $6.79 billion in 2023, similarly projected to grow to $13.35 billion by 2033, illustrating the increasing importance of real-time data processing in simulations. Offline Simulation and Hybrid Simulation, while smaller, are still vital segments introducing innovative methods to enhance traditional processes.
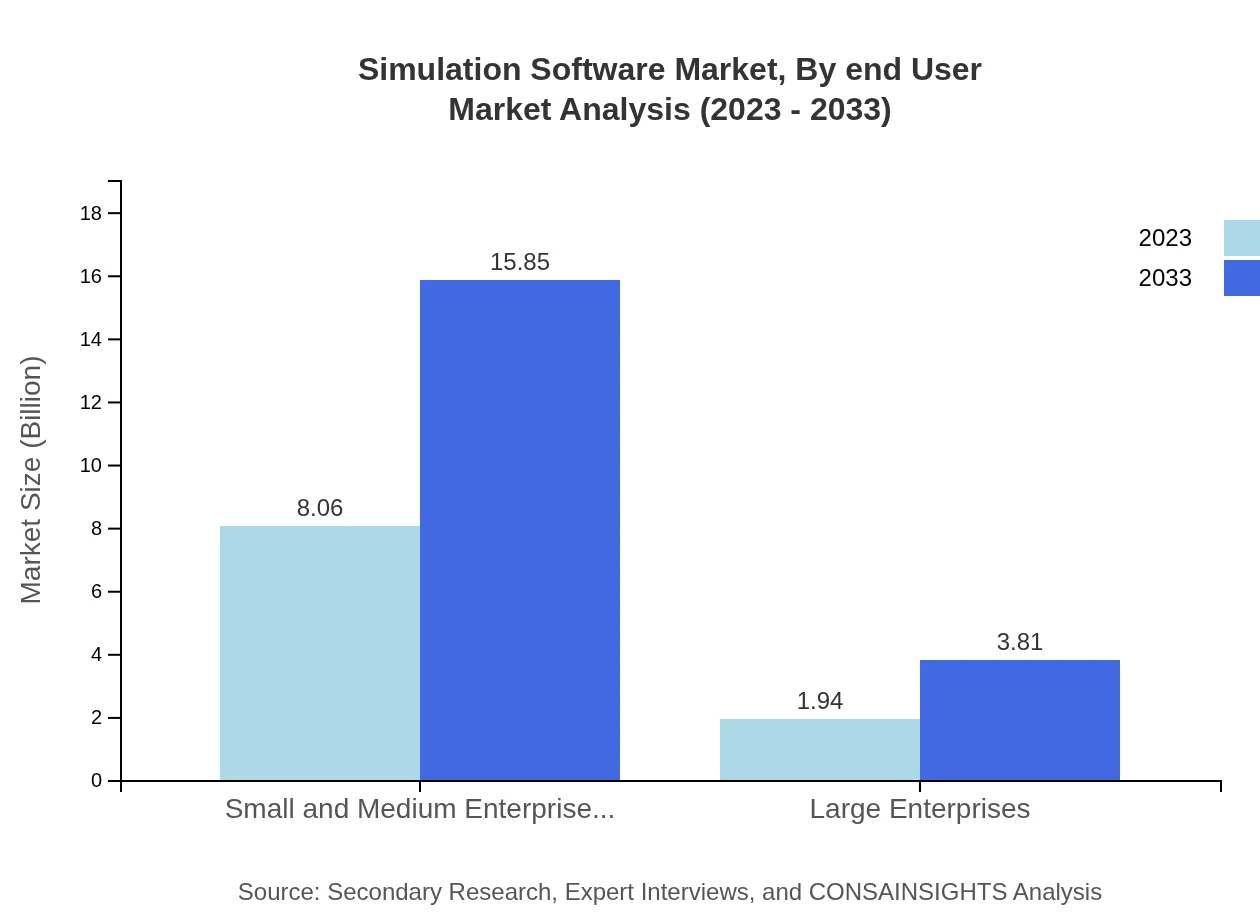
Simulation Software Market Analysis By End User
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) represent 80.63% share of the 2023 market at $8.06 billion, highlighting their reliance on simulation tools to enhance operational efficiency. Meanwhile, Large Enterprises capture a smaller but vital $1.94 billion share, focusing on advanced simulations for complex projects.
Simulation Software Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Simulation Software Industry
ANSYS, Inc.:
ANSYS provides engineering simulation software, facilitating product design and development across numerous industries. Its solutions help organizations save costs and reduce time-to-market.Siemens Digital Industries Software:
Siemens offers digital tools that enable manufacturers and engineers to simulate product performance throughout their lifecycle, ensuring optimized approaches to engineering challenges.Dassault Systèmes:
A pioneer in 3D design software, Dassault Systèmes empowers companies to create virtual simulations to enhance collaboration and accelerate innovation.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of simulation software?
The global simulation software market is valued at approximately $10 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 6.8% through 2033, indicating robust growth driven by increasing automation and the need for virtual testing across industries.
What are the key market players or companies in the simulation software industry?
Key players in the simulation software market include established companies such as ANSYS, Siemens, Dassault Systèmes, and Altair Engineering, which provide significant competitive advantages with their innovative solutions and extensive industry expertise.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the simulation software industry?
Factors driving growth include the rising demand for advanced simulation tools for product design and testing, increasing investments in R&D across sectors, and the pivotal role of automation in enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the simulation software market?
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the simulation software market, expected to reach approximately $3.73 billion by 2033, up from $1.90 billion in 2023, driven by rapid industrialization and technological advancements.
Does ConsInsights provide customized market report data for the simulation software industry?
Yes, ConsInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the specific needs of clients, enabling businesses to gain insights and make informed decisions based on comprehensive market analysis.
What deliverables can I expect from the simulation software market research project?
Deliverables include detailed market reports, analysis of key trends, regional insights, segment splits, competitive landscape evaluations, and strategic recommendations to support business planning and competitive positioning.
What are the market trends of simulation software?
Key market trends include increased adoption of cloud-based simulation solutions, advancements in AI and machine learning integration, a surge in demand for real-time simulation capabilities, and enhanced emphasis on regulatory compliance and sustainability.