Small Cell-5g Network Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: small-cell-5g-network
Small Cell-5g Network Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Small Cell-5G Network market, offering insights into market size, growth forecasts, industry trends, and regional analyses from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
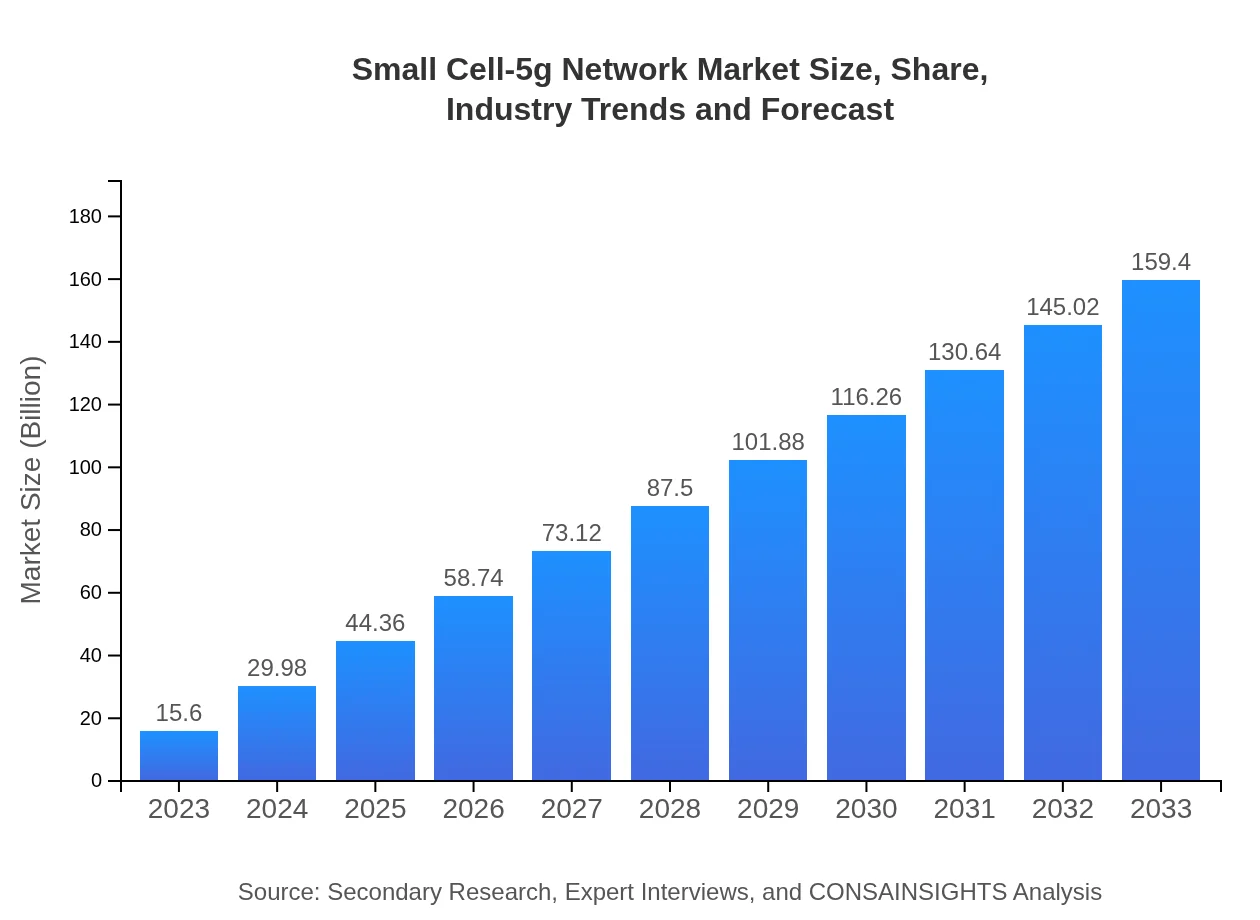
| 2023 Market Size | $15.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 24.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $159.40 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cisco Systems, Inc., Ericsson , Nokia Corporation, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Samsung Electronics |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Small Cell-5G Network Market Overview
Customize Small Cell-5g Network Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Small Cell-5g Network market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Small Cell-5g Network's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Small Cell-5g Network
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Small Cell-5G Network market in 2023 and 2033?
Small Cell-5G Network Industry Analysis
Small Cell-5G Network Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Small Cell-5G Network Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Small Cell-5g Network Market Report:
The European market is forecast to grow from $4.11 billion in 2023 to $41.98 billion by 2033 as the demand for high-speed internet access and the implementation of stringent government policies stimulate growth in 5G adoption.Asia Pacific Small Cell-5g Network Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is projected to grow significantly, from $3.11 billion in 2023 to $31.78 billion by 2033, with countries like China and India leading in 5G deployment. The increasing urban population and technological advancements propel the demand for enhanced network solutions.North America Small Cell-5g Network Market Report:
North America leads the market with an expected increase from $5.70 billion in 2023 to $58.28 billion in 2033, driven by substantial investments from key telecom players and government initiatives aimed at expanding 5G coverage.South America Small Cell-5g Network Market Report:
In South America, the Small Cell-5G Network is expected to expand from $1.25 billion in 2023 to $12.74 billion in 2033 as countries invest in mobile infrastructure to catch up with global digital transformation trends.Middle East & Africa Small Cell-5g Network Market Report:
The Middle East & Africa region, starting with a market size of $1.43 billion in 2023, is anticipated to reach $14.62 billion by 2033 as regional firms begin to invest in extensive 5G networks to support economic diversification initiatives.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
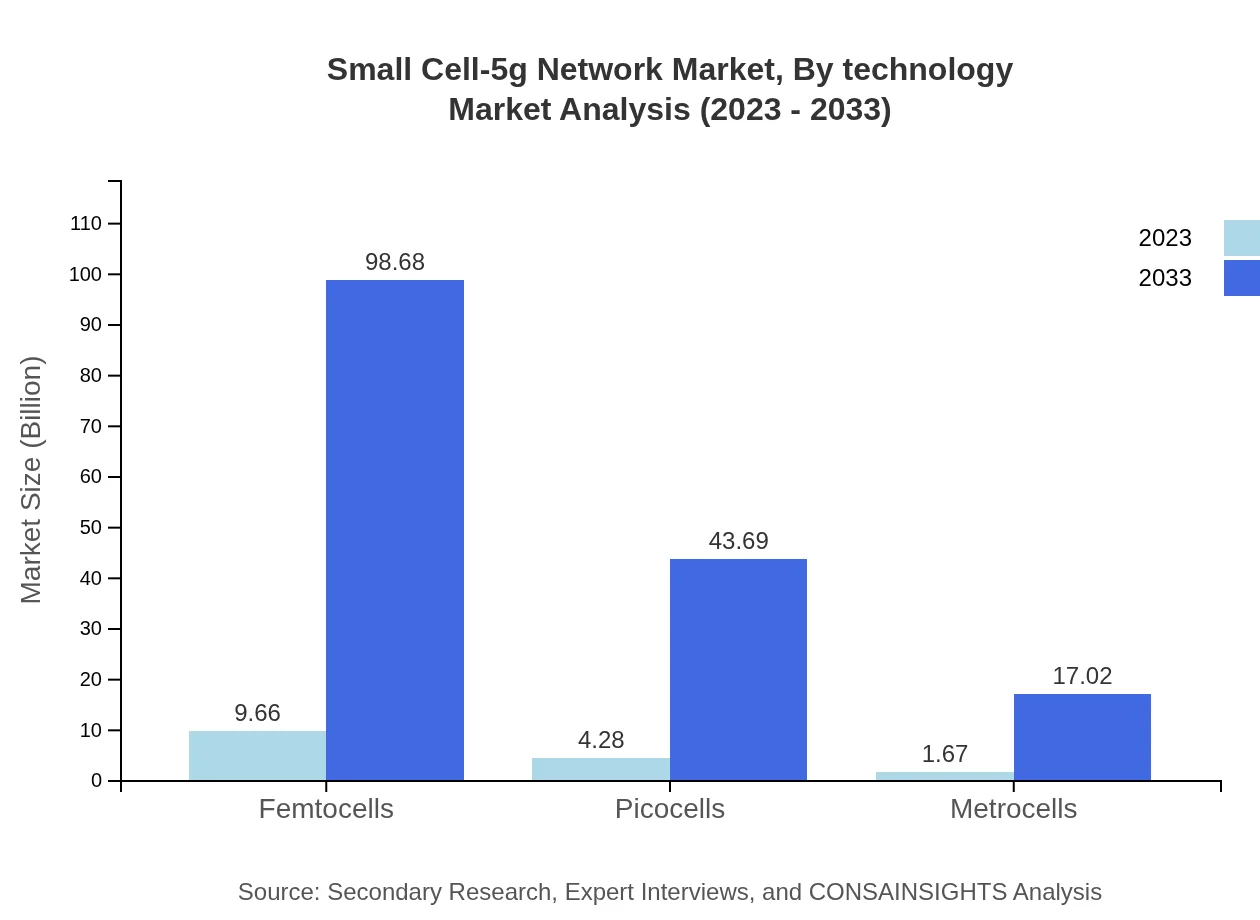
Small Cell-5g Network Market Analysis By Technology
The Small Cell-5G Network market is primarily segmented by technology, including femtocells, picocells, and metrocells. Femtocells dominate the market, accounting for a size of $9.66 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $98.68 billion by 2033, due to their efficiency in enhancing indoor coverage for consumers. Picocells and metrocells also contribute significantly, with anticipated increases aligned with urban densification and demand for better coverage.
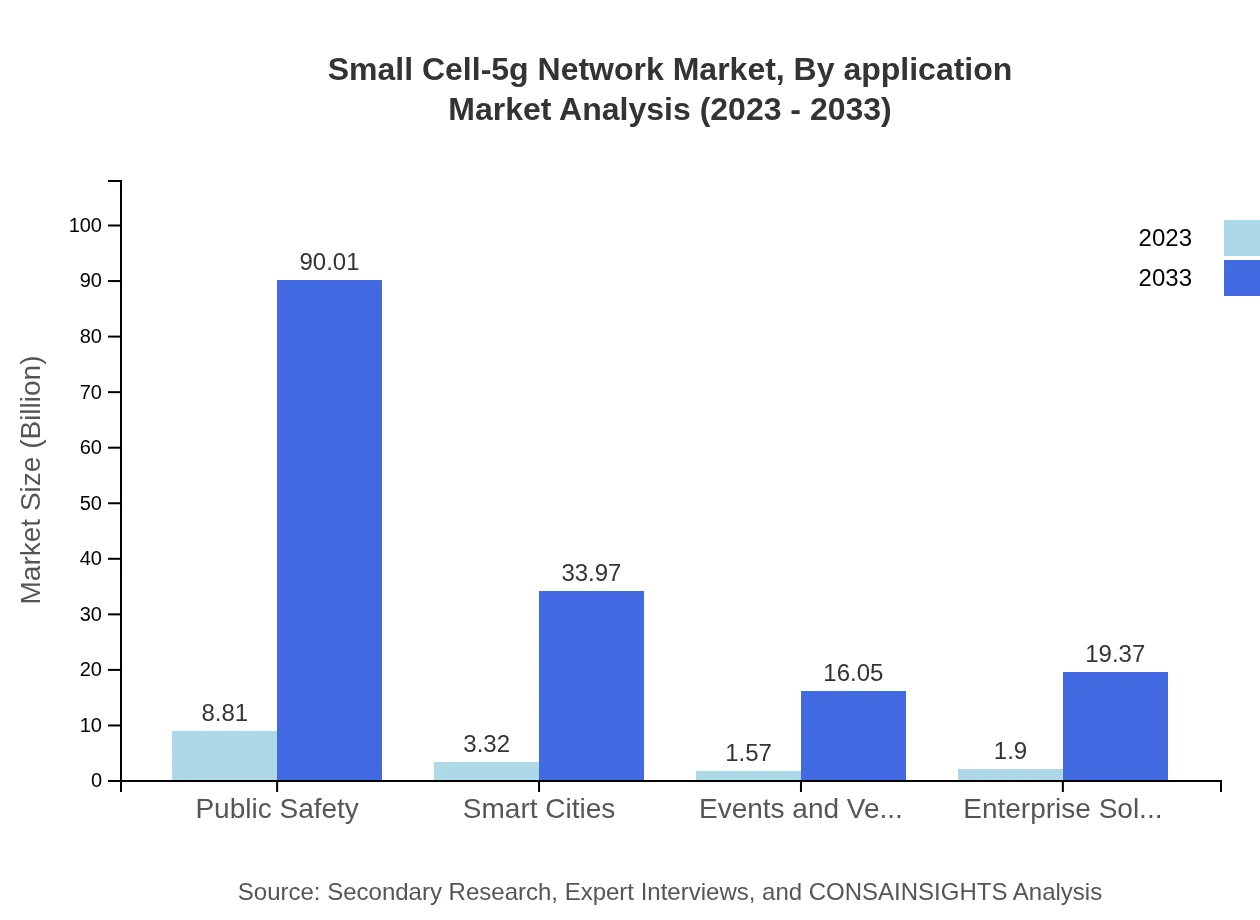
Small Cell-5g Network Market Analysis By Application
Application-wise, the public safety sector leads with a market size of $8.81 billion in 2023, surging to $90.01 billion by 2033. Applications related to smart cities are also growing, expected to see an increase from $3.32 billion in 2023 to $33.97 billion by 2033, driven by increased urbanization and infrastructural investment.
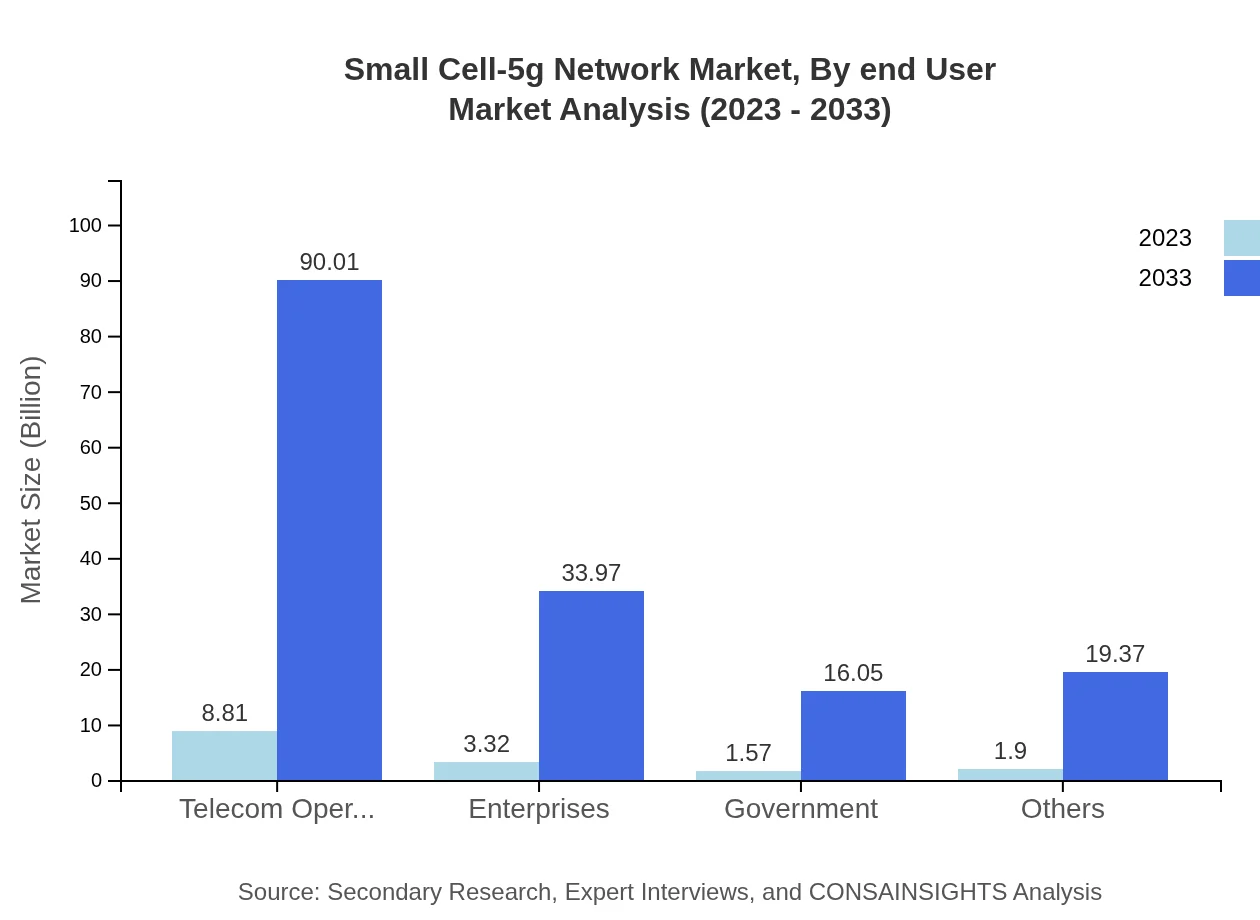
Small Cell-5g Network Market Analysis By End User
The end-user industry segmentation shows telecom operators occupying a major share with a market size of $8.81 billion in 2023, anticipated to reach $90.01 billion by 2033. Other segments, including enterprises and government applications, also show robust growth owing to the increasing adoption of digital technologies.
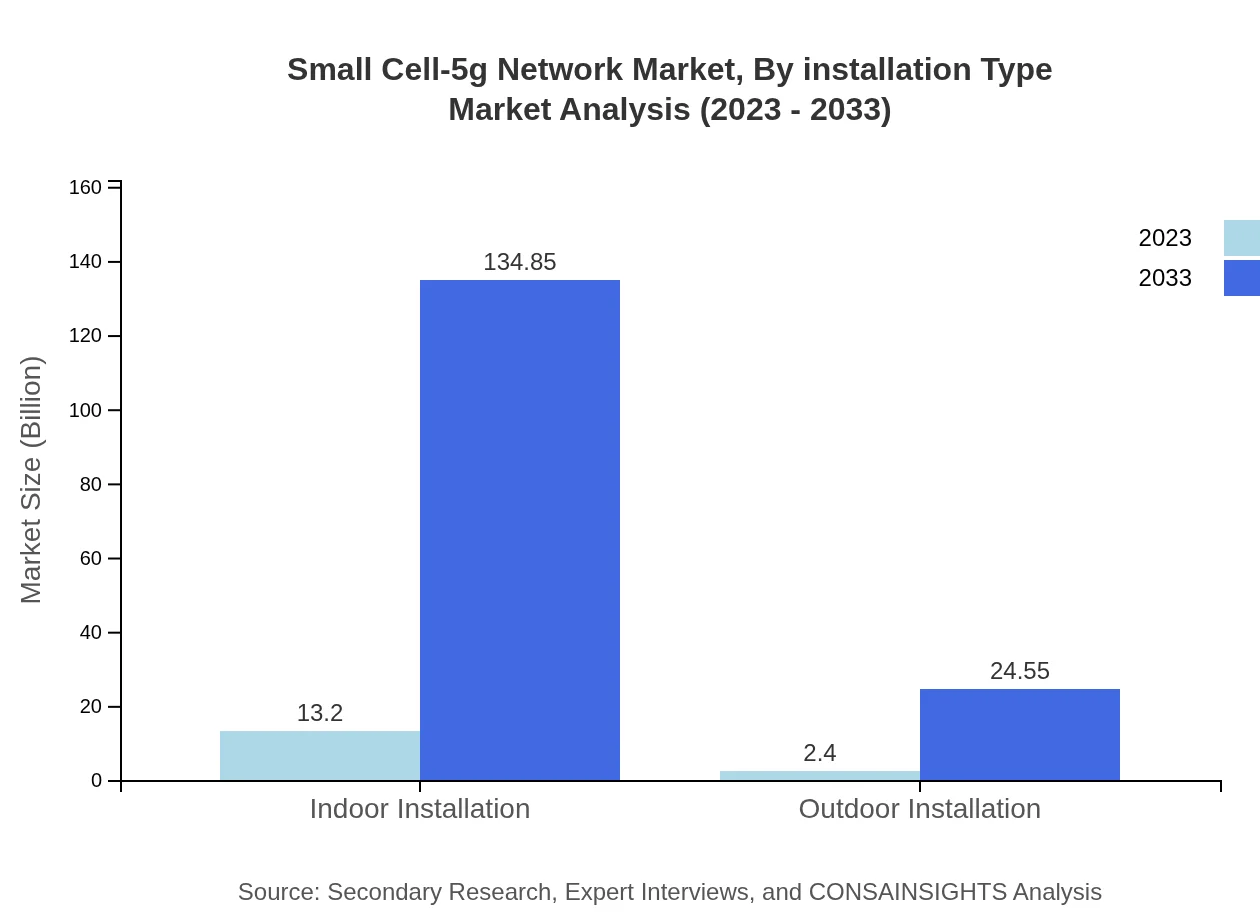
Small Cell-5g Network Market Analysis By Installation Type
Installation types are divided into indoor and outdoor segments. Indoor installations are leading the way with a market size of $13.20 billion in 2023, expected to escalate to $134.85 billion by 2033 due to rising demands for private and office networks. Outdoor installations are showing a steady growth pattern as well, increasing from $2.40 billion to $24.55 billion during the same period.
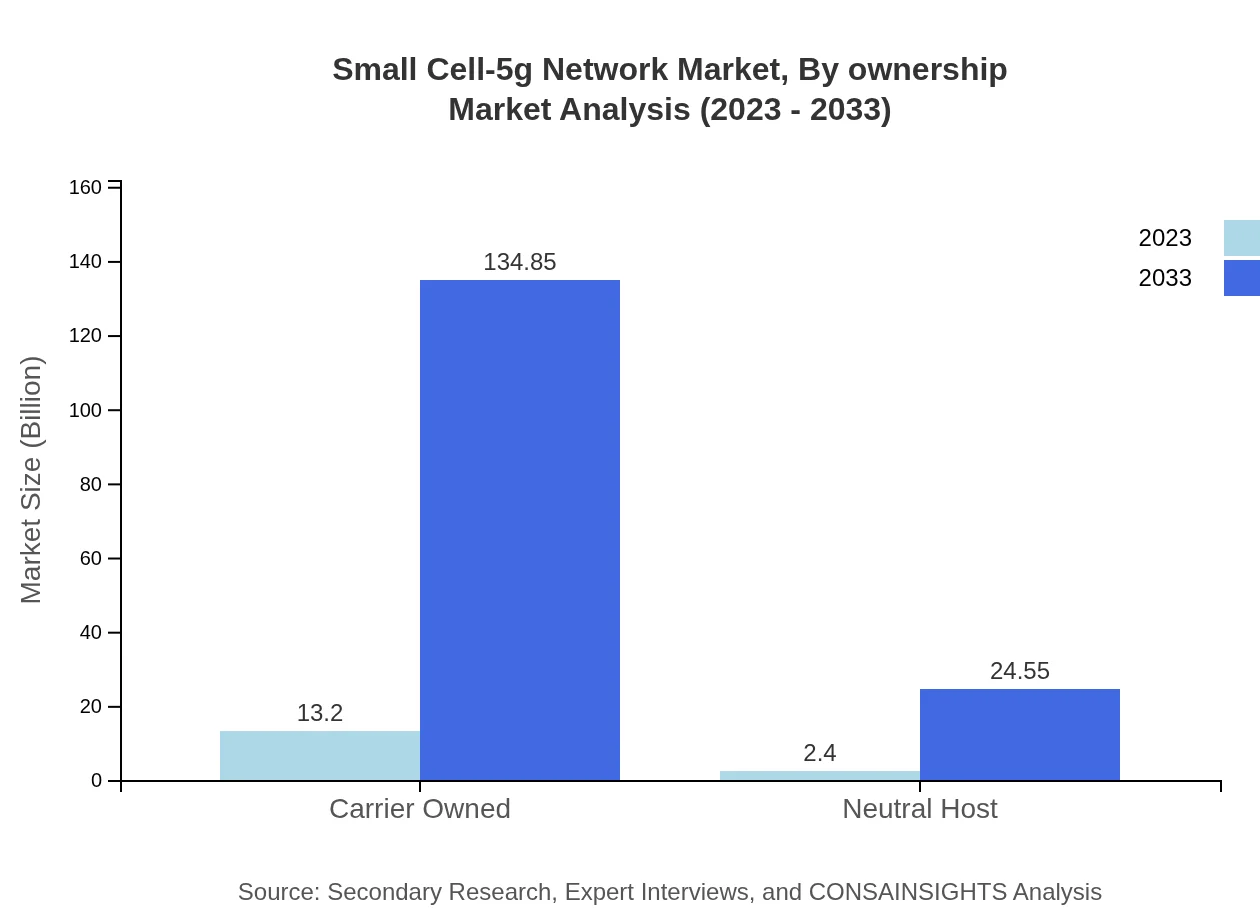
Small Cell-5g Network Market Analysis By Ownership
Market segmentation by ownership reveals that carrier-owned small cells dominate the landscape, valued at $13.20 billion in 2023, projected to surge to $134.85 billion by 2033. Neutral host models are also gaining traction, expected to increase significantly from $2.40 billion to $24.55 billion.
Small Cell-5G Network Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Small Cell-5G Network Industry
Cisco Systems, Inc.:
A global leader in IT and networking, Cisco provides innovative solutions in telecommunication networks, focusing on technologies that enhance 5G connectivity.Ericsson :
Ericsson is a major player in the telecommunications industry, offering comprehensive small cell solutions that enable seamless connectivity for 5G networks.Nokia Corporation:
Nokia focuses on enhancing connectivity through its advanced technologies in small cells, contributing significantly to 5G deployments across various sectors.Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.:
Huawei is recognized for its leadership in providing small cell technologies, driving various 5G initiatives globally.Samsung Electronics:
Samsung is actively involved in developing small cell infrastructure that supports advanced mobile communications for 5G networks.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Small Cell 5G Network?
The global Small Cell 5G Network market size is projected to reach $15.6 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 24.5%. This growth signifies the increasing demand for enhanced connectivity and the critical role small cells play in 5G deployment.
What are the key market players or companies in the Small Cell 5G Network industry?
Key players in the Small Cell 5G Network market include established telecom companies, network equipment manufacturers, and emerging technology firms specializing in 5G infrastructure solutions to address growing data and connectivity needs.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Small Cell 5G Network industry?
The rapid urbanization, increasing mobile data traffic, and the need for improved coverage are primary growth drivers for the Small Cell 5G Network industry. Additionally, advancements in technology and government initiatives to bolster 5G rollout further fuel market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Small Cell 5G Network?
The North America region is projected to exhibit the fastest growth in the Small Cell 5G Network market, with projected market size increasing from $5.70 billion in 2023 to $58.28 billion by 2033, supported by robust telecom infrastructure and investments.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Small Cell 5G Network industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to your specific needs in the Small Cell 5G Network industry, allowing businesses to gain insights and develop strategies relevant to their unique contexts.
What deliverables can I expect from this Small Cell 5G Network market research project?
Deliverables from the Small Cell 5G Network market research project include detailed market analysis, growth forecasts, segmentation data, competitive landscape overview, and actionable insights to guide investment and strategic decisions.
What are the market trends of Small Cell 5G Network?
Current trends in the Small Cell 5G Network industry include the growing adoption of femtocells and picocells, increase in deployment by telecom operators, and the emergence of smart cities leveraging enhanced connectivity for diverse applications.