Small Cell Networks Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: small-cell-networks
Small Cell Networks Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Small Cell Networks market, covering crucial insights and data regarding market trends, forecast years (2023-2033), and segmentation, along with industry leaders and regional performance.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
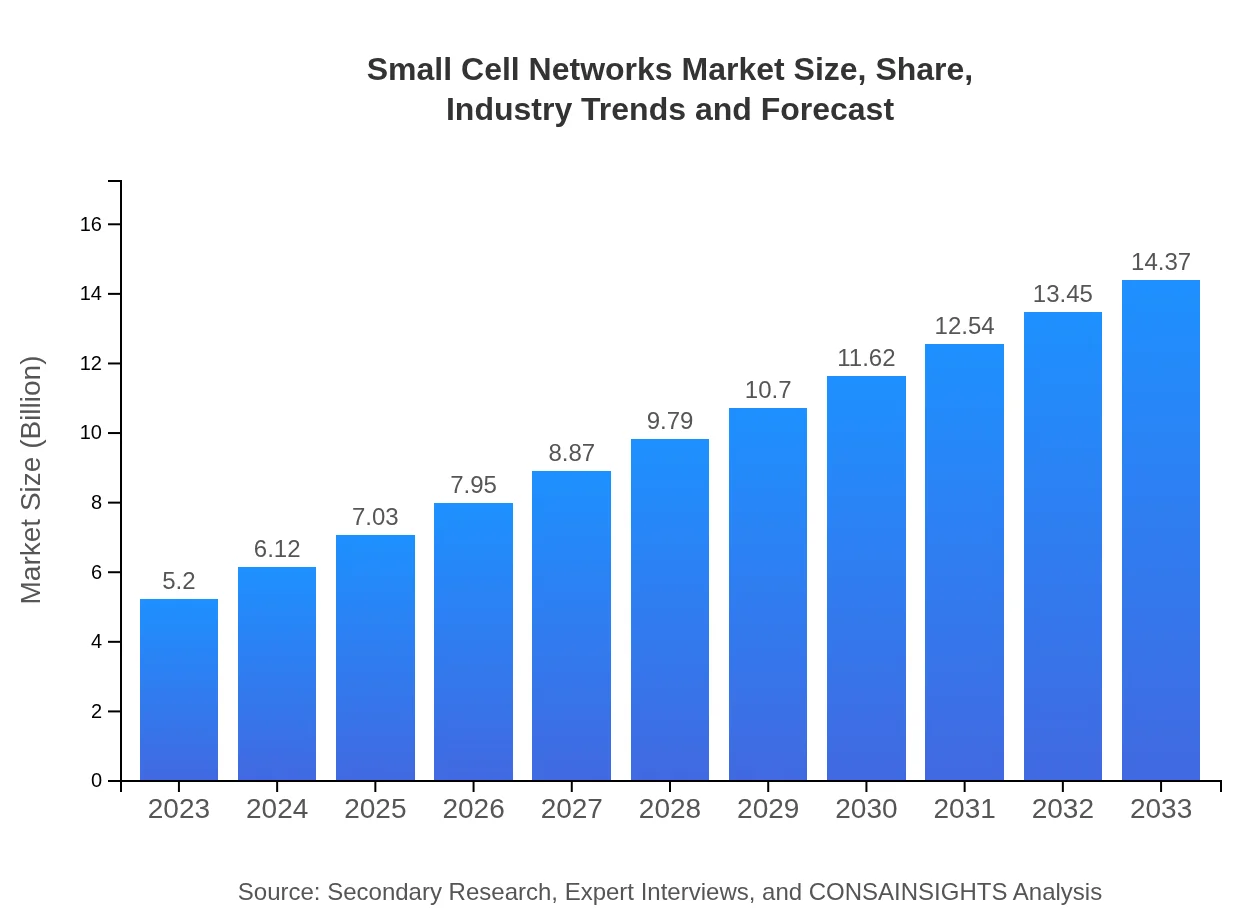
| 2023 Market Size | $5.20 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 10.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $14.37 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cisco Systems, Inc., Nokia Corporation, Ericsson , Samsung Electronics, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Small Cell Networks Market Overview
Customize Small Cell Networks Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Small Cell Networks market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Small Cell Networks's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Small Cell Networks
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Small Cell Networks market in 2023?
Small Cell Networks Industry Analysis
Small Cell Networks Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Small Cell Networks Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Small Cell Networks Market Report:
The European market for Small Cell Networks is expected to rise from $1.87 billion in 2023 to $5.17 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by initiatives to enhance 5G readiness and improve coverage in urban areas across the continent.Asia Pacific Small Cell Networks Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific Small Cell Networks market is expected to reach approximately $0.97 billion, growing to $2.69 billion by 2033. This region is fueled by high mobile data consumption, rapid urbanization, and significant investments in telecommunications infrastructure.North America Small Cell Networks Market Report:
North America showcases a substantial market environment with an estimated size of $1.72 billion in 2023, projected to extend to $4.74 billion by 2033. The region's growth is underpinned by substantial investment from telecom operators and increasing demand for high-speed internet and mobile connectivity.South America Small Cell Networks Market Report:
The Small Cell Networks market in South America faced challenges, reporting a market size of negative $0.08 billion in 2023, projected to decrease further to negative $0.22 billion in 2033. This decline is attributed to economic instability and slower adoption rates of advanced network technologies.Middle East & Africa Small Cell Networks Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is projected to grow from $0.72 billion in 2023 to $1.99 billion by 2033, benefitting from increasing investments in telecommunications infrastructure as countries aim to expand mobile broadband access.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
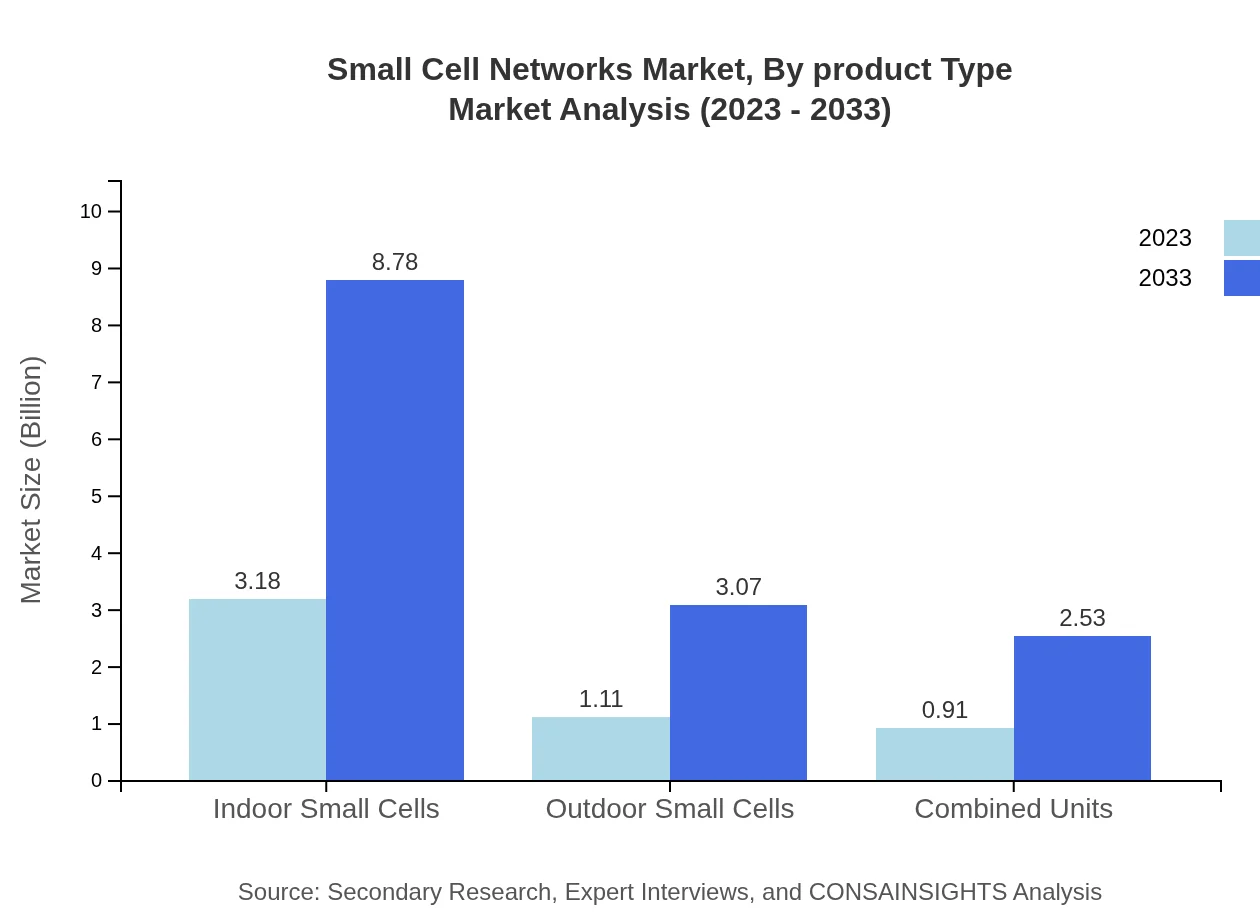
Small Cell Networks Market Analysis By Product Type
The Small Cell Networks market is majorly dominated by various product types. In 2023, indoor small cells contributed to a market size of $3.18 billion, anticipated to grow to $8.78 billion by 2033. Outdoor small cells and combined units contribute significantly as well, driven by the needs for enhanced mobile connectivity.
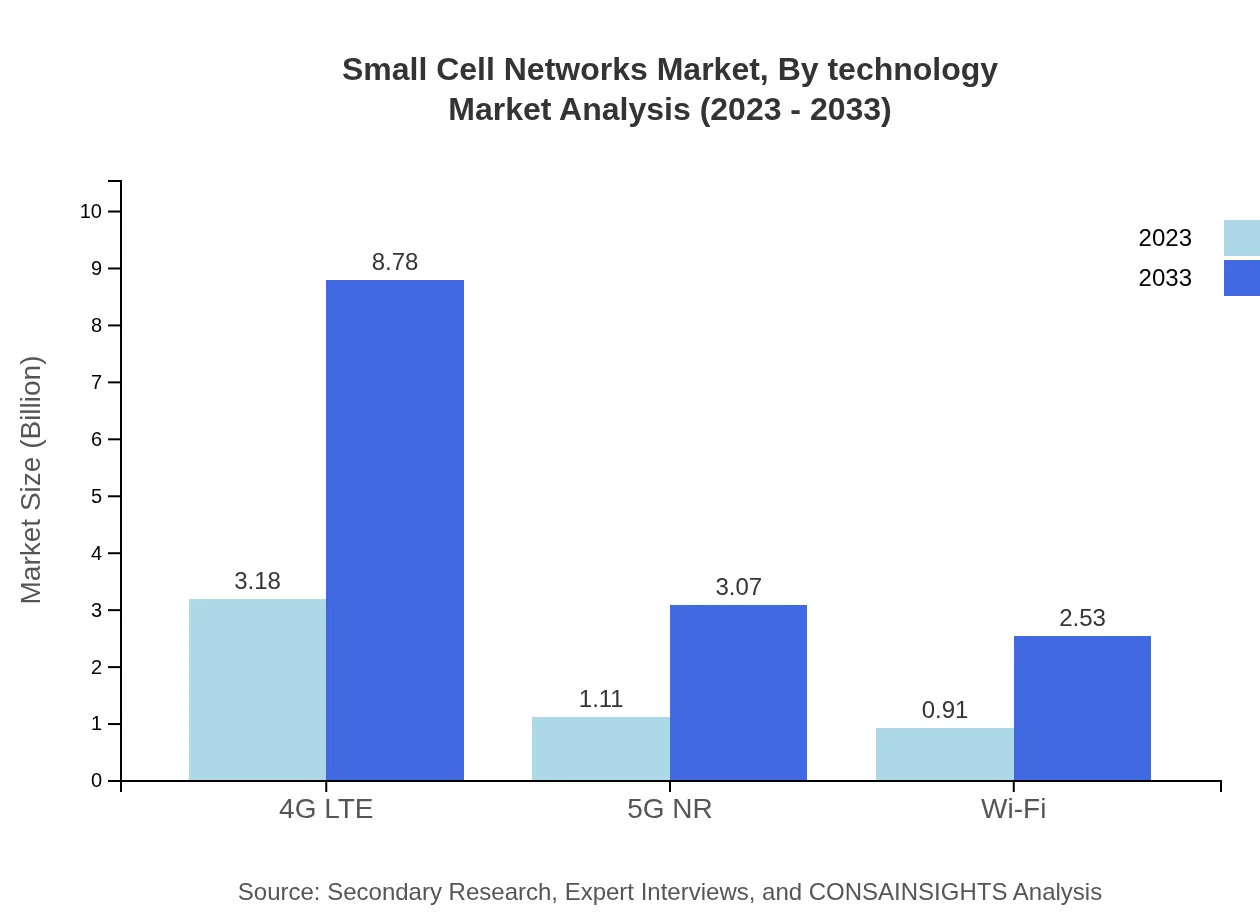
Small Cell Networks Market Analysis By Technology
The tech landscape within Small Cell Networks is characterized by 4G LTE leading with a market size of $3.18 billion in 2023, growing to $8.78 billion by 2033. Meanwhile, the 5G NR technology segment is also forecasted to grow from $1.11 billion in 2023 to $3.07 billion in 2033, underscoring the industry's shift towards adopting advanced technologies.
Small Cell Networks Market Analysis By Application
The primary applications for Small Cell Networks include telecom operators, enterprises, and the public sector. Telecom operators hold a substantial share with a market size of $3.18 billion in 2023. The public sector, while smaller, shows promise with growth projections as government agencies invest in enhancing connectivity.
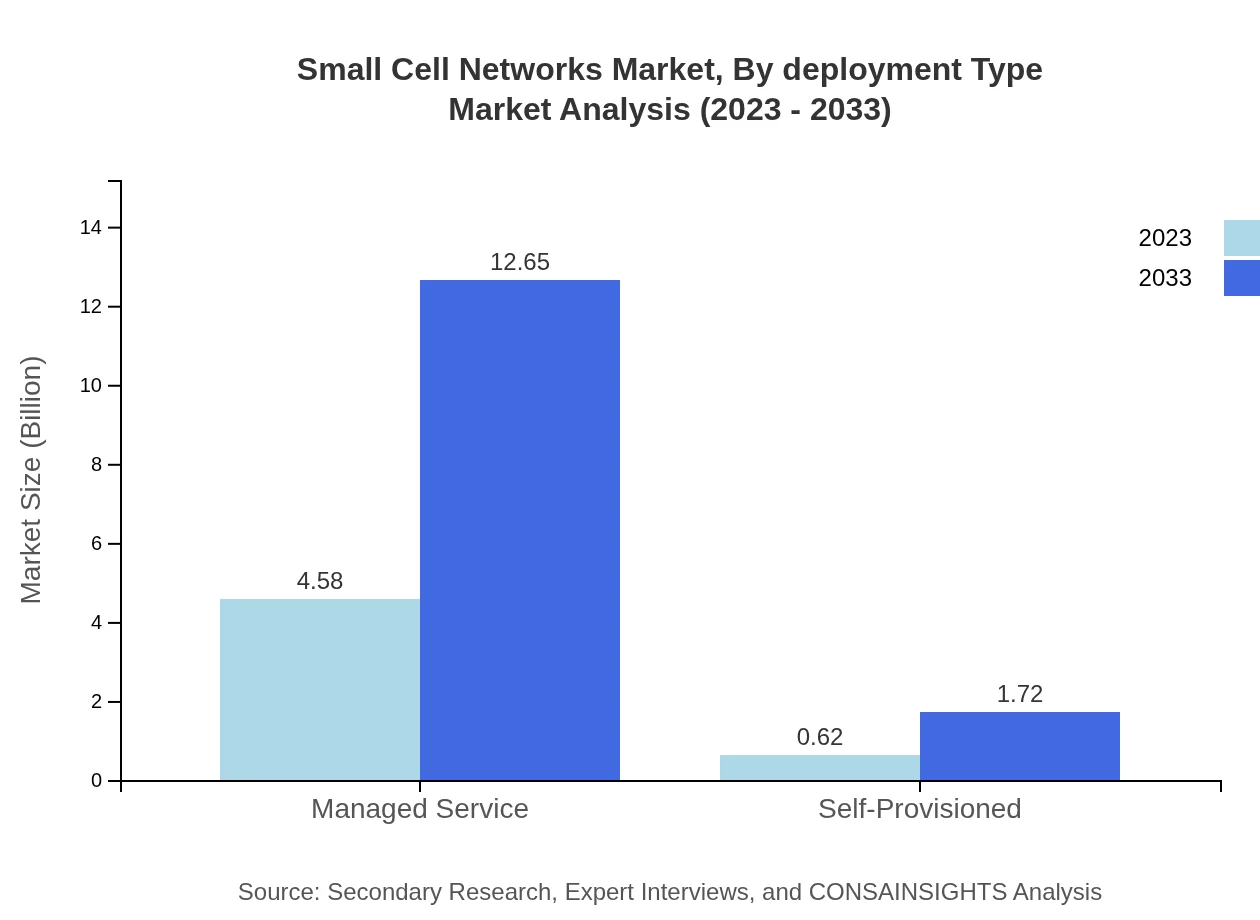
Small Cell Networks Market Analysis By Deployment Type
Regarding deployment types, managed services dominate, accounting for a size of $4.58 billion in 2023. Self-provisioned units are also present but with a smaller market size reflecting the readiness for managed services in optimizing operational efficiency.
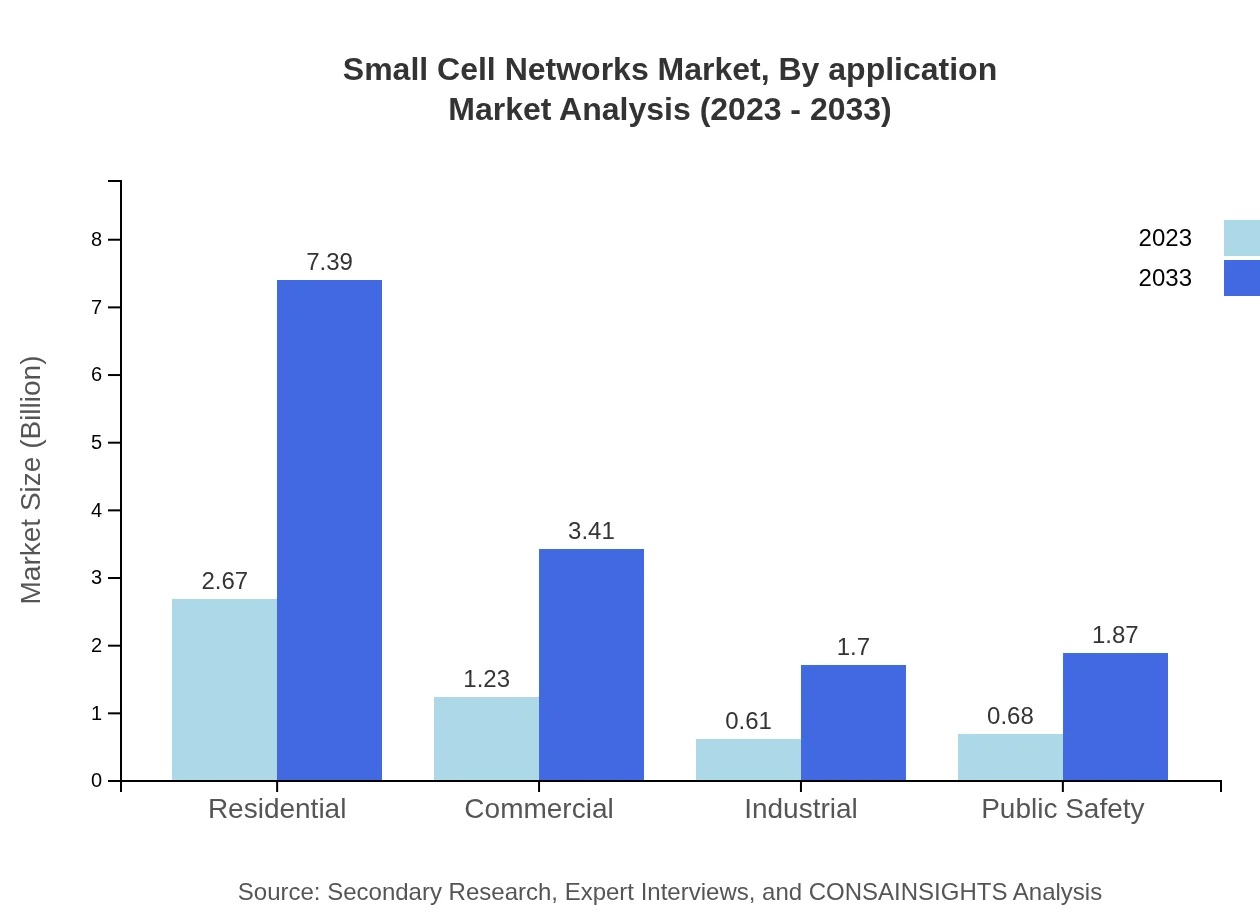
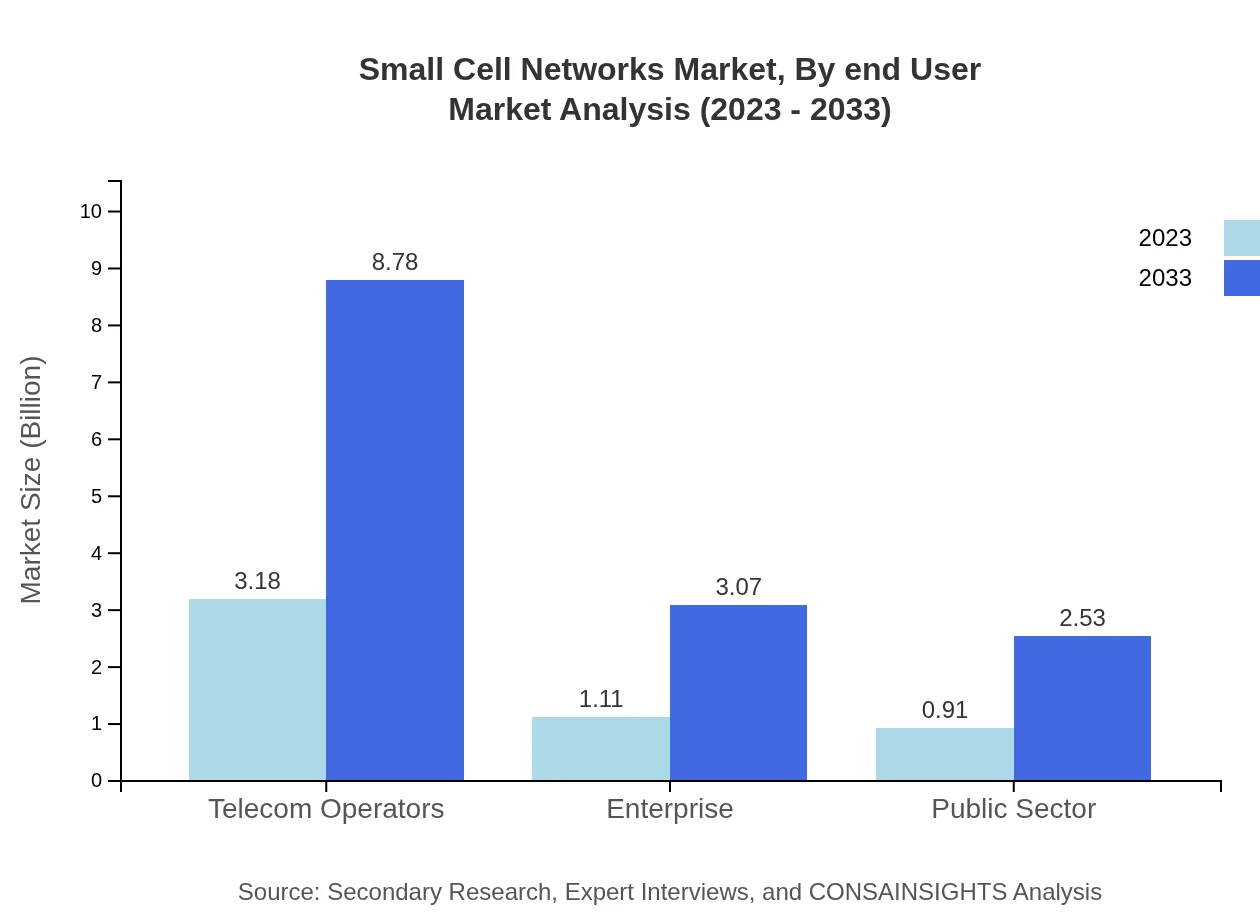
Small Cell Networks Market Analysis By End User
End-user segmentation includes residential, commercial, and industrial segments. The residential segment is substantial with a market size of $2.67 billion in 2023, catered towards increasing connectivity demands in households, while the industrial segment experiences growth due to technological advancements and automation.
Small Cell Networks Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Small Cell Networks Industry
Cisco Systems, Inc.:
Cisco offers innovative small cell solutions enhancing wireless connectivity and integrating seamlessly with existing networks, driving their adoption in urban settings.Nokia Corporation:
Nokia’s extensive portfolio includes small cell networks that support next-generation communication technologies, well-positioned for 5G deployment.Ericsson :
Ericsson leads through its advanced radio solutions and small cell technology, aiding telecom operators in expanding their service coverage.Samsung Electronics:
Samsung provides a robust lineup of small cell products designed to meet the high demands of urban areas and enterprise environments.Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.:
Huawei plays a significant role in the small cell market with its end-to-end solutions, emphasizing innovative designs and scalability for various applications.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of small Cell Networks?
The global small cell networks market is valued at approximately $5.2 billion in 2023, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.3% through to 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in this small Cell Networks industry?
Key players in the small-cell networks industry include major telecom operators and technology vendors that specialize in wireless network solutions and infrastructure development. Their continuous innovation drives competitiveness and market dynamics.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the small Cell Networks industry?
Key growth drivers in the small-cell networks sector include the rapid deployment of 5G networks, increasing mobile data traffic, urbanization, and the demand for enhanced connectivity in densely populated areas. These elements collectively stimulate market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the small Cell Networks?
Asia-Pacific is identified as the fastest-growing region in the small-cell networks market, experiencing a substantial increase from $0.97 billion in 2023 to an estimated $2.69 billion by 2033, driven by technological advancements and infrastructure investments.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the small Cell Networks industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customizable market report data tailored to specific needs in the small-cell networks industry, ensuring relevant insights and detailed analyses to meet unique business requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this small Cell Networks market research project?
Deliverables from the small-cell networks market research project may include comprehensive reports, analytical data, segment analysis by type, recommendations, and strategic insights to guide stakeholders in decision-making processes.
What are the market trends of small Cell Networks?
Current trends in the small-cell networks market include the transition towards 5G technology, increasing investments in smart city infrastructure, and a growing focus on improving indoor connectivity solutions, particularly through managed services and integrated networks.