Smart Automation Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: smart-automation
Smart Automation Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Smart Automation market from 2023 to 2033, covering market size, growth projections, technology trends, regional insights, and key players in the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
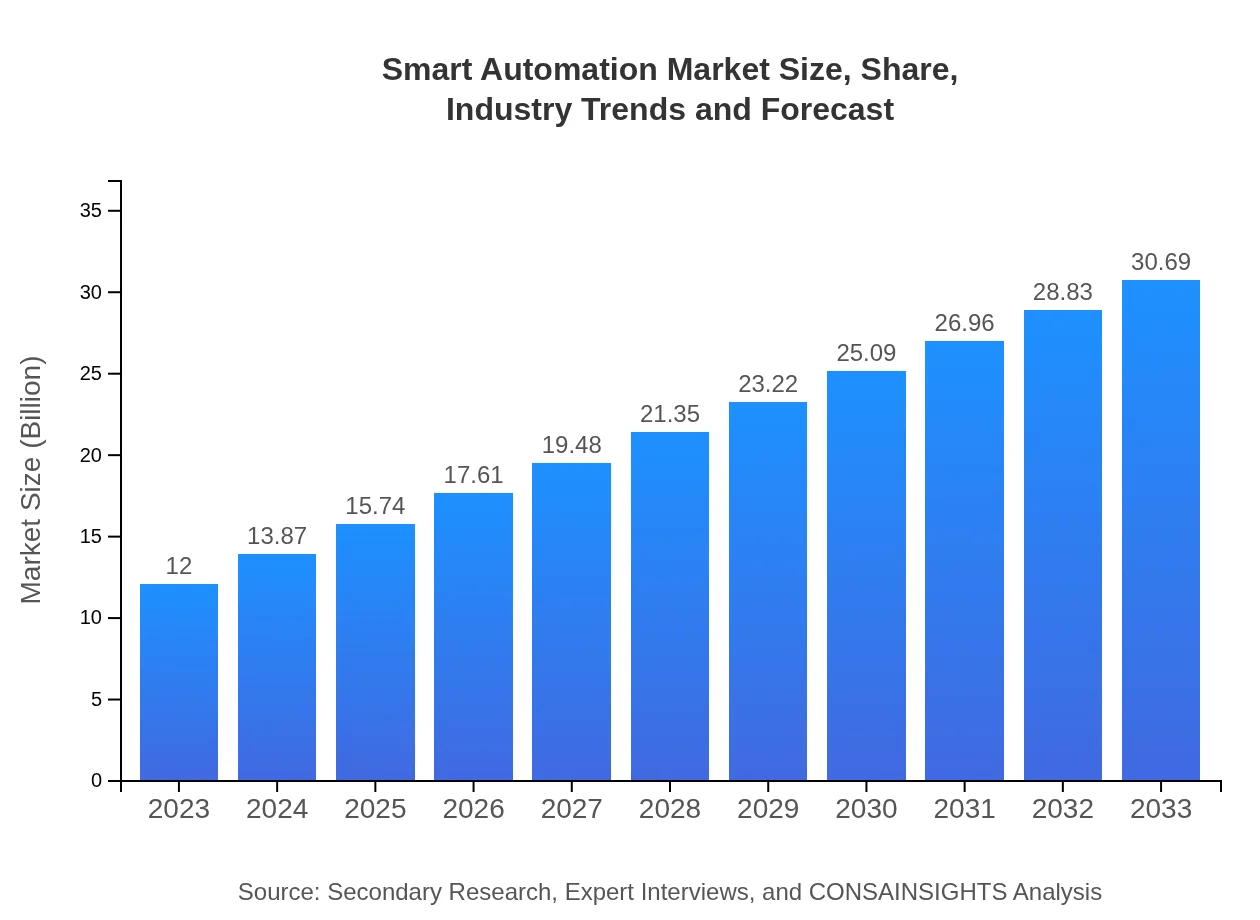
| 2023 Market Size | $12.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $30.69 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Rockwell Automation, ABB Ltd., Honeywell International Inc., Schneider Electric |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Smart Automation Market Overview
Customize Smart Automation Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Smart Automation market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Smart Automation's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Smart Automation
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Smart Automation market in 2023?
Smart Automation Industry Analysis
Smart Automation Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Smart Automation Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Smart Automation Market Report:
Europe's Smart Automation market is forecasted to grow significantly from 3.98 billion USD in 2023 to 10.17 billion USD by 2033. A focus on sustainability, data security, and advanced technologies in industries such as automotive and pharmaceuticals is propelling the demand for smart automation solutions.Asia Pacific Smart Automation Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is witnessing substantial growth in the Smart Automation market, projected to increase from 1.96 billion USD in 2023 to 5.02 billion USD by 2033. The rapid expansion of manufacturing industries and technological advancements in countries like China and India are driving this growth. Rising investments in smart factory initiatives and government support for automation are further propelling the market.North America Smart Automation Market Report:
The North American Smart Automation market is projected to increase from 4.33 billion USD in 2023 to 11.07 billion USD by 2033. Strong investments in AI and IoT technologies by major corporations, coupled with increasing operational efficiencies in manufacturing and logistics, are significant contributors to this growth.South America Smart Automation Market Report:
In South America, the Smart Automation market is expected to grow from 0.44 billion USD in 2023 to 1.12 billion USD by 2033. Economic growth and the push for technological advancements are motivating sectors such as agriculture and manufacturing to adopt automated solutions, thereby boosting market expansion.Middle East & Africa Smart Automation Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's Smart Automation market is anticipated to expand from 1.29 billion USD in 2023 to 3.31 billion USD by 2033. The growth is attributed to increased investment in infrastructure projects and the urgent need to enhance operational efficiency in oil and gas, agriculture, and logistics sectors.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
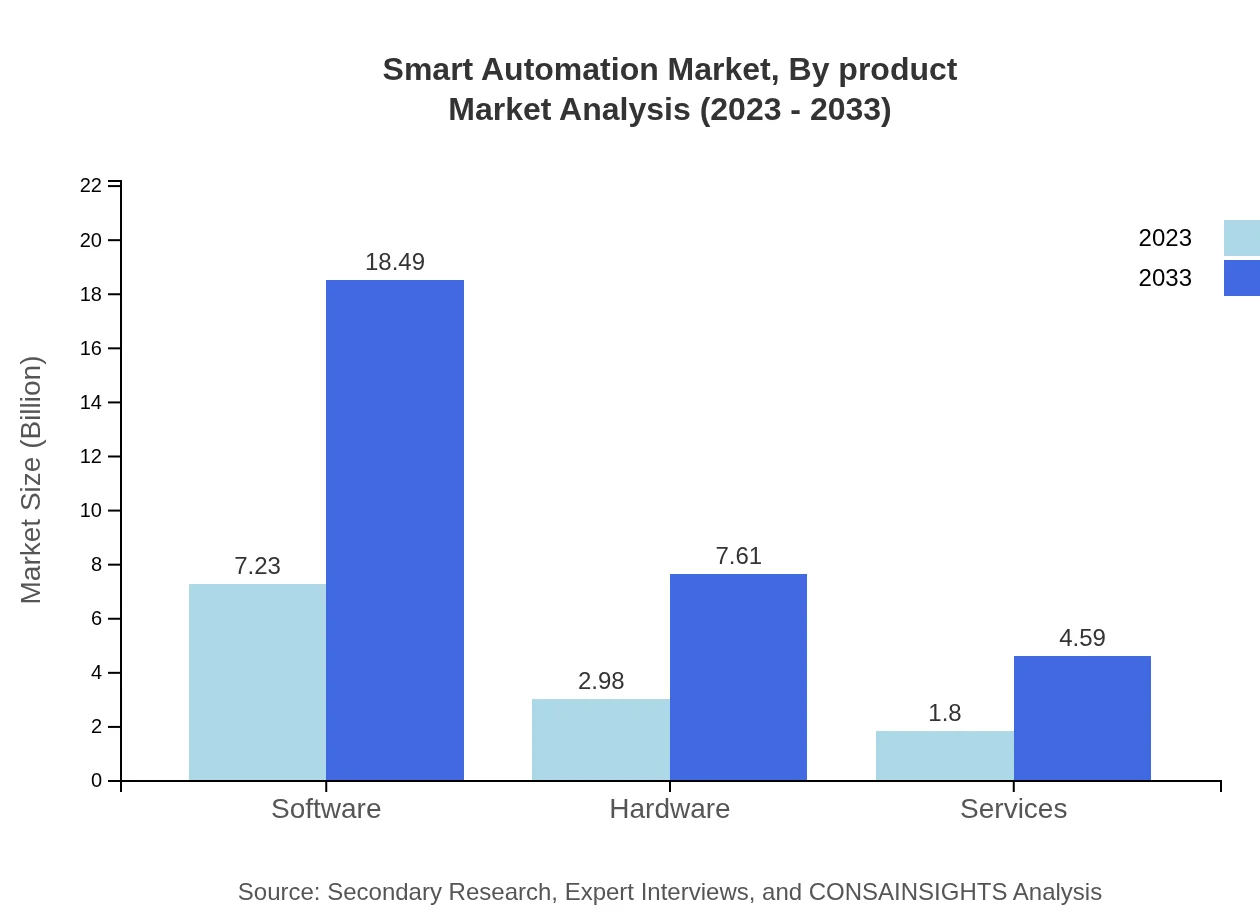
Smart Automation Market Analysis By Product
The Smart Automation market can be segmented into software, hardware, and services. In 2023, software accounts for a leading market size of approximately 7.23 billion USD, which is expected to reach 18.49 billion USD by 2033. Hardware holds a significant share as well, valued at 2.98 billion USD in 2023 and projected to grow to 7.61 billion USD by 2033. Services, primarily focused on consulting and integration, will increase from 1.80 billion USD to 4.59 billion USD in the same period.
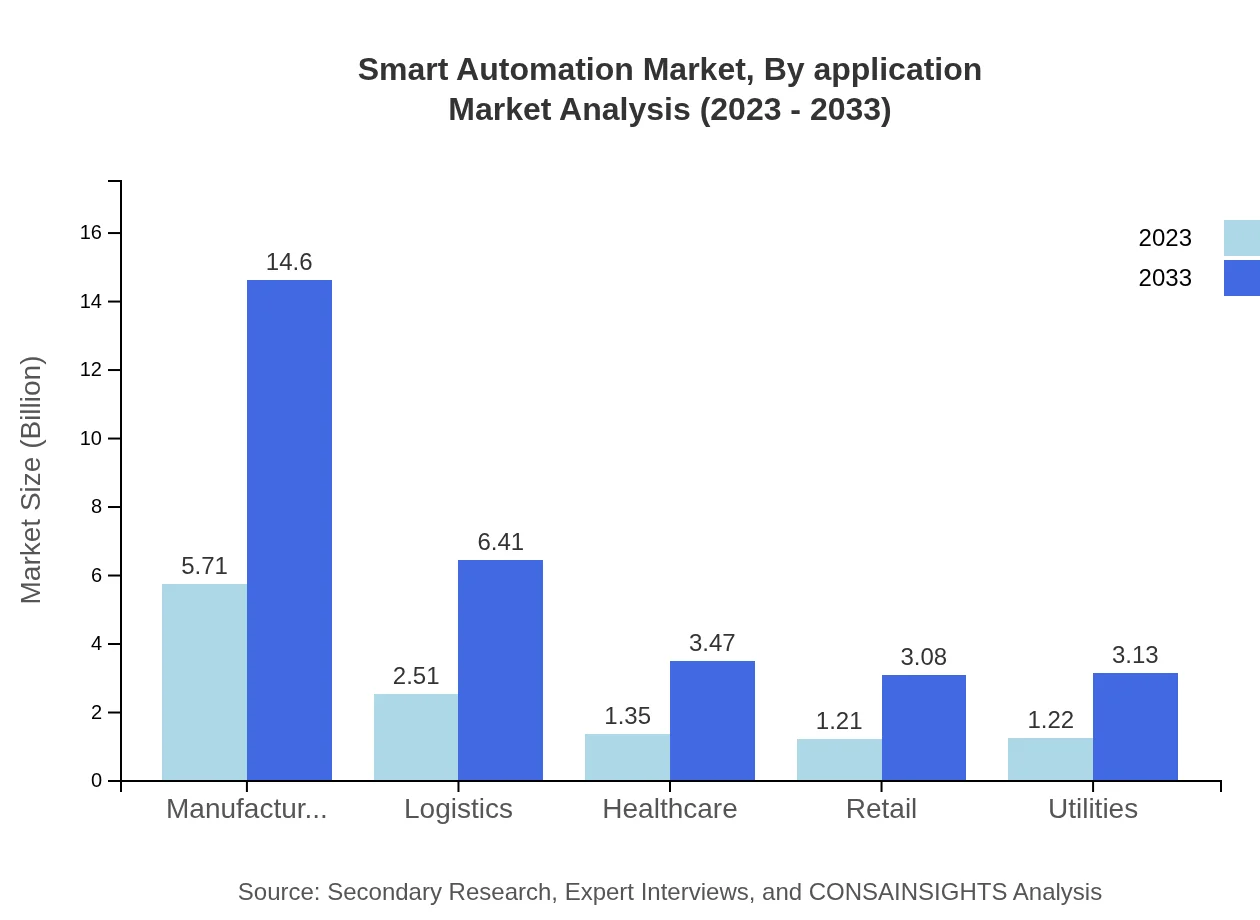
Smart Automation Market Analysis By Application
Key applications of Smart Automation span across various sectors including IT and Telecom, Manufacturing, Healthcare, Retail, Logistics and Transportation, and Utilities. The construction and logistics sectors are anticipated to exhibit significant growth due to their complex processes and need for efficiency. The IT and Telecom application segment is currently a major contributor, holding a market size of 5.71 billion USD in 2023 and predicted to reach 14.60 billion USD by 2033.
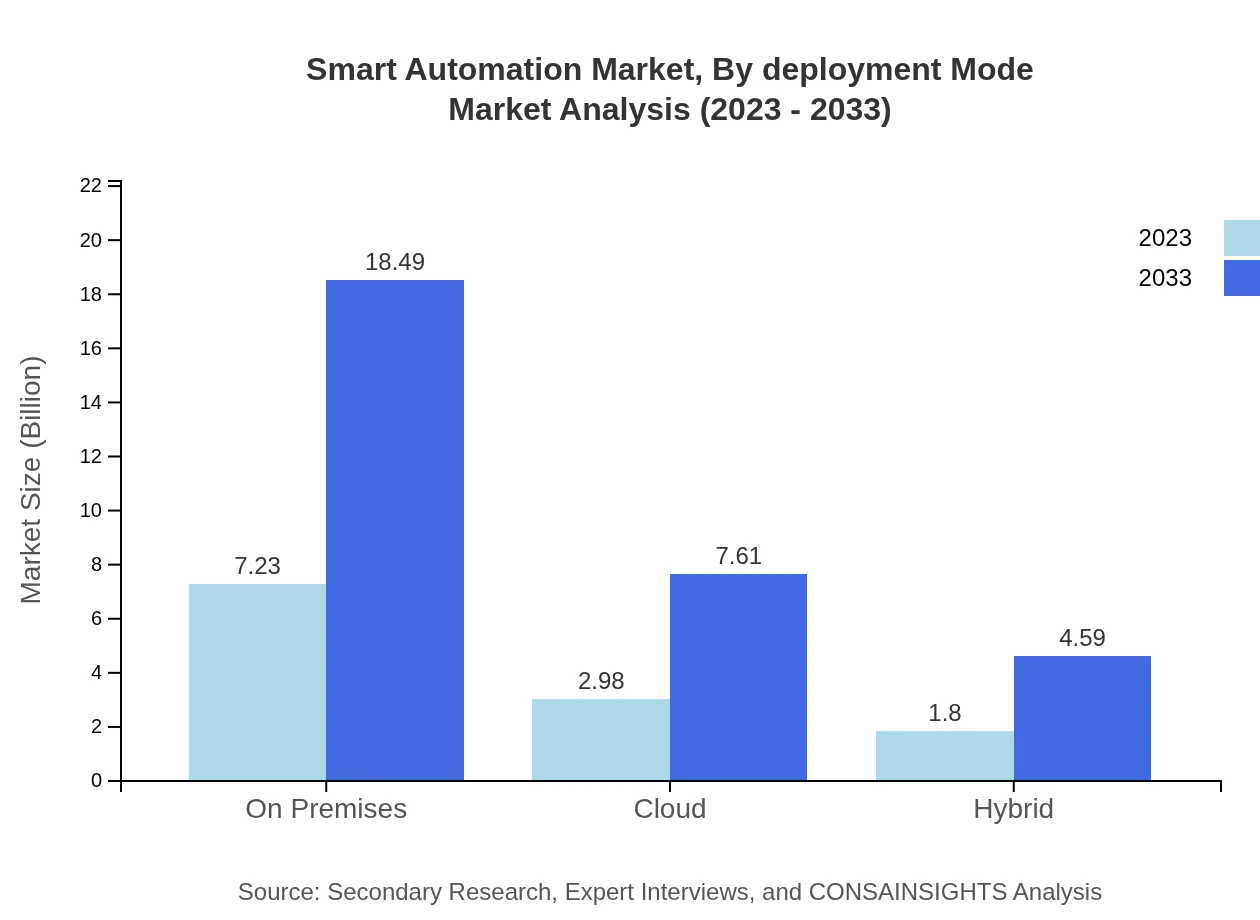
Smart Automation Market Analysis By Deployment Mode
The deployment modes for Smart Automation include on-premises, cloud, and hybrid solutions. In 2023, the on-premises deployment leads with a market size of 7.23 billion USD, expected to grow to 18.49 billion USD by 2033. Cloud solutions are gaining traction due to their flexibility, with market sizes projected to increase from 2.98 billion USD to 7.61 billion USD over the same period.
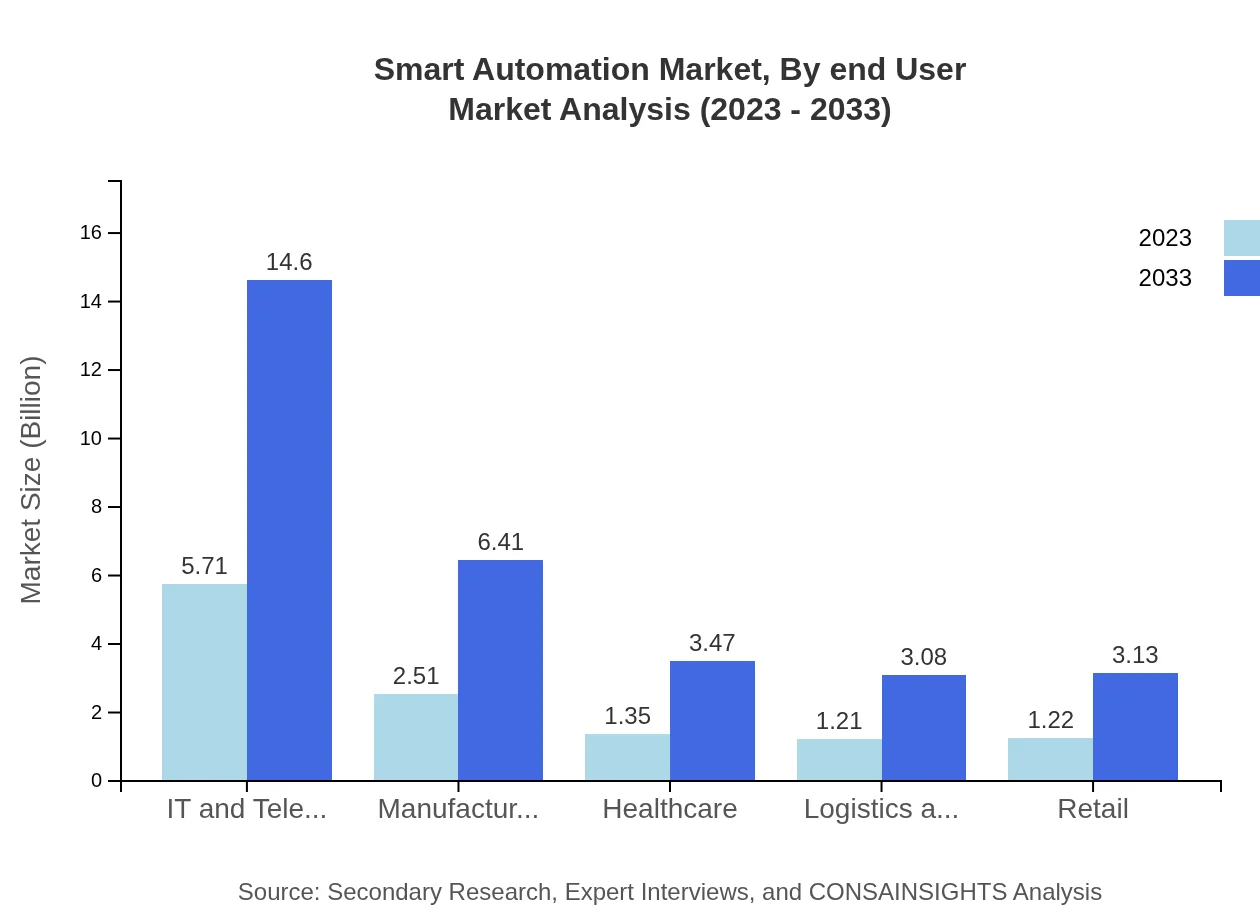
Smart Automation Market Analysis By End User
The end-user market segments include sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and retail, with manufacturing being a dominant segment due to continuous operational needs and efficiency improvements. The healthcare sector is also experiencing strong growth, estimated to rise from 1.35 billion USD in 2023 to 3.47 billion USD by 2033, thereby highlighting the segment's increasing reliance on automation.
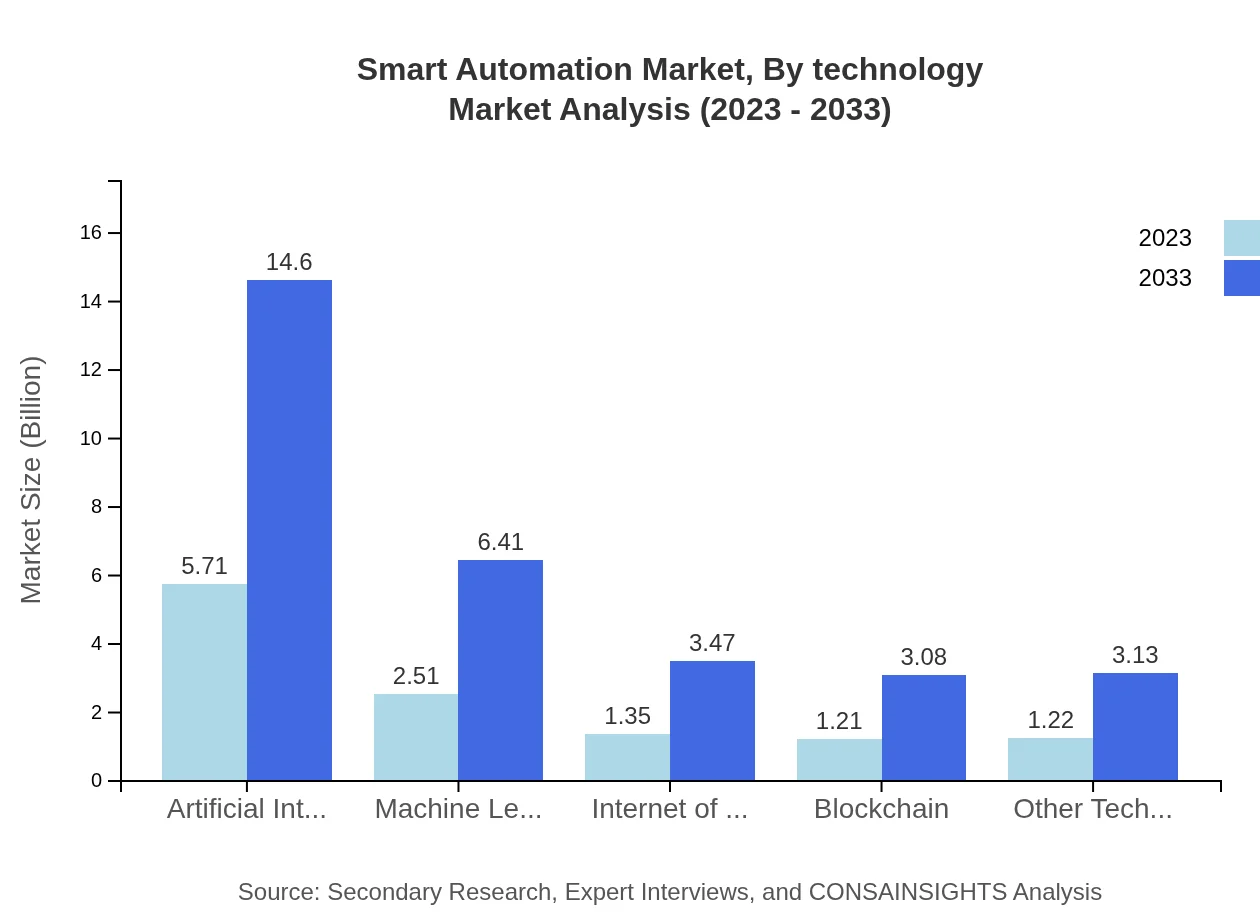
Smart Automation Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements significantly define the Smart Automation landscape. Key technologies include Artificial Intelligence (AI) leading at 5.71 billion USD in 2023 and expected to achieve 14.60 billion USD by 2033, while IoT is positioning itself as a vital technology with growth projections from 1.35 billion USD to 3.47 billion USD over the same timeline.
Smart Automation Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Smart Automation Industry
Siemens AG:
Siemens AG is a global leader in automation and digitalization, providing innovative solutions to enhance industrial productivity and efficiency.Rockwell Automation:
Rockwell Automation specializes in industrial automation and information, offering solutions that integrate control and information to enable operational excellence.ABB Ltd.:
ABB is a pioneering technology leader that works closely with utility, industry, transportation, and infrastructure customers to write the future of industrial digitalization.Honeywell International Inc.:
Honeywell is a global technology and manufacturing company that provides a wide range of products and services in the automation sector, driving efficiency and safety.Schneider Electric:
Schneider Electric specializes in digital transformation of energy management and automation, offering solutions that help companies optimize their operations.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of smart Automation?
The smart automation market is projected to reach approximately $12 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.5%. This substantial growth reflects increasing investments in automation technologies across various industries, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
What are the key market players or companies in this smart Automation industry?
Key players in the smart automation market include major technology firms specializing in AI, software, and hardware solutions. These companies lead in innovation and market share, significantly influencing industry trends and consumer adoption.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the smart automation industry?
Growth in the smart automation industry is driven by advancements in AI and machine learning technology, increased demand for operational efficiency, and the rise of the digital workplace. Additionally, the need for enhanced data analytics plays a vital role.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the smart automation?
North America is expected to be the fastest-growing region in the smart automation market, with growth projected from $4.33 billion in 2023 to $11.07 billion by 2033. Europe and Asia Pacific also show significant growth potential.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the smart automation industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the smart automation industry. Clients can benefit from detailed analyses that are adapted to their individual market demands.
What deliverables can I expect from this smart automation market research project?
Deliverables from the smart automation market research project typically include comprehensive market reports, data insights, trend analyses, and strategic recommendations, designed to provide actionable intelligence for stakeholders.
What are the market trends of smart automation?
Current trends in the smart automation market include the adoption of cloud-based solutions, integration of IoT technologies, and increasing reliance on AI-driven analytics. Companies are prioritizing automation to enhance efficiency and customer experience.