Smart Cities Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: smart-cities
Smart Cities Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This comprehensive report provides insights into the Smart Cities market, covering market trends, growth forecasts, competitive landscape, and regional analysis from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
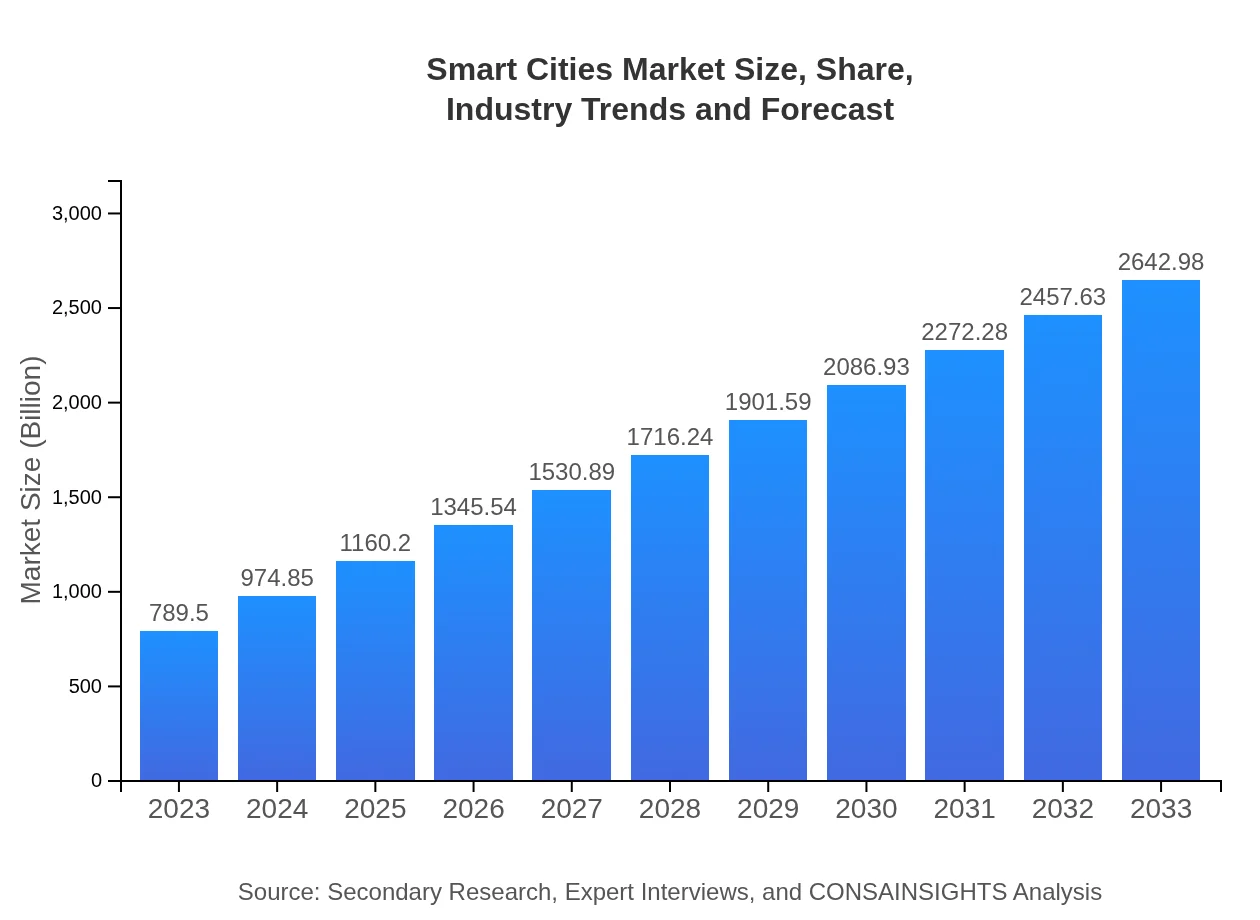
| 2023 Market Size | $789.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 12.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $2642.98 Billion |
| Top Companies | IBM, Cisco Systems, Siemens AG, Honeywell |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Smart Cities Market Overview
Customize Smart Cities Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Smart Cities market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Smart Cities's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Smart Cities
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Smart Cities market in 2023?
Smart Cities Industry Analysis
Smart Cities Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Smart Cities Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Smart Cities Market Report:
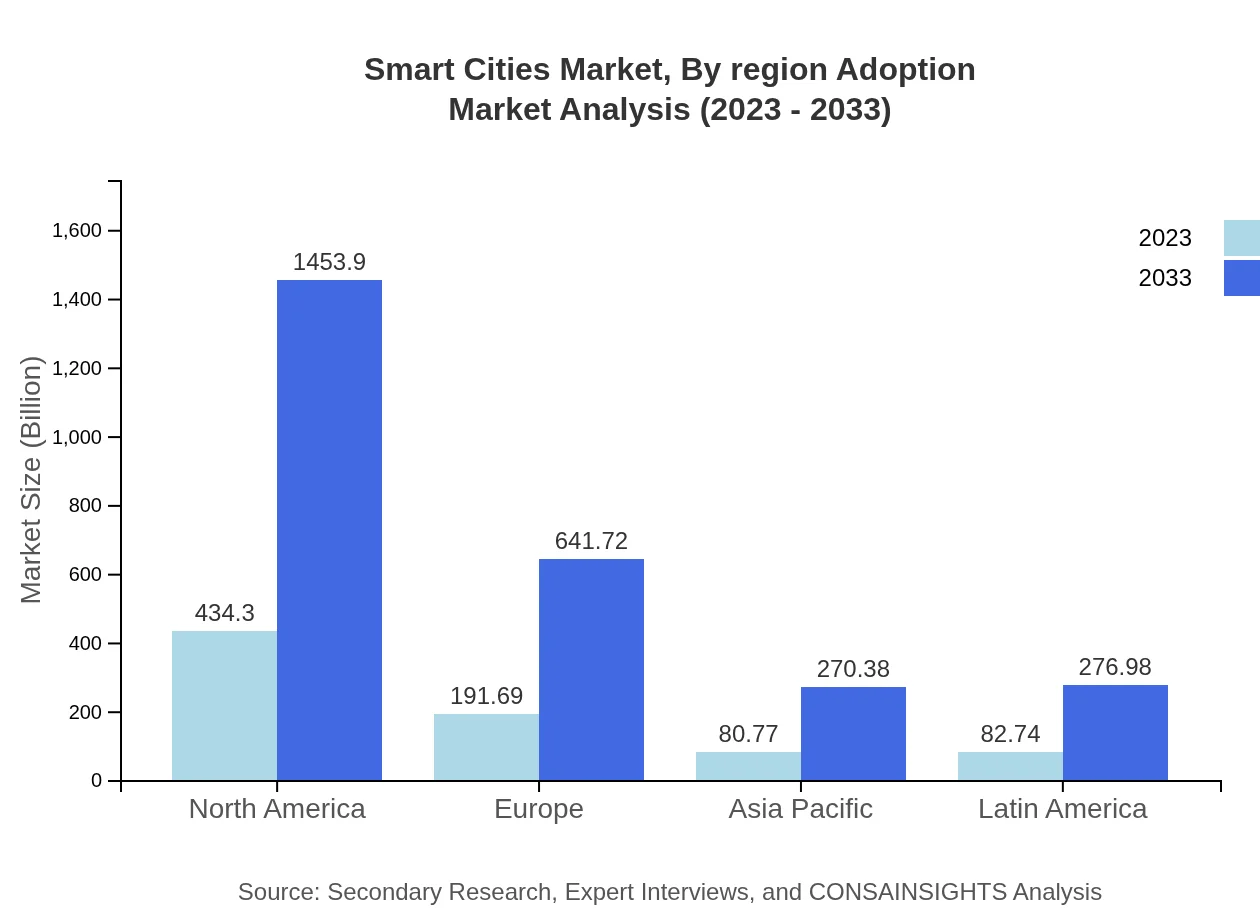
The European Smart Cities market is expected to grow from $207.09 billion in 2023 to $693.25 billion by 2033. European cities are renowned for sustainability initiatives and smart urban planning. Initiatives across the EU focus on integrating smart technologies into public infrastructure, launching pilot projects aimed at improving energy efficiency and mobility.Asia Pacific Smart Cities Market Report:
In 2023, the Smart Cities market in Asia Pacific is valued at $167.77 billion, projected to reach $561.63 billion by 2033. Rapid urbanization, government initiatives supporting sustainable urban development, and significant investments in infrastructure are driving this growth. Countries like China and India are at the forefront of implementing smart technologies, enhancing urban livability and operational efficiency.North America Smart Cities Market Report:
In North America, the Smart Cities market is projected to grow from $294.01 billion in 2023 to $984.25 billion by 2033. Driving forces include substantial government investments and technological advancements in IoT and AI. Major cities in the U.S. and Canada are early adopters of smart technologies that enhance urban mobility and resource management.South America Smart Cities Market Report:
The South America Smart Cities market is estimated at $52.74 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $176.55 billion by 2033. Urbanization and infrastructural challenges are prompting cities to adopt smart solutions. Initiatives in Brazil and Argentina focus on improving public safety and enhancing urban services, indicating a growing movement towards smarter city frameworks.Middle East & Africa Smart Cities Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region shows potential growth, with an estimated market size of $67.90 billion in 2023 projected to reach $227.30 billion by 2033. Countries like the UAE and South Africa are investing in smart city projects. The Vision 2021 strategy in the UAE, for example, aims to enhance its city’s technological infrastructure and sustainability.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
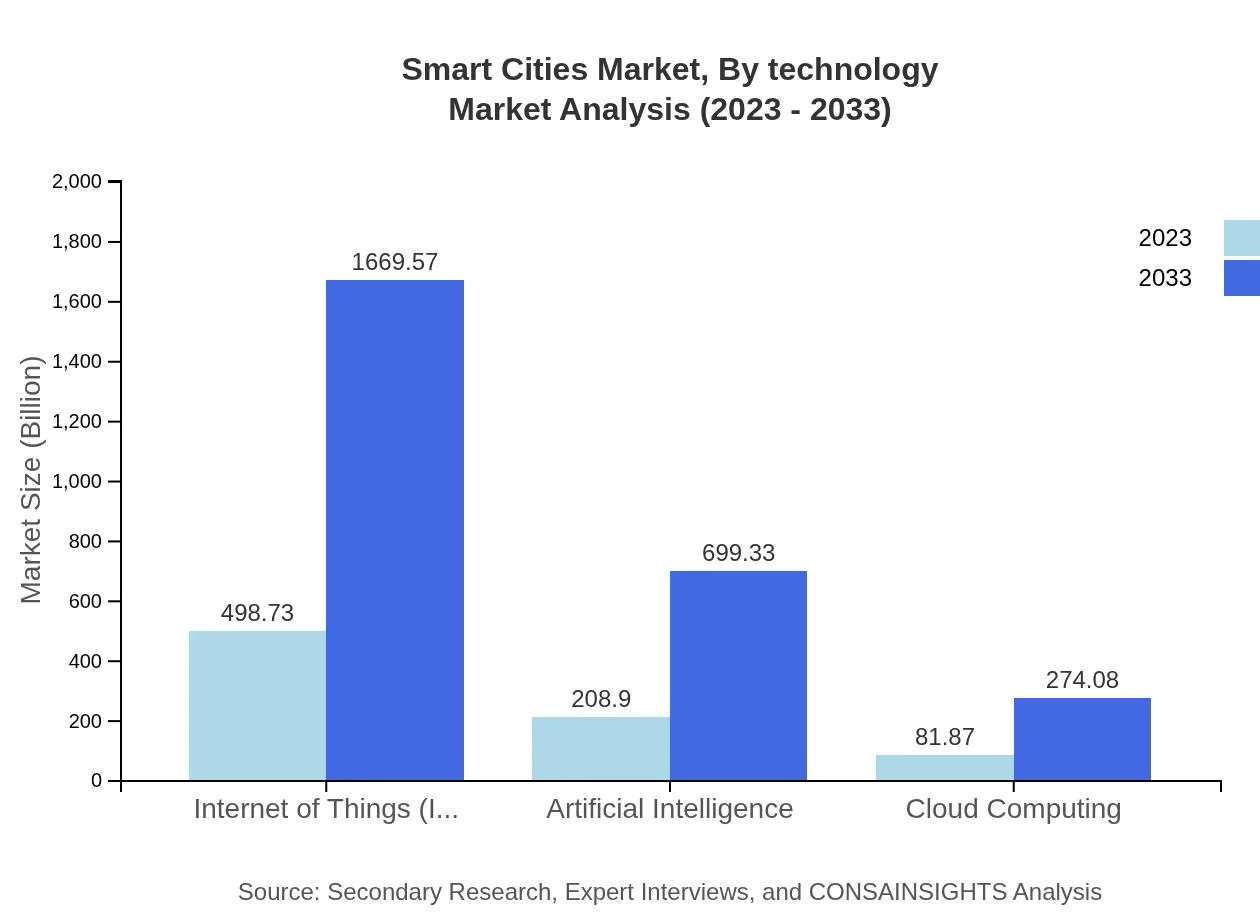
Smart Cities Market Analysis By Technology
The Smart Cities market by technology includes segments like IoT, Artificial Intelligence, Cloud Computing, and Big Data. IoT dominates the segment, with $498.73 billion in 2023, expected to reach $1,669.57 billion by 2033. AI also plays a significant role, projected to increase from $208.90 billion to $699.33 billion in the same timeframe. The integration of these technologies enhances data collection and analysis, paving the way for more informed decision-making in city management.
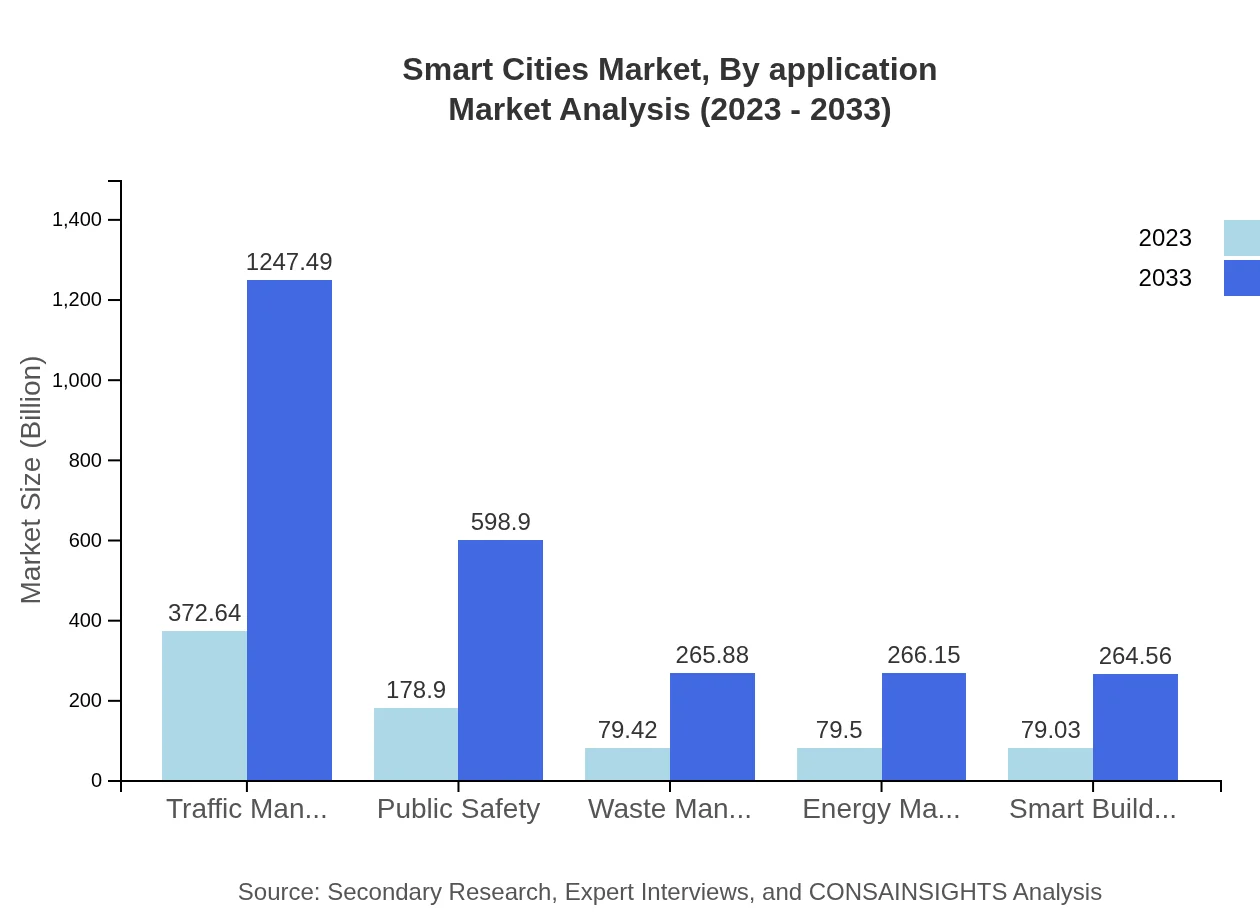
Smart Cities Market Analysis By Application
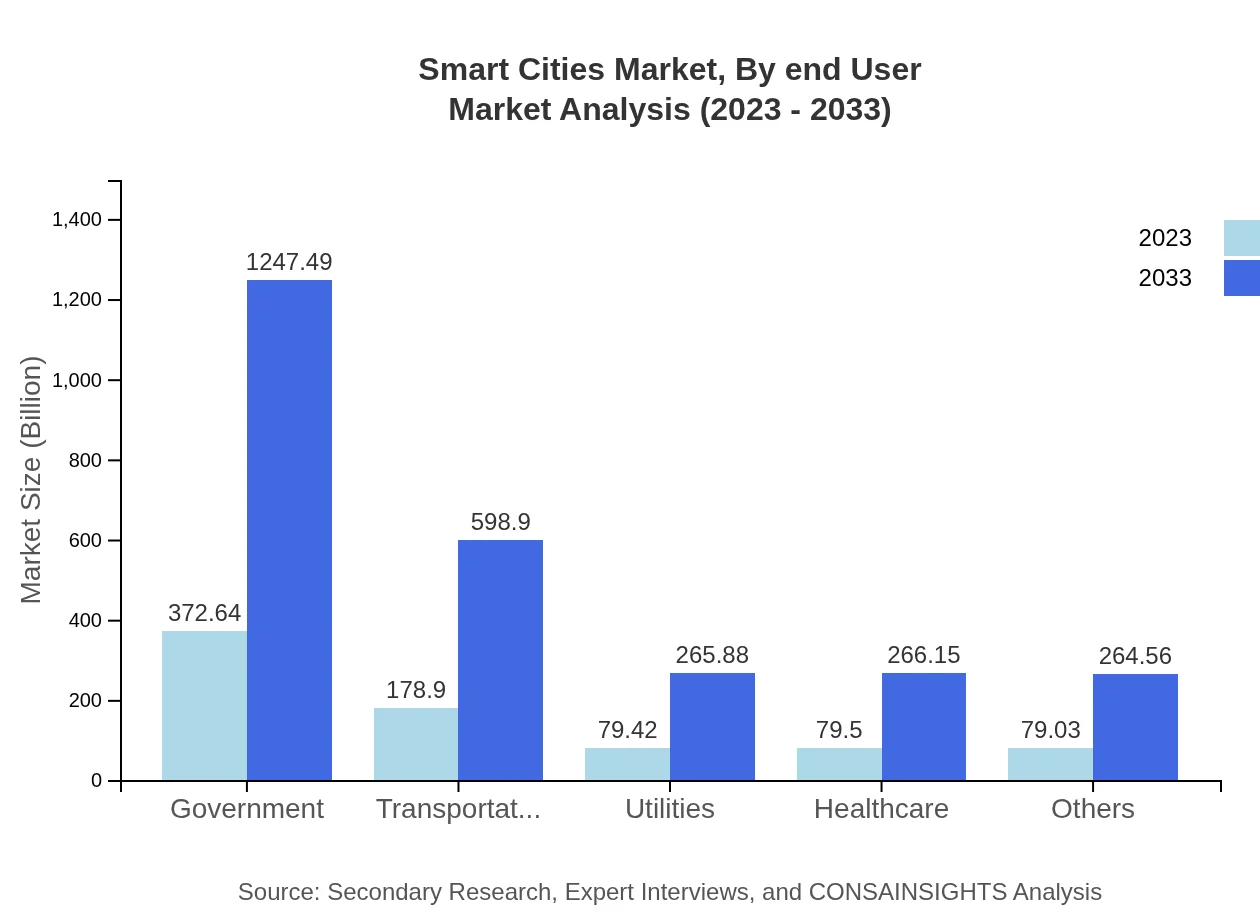
Markets can be segmented by application into areas like Transportation, Government, Utilities, and Healthcare. The Government segment was valued at $372.64 billion in 2023, increasing to $1,247.49 billion by 2033. Transportation applications, focusing on smart traffic management and mobility solutions, are also critical and expected to grow significantly as cities enhance infrastructure to accommodate urban demands.
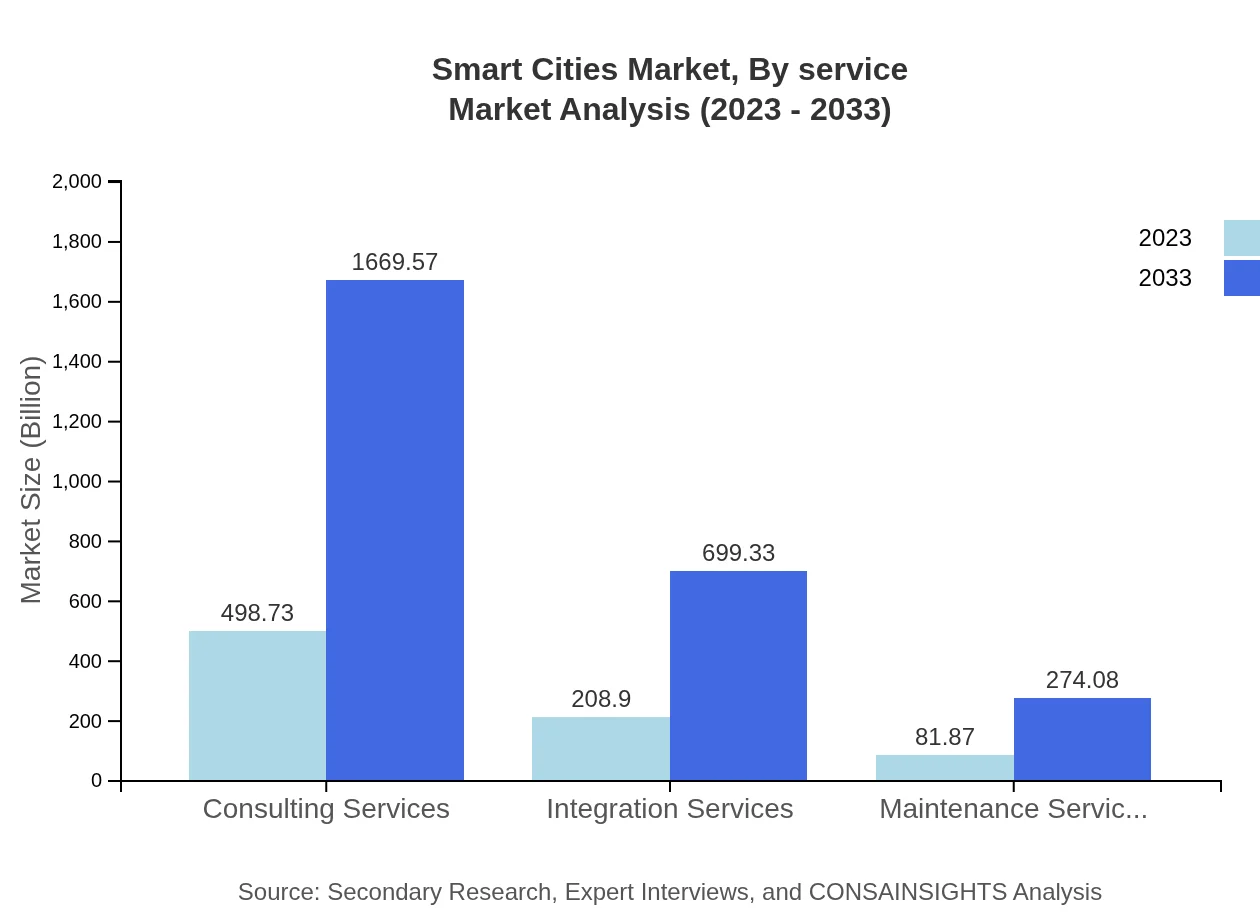
Smart Cities Market Analysis By Service
Service analysis includes Consulting Services, Integration Services, and Maintenance Services. Consulting Services are expected to grow from $498.73 billion in 2023 to $1,669.57 billion by 2033, highlighting the need for expert guidance in implementing smart technologies. Integration Services also anticipate growth as cities move towards fully integrated smart ecosystems.
Smart Cities Market Analysis By End User
Key end-users in the Smart Cities market include government bodies, utilities, and private enterprises. Government's role is substantial, holding a significant share in the market. With continuous investments in smart urban infrastructure, the engagement of private firms in collaborations signifies an evolving landscape focused on enhanced public service delivery.
Smart Cities Market Analysis By Region Adoption
Regional adoption insights indicate North America leading in adoption rates due to better technological readiness and investments. Europe follows, emphasizing sustainability. The Asia Pacific's rapid urbanization acts as a catalyst for smart city projects, while regions like South America and Africa are catching up, driven by infrastructural needs and technological support.
Smart Cities Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Smart Cities Industry
IBM:
IBM leverages its capabilities in AI and Cloud services to enhance urban efficiency through integrated smart systems for cities.Cisco Systems:
Cisco focuses on developing networking solutions that streamlines smart city infrastructures, enabling enhanced connectivity and cybersecurity measures.Siemens AG:
Siemens contributes by providing smart building technologies and infrastructure solutions that facilitate the development of smart urban environments.Honeywell :
Honeywell's diverse solutions encompass safety and security systems in urban areas, contributing to building smarter and safer environments.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of smart Cities?
The smart cities market is projected to reach approximately $789.5 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.3% from 2023 to 2033, indicating substantial growth in urban technology solutions.
What are the key market players or companies in the smart Cities industry?
Key players in the smart cities market include major technology firms like Cisco Systems, IBM, and Siemens that dominate sectors such as urban mobility, smart grids, and IoT solutions, driving innovation and development in urban environments.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the smart cities industry?
Growth in the smart cities industry is primarily driven by advancements in IoT technologies, increasing urbanization rates, the need for sustainable development, and government initiatives aimed at enhancing urban infrastructure and public services.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the smart cities market?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the smart cities market, projected to grow from $294.01 billion in 2023 to $984.25 billion by 2033, significantly outpacing other regions in urban technology investments.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the smart cities industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the smart cities industry, allowing clients to access tailored insights based on specific requirements or regional demands to support informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this smart cities market research project?
From a smart cities market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports detailing market size, growth projections, competitive analysis, regional insights, and in-depth examinations of various technology segments within the smart cities domain.
What are the market trends of smart cities?
Current trends in the smart cities market include the integration of AI and machine learning for predictive analytics, a focus on sustainability, the expansion of 5G networks for faster connectivity, and the growing role of citizen engagement in urban planning.